CURRENT AFFAIRS – 13/05/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 13/05/2024
- In village near Maharashtra’s Nashik, people fear being declared dead if they don’t vote / महाराष्ट्र के नासिक के पास के गांव में लोगों को डर है कि अगर उन्होंने वोट नहीं दिया तो उन्हें मृत घोषित कर दिया जाएगा
- Govt. to spend ₹2 cr. per km on roads along China border/सरकार चीन सीमा पर सड़कों पर प्रति किमी ₹2 करोड़ खर्च करेगी
- This worm develops food habits and its offspring ‘inherit’ them /यह गलत खाने की आदतें विकसित करता है और इसकी संतानें उन्हें ‘विरासत में’ पाती हैं
- The poll promise of affordable housing / किफायती आवास का चुनावी वादा
- Investment lessons from the India-EFTA trade deal / भारत-ईएफटीए व्यापार समझौते से निवेश सबक
- North America : Inland Drainage System and Lakes / उत्तरी अमेरिका: अंतर्देशीय जल निकासी प्रणाली और झीलें [Mapping]
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 13/05/2024
In village near Maharashtra’s Nashik, people fear being declared dead if they don’t vote / महाराष्ट्र के नासिक के पास के गांव में लोगों को डर है कि अगर उन्होंने वोट नहीं दिया तो उन्हें मृत घोषित कर दिया जाएगा
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
About:
- Politicians and celebrities are frequent visitors to the Trimbakeshwar temple in Nashik, but just 22 km from it is the Takeharsh gram panchayat where people have never seen a single political party campaigning for an election.
- Of the 250 households in the gram panchayat, 90 do not have ration cards, and those that got cards recently were asked to pay ₹500 per person. Despite that, they still do not get ration. During the COVID-19 lockdown, said the villagers, they did not receive foodgrains under the Prime Minister’s free ration scheme.
- Home to Scheduled Tribes such as Warli, Katkari and Kokni, the area does not have electricity, water connections and public transport. People here are not aware of the political representatives for the Lok Sabha election, but they vote anyway. “No one ever visited us. How will we be familiar with their faces and party symbols? We press whatever button (on the EVM) our eye catches first and get done with it,” said 52-year-old Tulsabai Gangaram Pingle from Takeharsh.
- Polling takes place in a government school 3 km away from the village. Bhaudu Ramu Pingle, 40, is a daily wage labourer who feels if he does not vote, he will be declared dead in the government documents. “We are scared that if we do not vote, the government will strike off our names from their documents and declare us dead. If that happens, then our existence will be in danger. What will happen to our family then?” he said.
Struggle for ration card
- Sonali Vijay Nirgude, a 25-year-old woman who runs a household of 10 members, said it has been “eight years since we have been trying to get ration cards for our family”.
- “We have visited all the government offices in Nashik and even sent applications to the Chief Minister’s office in Mumbai, but nothing has worked. We come from underprivileged families. For us, if we get foodgrains through ration, it will be helpful to feed our families,” she said.
- Umabai Madhukar Awhate, 40, from Nirgud Pada, registered for a ration card four years ago by paying ₹500 per card for her family of four, but only she and her husband could secure cards. “I only got ration once four years ago and it was wheat and rice,” she said. “During the lockdown, we did not receive any ration.”
‘No govt. facility’
- Umabai said except for the Indira Gandhi Awas Yojana, her village does not have any government facility such as the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana, piped water supply or electricity.
- Mirabai Panduranga Awhate, 37, from Nirgur Pada, married off her daughter at the age of 13 during the lockdown due to scarcity of food and income. Her 17-year-old son takes up small jobs at construction sites. In the absence of a ration card, she said, the family starved during the lockdown.
- “My husband passed away 15 years ago. Two years ago, I along with other villagers went to the tehsildar’s office asking for our ration cards, but we were insulted by the official,” Ms. Mirabai said.
- She had heard about the widow pension scheme last year, but her application remains on hold. “I was asked to submit documents such as income certificate, death certificate of my husband, Aadhaar card, bank account passbook, and residential proof. I paid them ₹100 to get an income certificate, but it has been over a year and there has been no word from them,” she said.
- Rakmabai Dagru Nirgude from Nirgud Pada is 60 years old. For the last 15 years, her husband, who is a farmer, has been partially paralysed. “Since there is no water and electricity, we cannot grow many crops, so my sons have to take up jobs as daily labourers. It has been days since we have not had drinking water. We live just a kilometre away from Vaitarna Dam, which supplies water to Mumbai city, but we do not receive water to drink or irrigate fields.”
Fight for water
- To source water, villagers mostly walk to the nearest backwater,Vaitarna, 2 km away, where they dig to source clean water for drinking. Some trespass on private property and take water from wells.
- “There are days we are caught, they shout and humiliate us, but we are left with no choice as we fall sick drinking from the backwaters,” said Yashoda Naresh Nirgude, 28.
- Two months ago, a pregnant Varsha Yogesh Nirgude, 24, had gone to the nearest Primary Health Centre, 30 km away in Anjanari village, for delivery. “There was not a single medical staff member and I delivered with the help of my mother. Hours later, a medical staff came and sent me to Nashik for further medical care. It was a nightmare,” she said.
- Among other government schemes, the villagers wish to getNamo Shetkari Yojana, sanitary napkins, electricity, toilets, potable water, healthcare, and employment within their village so that they do not have to migrate in search of jobs.
- Laxmikant Jadhav, from BELIEFS, an NGO working for the livelihood and empowerment of tribal communities, said, “The process and technicalities of getting work or access to government schemes are complicated and hence many are intimidated to approach officials. We have asked for an unemployment allowance for the villagers who have not been able to get work underMGNREGAwithin 15 days. If the villagers do not get work, they will be forced to migrate.”
- On December 22, 2023, 101 women of Nirgud Pada demanded regular work under MGNREGA. On January 26, 2024, they filed a complaint in the gram sabha and within a week some of them got work to construct a small dam with stones. However, only one-third of the labourers were accommodated, and the rest were not hired as they did not have KYC.
