CURRENT AFFAIRS – 15/06/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 15/06/2024
- Prerna Sthal will be inaugurated tomorrow / प्रेरणा स्थल का उद्घाटन कल होगा
- Law Ministry plans to place report on simultaneous polls before Cabinet at the earliest / कानून मंत्रालय जल्द से जल्द कैबिनेट के समक्ष एक साथ चुनाव कराने की रिपोर्ट पेश करने की योजना बना रहा है
- CIC upholds response of Rashtrapati Bhavan on RTI query on Presidential assent / सीआईसी ने राष्ट्रपति भवन के आरटीआई आवेदन पर राष्ट्रपति भवन के जवाब को बरकरार रखा
- Dividing a culture / संस्कृति का विभाजन
- U.S. Navy faces its most intense combat since Second World War against Houthis / अमेरिकी नौसेना को द्वितीय विश्व युद्ध के बाद से हौथियों के खिलाफ सबसे भीषण युद्ध का सामना करना पड़ रहा है
- Reimagining Indian federalism / भारतीय संघवाद की पुनर्कल्पना
- Major Straits of the world [Mapping] / दुनिया के प्रमुख जलडमरूमध्य [मानचित्र]
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 15/06/2024
Prerna Sthal will be inaugurated tomorrow / प्रेरणा स्थल का उद्घाटन कल होगा
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
The relocation of Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar statues from their prominent positions near Parliament to Prerna Sthal has sparked controversy.
- Opposition parties criticising it as an attempt to stifle democratic protests, while the Lok Sabha Secretariat cites redevelopment plans as justification.
- Prerna Sthal is an area within the Parliament complex in India.
- It houses key statues, including those of Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar.
- These statues were relocated from their earlier prominent positions near Parliament.
- The move has drawn criticism from the opposition, alleging it restricts democratic protests.
- The Lok Sabha Secretariat defends the relocation as part of a broader redevelopment plan for the parliamentary precincts.
- Prerna Sthal is set to be inaugurated amid ongoing debates about its symbolic and political implications.
प्रेरणा स्थल का उद्घाटन कल होगा
महात्मा गांधी और डॉ. बी.आर. अंबेडकर की मूर्तियों को संसद के निकट स्थित प्रमुख स्थानों से हटाकर प्रेरणा स्थल पर स्थानांतरित करने से विवाद उत्पन्न हो गया है।
- विपक्षी दल इसे लोकतांत्रिक विरोध को दबाने का प्रयास बताकर इसकी आलोचना कर रहे हैं, जबकि लोकसभा सचिवालय पुनर्विकास योजनाओं को औचित्य के रूप में बता रहा है।
- प्रेरणा स्थल भारत में संसद परिसर के भीतर एक क्षेत्र है।
- इसमें महात्मा गांधी और डॉ. बी.आर. अंबेडकर की प्रतिमाओं सहित प्रमुख प्रतिमाएँ हैं।
- इन प्रतिमाओं को संसद के पास उनके पहले के प्रमुख स्थानों से स्थानांतरित कर दिया गया था।
- इस कदम की विपक्ष ने आलोचना की है, उनका आरोप है कि यह लोकतांत्रिक विरोध को रोकता है।
- लोकसभा सचिवालय ने संसदीय परिसर के लिए व्यापक पुनर्विकास योजना के हिस्से के रूप में स्थानांतरण का बचाव किया है।
- प्रेरणा स्थल का उद्घाटन इसके प्रतीकात्मक और राजनीतिक निहितार्थों के बारे में चल रही बहस के बीच किया जाना है।
Law Ministry plans to place report on simultaneous polls before Cabinet at the earliest / कानून मंत्रालय जल्द से जल्द कैबिनेट के समक्ष एक साथ चुनाव कराने की रिपोर्ट पेश करने की योजना बना रहा है
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
Feasibility of simultaneous elections:
- Pros:
- Reduced Expenditure: Simultaneous elections would lower costs associated with frequent polls.
- Stable Governance: Ensures uninterrupted governance without frequent disruptions.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Officials can focus on governance rather than election preparations.
- Reduced Political Polarisation: May mitigate intense election-driven polarisation. Environmental Benefits: Lower environmental impact from reduced campaign activities.
- Cons:
- Constitutional Challenges: Requires significant constitutional amendments.
- Logistical Challenges: Complex coordination among Election Commission and states.
- Dominance of National Issues: Local issues may be overshadowed by national narratives.
- Increased Centralization: Potential for greater centralization of political power.
- Impact on Federalism: States may lose autonomy in setting election schedules for local body elections.
कानून मंत्रालय जल्द से जल्द कैबिनेट के समक्ष एक साथ चुनाव कराने की रिपोर्ट पेश करने की योजना बना रहा है
एक साथ चुनाव की व्यवहार्यता:
लाभ:
- कम खर्च: एक साथ चुनाव होने से बार-बार होने वाले चुनावों से जुड़ी लागत कम होगी।
- स्थिर शासन: बार-बार व्यवधानों के बिना निर्बाध शासन सुनिश्चित करता है।
- बढ़ी हुई दक्षता: अधिकारी चुनाव की तैयारियों के बजाय शासन पर ध्यान केंद्रित कर सकते हैं।
- कम राजनीतिक ध्रुवीकरण: चुनाव-संचालित तीव्र ध्रुवीकरण को कम कर सकता है। पर्यावरणीय लाभ: कम अभियान गतिविधियों से पर्यावरण पर कम प्रभाव पड़ता है।
नुकसान:
- संवैधानिक चुनौतियाँ: महत्वपूर्ण संवैधानिक संशोधनों की आवश्यकता है।
- तार्किक चुनौतियाँ: चुनाव आयोग और राज्यों के बीच जटिल समन्वय।
- राष्ट्रीय मुद्दों का प्रभुत्व: स्थानीय मुद्दे राष्ट्रीय आख्यानों से प्रभावित हो सकते हैं।
- बढ़ा हुआ केंद्रीकरण: राजनीतिक शक्ति के अधिक केंद्रीकरण की संभावना।
- संघवाद पर प्रभाव: स्थानीय निकाय चुनावों के लिए चुनाव कार्यक्रम निर्धारित करने में राज्य स्वायत्तता खो सकते हैं।
CIC upholds response of Rashtrapati Bhavan on RTI query on Presidential assent / सीआईसी ने राष्ट्रपति भवन के आरटीआई आवेदन पर राष्ट्रपति भवन के जवाब को बरकरार रखा
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
The Central Information Commission (CIC) upheld Rashtrapati Bhavan’s response to an RTI query regarding the number of times former President Kovind returned decisions by the Prime Minister/Union Council of Ministers for reconsideration.
