CURRENT AFFAIRS – 24/12/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 24/12/2024
- Kashmiri artisans give wings to the dodo /कश्मीरी कारीगरों ने डोडो को पंख दिए
- Former SC judge named human rights panel chief /पूर्व सुप्रीम कोर्ट जज को मानवाधिकार पैनल का अध्यक्ष बनाया गया
- Filmmaker who gave a voice to the voiceless, held dear the idea of India /फिल्म निर्माता जिन्होंने बेजुबानों को आवाज़ दी, भारत के विचार को बहुत महत्व दिया
- India’s reliance on China for critical minerals /महत्वपूर्ण खनिजों के लिए चीन पर भारत की निर्भरता
- The MSME Revolution: Transforming India’s Economic Landscape /MSME क्रांति: भारत के आर्थिक परिदृश्य को बदलना
- Envisioning India as a global skill supplier / भारत को वैश्विक कौशल आपूर्तिकर्ता के रूप में देखना
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 24/12/2024
Kashmiri artisans give wings to the dodo /कश्मीरी कारीगरों ने डोडो को पंख दिए
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
- Kashmir’s papier mache artisans are reviving the memory of dodos, a bird extinct since 1681, by crafting colorful models adorned with symbolic floral and forest prints.
- These handcrafted dodos are in high demand, particularly in Europe and Mauritius.
- The bird’s introduction to Kashmir’s craft scene is relatively recent and growing.
About Dodo:
- Scientific Name: Raphus cucullatus, an extinct flightless bird.
- Native Habitat: Exclusive to Mauritius, a tropical island in the Indian Ocean, with no natural predators before human arrival.
- Physical Description: Stood about 3 feet (1 meter) tall, weighing 10–20 kg, with grayish feathers, a large hooked beak, stubby wings, and stout legs.
- Diet: Primarily frugivorous, feeding on fruits, seeds, roots, nuts, and possibly crabs or small animals.
- Reproduction: Nested on the ground, laying one egg at a time, making it vulnerable to predators.
- Extinction: Declared extinct by 1681 due to overhunting by sailors, habitat destruction, and the introduction of invasive species like rats and pigs.
- Historical Significance: Its extinction marked one of the earliest documented human-caused extinctions, highlighting the impact of human activity on biodiversity.
कश्मीरी कारीगरों ने डोडो को पंख दिए
कश्मीर के पेपर माचे कारीगर 1681 से विलुप्त हो चुके पक्षी डोडो की याद को फिर से ताज़ा कर रहे हैं, इसके लिए वे प्रतीकात्मक पुष्प और वन प्रिंट से सजे रंगीन मॉडल तैयार कर रहे हैं।
- ये हस्तनिर्मित डोडो खास तौर पर यूरोप और मॉरीशस में बहुत ज़्यादा मांग में हैं।
- कश्मीर के शिल्प परिदृश्य में इस पक्षी का प्रवेश अपेक्षाकृत हाल ही में हुआ है और यह बढ़ता जा रहा है।
डोडो के बारे में:
- वैज्ञानिक नाम: राफस क्यूकुलैटस, एक विलुप्त उड़ान रहित पक्षी।
- मूल निवास स्थान: मॉरीशस के लिए विशेष, हिंद महासागर में एक उष्णकटिबंधीय द्वीप, जहाँ मानव आगमन से पहले कोई प्राकृतिक शिकारी नहीं था।
- शारीरिक वर्णन: यह लगभग 3 फीट (1 मीटर) लंबा, 10-20 किलोग्राम वजन वाला, भूरे रंग के पंख, बड़ी हुकदार चोंच, छोटे पंख और मजबूत पैर वाला होता है।
- आहार: मुख्य रूप से फल खाने वाला, फल, बीज, जड़ें, मेवे और संभवतः केकड़े या छोटे जानवर खाता है।
- प्रजनन: जमीन पर घोंसला बनाकर, एक बार में एक अंडा देता है, जिससे यह शिकारियों के लिए कमज़ोर हो जाता है।
- विलुप्ति: नाविकों द्वारा अत्यधिक शिकार, निवास स्थान के विनाश और चूहों और सूअरों जैसी आक्रामक प्रजातियों के आने के कारण 1681 में विलुप्त घोषित किया गया।
- ऐतिहासिक महत्व: इसका विलुप्त होना सबसे पहले प्रलेखित मानव-कारण विलुप्त होने में से एक था, जिसने जैव विविधता पर मानव गतिविधि के प्रभाव को उजागर किया।
Former SC judge named human rights panel chief /पूर्व सुप्रीम कोर्ट जज को मानवाधिकार पैनल का अध्यक्ष बनाया गया
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
The President of India appointed Justice V. Ramasubramanian (retd.) as Chairperson of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), filling a vacancy since June.