Camps for Aadhaar
Shweta Sancheti, Tahsildar from Trimbakeshwar, said, “Two months ago, we began camps to get the villagers registered for Aadhaar cards as most of them do not have documents. So far, we have approved 740 ration cards. The work is on hold due to the model code of conduct norms. We will continue the work after the election is over.”
टॉपिक के बारे में:
- नासिक के त्र्यंबकेश्वर मंदिर में राजनेता और मशहूर हस्तियां अक्सर आते हैं, लेकिन इससे सिर्फ 22 किमी दूर ताकेहर्ष ग्राम पंचायत है जहां लोगों ने कभी भी किसी भी राजनीतिक दल को चुनाव प्रचार करते नहीं देखा है।
- ग्राम पंचायत के 250 परिवारों में से 90 के पास राशन कार्ड नहीं हैं, और जिन्हें हाल ही में कार्ड मिले हैं, उनसे प्रति व्यक्ति ₹500 का भुगतान करने के लिए कहा गया था। इसके बावजूद भी उन्हें अब तक राशन नहीं मिल पाता है। ग्रामीणों ने कहा कि सीओवीआईडी-19 लॉकडाउन के दौरान, उन्हें प्रधान मंत्री की मुफ्त राशन योजना के तहत खाद्यान्न नहीं मिला।
- वारली, कटकारी और कोकनी जैसी अनुसूचित जनजातियों का घर, इस क्षेत्र में बिजली, पानी कनेक्शन और सार्वजनिक परिवहन नहीं है। यहां के लोगों को लोकसभा चुनाव के लिए राजनीतिक प्रतिनिधियों के बारे में जानकारी नहीं है, लेकिन फिर भी वे मतदान करते हैं। “कभी कोई हमसे मिलने नहीं आया। हम उनके चेहरों और पार्टी चिन्हों से कैसे परिचित होंगे? ताकेहर्ष की 52 वर्षीय तुलसाबाई गंगाराम पिंगले ने कहा, ”ईवीएम पर जो भी बटन हमारी नजर में सबसे पहले आता है, हम उसे दबाते हैं और काम पूरा कर लेते हैं।”
- मतदान गांव से 3 किमी दूर सरकारी स्कूल में होता है. 40 वर्षीय भाऊदु रामू पिंगले एक दिहाड़ी मजदूर हैं जिन्हें लगता है कि अगर उन्होंने वोट नहीं दिया तो सरकारी दस्तावेजों में उन्हें मृत घोषित कर दिया जाएगा। “हमें डर है कि अगर हम वोट नहीं देंगे तो सरकार अपने दस्तावेज़ों से हमारा नाम काट देगी और हमें मृत घोषित कर देगी। यदि ऐसा हुआ तो हमारा अस्तित्व खतरे में पड़ जायेगा। तब हमारे परिवार का क्या होगा?” उसने कहा।
राशन कार्ड के लिए संघर्ष
- 10 सदस्यों का घर चलाने वाली 25 वर्षीय महिला सोनाली विजय निरगुडे ने कहा, “हमें अपने परिवार के लिए राशन कार्ड प्राप्त करने की कोशिश करते हुए आठ साल हो गए हैं”।
- “हमने नासिक के सभी सरकारी कार्यालयों का दौरा किया और यहां तक कि मुंबई में मुख्यमंत्री कार्यालय को भी आवेदन भेजा, लेकिन कुछ भी काम नहीं हुआ। हम वंचित परिवारों से आते हैं। हमारे लिए, अगर हमें राशन के माध्यम से खाद्यान्न मिलता है, तो यह हमारे परिवारों को खिलाने में मददगार होगा, ”उसने कहा।
- निर्गुड पाड़ा की 40 वर्षीय उमाबाई मधुकर अव्हाटे ने चार साल पहले अपने चार लोगों के परिवार के लिए प्रति कार्ड ₹500 का भुगतान करके राशन कार्ड के लिए पंजीकरण कराया था, लेकिन केवल वह और उनके पति ही कार्ड सुरक्षित कर सके। “मुझे चार साल पहले केवल एक बार राशन मिला था और वह गेहूं और चावल था,” उसने कहा। “लॉकडाउन के दौरान, हमें कोई राशन नहीं मिला।”
‘कोई सरकारी सुविधा नहीं’
- सुश्री उमाबाई ने कहा कि इंदिरा गांधी आवास योजना को छोड़कर, उनके गांव में प्रधानमंत्री उज्ज्वला योजना, पाइप जलापूर्ति या बिजली जैसी कोई सरकारी सुविधा नहीं है।
- निर्गुर पाड़ा की 37 वर्षीय मीराबाई पांडुरंगा अव्हाटे ने भोजन और आय की कमी के कारण लॉकडाउन के दौरान 13 साल की उम्र में अपनी बेटी की शादी कर दी। उसका 17 वर्षीय बेटा निर्माण स्थलों पर छोटी-मोटी नौकरियां करता है। उन्होंने कहा, राशन कार्ड के अभाव में, परिवार लॉकडाउन के दौरान भूखा मर गया।
- “मेरे पति का 15 साल पहले निधन हो गया। दो साल पहले, मैं अन्य ग्रामीणों के साथ अपने राशन कार्ड मांगने के लिए तहसीलदार के कार्यालय में गई थी, लेकिन अधिकारी ने हमारा अपमान किया, ”सुश्री मीराबाई ने कहा।
- उसने पिछले साल विधवा पेंशन योजना के बारे में सुना था, लेकिन उसका आवेदन रुका हुआ है। “मुझसे आय प्रमाण पत्र, मेरे पति का मृत्यु प्रमाण पत्र, आधार कार्ड, बैंक खाता पासबुक और आवासीय प्रमाण जैसे दस्तावेज जमा करने के लिए कहा गया था। मैंने आय प्रमाण पत्र प्राप्त करने के लिए उन्हें ₹100 का भुगतान किया, लेकिन एक साल से अधिक समय हो गया है और उनकी ओर से कोई जानकारी नहीं आई है, ”उन्होंने कहा।