- The President’s Secretariat stated that no information was available on record regarding such returns.
Instances where President’s consent is required:
- Ordinance: The President’s consent is required for promulgating ordinances by the Union Cabinet during parliamentary recess, which have the same force as laws passed by Parliament.
- Appointments: Certain key appointments such as the Chief Election Commissioner, Chairman and members of the Union Public Service Commission, and judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts require the President’s approval.
- Legislation: Bills passed by Parliament must receive the President’s assent to become laws. The President can either give assent or withhold it, which may necessitate reconsideration by Parliament.
- Emergency Provisions: During a national emergency, the President exercises special powers, including the suspension of fundamental rights and the promulgation of ordinances, subject to parliamentary approval.
- Dissolution of Lok Sabha: If there is a deadlock in forming a government after elections or if no party has a clear majority, the President decides whether to dissolve the Lok Sabha and call for fresh elections.
- Foreign Treaties: The President ratifies international treaties and agreements negotiated by the Government of India, ensuring they align with national interests and constitutional provisions.
Right to Information (RTI)
- The RTI Act of 2005 grants Indian citizens the right to access government-held information, with exceptions.
- Its goal is to enhance transparency and accountability in public authorities.
- This Act replaced the earlier Freedom of Information Act of 2002.
- RTI aligns with Freedom of Speech and Expression (Article 19) in India’s Constitution.
Central Information Commission (CIC)
| Details | |
| Establishment | Set up under the Section 12 of the Right to Information Act, 2005. |
| Function | · Oversees implementation of RTI Act in Central Government and Union Territories.
· Resolves complaints and decides appeals related to the Act. |
| Composition | · Chief Information Commissioner (CIC)
· Up to 10 Information Commissioners (IC), (appointed by President on recommendation of PM-led Committee consisting Leader of Opposition and Cabinet Ministers.) |
| Qualifications | CIC and IC must be persons of eminence in public life with wide knowledge and experience in: Law, Science and Technology, Social Service, Management, Journalism, Mass Media, Administration, and Governance.
NON-ELIGIBLITY: Members of Parliament or Legislature of any State or Union Territory, hold any office of profit, be connected with any political party, or carry on any business or profession. |
| Tenure | · CIC and IC hold office for such term as prescribed by Central Government or until they attain age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
· NO Reappointment. · IC can be appointed as Chief Information Commissioner, but total tenure including term as IC should not exceed 5 years. |
| Removal | · President can remove CIC or IC on grounds like insolvency, conviction for moral turpitude, engaging in another office of profit, etc.
· Removal for misbehaviour requires Supreme Court enquiry and recommendation. |
| Salary & Conditions | Salary, allowances, and service conditions determined by Central Government, cannot be varied to their disadvantage during service (After RTI Amendment Act,2019) |
| How RTI amendment, 2019 has changed CIC? | · Before the 2019 amendment to the RTI Act, ICs at the CIC held a 5-year fixed term and were considered equal in status to the Chief Election Commissioner and Supreme Court judges.
· The 2019 amendments granted the Centre the power to alter these terms at its discretion. |
| Functions | · Receives and inquires into complaints related to RTI Act violations, including non-appointment of Public Information Officer, refusal or delay in information, unreasonable fees, incomplete or false information.
· Submits annual report on Act’s implementation to Central Government, presented to Parliament. |
| Powers | · Can suo-moto order inquiries, summon persons, enforce oaths, access and inspect documents, receive evidence on affidavit, requisition public records, summon witnesses, and enforce compliance of decisions.