- Child rights advocate Priyank Kanoongo and Justice Bidyut Ranjan Sarangi were appointed as members.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC):
- Acts as a watchdog for human rights in India, covering rights related to life, liberty, equality, and dignity, as guaranteed by the Constitution and international covenants enforceable by Indian courts.
- Establishment:
- Established on 12th October 1993 under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- Amended through the Protection of Human Rights (Amendment) Act, 2006 and the Human Rights (Amendment) Act, 2019.
- Conforms to the Paris Principles (1991) for human rights promotion and protection, endorsed by the UN General Assembly in 1993.
- Composition:
- Comprises a Chairman (former Chief Justice of India or Supreme Court judge) and five members.
- Appointment:
- Members are appointed by the President based on the recommendation of a six-member committee headed by the Prime Minister, including the Speaker of Lok Sabha, Deputy Chairman of Rajya Sabha, Leaders of the Opposition, and the Union Home Minister.
- Tenure:
- Members serve a term of three years or until 70 years of age, whichever is earlier.
- Role and Functions:
- Investigates human rights violations with the powers of a civil court.
- Cannot inquire into cases older than one year.
- Functions mainly as a recommendatory body without punitive powers.
- Limited jurisdiction over armed forces and no power to act on violations by private parties.
पूर्व सुप्रीम कोर्ट जज को मानवाधिकार पैनल का अध्यक्ष बनाया गया
भारत के राष्ट्रपति ने न्यायमूर्ति वी. रामसुब्रमण्यम (सेवानिवृत्त) को राष्ट्रीय मानवाधिकार आयोग (NHRC) का अध्यक्ष नियुक्त किया, जो जून से रिक्त पद पर कार्यरत हैं।
- बाल अधिकार अधिवक्ता प्रियांक कानूनगो और न्यायमूर्ति बिद्युत रंजन सारंगी को सदस्य नियुक्त किया गया।
राष्ट्रीय मानवाधिकार आयोग (NHRC):
- भारत में मानवाधिकारों के लिए एक प्रहरी के रूप में कार्य करता है, जिसमें संविधान द्वारा गारंटीकृत जीवन, स्वतंत्रता, समानता और सम्मान से संबंधित अधिकार और भारतीय न्यायालयों द्वारा लागू किए जाने वाले अंतर्राष्ट्रीय अनुबंध शामिल हैं।
- स्थापना:
- मानवाधिकार संरक्षण अधिनियम (PHRA), 1993 के तहत 12 अक्टूबर 1993 को स्थापित।
- मानवाधिकार संरक्षण (संशोधन) अधिनियम, 2006 और मानवाधिकार (संशोधन) अधिनियम, 2019 के माध्यम से संशोधित।
- 1993 में संयुक्त राष्ट्र महासभा द्वारा समर्थित मानवाधिकार संवर्धन और संरक्षण के लिए पेरिस सिद्धांतों (1991) के अनुरूप है।
- संरचना:
- इसमें एक अध्यक्ष (भारत के पूर्व मुख्य न्यायाधीश या सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के न्यायाधीश) और पांच सदस्य शामिल हैं।
- नियुक्ति:
- सदस्यों की नियुक्ति राष्ट्रपति द्वारा प्रधानमंत्री की अध्यक्षता वाली छह सदस्यीय समिति की सिफारिश के आधार पर की जाती है, जिसमें लोकसभा के अध्यक्ष, राज्यसभा के उपसभापति, विपक्ष के नेता और केंद्रीय गृह मंत्री शामिल होते हैं।
- कार्यकाल:
- सदस्य तीन वर्ष या 70 वर्ष की आयु तक, जो भी पहले हो, तक कार्य करते हैं।
- भूमिका और कार्य:
- सिविल कोर्ट की शक्तियों के साथ मानवाधिकार उल्लंघन की जांच करता है।
- एक वर्ष से अधिक पुराने मामलों की जांच नहीं कर सकता।
- दंडात्मक शक्तियों के बिना मुख्य रूप से एक सिफारिशी निकाय के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- सशस्त्र बलों पर सीमित अधिकार क्षेत्र और निजी पक्षों द्वारा उल्लंघन पर कार्रवाई करने की कोई शक्ति नहीं।
Filmmaker who gave a voice to the voiceless, held dear the idea of India /फिल्म निर्माता जिन्होंने बेजुबानों को आवाज़ दी, भारत के विचार को बहुत महत्व दिया
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
Renowned filmmaker Shyam Benegal, a pioneer of Indian New Wave cinema, passed away at 90.
- Tributes poured in from leaders and celebrities, recognizing his profound contributions to Indian cinema and society.
More About Shyam Benegal:
- Legacy: Peerless filmmaker and Dada Saheb Phalke Award winner who passed away at 90, documented India’s social fabric through cinema.