- निरगुड पाड़ा की रकमाबाई दगरू निरगुडे 60 साल की हैं। पिछले 15 वर्षों से, उनके पति, जो एक किसान हैं, आंशिक रूप से लकवाग्रस्त हैं। “चूंकि पानी और बिजली नहीं है, हम कई फसलें नहीं उगा सकते हैं, इसलिए मेरे बेटों को दैनिक मजदूर के रूप में नौकरी करनी पड़ती है। कई दिन हो गए हमें पीने का पानी नहीं मिला। हम वैतरणा बांध से सिर्फ एक किलोमीटर दूर रहते हैं, जो मुंबई शहर को पानी की आपूर्ति करता है, लेकिन हमें पीने या खेतों की सिंचाई के लिए पानी नहीं मिलता है।
पानी के लिए लड़ाई
- पानी के स्रोत के लिए, ग्रामीण ज्यादातर 2 किमी दूर निकटतम बैकवाटर, वैतरणा तक जाते हैं, जहां वे पीने के लिए साफ पानी के स्रोत के लिए खुदाई करते हैं। कुछ लोग निजी संपत्ति पर अतिक्रमण करते हैं और कुओं से पानी लेते हैं।
- 28 वर्षीय यशोदा नरेश निरगुडे ने कहा, “कई बार हम पकड़े जाते हैं, वे चिल्लाते हैं और हमें अपमानित करते हैं, लेकिन हमारे पास कोई विकल्प नहीं बचता क्योंकि हम बैकवाटर से पानी पीकर बीमार पड़ जाते हैं।”
- दो महीने पहले, 24 वर्षीय गर्भवती वर्षा योगेश निर्गुडे प्रसव के लिए 30 किमी दूर अंजनारी गांव के नजदीकी प्राथमिक स्वास्थ्य केंद्र में गई थी। “वहां एक भी मेडिकल स्टाफ सदस्य नहीं था और मैंने अपनी मां की मदद से प्रसव कराया। कुछ घंटों बाद, एक मेडिकल स्टाफ आया और मुझे आगे की चिकित्सा देखभाल के लिए नासिक भेजा। यह एक बुरा सपना था,” उन्होंने कहा।
- अन्य सरकारी योजनाओं के अलावा, ग्रामीण नमो शेतकारी योजना, सैनिटरी नैपकिन, बिजली, शौचालय, पीने योग्य पानी, स्वास्थ्य देखभाल और अपने गांव के भीतर रोजगार चाहते हैं ताकि उन्हें नौकरियों की तलाश में पलायन न करना पड़े।
- आदिवासी समुदायों की आजीविका और सशक्तिकरण के लिए काम करने वाले गैर सरकारी संगठन BELIEFS के लक्ष्मीकांत जाधव ने कहा, “काम पाने या सरकारी योजनाओं तक पहुंच पाने की प्रक्रिया और तकनीकीताएं जटिल हैं और इसलिए कई लोग अधिकारियों से संपर्क करने से डरते हैं। हमने उन ग्रामीणों के लिए 15 दिनों के भीतर बेरोजगारी भत्ता मांगा है जिन्हें मनरेगा के तहत काम नहीं मिल पाया है। अगर ग्रामीणों को काम नहीं मिलेगा तो वे पलायन करने को मजबूर हो जायेंगे.’
- 22 दिसंबर 2023 को निरगुड पाड़ा की 101 महिलाओं ने मनरेगा के तहत नियमित काम की मांग की. 26 जनवरी, 2024 को, उन्होंने ग्राम सभा में शिकायत दर्ज की और एक सप्ताह के भीतर उनमें से कुछ को पत्थरों से एक छोटा बांध बनाने का काम मिल गया। हालाँकि, केवल एक तिहाई मजदूरों को ही समायोजित किया गया था, और बाकी को काम पर नहीं रखा गया क्योंकि उनके पास केवाईसी नहीं था।
आधार के लिए शिविर
त्र्यंबकेश्वर की तहसीलदार श्वेता संचेती ने कहा, “दो महीने पहले, हमने ग्रामीणों को आधार कार्ड के लिए पंजीकृत करने के लिए शिविर शुरू किए थे क्योंकि उनमें से अधिकांश के पास दस्तावेज नहीं थे। अब तक हमने 740 राशन कार्ड स्वीकृत किये हैं. आदर्श आचार संहिता के कारण काम रुका हुआ है। चुनाव खत्म होने के बाद भी हम काम जारी रखेंगे।”
Govt. to spend ₹2 cr. per km on roads along China border/सरकार चीन सीमा पर सड़कों पर प्रति किमी ₹2 करोड़ खर्च करेगी
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
Vibrant Villages Programme
- About:
- It is a Centrally sponsored scheme, announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 (to 2025-26) for development of villages on the northern border, thus improving the quality of life of people living in identified border villages.
- It will cover the border areas of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim and Ladakh.
- It will cover 2,963 villages with 663 of them to be covered in the first phase.
- Vibrant Village Action Plans will be created by the district adminstration with the help of Gram Panchayats.
- There will not be overlap with Border Area Development Programme.
- Objective:
- The scheme aids to identify and develop the economic drivers based on local, natural, human and other resources of the border villages on the northern border;
- Development of growth centres on ‘hub and spoke model’ through promotion of social entrepreneurship, empowerment of youth and women through skill development and entrepreneurship;
- Leveraging the tourism potential through promotion of local, cultural, traditional knowledge and heritage;
- Development of sustainable eco-agri businesses on the concept of ‘one village-one product’ through community-based organisations, cooperatives, NGOs.