· Can direct public authorities on information access, officer appointments, record management, training, and impose penalties or compensation for non-compliance. |
सीआईसी ने राष्ट्रपति भवन के आरटीआई आवेदन पर राष्ट्रपति भवन के जवाब को बरकरार रखा
केंद्रीय सूचना आयोग (CIC) ने पूर्व राष्ट्रपति कोविंद द्वारा प्रधानमंत्री/केंद्रीय मंत्रिपरिषद द्वारा लिए गए निर्णयों को पुनर्विचार के लिए लौटाए जाने की संख्या के बारे में RTI के तहत पूछे गए प्रश्न पर राष्ट्रपति भवन के जवाब को बरकरार रखा।
- राष्ट्रपति सचिवालय ने कहा कि इस तरह के रिटर्न के बारे में कोई जानकारी रिकॉर्ड में उपलब्ध नहीं है।
ऐसे उदाहरण जहां राष्ट्रपति की सहमति आवश्यक है:
- अध्यादेश: संसद के अवकाश के दौरान केंद्रीय मंत्रिमंडल द्वारा अध्यादेश जारी करने के लिए राष्ट्रपति की सहमति आवश्यक है, जो संसद द्वारा पारित कानूनों के समान ही प्रभावी है।
- नियुक्तियाँ: मुख्य चुनाव आयुक्त, संघ लोक सेवा आयोग के अध्यक्ष और सदस्य, तथा सर्वोच्च न्यायालय और उच्च न्यायालयों के न्यायाधीशों जैसी कुछ प्रमुख नियुक्तियों के लिए राष्ट्रपति की स्वीकृति की आवश्यकता होती है।
- विधान: संसद द्वारा पारित विधेयकों को कानून बनने के लिए राष्ट्रपति की स्वीकृति प्राप्त करनी होती है। राष्ट्रपति या तो स्वीकृति दे सकते हैं या इसे रोक सकते हैं, जिसके लिए संसद द्वारा पुनर्विचार की आवश्यकता हो सकती है।
- आपातकालीन प्रावधान: राष्ट्रीय आपातकाल के दौरान, राष्ट्रपति संसदीय स्वीकृति के अधीन मौलिक अधिकारों के निलंबन और अध्यादेशों की घोषणा सहित विशेष शक्तियों का प्रयोग करते हैं।
- लोकसभा का विघटन: यदि चुनाव के बाद सरकार बनाने में गतिरोध होता है या किसी भी पार्टी के पास स्पष्ट बहुमत नहीं होता है, तो राष्ट्रपति यह निर्णय लेते हैं कि लोकसभा को भंग किया जाए या नए चुनाव कराए जाएं।
- विदेशी संधियाँ: राष्ट्रपति भारत सरकार द्वारा की गई अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संधियों और समझौतों की पुष्टि करते हैं, यह सुनिश्चित करते हुए कि वे राष्ट्रीय हितों और संवैधानिक प्रावधानों के अनुरूप हों।
सूचना का अधिकार (RTI)
- आरटीआई अधिनियम 2005 भारतीय नागरिकों को अपवादों के साथ सरकारी जानकारी तक पहुँचने का अधिकार देता है।
- इसका लक्ष्य सार्वजनिक प्राधिकरणों में पारदर्शिता और जवाबदेही बढ़ाना है।
- इस अधिनियम ने 2002 के पहले के सूचना की स्वतंत्रता अधिनियम की जगह ली।
- आरटीआई भारत के संविधान में भाषण और अभिव्यक्ति की स्वतंत्रता (अनुच्छेद 19) के अनुरूप है।
केंद्रीय सूचना आयोग (CIC)
| विवरण | |
| स्थापना | सूचना का अधिकार अधिनियम, 2005 की धारा 12 के तहत स्थापित। |
| कार्य | • केंद्र सरकार और केंद्र शासित प्रदेशों में आरटीआई अधिनियम के कार्यान्वयन की देखरेख करना।
• अधिनियम से संबंधित शिकायतों का समाधान करना और अपीलों पर निर्णय लेना। |
| संरचना | • मुख्य सूचना आयुक्त (सीआईसी)
• अधिकतम 10 सूचना आयुक्त (आईसी), (प्रधानमंत्री के नेतृत्व वाली समिति की सिफारिश पर राष्ट्रपति द्वारा नियुक्त, जिसमें विपक्ष के नेता और कैबिनेट मंत्री शामिल होते हैं।) |
| योग्यताएँ | सीआईसी और आईसी को कानून, विज्ञान और प्रौद्योगिकी, सामाजिक सेवा, प्रबंधन, पत्रकारिता, मास मीडिया, प्रशासन और शासन में व्यापक ज्ञान और अनुभव के साथ सार्वजनिक जीवन में प्रतिष्ठित व्यक्ति होना चाहिए।
अपात्रता: किसी भी राज्य या केंद्र शासित प्रदेश के संसद या विधानमंडल के सदस्य, किसी भी लाभ के पद पर आसीन, किसी भी राजनीतिक दल से जुड़े या कोई व्यवसाय या पेशा चलाने वाले। |
| कार्यकाल | • सीआईसी और आईसी केंद्र सरकार द्वारा निर्धारित अवधि तक या 65 वर्ष की आयु प्राप्त करने तक, जो भी पहले हो, पद पर बने रहते हैं।
• पुनर्नियुक्ति नहीं।
• आईसी को मुख्य सूचना आयुक्त के रूप में नियुक्त किया जा सकता है, लेकिन आईसी के रूप में कार्यकाल सहित कुल कार्यकाल 5 वर्ष से अधिक नहीं होना चाहिए। |
| हटाना | • राष्ट्रपति सीआईसी या आईसी को दिवालियापन, नैतिक पतन के लिए दोषसिद्धि, किसी अन्य लाभ के पद पर संलिप्त होने आदि के आधार पर हटा सकते हैं।
• दुर्व्यवहार के लिए हटाने के लिए सर्वोच्च न्यायालय की जांच और सिफारिश की आवश्यकता होती है। |
| वेतन और शर्तें | केंद्र सरकार द्वारा निर्धारित वेतन, भत्ते और सेवा शर्तों में सेवा के दौरान उनके लिए अहितकर परिवर्तन नहीं किया जा सकता (आरटीआई संशोधन अधिनियम, 2019 के बाद) |
| आरटीआई संशोधन, 2019 ने सीआईसी को कैसे बदल दिया है? | • आरटीआई अधिनियम में 2019 के संशोधन से पहले, सीआईसी में आईसी का कार्यकाल 5 साल का होता था और उन्हें मुख्य चुनाव आयुक्त और सुप्रीम कोर्ट के न्यायाधीशों के बराबर दर्जा दिया जाता था।
• 2019 के संशोधनों ने केंद्र को अपने विवेक से इन शर्तों को बदलने की शक्ति प्रदान की। |
| कार्य | • जन सूचना अधिकारी की नियुक्ति न होना, सूचना देने से इनकार करना या देरी करना, अनुचित शुल्क लेना, अधूरी या गलत सूचना देना सहित आरटीआई अधिनियम के उल्लंघन से संबंधित शिकायतों को प्राप्त करना और उनकी जांच करना।
• अधिनियम के कार्यान्वयन पर वार्षिक रिपोर्ट केंद्र सरकार को प्रस्तुत करना, जिसे संसद में प्रस्तुत किया जाता है। |
| शक्तियाँ | • स्वप्रेरणा से जांच का आदेश दे सकता है, व्यक्तियों को बुला सकता है, शपथ दिला सकता है, दस्तावेजों तक पहुंच सकता है और उनका निरीक्षण कर सकता है, हलफनामे पर साक्ष्य प्राप्त कर सकता है, सार्वजनिक अभिलेखों की मांग कर सकता है, गवाहों को बुला सकता है और निर्णयों के अनुपालन को लागू कर सकता है।
• सूचना तक पहुंच, अधिकारी नियुक्तियों, रिकॉर्ड प्रबंधन, प्रशिक्षण पर सार्वजनिक अधिकारियों को निर्देश दे सकता है और गैर-अनुपालन के लिए दंड या मुआवजा लगा सकता है। |
Dividing a culture / संस्कृति का विभाजन
(General Studies- Paper I)
Source : The Hindu
The division of cultural artefacts between Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, including Buddha relics and historical manuscripts, follows the bifurcation plan post-Hyderabad’s status change.