- Indian New Wave: Known for films like Ankur (1974), Nishant (1975), and Manthan (1976) that highlighted the struggles of marginalized communities.
- Style: Used cinema to reflect the act of living, combining realism with searing social commentary.
- Range of Work: Explored themes from idealism (Bhumika, Sardari Begum) to satire (Welcome to Sajjanpur, Well Done Abba).
- Pioneering Efforts: Introduced crowdfunding (Manthan), and created iconic works like Bharat Ek Khoj and Samvidhan.
- Team & Actors: Collaborated with creatives like Govind Nihalani and introduced talents like Shabana Azmi and Naseeruddin Shah.
- Ideology: Advocated pluralism and spoke against intolerance.
- Notable Biopics: Directed The Making of Mahatma, The Forgotten Hero, and Sheikh Mujibur Rahman’s biopic (2023).
फिल्म निर्माता जिन्होंने बेजुबानों को आवाज़ दी, भारत के विचार को बहुत महत्व दिया
भारतीय न्यू वेव सिनेमा के अग्रणी, प्रसिद्ध फिल्म निर्माता श्याम बेनेगल का 90 वर्ष की आयु में निधन हो गया।
- भारतीय सिनेमा और समाज में उनके गहन योगदान को मान्यता देते हुए नेताओं और मशहूर हस्तियों ने उन्हें श्रद्धांजलि दी।
श्याम बेनेगल के बारे में अधिक जानकारी:
- विरासत: बेमिसाल फिल्म निर्माता और दादा साहब फाल्के पुरस्कार विजेता, जिनका 90 वर्ष की आयु में निधन हो गया, ने सिनेमा के माध्यम से भारत के सामाजिक ताने-बाने को दर्शाया।
- भारतीय नई लहर: अंकुर (1974), निशांत (1975) और मंथन (1976) जैसी फिल्मों के लिए जाने जाते हैं, जिसमें हाशिए पर पड़े समुदायों के संघर्षों को उजागर किया गया।
- शैली: सिनेमा का उपयोग जीवन जीने के तरीके को दर्शाने के लिए किया, जिसमें यथार्थवाद को तीखी सामाजिक टिप्पणियों के साथ जोड़ा गया।
- कार्य की सीमा: आदर्शवाद (भूमिका, सरदारी बेगम) से लेकर व्यंग्य (वेलकम टू सज्जनपुर, वेल डन अब्बा) तक के विषयों की खोज की।
- अग्रणी प्रयास: क्राउडफंडिंग (मंथन) की शुरुआत की और भारत एक खोज और संविधान जैसी प्रतिष्ठित कृतियाँ बनाईं।
- टीम और अभिनेता: गोविंद निहलानी जैसे रचनात्मक लोगों के साथ सहयोग किया और शबाना आज़मी और नसीरुद्दीन शाह जैसी प्रतिभाओं को पेश किया।
- विचारधारा: बहुलवाद की वकालत की और असहिष्णुता के खिलाफ़ आवाज़ उठाई।
- उल्लेखनीय बायोपिक: द मेकिंग ऑफ महात्मा, द फॉरगॉटन हीरो और शेख मुजीबुर रहमान की बायोपिक (2023) का निर्देशन किया।
India’s reliance on China for critical minerals /महत्वपूर्ण खनिजों के लिए चीन पर भारत की निर्भरता
Syllabus : GS 2 & 3: International Relations &Indian Economy
Source : The Hindu
India’s dependency on China for critical minerals poses significant challenges to its economic and national security.
- With China dominating mineral reserves, processing, and refining, India’s vulnerability in sectors like electronics, energy, and defense has increased.
- India is taking steps to diversify supply sources and reduce this reliance.
Identification of Critical Minerals
- In 2023, the Ministry of Mines identified 30 critical minerals crucial for India’s economic development and national security.
- While India’s import dependency on 10 minerals was highlighted, the article points out the significant issue of dependency on China.
China’s Dominance in the Global Mineral Market
China’s Vast Resource Base and Mining Capabilities
- China is the world’s largest mining nation, having discovered 173 types of minerals, including key minerals like copper, nickel, lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements.
- China controls nearly 40% of global reserves for critical minerals and has invested significantly in exploration, discovering 132 new mineral deposits, including 34 large ones.
- Processing and Refining Dominance
- China dominates mineral processing and refining, controlling 87% of rare earth processing, 58% of lithium refining, and 68% of silicon processing, giving it a significant influence over global supply chains.
China’s Export Controls Strategy
Strategic Export Restrictions
- China strategically controls exports of critical minerals like antimony, gallium, and germanium, especially those vital for semiconductor, battery, and high-tech manufacturing.
- However, China carefully balances these restrictions to avoid harming its own domestic industries that rely on these minerals and ensures it doesn’t disrupt its key economic sectors.