वाइब्रेंट विलेज प्रोग्राम
- वाइब्रेंट विलेजेज कार्यक्रम के बारे में:
- यह एक केंद्र प्रायोजित योजना है, जिसकी घोषणा केंद्रीय बजट 2022-23 (2025-26 तक) में उत्तरी सीमा पर गांवों के विकास के लिए की गई थी, जिससे चिन्हित सीमावर्ती गांवों में रहने वाले लोगों के जीवन की गुणवत्ता में सुधार होगा।
- यह हिमाचल प्रदेश, उत्तराखंड, अरुणाचल प्रदेश, सिक्किम और लद्दाख के सीमावर्ती क्षेत्रों को कवर करेगा।
- इसमें 2,963 गांवों को शामिल किया जाएगा, जिनमें से 663 गांवों को पहले चरण में कवर किया जाएगा।
- ग्राम पंचायतों की मदद से जिला प्रशासन द्वारा जीवंत ग्राम कार्य योजनाएं बनाई जाएंगी।
- सीमा क्षेत्र विकास कार्यक्रम के साथ ओवरलैप नहीं होगा।
- उद्देश्य:
- यह योजना उत्तरी सीमा पर सीमावर्ती गांवों के स्थानीय, प्राकृतिक, मानव और अन्य संसाधनों के आधार पर आर्थिक चालकों की पहचान करने और विकसित करने में सहायता करती है;
- सामाजिक उद्यमिता को बढ़ावा देने, कौशल विकास और उद्यमिता के माध्यम से युवाओं और महिलाओं के सशक्तिकरण के माध्यम से ‘हब और स्पोक मॉडल’ पर विकास केंद्रों का विकास;
- स्थानीय, सांस्कृतिक, पारंपरिक ज्ञान और विरासत को बढ़ावा देकर पर्यटन क्षमता का लाभ उठाना;
- समुदाय-आधारित संगठनों, सहकारी समितियों, गैर सरकारी संगठनों के माध्यम से ‘एक गांव-एक उत्पाद’ की अवधारणा पर टिकाऊ पर्यावरण-कृषि व्यवसायों का विकास।
This worm develops food habits and its offspring ‘inherit’ them /यह गलत खाने की आदतें विकसित करता है और इसकी संतानें उन्हें ‘विरासत में’ पाती हैं
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
Researchers from Princeton University have reported that after the Caenorhabditis elegans worms ate a disease-causing strain of bacteria, its progeny were born with the ‘knowledge’ to avoid making the same mistake for up to four generations.
Caenorhabditis elegans
- Researchers fondly call the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans “the worm” because of its widespread use in research to understand neuronal and molecular biology.
- It was the first multicellular organism to have its full genome sequenced and neural wiring mapped.
- elegans grows within 3-5 days from a fertilised egg to a millimetre-long adult, and it has informed profound insights into the human body, as well as biology more broadly.
Message in a bottle
- Pseudomonas vranovensis is a disease-causing bacterium found in C. elegans’s natural environment.
- The researchers found that P. vranovensis makes a small RNA molecule called sRNA.
- When the worms ingest this strain, they also take in the sRNA. The sRNA then altered the worm’s feeding behaviour such that, from that point on, the worms ‘know’ to avoid feeding on this bacterium and save themselves from getting sick.
- Remarkably, this learned avoidance behaviour was found to be transmitted to the trained worm’s progeny, grand-progeny, great-grand progeny, and great-great-grand progeny. The ability decayed only from the fifth generation.
- The same team of researchers had previously discovered this trans-generational ability in C. elegans worms against P. aeruginosa bacteria (which also cause disease in humans).
Understanding RNA, large and small
- A DNA molecule is like a big ladder. Its two side rails, or strands, are made of a long series of alternating units of phosphate and the sugar deoxyribose molecules.
- Each sugar unit is attached to one of four chemical bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
- The As and Cs on one strand are bonded with Ts and Cs on the other by hydrogen bonds. These bonds form the rungs that hold the strands together.
- In contrast to DNA, the RNA molecule is like a half-ladder or a comb. Its spine is made up of alternating units of phosphate and the sugar ribose.
- Each ribose molecule is attached to one of four bases: A, C, G or uridine (U), which jut out from the strand like the comb’s tines.
- A cell copies the sequence of As, Ts, Cs, and Gs in a gene in the DNA into the sequence of Us, As, Gs, and Cs in an RNA molecule.
- This RNA is called the messenger (mRNA). The length of this mRNA is comparable to that of the gene from which it is derived. The mRNA moves to structures called ribosomes, where the cell assembles the corresponding protein.
Diet control
- But not all genes encode mRNAs and proteins. The end product of some genes, especially small genes that are only about a tenth as long (~100-200 rungs), is sRNA.
- These sRNA bind to other proteins and RNAs, and either enhance or reduce the expression of other genes.
- This sRNA reduced the expression of a gene in the worm called maco-1, which plays an important neurological role. As it happens, maco-1 is also found in humans.
- elegans worms on a diet of Escherichia coli bacteria.
Good ‘memory loss’
- Another Pseudomonas bacterium, P. mendocina, is also present in the worm’s habitat but it doesn’t cause disease.
- Instead, P. mendocina is a source of nutrition. C. elegans worms trained to avoid the pathogenic P. vranovensis strain avoided feeding on the non-pathogenic P. mendocina as well.
- The sRNA that triggered learned avoidance behaviour came initially from the bacteria and was taken up by the worm that fed on them.
- Thereafter, the sRNA was maintained in the worms’ bodies, transmitted to their descendants, and maintained in them. This happened through a mechanism called RNA interference — which scientists first discovered by studying C. elegans worms.
Conclusion
In fact, discoveries based on studying C. elegans were recognised by Nobel Prizes in 2002, 2006, and 2008. This tiny worm has played an outsized role in the advancement of scientific and medical research. So a question arises: whether our bodies can also take up sRNA molecules from the microbes in our gut, mouth or vagina, and whether they can modify our behaviour, and possibly the behaviour of our children and later generations.