- This process aims to distribute heritage based on acquisition time and provenance, impacting museum collections and historical narratives.
About Bavikonda Buddhist Complex
- Bavikonda, a significant ancient Buddhist site dating from the 3rd century BC to the 3rd century AD, is located along the Eastern Coastline of Andhra Pradesh near Visakhapatnam on the way to Bheemunipatnam.
- It is located an ancient trade route linking Andhradesa with North India via Kalinga, along with its proximity to ancient ports.
- The discovery of Roman silver coins further supports this historical context.
- The site also features Buddhapada slabs intricately carved with Ashtamangala symbols, found on the platforms surrounding the Mahachaitya.
Buddha Relics from Bavikonda
- The relics were discovered in 1993 during archaeological excavations conducted by the Andhra Pradesh Department of Archaeology and Museums (DAM).
- These discoveries have significantly contributed to our understanding of the spread of Buddhism in the region during the post-Ashoka period along the Krishna River basin.
- Nature of Relics:
- The site at Bavikonda yielded several earthen vessels containing gold objects and precious beads.
- These relics are believed to include corporeal remains (related to skull) of the Buddha, along with silver and gold caskets.
- These were found alongside an earthen urn or receptacle (Samudgaka) containing ashy deposits and burnt charcoal.
Concerns Over Missing Artefacts
- Some prized assets have disappeared over the years, such as a painting now found in the San Diego Museum of Art.
- The division and preservation of cultural objects raise questions about the best methods to maintain and understand the shared history of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
Conclusion
- The exchange of artefacts, books, and manuscripts according to provenance and acquisition time offers a unique case study in cultural preservation.
- The ongoing division process aims to respect the historical significance of these objects while addressing the practical challenges of shared heritage between the two States.
संस्कृति का विभाजन
तेलंगाना और आंध्र प्रदेश के बीच सांस्कृतिक कलाकृतियों का विभाजन, जिसमें बुद्ध अवशेष और ऐतिहासिक पांडुलिपियाँ शामिल हैं, हैदराबाद की स्थिति में बदलाव के बाद विभाजन योजना का अनुसरण करता है।
- इस प्रक्रिया का उद्देश्य अधिग्रहण समय और उद्गम के आधार पर विरासत को वितरित करना है, जिससे संग्रहालय संग्रह और ऐतिहासिक आख्यानों पर प्रभाव पड़ता है।
बाविकोंडा बौद्ध परिसर के बारे में
- बाविकोंडा, तीसरी शताब्दी ईसा पूर्व से तीसरी शताब्दी ईस्वी तक का एक महत्वपूर्ण प्राचीन बौद्ध स्थल है, जो विशाखापत्तनम के पास भीमुनिपट्टनम के रास्ते पर आंध्र प्रदेश के पूर्वी तट पर स्थित है।
- यह प्राचीन बंदरगाहों के निकट होने के साथ-साथ कलिंग के माध्यम से आंध्रदेश को उत्तर भारत से जोड़ने वाला एक प्राचीन व्यापार मार्ग है।
- रोमन चांदी के सिक्कों की खोज इस ऐतिहासिक संदर्भ को और पुष्ट करती है।
- इस स्थल पर महाचैत्य के आसपास के प्लेटफार्मों पर पाए गए अष्टमंगल प्रतीकों के साथ जटिल रूप से उकेरे गए बुद्धपद स्लैब भी हैं।
बाविकोंडा से बुद्ध अवशेष
- आंध्र प्रदेश पुरातत्व और संग्रहालय विभाग (डीएएम) द्वारा किए गए पुरातात्विक उत्खनन के दौरान 1993 में अवशेषों की खोज की गई थी।
- इन खोजों ने कृष्णा नदी बेसिन के साथ अशोक काल के बाद के क्षेत्र में बौद्ध धर्म के प्रसार को समझने में महत्वपूर्ण योगदान दिया है।
अवशेषों की प्रकृति:
- बाविकोंडा में स्थल से सोने की वस्तुएं और कीमती मोतियों से भरे कई मिट्टी के बर्तन मिले हैं।
- माना जाता है कि इन अवशेषों में बुद्ध के भौतिक अवशेष (खोपड़ी से संबंधित) के साथ-साथ चांदी और सोने के ताबूत भी शामिल हैं।
- ये राख और जले हुए कोयले से भरे मिट्टी के कलश या पात्र (समुद्गका) के साथ पाए गए थे।
लापता कलाकृतियों पर चिंता
- पिछले कुछ वर्षों में कुछ बेशकीमती संपत्तियां गायब हो गई हैं, जैसे कि अब सैन डिएगो म्यूजियम ऑफ आर्ट में एक पेंटिंग मिली है।
- सांस्कृतिक वस्तुओं का विभाजन और संरक्षण तेलंगाना और आंध्र प्रदेश के साझा इतिहास को बनाए रखने और समझने के सर्वोत्तम तरीकों के बारे में सवाल उठाता है।
निष्कर्ष
- उत्पत्ति और अधिग्रहण समय के अनुसार कलाकृतियों, पुस्तकों और पांडुलिपियों का आदान-प्रदान सांस्कृतिक संरक्षण में एक अनूठा मामला अध्ययन प्रस्तुत करता है।
- चल रही विभाजन प्रक्रिया का उद्देश्य दोनों राज्यों के बीच साझा विरासत की व्यावहारिक चुनौतियों का समाधान करते हुए इन वस्तुओं के ऐतिहासिक महत्व का सम्मान करना है।
U.S. Navy faces its most intense combat since Second World War against Houthis / अमेरिकी नौसेना को द्वितीय विश्व युद्ध के बाद से हौथियों के खिलाफ सबसे भीषण युद्ध का सामना करना पड़ रहा है
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
The U.S. Navy, traditionally prepared for conflicts with major global powers, now faces intense sea battles against Iran-backed Houthi rebels in Yemen.