India’s Dependency on Chinese Imports
High Dependency on Chinese Supplies
- India’s vulnerability to Chinese supplies is particularly high for six critical minerals: bismuth (85.6%), lithium (82%), silicon (76%), titanium (50.6%), tellurium (48.8%), and graphite (42.4%).
- Bismuth, lithium, and graphite are critical for various industries, including pharmaceuticals, EV batteries, and solar panels, all of which rely heavily on Chinese processing and production.
Challenges Behind India’s Import Reliance
Structural Issues in Mining and Processing
- Despite possessing significant mineral resources, India faces challenges in mining technologies and processing capabilities, limiting domestic production.
- Lack of private sector participation and inadequate policy incentives hinder the development of India’s mining sector.
India’s Strategy to Reduce Dependency
Multi-Pronged Approach
- India has launched initiatives like KABIL, a joint venture of three State-owned companies, to secure overseas mineral assets and diversify supply sources.
- India is engaging in global partnerships, such as the Minerals Security Partnership and the Critical Raw Materials Club, to reduce its dependence on China.
Focus on Research and Recycling
- India is investing in research through institutions like the Geological Survey of India and the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research.
- The country is also promoting recycling and circular economy practices, including production-linked incentives for extracting critical minerals through recycling.
Long-Term Commitment Needed
- While these efforts are promising, a sustained investment and long-term commitment are necessary for India to successfully reduce its dependency on China.
महत्वपूर्ण खनिजों के लिए चीन पर भारत की निर्भरता
महत्वपूर्ण खनिजों के लिए चीन पर भारत की निर्भरता इसकी आर्थिक और राष्ट्रीय सुरक्षा के लिए गंभीर चुनौतियां पेश करती है।
- खनिज भंडार, प्रसंस्करण और शोधन में चीन के दबदबे के कारण इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स, ऊर्जा और रक्षा जैसे क्षेत्रों में भारत की भेद्यता बढ़ गई है।
- भारत आपूर्ति स्रोतों में विविधता लाने और इस निर्भरता को कम करने के लिए कदम उठा रहा है।
महत्वपूर्ण खनिजों की पहचान
- खान मंत्रालय ने 2023 में भारत के आर्थिक विकास और राष्ट्रीय सुरक्षा के लिए महत्वपूर्ण 30 खनिजों की पहचान की है।
- जबकि 10 खनिजों पर भारत की आयात निर्भरता पर प्रकाश डाला गया, लेख में चीन पर निर्भरता के महत्वपूर्ण मुद्दे को इंगित किया गया है।
वैश्विक खनिज बाजार में चीन का प्रभुत्व
चीन का विशाल संसाधन आधार और खनन क्षमताएँ
- चीन दुनिया का सबसे बड़ा खनन राष्ट्र है, जिसने 173 प्रकार के खनिजों की खोज की है, जिसमें तांबा, निकल, लिथियम, कोबाल्ट और दुर्लभ पृथ्वी तत्व जैसे प्रमुख खनिज शामिल हैं।
- चीन महत्वपूर्ण खनिजों के लिए वैश्विक भंडार का लगभग 40% नियंत्रित करता है और उसने अन्वेषण में महत्वपूर्ण निवेश किया है, जिसमें 34 बड़े सहित 132 नए खनिज भंडार की खोज की गई है।
प्रसंस्करण और शोधन प्रभुत्व
- चीन खनिज प्रसंस्करण और शोधन में प्रभुत्व रखता है, दुर्लभ पृथ्वी प्रसंस्करण का 87%, लिथियम शोधन का 58% और सिलिकॉन प्रसंस्करण का 68% नियंत्रित करता है, जिससे वैश्विक आपूर्ति श्रृंखलाओं पर इसका महत्वपूर्ण प्रभाव पड़ता है।
चीन की निर्यात नियंत्रण रणनीति
रणनीतिक निर्यात प्रतिबंध
- चीन रणनीतिक रूप से एंटीमनी, गैलियम और जर्मेनियम जैसे महत्वपूर्ण खनिजों के निर्यात को नियंत्रित करता है, विशेष रूप से अर्धचालक, बैटरी और उच्च तकनीक निर्माण के लिए महत्वपूर्ण।