- प्रिंसटन यूनिवर्सिटी के शोधकर्ताओं ने बताया है कि केनोरहेबडाइटिस एलिगेंस कीड़े ने बैक्टीरिया के रोग पैदा करने वाले तनाव को खा लिया, इसके बाद इसकी संतानें चार पीढ़ियों तक वही गलती करने से बचने के लिए ‘ज्ञान’ के साथ पैदा हुईं।
काईऩोर्हेब्डीटीज एलिगेंस
- न्यूरोनल और आणविक जीव विज्ञान को समझने के लिए अनुसंधान में इसके व्यापक उपयोग के कारण शोधकर्ता राउंडवॉर्म कैनोर्हाडाइटिस एलिगेंस को प्यार से “कीड़ा” कहते हैं।
- यह पहला बहुकोशिकीय जीव था जिसका पूर्ण जीनोम अनुक्रम और तंत्रिका तारों का मानचित्रण किया गया था।
- सी एलिगेंस एक निषेचित अंडे से एक मिलीमीटर लंबे वयस्क तक 3-5 दिनों के भीतर बढ़ता है, और इसने मानव शरीर के साथ-साथ जीव विज्ञान में अधिक व्यापक अंतर्दृष्टि प्रदान की है।
एक बोतल में संदेश
- स्यूडोमोनास व्रानोवेन्सिस सी एलिगेंस के प्राकृतिक वातावरण में पाया जाने वाला एक रोग पैदा करने वाला जीवाणु है।
- शोधकर्ताओं ने पाया कि पी व्रानोवेन्सिस एक छोटा आरएनए अणु बनाता है जिसे एसआरएनए कहा जाता है।
- जब कीड़े इस स्ट्रेन को ग्रहण करते हैं, तो वे sRNA को भी ग्रहण कर लेते हैं। इसके बाद एसआरएनए ने कृमि के आहार व्यवहार को इस तरह बदल दिया कि, उस बिंदु से, कृमि इस जीवाणु को खाने से बचना और खुद को बीमार होने से बचाना ‘जानते’ हैं।
- उल्लेखनीय रूप से, यह सीखा हुआ परिहार व्यवहार प्रशिक्षित कृमि की संतानों, भव्य-संतानों, पर-पौत्रों की संतानों और पर-परदादा-संतानों में प्रसारित होता पाया गया। पाँचवीं पीढ़ी से ही योग्यता क्षीण हो गई।
- शोधकर्ताओं की इसी टीम ने पहले पी एरुगिनोसा बैक्टीरिया (जो मनुष्यों में भी बीमारी का कारण बनता है) के खिलाफ सी एलिगेंस कीड़े में इस ट्रांस-जेनरेशनल क्षमता की खोज की थी।
बड़े और छोटे RNA को समझना
- डीएनए अणु एक बड़ी सीढ़ी की तरह है। इसकी दो साइड रेल्स, या स्ट्रैंड्स, फॉस्फेट और चीनी डीऑक्सीराइबोज अणुओं की वैकल्पिक इकाइयों की एक लंबी श्रृंखला से बनी होती हैं।
- प्रत्येक चीनी इकाई चार रासायनिक आधारों में से एक से जुड़ी होती है: एडेनिन (A), साइटोसिन (C), गुआनिन (G), और थाइमिन (T)।
- एक स्ट्रैंड पर As और Cs हाइड्रोजन बॉन्ड द्वारा दूसरे स्ट्रैंड पर Ts और Cs से जुड़े होते हैं। ये बंधन पायदान बनाते हैं जो धागों को एक साथ बांधे रखते हैं।
- डीएनए के विपरीत, आरएनए अणु आधी सीढ़ी या कंघी की तरह होता है। इसकी रीढ़ फॉस्फेट और शर्करा राइबोज की वैकल्पिक इकाइयों से बनी होती है।
- प्रत्येक राइबोस अणु चार आधारों में से एक से जुड़ा होता है: A, C, G या यूरिडीन (U), जो कंघी के दांतों की तरह स्ट्रैंड से बाहर निकलते हैं।
- एक कोशिका डीएनए में एक जीन में As, Ts, Cs और Gs के अनुक्रम को RNA अणु में Us, As, Gs और Cs के अनुक्रम में कॉपी करती है।
- इस RNA को मैसेंजर (mRNA) कहा जाता है। इस एमआरएनए की लंबाई उस जीन की लंबाई के बराबर है जिससे इसे प्राप्त किया गया है। एमआरएनए राइबोसोम नामक संरचनाओं में चला जाता है, जहां कोशिका संबंधित प्रोटीन को इकट्ठा करती है।
आहार नियंत्रण
- लेकिन सभी जीन एमआरएनए और प्रोटीन को एनकोड नहीं करते हैं। कुछ जीनों का अंतिम उत्पाद, विशेष रूप से छोटे जीन जो केवल दसवें हिस्से (~ 100-200 पायदान) तक लंबे होते हैं, एसआरएनए है।
- ये एसआरएनए अन्य प्रोटीन और आरएनए से जुड़ते हैं और अन्य जीनों की अभिव्यक्ति को या तो बढ़ाते हैं या कम करते हैं।
- इस एसआरएनए ने मैको-1 नामक कृमि में एक जीन की अभिव्यक्ति को कम कर दिया, जो एक महत्वपूर्ण न्यूरोलॉजिकल भूमिका निभाता है। जैसा कि होता है, मैको-1 इंसानों में भी पाया जाता है।
- एस्चेरिचिया कोलाई बैक्टीरिया के आहार पर सी एलिगेंस कीड़े।
अच्छा ‘स्मृति हानि’
- एक अन्य स्यूडोमोनास जीवाणु, P मेंडोसिना, भी कृमि के आवास में मौजूद है लेकिन यह बीमारी का कारण नहीं बनता है।
- इसके बजाय, P मेंडोसिना पोषण का एक स्रोत है। रोगजनक P व्रानोवेन्सिस स्ट्रेन से बचने के लिए प्रशिक्षित C एलिगेंस कीड़े गैर-रोगजनक पी मेंडोसिना को भी खाने से बचते हैं।
- एसआरएनए जिसने सीखा हुआ परहेज व्यवहार शुरू किया वह शुरू में बैक्टीरिया से आया था और उन्हें खाने वाले कीड़ों द्वारा ग्रहण किया गया था।
- इसके बाद, एसआरएनए को कीड़ों के शरीर में बनाए रखा गया, उनके वंशजों तक पहुंचाया गया और उनमें बनाए रखा गया। यह आरएनए हस्तक्षेप नामक एक तंत्र के माध्यम से हुआ, जिसे वैज्ञानिकों ने पहली बार सी एलिगेंस कीड़े का अध्ययन करके खोजा था।
निष्कर्ष
वास्तव में, सी एलिगेंस के अध्ययन पर आधारित खोजों को 2002, 2006 और 2008 में नोबेल पुरस्कारों द्वारा मान्यता दी गई थी। इस छोटे से कीड़े ने वैज्ञानिक और चिकित्सा अनुसंधान की प्रगति में एक बड़ी भूमिका निभाई है। तो एक सवाल उठता है: क्या हमारा शरीर हमारी आंत, मुंह या योनि में रोगाणुओं से एसआरएनए अणुओं को भी ले सकता है और क्या वे हमारे व्यवहार और संभवतः हमारे बच्चों और बाद की पीढ़ियों के व्यवहार को संशोधित कर सकते हैं।
The poll promise of affordable housing / किफायती आवास का चुनावी वादा
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U) Scheme
- PMAY-U, being implemented since June 2015, is one of the major flagship programmes being implemented by the Government of India under the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- Objective: To provide all weather pucca houses to all eligible beneficiaries in the urban areas of the country by the year 2022, through States/UTs/Central Nodal Agencies.