- This unexpected challenge highlights ongoing tensions in the region and the Navy’s strategic role in protecting international maritime interests.
Conflict Background:
- The U.S. Navy, originally prepared for major powers like Russia and China, is now engaged in intense sea battles with Iran-backed Houthi rebels in Yemen.
- Houthi attacks, intensified since November, target both commercial vessels and warships in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden.
Military Operations:
- S.-led efforts include airstrikes inside Yemen to target Houthi positions, aiming to weaken their capabilities.
- Recent strikes by U.S. and British forces on May 30 resulted in significant casualties among the rebels.
Naval Operations:
- Daily attacks by the Houthis include missiles, drones, and other weaponry, posing constant threats to ships navigating critical waterways.
- The Navy’s response involves constant vigilance and rapid deployment of defensive measures to intercept incoming threats.
Strategic Significance:
- The conflict underscores the Navy’s ongoing role in safeguarding international shipping routes vital for global trade, despite the unexpected adversary.
- Iranian support for the Houthis, including training and intelligence, complicates the security landscape in the region.
अमेरिकी नौसेना को द्वितीय विश्व युद्ध के बाद से हौथियों के खिलाफ सबसे भीषण युद्ध का सामना करना पड़ रहा है
अमेरिकी नौसेना, जो परंपरागत रूप से प्रमुख वैश्विक शक्तियों के साथ संघर्ष के लिए तैयार रहती है, अब यमन में ईरान समर्थित हौथी विद्रोहियों के खिलाफ़ भीषण समुद्री युद्ध का सामना कर रही है।
- यह अप्रत्याशित चुनौती क्षेत्र में चल रहे तनाव और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय समुद्री हितों की रक्षा में नौसेना की रणनीतिक भूमिका को उजागर करती है।
संघर्ष की पृष्ठभूमि:
- अमेरिकी नौसेना, जो मूल रूप से रूस और चीन जैसी प्रमुख शक्तियों के लिए तैयार थी, अब यमन में ईरान समर्थित हौथी विद्रोहियों के साथ भीषण समुद्री युद्ध में लगी हुई है।
- नवंबर से ही हौथी हमले तेज हो गए हैं, जो लाल सागर और अदन की खाड़ी में वाणिज्यिक जहाजों और युद्धपोतों को निशाना बनाते हैं।
सैन्य अभियान:
- अमेरिकी नेतृत्व वाले प्रयासों में यमन के अंदर हवाई हमले शामिल हैं, ताकि हौथी ठिकानों को निशाना बनाया जा सके, जिसका उद्देश्य उनकी क्षमताओं को कमज़ोर करना है।
- 30 मई को अमेरिकी और ब्रिटिश सेना द्वारा किए गए हालिया हमलों में विद्रोहियों के बीच काफी हताहत हुए।
नौसेना अभियान:
- हौथियों द्वारा किए जाने वाले दैनिक हमलों में मिसाइल, ड्रोन और अन्य हथियार शामिल हैं, जो महत्वपूर्ण जलमार्गों पर चलने वाले जहाजों के लिए लगातार खतरा पैदा करते हैं।
- नौसेना की प्रतिक्रिया में लगातार सतर्कता और आने वाले खतरों को रोकने के लिए रक्षात्मक उपायों की तेजी से तैनाती शामिल है।
रणनीतिक महत्व:
- यह संघर्ष अप्रत्याशित प्रतिकूलता के बावजूद, वैश्विक व्यापार के लिए महत्वपूर्ण अंतर्राष्ट्रीय शिपिंग मार्गों की सुरक्षा में नौसेना की चल रही भूमिका को रेखांकित करता है।
- प्रशिक्षण और खुफिया जानकारी सहित हौथियों को ईरानी समर्थन, क्षेत्र में सुरक्षा परिदृश्य को जटिल बनाता है।
Reimagining Indian federalism / भारतीय संघवाद की पुनर्कल्पना
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
Context : The article critiques the present government’s tendency of centralization of power and challenges to India’s federal structure. The article also addresses regional concerns over demographic shifts and fiscal imbalances, emphasising the need for coalition governance to restore balance and strengthen cooperative federalism.