- हालांकि, चीन इन प्रतिबंधों को सावधानीपूर्वक संतुलित करता है ताकि इन खनिजों पर निर्भर अपने घरेलू उद्योगों को नुकसान न पहुंचे और यह सुनिश्चित हो सके कि यह उसके प्रमुख आर्थिक क्षेत्रों को बाधित न करे।
चीनी आयात पर भारत की निर्भरता
चीनी आपूर्ति पर उच्च निर्भरता
- चीनी आपूर्ति के लिए भारत की भेद्यता विशेष रूप से छह महत्वपूर्ण खनिजों के लिए अधिक है: बिस्मथ (6%), लिथियम (82%), सिलिकॉन (76%), टाइटेनियम (50.6%), टेल्यूरियम (48.8%), और ग्रेफाइट (42.4%)।
- बिस्मथ, लिथियम और ग्रेफाइट विभिन्न उद्योगों के लिए महत्वपूर्ण हैं, जिनमें फार्मास्यूटिकल्स, ईवी बैटरी और सौर पैनल शामिल हैं, जो सभी चीनी प्रसंस्करण और उत्पादन पर बहुत अधिक निर्भर हैं।
भारत की आयात निर्भरता के पीछे की चुनौतियाँ
खनन और प्रसंस्करण में संरचनात्मक मुद्दे
- महत्वपूर्ण खनिज संसाधनों के होने के बावजूद, भारत को खनन प्रौद्योगिकियों और प्रसंस्करण क्षमताओं में चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ रहा है, जिससे घरेलू उत्पादन सीमित हो रहा है।
- निजी क्षेत्र की भागीदारी की कमी और अपर्याप्त नीतिगत प्रोत्साहन भारत के खनन क्षेत्र के विकास में बाधा डालते हैं।
निर्भरता कम करने की भारत की रणनीति
बहुआयामी दृष्टिकोण
- भारत ने विदेशी खनिज परिसंपत्तियों को सुरक्षित करने और आपूर्ति स्रोतों में विविधता लाने के लिए तीन सरकारी स्वामित्व वाली कंपनियों के संयुक्त उद्यम KABIL जैसी पहल शुरू की है।
- भारत चीन पर अपनी निर्भरता कम करने के लिए खनिज सुरक्षा भागीदारी और महत्वपूर्ण कच्चे माल क्लब जैसी वैश्विक साझेदारियों में शामिल हो रहा है।
शोध और पुनर्चक्रण पर ध्यान
- भारत भारतीय भूवैज्ञानिक सर्वेक्षण और वैज्ञानिक और औद्योगिक अनुसंधान परिषद जैसी संस्थाओं के माध्यम से शोध में निवेश कर रहा है।
- देश पुनर्चक्रण और परिपत्र अर्थव्यवस्था प्रथाओं को भी बढ़ावा दे रहा है, जिसमें पुनर्चक्रण के माध्यम से महत्वपूर्ण खनिजों को निकालने के लिए उत्पादन से जुड़े प्रोत्साहन शामिल हैं।
दीर्घकालिक प्रतिबद्धता की आवश्यकता
- हालांकि ये प्रयास आशाजनक हैं, लेकिन भारत को चीन पर अपनी निर्भरता को सफलतापूर्वक कम करने के लिए निरंतर निवेश और दीर्घकालिक प्रतिबद्धता की आवश्यकता है।
The MSME Revolution: Transforming India’s Economic Landscape /MSME क्रांति: भारत के आर्थिक परिदृश्य को बदलना
In News
The MSME sector in India has witnessed remarkable growth, significantly boosting exports, contributing to GDP, and driving economic development.
- Despite challenges like the COVID-19 pandemic, MSMEs demonstrated resilience and adaptability, scaling up enterprises and enhancing export competitiveness.

MSMEs’ Contribution to India’s Export Growth
- MSME exports rose significantly from ₹3.95 lakh crore in 2020-21 to ₹12.39 lakh crore in 2024-25.
- The number of exporting MSMEs increased from 52,849 in 2020-21 to 1,73,350 in 2024-25.
- MSMEs contributed 45.73% to India’s exports in 2023-24, which further increased to 45.79% by May 2024.
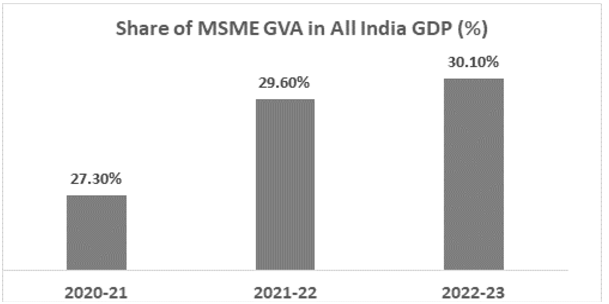
MSMEs’ Role in India’s GDP
- The Gross Value Added (GVA) by MSMEs in GDP grew from 29.7% in 2017-18 to 30.1% in 2022-23.
- Even during the COVID-19 pandemic, MSMEs maintained a significant GDP contribution of 27.3% in 2020-21 and rebounded to 29.6% in 2021-22.
- This demonstrates MSMEs’ resilience and pivotal role in India’s economic stability.
Growth and Upgradation of Enterprises
- MSMEs are classified into Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises based on investment and turnover criteria revised on July 1, 2020.