- The scheme covers the entire urban area of the country, i.e., all statutory towns as per Census 2011 and towns notified subsequently, including Notified Planning/ Development Areas.
- The scheme is being implemented through four verticals:
- Beneficiary Led Construction/ Enhancement (BLC)
- Affordable Housing in Partnership (AHP)
- In-situ Slum Redevelopment (ISSR)
- Credit Linked Subsidy Scheme (CLSS).
- In August 2022, the Union Cabinet approved the continuation of PMAY-U up to 31st December 2024, with all verticals except CLSS, for the completion of already sanctioned houses till 31st March 2022.
- Funding: The credit linked subsidy component will be implemented as a Central Sector Scheme while other three components will be implemented as Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS).
- All houses under PMAY-U have basic amenities like toilet, water supply, electricity, and kitchen.
- The Mission promotes women empowerment by providing ownership of houses in the name of female member or in joint name.
- Preference has also been given to differently abled persons, senior citizens, SCs, STs, OBCs, Minority, single women, transgender and other weaker & vulnerable sections of the society.
- PMAY-U has adopted a cafeteria approach to suit the needs of individuals based on the geographical conditions, topography, economic conditions, availability of land, infrastructure etc.
प्रधानमंत्री आवास योजना – शहरी (PMAY-U) योजना
- जून 2015 से कार्यान्वित किया जा रहा PMAY-U, आवास और शहरी मामलों के मंत्रालय (MoHUA) के तहत भारत सरकार द्वारा कार्यान्वित किए जा रहे प्रमुख प्रमुख कार्यक्रमों में से एक है।
- उद्देश्य: राज्यों/केंद्रशासित प्रदेशों/केंद्रीय नोडल एजेंसियों के माध्यम से वर्ष 2022 तक देश के शहरी क्षेत्रों में सभी पात्र लाभार्थियों को हर मौसम में पक्के मकान उपलब्ध कराना।
- यह योजना देश के पूरे शहरी क्षेत्र को कवर करती है, यानी जनगणना 2011 के अनुसार सभी वैधानिक कस्बों और बाद में अधिसूचित कस्बों, जिनमें अधिसूचित योजना/विकास क्षेत्र भी शामिल हैं।
- यह योजना चार कार्यक्षेत्रों के माध्यम से कार्यान्वित की जा रही है:
- लाभार्थी आधारित निर्माण/संवर्द्धन (BLC)
- साझेदारी में किफायती आवास (AHP)
- इन-सीटू स्लम पुनर्विकास (ISSR)
- क्रेडिट लिंक्ड सब्सिडी योजना (CLSS)।
- अगस्त 2022 में, केंद्रीय मंत्रिमंडल ने 31 मार्च 2022 तक पहले से स्वीकृत घरों को पूरा करने के लिए सीएलएसएस को छोड़कर सभी वर्टिकल के साथ पीएमएवाई-यू को 31 दिसंबर 2024 तक जारी रखने की मंजूरी दे दी।
- फंडिंग: क्रेडिट लिंक्ड सब्सिडी घटक को केंद्रीय क्षेत्र योजना के रूप में लागू किया जाएगा जबकि अन्य तीन घटकों को केंद्र प्रायोजित योजना (CSS) के रूप में लागू किया जाएगा।
- PMAY-U के तहत सभी घरों में शौचालय, पानी की आपूर्ति, बिजली और रसोई जैसी बुनियादी सुविधाएं हैं।
- मिशन महिला सदस्य के नाम पर या संयुक्त नाम पर घरों का स्वामित्व प्रदान करके महिला सशक्तिकरण को बढ़ावा देता है।
- दिव्यांग व्यक्तियों, वरिष्ठ नागरिकों, एससी, एसटी, ओबीसी, अल्पसंख्यक, एकल महिलाओं, ट्रांसजेंडर और समाज के अन्य कमजोर और कमजोर वर्गों को भी प्राथमिकता दी गई है।
- PMAY-U ने भौगोलिक परिस्थितियों, स्थलाकृति, आर्थिक स्थितियों, भूमि की उपलब्धता, बुनियादी ढांचे आदि के आधार पर व्यक्तियों की आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप कैफेटेरिया दृष्टिकोण अपनाया है।
Investment lessons from the India-EFTA trade deal / भारत-ईएफटीए व्यापार समझौते से निवेश सबक
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
Context:
- India’s free trade agreement (FTA) negotiations with countries such as the United Kingdom and the European Union (EU) seem to be on ice due to the ongoing parliamentary elections in India.