Introduction
- The return to New Delhi of coalition governance offers another hope: that of revitalising India’s beleaguered federal structure, which has sustained countless death blows over the past decade.
A brand of federalism
- One must add to this litany, the tendency to undermine the careful balance in our fiscal federalism that previous governments had maintained, distributing revenues in a way that left it to our States to pursue their own priorities.
- This balance has been disturbed using a number of cynical tools, such as levying cess on a large number of items.
- Unlike tax, cess does not go into the divisible revenue pool and does not need to be shared with States.
- Another shadow hangs over the federal system with the impending lapse of the 91st Amendment in 2026.
- This guarantees that the share of parliamentary constituencies across States would be based on the 1971 Census, in order not to punish those States that had empowered their women, improved human development indicators and curbed their population.
- The ruling party has made it clear that they have no intention of renewing this provision and are looking forward with glee to a fresh Census and a new delimitation exercise.
The concerns of the southern States
- Most people in the south are staunch Indian nationalists who recognise full well the need to correct regional imbalances, and for richer States to subsidise poorer ones.
- But we must ensure that this balancing act does not become financial persecution of our southern States.
- For, unlike most federal systems, India’s revenues are going disproportionately to its worst-performing States, those with rampant illiteracy, high rates of fertility and population growth, while the high-performing southern States get short shrift.
- On June 10, 2024, Uttar Pradesh received a whopping ₹25,069 crore of tax devolution, a figure greater than all our five southern States collectively received. Bihar and Madhya Pradesh got the next largest allocations.
- The concerns of our southern States about delimitation are not unfounded:
- The interests of millions are entwined with the success of this exercise, in which the principles of equitable redistribution and representation should weigh heavily. All States, ultimately, must work together to devise a solution.
Revive the Inter-State Council
- A good starting point would be extracting the Inter-State Council from the throes of desuetude.
- Though its rationale had long been outlined in Article 263 of the Constitution, it was convened only in the 1990s on the recommendation of the Sarkaria Commission.
- But, despite having the potential to become a formidable forum of deliberation, the Council has degenerated into a mere appendage of the Ministry of Home Affairs, in whose shadow it scarcely has any authority.
- So the Inter-State Council must be overhauled and revived to serve as an independent arena for consultation, decision-making, dispute resolution, and coordination between States and various governmental departments and levels of government on issues that affect the States.
Conclusion
- India’s federalism faces challenges from centralised tendencies and demographic shifts that could marginalise certain regions.
- To preserve unity amidst diversity, it is crucial to strengthen cooperative federalism, ensuring all states have equitable representation and resources.
- The revival of forums like the Inter-State Council could foster dialogue and consensus-building among states, crucial for maintaining India’s federal structure.
भारतीय संघवाद की पुनर्कल्पना
प्रसंग : लेख में वर्तमान सरकार की सत्ता के केंद्रीकरण की प्रवृत्ति और भारत के संघीय ढांचे के लिए चुनौतियों की आलोचना की गई है। लेख में जनसांख्यिकीय बदलावों और राजकोषीय असंतुलन पर क्षेत्रीय चिंताओं को भी संबोधित किया गया है, तथा संतुलन बहाल करने और सहकारी संघवाद को मजबूत करने के लिए गठबंधन शासन की आवश्यकता पर जोर दिया गया है।
परिचय
- नई दिल्ली में गठबंधन शासन की वापसी एक और उम्मीद जगाती है: भारत के संकटग्रस्त संघीय ढांचे को पुनर्जीवित करने की, जिसने पिछले दशक में अनगिनत घातक प्रहार झेले हैं।