- Micro Enterprise: Investment ≤ ₹1 crore; Turnover ≤ ₹5 crore.Small Enterprise: Investment ≤ ₹10 crore; Turnover ≤ ₹50 crore.
- Medium Enterprise: Investment ≤ ₹50 crore; Turnover ≤ ₹250 crore.From 2020-21 to 2021-22, 714 Micro enterprises and 3,701 Small enterprises scaled up to Medium.
- The trend grew stronger in 2023-24 to 2024-25, with 2,372 Micro enterprises and 17,745 Small enterprises upgrading to Medium enterprises.
Significance of MSMEs for Economic Development
- MSMEs are instrumental in employment generation, entrepreneurship promotion, and inclusive growth.
- The sector fosters innovation, supports export competitiveness, and strengthens India’s position as a global economic leader.
- By creating employment opportunities and driving economic development, MSMEs serve as the backbone of India’s economy.
MSME क्रांति: भारत के आर्थिक परिदृश्य को बदलना
भारत में एमएसएमई क्षेत्र ने उल्लेखनीय वृद्धि देखी है, निर्यात को काफी बढ़ावा दिया है, जीडीपी में योगदान दिया है और आर्थिक विकास को गति दी है।
- कोविड-19 महामारी जैसी चुनौतियों के बावजूद, एमएसएमई ने लचीलापन और अनुकूलनशीलता का प्रदर्शन किया, उद्यमों का विस्तार किया और निर्यात प्रतिस्पर्धात्मकता को बढ़ाया।
भारत के निर्यात वृद्धि में MSME का योगदान
- एमएसएमई निर्यात 2020-21 में ₹3.95 लाख करोड़ से बढ़कर 2024-25 में ₹12.39 लाख करोड़ हो गया।
- निर्यात करने वाले एमएसएमई की संख्या 2020-21 में 52,849 से बढ़कर 2024-25 में 1,73,350 हो गई।
- एमएसएमई ने 2023-24 में भारत के निर्यात में 73% का योगदान दिया, जो मई 2024 तक बढ़कर 45.79% हो गया।
भारत के सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में MSME की भूमिका
- जीडीपी में एमएसएमई द्वारा सकल मूल्य वर्धन (जीवीए) 2017-18 में 7% से बढ़कर 2022-23 में 30.1% हो गया।
- यहां तक कि कोविड-19 महामारी के दौरान भी एमएसएमई ने 2020-21 में 3% का महत्वपूर्ण जीडीपी योगदान बनाए रखा और 2021-22 में 29.6% तक पहुंच गया।
- यह एमएसएमई के लचीलेपन और भारत की आर्थिक स्थिरता में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका को दर्शाता है।
उद्यमों का विकास और उन्नयन
- 1 जुलाई, 2020 को संशोधित निवेश और टर्नओवर मानदंडों के आधार पर एमएसएमई को सूक्ष्म, लघु और मध्यम उद्यमों में वर्गीकृत किया गया है।
- सूक्ष्म उद्यम: निवेश ≤ ₹1 करोड़; टर्नओवर ≤ ₹5 करोड़। लघु उद्यम: निवेश ≤ ₹10 करोड़; टर्नओवर ≤ ₹50 करोड़। मध्यम उद्यम: निवेश ≤ ₹50 करोड़; टर्नओवर ≤ ₹250 करोड़।
- 2020-21 से 2021-22 तक, 714 सूक्ष्म उद्यम और 3,701 लघु उद्यम मध्यम उद्यमों में अपग्रेड हुए।
- 2023-24 से 2024-25 में यह प्रवृत्ति और मजबूत हुई, जिसमें 2,372 सूक्ष्म उद्यम और 17,745 लघु उद्यम मध्यम उद्यमों में अपग्रेड हुए।
आर्थिक विकास के लिए एमएसएमई का महत्व
- एमएसएमई रोजगार सृजन, उद्यमिता संवर्धन और समावेशी विकास में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं।
- यह क्षेत्र नवाचार को बढ़ावा देता है, निर्यात प्रतिस्पर्धा का समर्थन करता है और वैश्विक आर्थिक नेता के रूप में भारत की स्थिति को मजबूत करता है।
- रोजगार के अवसर पैदा करके और आर्थिक विकास को गति देकर, एमएसएमई भारत की अर्थव्यवस्था की रीढ़ की हड्डी के रूप में काम करते हैं।
Envisioning India as a global skill supplier / भारत को वैश्विक कौशल आपूर्तिकर्ता के रूप में देखना
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 & 3: International Relations &Indian Economy
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- The article discusses India’s potential to contribute to the global job market through skilled labor migration.
- It highlights the need for a comprehensive policy framework to address skill gaps, improve training standards, and facilitate the effective integration of returning migrants.
- Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of data-driven migration policies.