A Historic Trade Deal : EFTA
- However, before election fever gripped the country, India managed to clinch a historic trade deal, in March, with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), comprising Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
- The newly minted Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (which we refer to as FTA) between India and EFTA is expected to give a much-needed leg-up to the low levels of extant trade between the two sides.
- The FTA between India and EFTA is also important because, as India has agreed to include issues such as environment and labour, which it has traditionally opposed incorporating in trade agreements.
On investment
- Another reason sets this FTA apart from those India signed recently with countries such as Australia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Mauritius.
- The India-EFTA FTA includes a somewhat detailed investment chapter, which is missing in the other recent Indian FTAs.
- This chapter focuses on investment facilitation issues, not investment protection.
- But it has a remarkable and unprecedented characteristic. India has managed to extract a promise from the EFTA countries that they shall “aim to” increase foreign direct investment (FDI) to India to $50 billion within 10 years of the FTA coming into force, followed by another $50 billion in the succeeding five years.
- Likewise, EFTA states shall “aim to” facilitate the generation of one million jobs in India.
- In legal terms, these articles codify what is known as an obligation of conduct — an obligation to make an honest endeavour towards achieving a goal, notwithstanding the outcome or the result.
- This differs from an obligation of result, which would require achieving a specified outcome.
- In other words, the EFTA countries are legally obligated to make an honest effort to invest $100 billion and generate one million jobs in India.
- Nonetheless, the Indian negotiators need to be complimented for incorporating such path-breaking specified obligations of conduct in the investment chapter, which are typically not found in FTAs or investment treaties.
- Notably, this creates a template worth emulating in the ongoing negotiations with the U.K., the EU, and other countries.
Trade and investment
- Economic theory has long demonstrated the inextricable linkage between trade and investment. This is truer in a world where the production process is scattered along global supply/value chains, a function of trade and investment.
- Thus, unsurprisingly, FTAs routinely contain binding rules on both trade and investment.
- India’s FTAs signed in the first decade of this century with countries such as Japan, Korea, Malaysia and Singapore are based on this economic logic.
- In addition to binding trade rules, they all contain an investment chapter with provisions for protecting investment.
- However, India departed from this model as part of its FTA 2.0 approach.
- In other words, India decoupled international trade law from international investment law. This is evident in its FTAs with Australia, Mauritius, and the UAE which contain binding trade but not investment rules India’s approach seems to be to have separate agreements on trade and investment with the same country. This is most markedly seen in the case of the UAE.
FTA 3.0
- India needs a clear FTA policy, especially in dealing with international trade and foreign investment laws.
- Suppose India expects not just trade but also higher investment flows from a particular country, which is undoubtedly true with most of its FTA-negotiating partners.
- In that case, two critical elements must be incorporated into its FTA policy. First, India should negotiate trade and investment as part of one comprehensive economic treaty. Decoupling trade from investment is not a good idea. Combining the two would give India a clear negotiating leverage to strike a beneficial deal.
- Second, India should consider expanding the scope of investment issues from mere facilitation to effective protection, with an efficacious dispute settlement mechanism under international law. Providing enforceable legal protection to foreign investors under international law will boost their confidence.
Conclusion
- This is critical at a time when foreign direct investment levels in India have dropped. A clear and comprehensive FTA policy is imperative for launching India to a higher economic growth trajectory.
India-EFTA Pact: Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA)
- Signed on: March 10, 2024
- Involves: India and EFTA member states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland.
- Goal: Promote investments and exports, particularly in India’s IT, audio-visual sectors, and skilled professional movement.
- Investment target: The EFTA states shall aim to increase FDI into India by $50 billion within 10 years, and another $50 billion in the five years thereafter.
- Additional provisions: For the first time, the FTA also included a chapter on commitments to human rights and sustainable development.
- The agreement will come into force after ratification by the EFTA states, expected possibly by the end of the year.
Potential benefits for India
- Tariff reduction: After the treaty comes into effect, the EFTA nations will see a reduction in tariffs on most industrial goods exported to India, such as pharmaceutical products, machinery, watches, fertilisers, medicine, chemical products and others.
- Increased trade and investment: EFTA investment already stood at $10.7 billion in 2022 and Switzerland is India’s largest trading partner in this bloc of nations, followed by Norway.
- Job creation: As per the newly signed agreement, the EFTA states shall aim to increase FDI into India by $1o0 billion within 15 years. This could facilitate the generation of one million direct jobs in the country.
- Access to the EFTA markets: Markets of these four countries will be opened for Indian products, thereby enhancing the export avenues for Indian products.
- Services sector: The services sector also forms a vital part of this trade agreement. The agreement would help stimulate services exports in areas such as information technology and facilitate the movement of key skilled personnel.
Challenges for India
- Trade with Swiss: Switzerland accounted for $1.38 billion of the total $1.87 billion of Indian exports to the EFTA in CY2023.
- But, 98% of India’s exports to Switzerland are industrial goods already entering at zero tariffs and won’t benefit from the FTA.
- Agri products are out of the deal: India is offering “82.7 percent of its tariff lines which cover 95.3 per cent” of the grouping’s exports. However, most agricultural items have reportedly been kept outside the purview of this deal.
- Low scope for access: The low scope for increasing market access for goods in EFTA could be of concern as India had a trade deficit of $18.58 billion with the bloc in CY23, with its imports at $20.45 billion.
- Of this, gold and other precious metals, stones and coins, all imported from Switzerland, accounted for $16.7 billion. Gold, making up 80% of India’s imports from Switzerland, is a critical factor.
- Little competition: The Joint Venture areas that the countries have short-listed, where investments are to be made, mostly do not have competition from India.
Way Ahead
- The Indian government had set an ambitious target of $2 trillion in exports of goods and services by 2030. Achieving this will require policy action on a range of issues — from lowering tariffs to entering into deeper, more expansive free trade agreements while safeguarding the country’s interests.