संघवाद का एक ब्रांड
- इस सूची में, पिछली सरकारों द्वारा बनाए गए हमारे राजकोषीय संघवाद में सावधानीपूर्वक संतुलन को कमज़ोर करने की प्रवृत्ति को जोड़ना चाहिए, राजस्व को इस तरह से वितरित करना कि हमारे राज्यों को अपनी प्राथमिकताओं को आगे बढ़ाने के लिए छोड़ दिया जाए।
- इस संतुलन को कई निंदनीय उपकरणों का उपयोग करके बिगाड़ा गया है, जैसे कि बड़ी संख्या में वस्तुओं पर उपकर लगाना।
- कर के विपरीत, उपकर विभाज्य राजस्व पूल में नहीं जाता है और इसे राज्यों के साथ साझा करने की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है।
- 2026 में 91वें संशोधन की आसन्न समाप्ति के साथ संघीय प्रणाली पर एक और छाया मंडरा रही है।
- यह गारंटी देता है कि राज्यों में संसदीय निर्वाचन क्षेत्रों का हिस्सा 1971 की जनगणना के आधार पर होगा, ताकि उन राज्यों को दंडित न किया जाए जिन्होंने अपनी महिलाओं को सशक्त बनाया, मानव विकास संकेतकों में सुधार किया और अपनी जनसंख्या पर अंकुश लगाया।
- सत्तारूढ़ दल ने यह स्पष्ट कर दिया है कि उनका इस प्रावधान को नवीनीकृत करने का कोई इरादा नहीं है और वे नई जनगणना और नए परिसीमन अभ्यास का बेसब्री से इंतजार कर रहे हैं।
दक्षिणी राज्यों की चिंताएँ
- दक्षिण में ज़्यादातर लोग कट्टर भारतीय राष्ट्रवादी हैं जो क्षेत्रीय असंतुलन को ठीक करने और अमीर राज्यों द्वारा गरीब राज्यों को सब्सिडी देने की ज़रूरत को अच्छी तरह समझते हैं।
- लेकिन हमें यह सुनिश्चित करना चाहिए कि यह संतुलन बनाने का काम हमारे दक्षिणी राज्यों के लिए वित्तीय उत्पीड़न न बन जाए।
- क्योंकि, ज़्यादातर संघीय प्रणालियों के विपरीत, भारत का राजस्व अनुपातहीन रूप से सबसे खराब प्रदर्शन करने वाले राज्यों को जा रहा है, जहाँ निरक्षरता बहुत ज़्यादा है, प्रजनन दर और जनसंख्या वृद्धि दर बहुत ज़्यादा है, जबकि उच्च प्रदर्शन करने वाले दक्षिणी राज्यों को कम महत्व दिया जाता है।
- 10 जून, 2024 को, उत्तर प्रदेश को कर हस्तांतरण के रूप में ₹25,069 करोड़ मिले, जो हमारे सभी पाँच दक्षिणी राज्यों को मिले कुल आवंटन से ज़्यादा है। बिहार और मध्य प्रदेश को अगला सबसे बड़ा आवंटन मिला।
परिसीमन के बारे में हमारे दक्षिणी राज्यों की चिंताएँ निराधार नहीं हैं:
- इस अभ्यास की सफलता के साथ लाखों लोगों के हित जुड़े हुए हैं, जिसमें न्यायसंगत पुनर्वितरण और प्रतिनिधित्व के सिद्धांतों का बहुत अधिक महत्व होना चाहिए। अंततः, सभी राज्यों को एक समाधान निकालने के लिए मिलकर काम करना चाहिए।
अंतर-राज्य परिषद को पुनर्जीवित करें
- अंतर-राज्य परिषद को अप्रचलन की स्थिति से बाहर निकालना एक अच्छा प्रारंभिक बिंदु होगा।
- हालांकि संविधान के अनुच्छेद 263 में इसके औचित्य को बहुत पहले ही रेखांकित किया जा चुका था, लेकिन इसे सरकारिया आयोग की सिफारिश पर 1990 के दशक में ही बुलाया गया था।
- लेकिन, विचार-विमर्श का एक मजबूत मंच बनने की क्षमता होने के बावजूद, परिषद गृह मंत्रालय का एक मात्र अंग बनकर रह गई है, जिसकी छाया में इसका कोई अधिकार नहीं है।
- इसलिए अंतर-राज्य परिषद को राज्यों को प्रभावित करने वाले मुद्दों पर परामर्श, निर्णय लेने, विवाद समाधान और राज्यों और विभिन्न सरकारी विभागों और सरकार के स्तरों के बीच समन्वय के लिए एक स्वतंत्र क्षेत्र के रूप में काम करने के लिए पूरी तरह से बदल दिया जाना चाहिए और पुनर्जीवित किया जाना चाहिए।
निष्कर्ष
- भारत के संघवाद को केंद्रीकृत प्रवृत्तियों और जनसांख्यिकीय बदलावों से चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ रहा है, जो कुछ क्षेत्रों को हाशिए पर डाल सकते हैं।
- विविधता के बीच एकता को बनाए रखने के लिए, सहकारी संघवाद को मजबूत करना महत्वपूर्ण है, यह सुनिश्चित करना कि सभी राज्यों को समान प्रतिनिधित्व और संसाधन मिले।
- अंतर-राज्य परिषद जैसे मंचों का पुनरुद्धार राज्यों के बीच संवाद और आम सहमति बनाने को बढ़ावा दे सकता है, जो भारत के संघीय ढांचे को बनाए रखने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
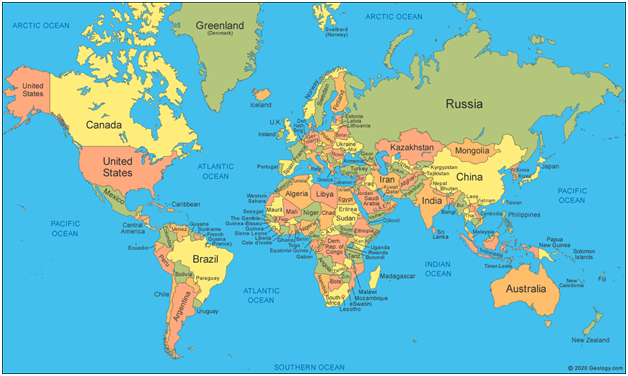
Major Straits of the world [Mapping] / दुनिया के प्रमुख जलडमरूमध्य [मानचित्र]
A strait is a thin channel of waterways i.e. narrow passage of water that connects two seas or two other large areas of water.
The following are the main characteristics of a strait:
- Formed by natural processes
- Narrower than the seas it connects
- Navigable
Major Straits Of The World
Straits of the world are used by commercial shipping to travel from one sea or exclusive economic zone to another and they are of immense strategic and commercial importance. Straits serve as a channel through which ocean currents pass, modifying the climate of that area.