India’s Skilled Workforce and Global Migration Trends
- Prime Minister Modi expressed hope that India’s skilled workforce will play a significant role in the global job market.
- Global mega trends such as demographic transitions, technological advancements, and climate change are altering the demand and supply of international migrant workers.
- Skills are becoming central to public policy discourse as countries adjust their immigration policies to address challenges like an ageing society, digitalisation, and declining fertility rates.
Skill-Selective Immigration Policies of Key Countries
- Traditional migration destinations like the U.S., U.K., Canada, and Gulf Cooperation Council countries, along with new destinations like Germany, South Korea, and Japan, are increasingly prioritising skilled workers.
- These countries recognise that economic diversification and addressing societal challenges can be achieved by welcoming skilled international migrants.
India’s Challenges in Meeting Global Skill Gaps
- India faces a complex task in responding to the skill needs of various destination countries.
- Effective policy interventions based on robust evidence are essential for facilitating skill-centred migration.
- India lacks a comprehensive policy framework for international labour mobility, with interventions often being fragmented and not data-driven.
- The only data source available for migrant labour outflows is emigration clearance data, which primarily covers low-skilled workers, creating a major obstacle for formulating effective policies.
Lack of a Comprehensive National Policy on Migration
- India’s efforts have largely focused on bilateral agreements with other countries concerning social security, skills, protection, and welfare, but these agreements are not part of a larger policy framework.
- There is a lack of evaluations to assess the effectiveness of these agreements, highlighting the need for a more cohesive and structured approach.
The Path Forward for India
- India needs to design a comprehensive national policy on international labour migration, with skill-centred migration as a central pillar.
- A critical step is identifying the skills in demand in destination countries, forecasting skill needs, and using data analytics from job vacancies to address skill gaps.
- India must assess its own capacity to provide the required skills, mapping existing skill development efforts and aligning them with the needs of destination countries.
Enhancing Skill Development Standards
- To meet global standards, India must improve its skill development efforts, including integrating specific skills into curricula, reorienting training programmes, and creating targeted short-term courses for destination countries.
- A review of the National Skills Qualification Framework is necessary to align India’s qualifications with those of major migration destinations.
Focus on Return Migration and Reintegration
- As international migration policies encourage temporary migration, return migration is becoming increasingly important.
- India must better utilise the skills of returning migrants by ensuring their competencies are recognised and accredited, facilitating their effective reintegration into the Indian labour market.
Need for a Skill-Centred Migration Information System
- India requires a comprehensive skill-centred international labour migration information system to collect, analyse, and report data on migration trends.
- Such a system will support evidence-based interventions, foster partnerships with destination countries, and enhance migration and development outcomes.
भारत को वैश्विक कौशल आपूर्तिकर्ता के रूप में देखना
संदर्भ :
- लेख में कुशल श्रम प्रवास के माध्यम से वैश्विक नौकरी बाजार में योगदान करने की भारत की क्षमता पर चर्चा की गई है।