| Strait | Contiguous Landmass | Joining Seas/Water Bodies |
| Formosa Strait | China and Taiwan | The South China Sea and the East China Sea |
| Strait of Tartary | Russia (East Russia-Sakhalin Islands) | Sea of Okhotsk and the Sea of Japan |
| Yucatan Strait | Mexico and Cuba | The Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea |
| Otranto Strait | Italy and Albania | Adriatic Sea & Ionian Sea |
| Cook Strait | New Zealand | The Tasman Sea and South Pacific Ocean |
| Mozambique Channel | Mozambique and Madagascar | Indian Ocean |
| North Channel | Ireland and Scotland | Irish Sea and Atlantic Ocean |
| Hormuz Strait | Iran and Oman | The Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf |
| Bab-el-Mandeb | Djibouti, Yemen, and Eritrea of the Somali Peninsula | The Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea |
| Ten Degree Channel | Car Nicobar Islands and Little Andaman | Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal |
| Sunda Strait | Java island of Indonesia with its Sumatra island. | Java Sea and the Indian Ocean |
| Florida Strait | Cuba and the USA | Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean |
| Bering Strait | Asia from America | The Arctic Ocean and East Pacific ocean |
| Strait of Gibraltar | Spain and Morocco | The Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea |
| Korea Strait | Japan and South Korea | The East China Sea and the Sea of Japan |
| Strait of Malacca | Malaysia and Sumatra | The Pacific Ocean to the east with the Indian Ocean to the west |
| Palk Strait | India and Sri Lanka | The Bay of Bengal in the northeast with the Palk Bay/Arabian Sea in the southwest |
| Bosporus Strait | Divides Europe from Asia | The Black Sea to Sea of Marmara |
| Bass Strait | Tasmania island and mainland Australia | The Great Australian Bight and the Tasman Sea |
| Davis Strait | Between Greenland and Canada | The Baffin Bay and the Labrador Sea |
| Jamaica Channel | Jamaica and Hispaniola | The Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic |
| Hudson Strait | Baffin Island and Labrador peninsula | Hudson Bay and the Labrador Sea |
दुनिया के प्रमुख जलडमरूमध्य [मानचित्र]
जलडमरूमध्य जलमार्गों का एक पतला चैनल है यानी पानी का संकीर्ण मार्ग जो दो समुद्रों या पानी के दो अन्य बड़े क्षेत्रों को जोड़ता है।
जलडमरूमध्य की मुख्य विशेषताएँ निम्नलिखित हैं:
- प्राकृतिक प्रक्रियाओं द्वारा निर्मित
- इससे जुड़ने वाले समुद्रों की तुलना में संकरा
- नौगम्य
दुनिया के प्रमुख जलडमरूमध्य
दुनिया के जलडमरूमध्य का उपयोग वाणिज्यिक शिपिंग द्वारा एक समुद्र या विशेष आर्थिक क्षेत्र से दूसरे समुद्र या विशेष आर्थिक क्षेत्र में यात्रा करने के लिए किया जाता है और इनका बहुत अधिक सामरिक और वाणिज्यिक महत्व है। जलडमरूमध्य एक चैनल के रूप में कार्य करता है जिसके माध्यम से समुद्री धाराएँ गुजरती हैं, जो उस क्षेत्र की जलवायु को संशोधित करती हैं।
| जलडमरूमध्य | समीपवर्ती भूभाग | जुड़ने वाले समुद्र/जल निकाय |
| फॉर्मोसा जलडमरूमध्य | चीन और ताइवान | दक्षिण चीन सागर और पूर्वी चीन सागर |
| टारटरी जलडमरूमध्य | रूस (पूर्वी रूस-सखालिन द्वीप) | ओखोटस्क सागर और जापान सागर |
| युकाटन जलडमरूमध्य | मेक्सिको और क्यूबा | मेक्सिको की खाड़ी और कैरेबियन सागर |
| ओट्रान्टो जलडमरूमध्य | इटली और अल्बानिया | एड्रियाटिक सागर और आयोनियन सागर |
| कुक जलडमरूमध्य | न्यूजीलैंड | तस्मान सागर और दक्षिण प्रशांत महासागर |
| मोजाम्बिक चैनल | मोजाम्बिक और मेडागास्कर | हिंद महासागर |
| उत्तरी चैनल | आयरलैंड और स्कॉटलैंड | आयरिश सागर और अटलांटिक महासागर |
| होर्मुज जलडमरूमध्य | ईरान और ओमान | ओमान की खाड़ी और फारस की खाड़ी |
| बाब-अल-मंडेब | सोमाली प्रायद्वीप के जिबूती, यमन और इरिट्रिया | अदन की खाड़ी और लाल सागर |
| दस डिग्री चैनल | कार निकोबार द्वीप और छोटा अंडमान | अंडमान सागर और बंगाल की खाड़ी |
| सुंडा जलडमरूमध्य | इंडोनेशिया का जावा द्वीप और उसका सुमात्रा द्वीप। | जावा सागर और हिंद महासागर |
| फ्लोरिडा जलडमरूमध्य | क्यूबा और यूएसए | मेक्सिको की खाड़ी और अटलांटिक महासागर |
| बेरिंग जलडमरूमध्य | अमेरिका से एशिया | आर्कटिक महासागर और पूर्वी प्रशांत महासागर |
| जिब्राल्टर जलडमरूमध्य | स्पेन और मोरक्को | अटलांटिक महासागर और भूमध्य सागर |
| कोरिया जलडमरूमध्य | जापान और दक्षिण कोरिया | पूर्वी चीन सागर और जापान सागर |
| मलक्का जलडमरूमध्य | मलेशिया और सुमात्रा | पूर्व में प्रशांत महासागर और पश्चिम में हिंद महासागर |
| पाक जलडमरूमध्य | भारत और श्रीलंका | उत्तर-पूर्व में बंगाल की खाड़ी और दक्षिण-पश्चिम में पाक खाड़ी/अरब सागर |
| बोस्पोरस जलडमरूमध्य | एशिया से यूरोप को अलग करता है | काला सागर से मरमारा सागर |
| बास जलडमरूमध्य | तस्मानिया द्वीप और मुख्य भूमि ऑस्ट्रेलिया | ग्रेट ऑस्ट्रेलियन बाइट और तस्मान सागर |
| डेविस जलडमरूमध्य | ग्रीनलैंड और कनाडा के बीच | बाफिन खाड़ी और लैब्राडोर सागर |
| जमैका चैनल | जमैका और हिस्पानियोला | कैरेबियन सागर और उत्तरी अटलांटिक |
| हडसन जलडमरूमध्य | बाफिन द्वीप और लैब्राडोर प्रायद्वीप | हडसन खाड़ी और लैब्राडोर सागर |