- यह कौशल अंतराल को दूर करने, प्रशिक्षण मानकों में सुधार करने और वापस लौटने वाले प्रवासियों के प्रभावी एकीकरण को सुविधाजनक बनाने के लिए एक व्यापक नीति ढांचे की आवश्यकता पर प्रकाश डालता है।
- इसके अतिरिक्त, यह डेटा-संचालित प्रवास नीतियों के महत्व पर जोर देता है।
भारत का कुशल कार्यबल और वैश्विक प्रवास रुझान
- प्रधानमंत्री मोदी ने उम्मीद जताई कि भारत का कुशल कार्यबल वैश्विक नौकरी बाजार में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाएगा।
- जनसांख्यिकीय परिवर्तन, तकनीकी प्रगति और जलवायु परिवर्तन जैसे वैश्विक मेगा रुझान अंतरराष्ट्रीय प्रवासी श्रमिकों की मांग और आपूर्ति को बदल रहे हैं।
- जैसे-जैसे देश वृद्ध होते समाज, डिजिटलीकरण और घटती प्रजनन दर जैसी चुनौतियों का समाधान करने के लिए अपनी आव्रजन नीतियों को समायोजित कर रहे हैं, कौशल सार्वजनिक नीति चर्चा का केंद्र बन रहे हैं।
प्रमुख देशों की कौशल-चयनात्मक आव्रजन नीतियाँ
- अमेरिका, ब्रिटेन, कनाडा और खाड़ी सहयोग परिषद देशों जैसे पारंपरिक प्रवास गंतव्यों के साथ-साथ जर्मनी, दक्षिण कोरिया और जापान जैसे नए गंतव्यों में कुशल श्रमिकों को प्राथमिकता दी जा रही है।
- ये देश मानते हैं कि कुशल अंतरराष्ट्रीय प्रवासियों का स्वागत करके आर्थिक विविधीकरण और सामाजिक चुनौतियों का समाधान किया जा सकता है।
वैश्विक कौशल अंतराल को पूरा करने में भारत की चुनौतियाँ
- भारत को विभिन्न गंतव्य देशों की कौशल आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने में एक जटिल कार्य का सामना करना पड़ता है।
- कौशल-केंद्रित प्रवास को सुविधाजनक बनाने के लिए मजबूत साक्ष्यों पर आधारित प्रभावी नीतिगत हस्तक्षेप आवश्यक हैं।
- भारत में अंतरराष्ट्रीय श्रम गतिशीलता के लिए एक व्यापक नीतिगत ढाँचे का अभाव है, जिसमें हस्तक्षेप अक्सर खंडित होते हैं और डेटा-संचालित नहीं होते हैं।
- प्रवासी श्रम बहिर्वाह के लिए उपलब्ध एकमात्र डेटा स्रोत उत्प्रवास निकासी डेटा है, जो मुख्य रूप से कम कुशल श्रमिकों को कवर करता है, जो प्रभावी नीतियों को तैयार करने में एक बड़ी बाधा पैदा करता है।
प्रवास पर एक व्यापक राष्ट्रीय नीति का अभाव
- भारत के प्रयास मुख्य रूप से सामाजिक सुरक्षा, कौशल, संरक्षण और कल्याण से संबंधित अन्य देशों के साथ द्विपक्षीय समझौतों पर केंद्रित रहे हैं, लेकिन ये समझौते एक बड़े नीतिगत ढांचे का हिस्सा नहीं हैं।
- इन समझौतों की प्रभावशीलता का आकलन करने के लिए मूल्यांकन की कमी है, जो अधिक सुसंगत और संरचित दृष्टिकोण की आवश्यकता को उजागर करता है।
भारत के लिए आगे का रास्ता
- भारत को अंतरराष्ट्रीय श्रम प्रवास पर एक व्यापक राष्ट्रीय नीति तैयार करने की आवश्यकता है, जिसमें कौशल-केंद्रित प्रवासन एक केंद्रीय स्तंभ हो।
- एक महत्वपूर्ण कदम गंतव्य देशों में मांग में कौशल की पहचान करना, कौशल आवश्यकताओं का पूर्वानुमान लगाना और कौशल अंतराल को दूर करने के लिए नौकरी रिक्तियों से डेटा एनालिटिक्स का उपयोग करना है।
- भारत को आवश्यक कौशल प्रदान करने की अपनी क्षमता का आकलन करना चाहिए, मौजूदा कौशल विकास प्रयासों का मानचित्रण करना चाहिए और उन्हें गंतव्य देशों की आवश्यकताओं के साथ संरेखित करना चाहिए।
कौशल विकास मानकों को बढ़ाना
- वैश्विक मानकों को पूरा करने के लिए, भारत को अपने कौशल विकास प्रयासों में सुधार करना चाहिए, जिसमें पाठ्यक्रम में विशिष्ट कौशल को एकीकृत करना, प्रशिक्षण कार्यक्रमों को पुनः उन्मुख करना और गंतव्य देशों के लिए लक्षित अल्पकालिक पाठ्यक्रम बनाना शामिल है।
- भारत की योग्यताओं को प्रमुख प्रवास गंतव्यों के साथ संरेखित करने के लिए राष्ट्रीय कौशल योग्यता ढांचे की समीक्षा आवश्यक है।
वापसी प्रवास और पुनः एकीकरण पर ध्यान दें
- चूंकि अंतर्राष्ट्रीय प्रवास नीतियां अस्थायी प्रवास को प्रोत्साहित करती हैं, इसलिए वापसी प्रवास तेजी से महत्वपूर्ण होता जा रहा है।
- भारत को यह सुनिश्चित करके लौटने वाले प्रवासियों के कौशल का बेहतर उपयोग करना चाहिए कि उनकी योग्यताओं को मान्यता दी जाए और उन्हें मान्यता दी जाए, जिससे उन्हें भारतीय श्रम बाजार में प्रभावी रूप से पुनः एकीकृत करने में सुविधा हो।
कौशल-केंद्रित प्रवासन सूचना प्रणाली की आवश्यकता
- भारत को प्रवासन प्रवृत्तियों पर डेटा एकत्र करने, उसका विश्लेषण करने और रिपोर्ट करने के लिए एक व्यापक कौशल-केंद्रित अंतर्राष्ट्रीय श्रम प्रवासन सूचना प्रणाली की आवश्यकता है।
- ऐसी प्रणाली साक्ष्य-आधारित हस्तक्षेपों का समर्थन करेगी, गंतव्य देशों के साथ साझेदारी को बढ़ावा देगी और प्रवासन और विकास परिणामों को बढ़ाएगी।