- It also calls for ensuring that measures are taken so that the benefits from these trade agreements are fully reaped.
Context:
- भारत में चल रहे संसदीय चुनावों के कारण यूनाइटेड किंगडम और यूरोपीय संघ (ईयू) जैसे देशों के साथ भारत के मुक्त व्यापार समझौते (FTA) की बातचीत ठंडे बस्ते में पड़ती दिख रही है।
एक ऐतिहासिक व्यापार समझौता: EFTA
- हालाँकि, देश में चुनावी बुखार चढ़ने से पहले, भारत मार्च में यूरोपीय मुक्त व्यापार संघ (ईएफटीए) के साथ एक ऐतिहासिक व्यापार समझौता करने में कामयाब रहा, जिसमें आइसलैंड, लिकटेंस्टीन, नॉर्वे और स्विट्जरलैंड शामिल थे।
- भारत और ईएफटीए के बीच नवनिर्मित व्यापार और आर्थिक साझेदारी समझौते (जिसे हम एफटीए के रूप में संदर्भित करते हैं) से दोनों पक्षों के बीच मौजूदा व्यापार के निम्न स्तर को बहुत जरूरी बढ़ावा मिलने की उम्मीद है।
- भारत और ईएफटीए के बीच एफटीए इसलिए भी महत्वपूर्ण है, क्योंकि भारत पर्यावरण और श्रम जैसे मुद्दों को शामिल करने पर सहमत हुआ है, जिन्हें वह पारंपरिक रूप से व्यापार समझौतों में शामिल करने का विरोध करता रहा है।
निवेश पर
- एक अन्य कारण इस एफटीए को उन एफटीए से अलग करता है जिन पर भारत ने हाल ही में ऑस्ट्रेलिया, संयुक्त अरब अमीरात (यूएई) और मॉरीशस जैसे देशों के साथ हस्ताक्षर किए हैं।
- भारत-ईएफटीए एफटीए में कुछ हद तक विस्तृत निवेश अध्याय शामिल है, जो अन्य हालिया भारतीय एफटीए में गायब है।
- यह अध्याय निवेश सुविधा के मुद्दों पर केंद्रित है, न कि निवेश सुरक्षा पर।
- लेकिन इसकी एक उल्लेखनीय और अभूतपूर्व विशेषता है। भारत ईएफटीए देशों से एक वादा हासिल करने में कामयाब रहा है कि उनका लक्ष्य एफटीए लागू होने के 10 वर्षों के भीतर भारत में प्रत्यक्ष विदेशी निवेश (FDI) को 50 अरब डॉलर तक बढ़ाना होगा, इसके बाद अगले पांच वर्षों में 50 अरब डॉलर और बढ़ाना होगा।
- इसी तरह, ईएफटीए राज्यों का लक्ष्य भारत में दस लाख नौकरियों के सृजन को सुविधाजनक बनाना होगा।
- कानूनी शब्दों में, ये लेख आचरण के दायित्व के रूप में जाने जाने वाले को संहिताबद्ध करते हैं – परिणाम या परिणाम के बावजूद, किसी लक्ष्य को प्राप्त करने के लिए एक ईमानदार प्रयास करने का दायित्व।
- यह परिणाम की बाध्यता से भिन्न है, जिसके लिए एक निर्दिष्ट परिणाम प्राप्त करने की आवश्यकता होगी।
- दूसरे शब्दों में, ईएफटीए देश भारत में 100 अरब डॉलर का निवेश करने और दस लाख नौकरियां पैदा करने के लिए ईमानदार प्रयास करने के लिए कानूनी रूप से बाध्य हैं।
- फिर भी, निवेश अध्याय में आचरण के ऐसे पथ-प्रदर्शक निर्दिष्ट दायित्वों को शामिल करने के लिए भारतीय वार्ताकारों की सराहना की जानी चाहिए, जो आमतौर पर एफटीए या निवेश संधियों में नहीं पाए जाते हैं।
- उल्लेखनीय रूप से, यह यू.के., यूरोपीय संघ और अन्य देशों के साथ चल रही बातचीत में अनुकरण के लायक एक टेम्पलेट तैयार करता है।
व्यापार और निवेश
- आर्थिक सिद्धांत ने लंबे समय से व्यापार और निवेश के बीच अटूट संबंध का प्रदर्शन किया है। यह उस दुनिया में अधिक सच है जहां उत्पादन प्रक्रिया वैश्विक आपूर्ति/मूल्य श्रृंखलाओं, व्यापार और निवेश का एक कार्य, के साथ बिखरी हुई है।
- इस प्रकार, आश्चर्य की बात नहीं है कि, एफटीए में नियमित रूप से व्यापार और निवेश दोनों पर बाध्यकारी नियम होते हैं।
- इस सदी के पहले दशक में जापान, कोरिया, मलेशिया और सिंगापुर जैसे देशों के साथ हस्ताक्षरित भारत के एफटीए इसी आर्थिक तर्क पर आधारित हैं।
- बाध्यकारी व्यापार नियमों के अलावा, उन सभी में निवेश की सुरक्षा के प्रावधानों के साथ एक निवेश अध्याय शामिल है।
- हालाँकि, भारत अपने FTA 2.0 दृष्टिकोण के हिस्से के रूप में इस मॉडल से हट गया।
- दूसरे शब्दों में, भारत ने अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार कानून को अंतर्राष्ट्रीय निवेश कानून से अलग कर दिया। यह ऑस्ट्रेलिया, मॉरीशस और संयुक्त अरब अमीरात के साथ उसके एफटीए में स्पष्ट है, जिसमें बाध्यकारी व्यापार तो है, लेकिन निवेश नियम नहीं हैं। ऐसा लगता है कि भारत का दृष्टिकोण एक ही देश के साथ व्यापार और निवेश पर अलग-अलग समझौते करना है। यह संयुक्त अरब अमीरात के मामले में सबसे स्पष्ट रूप से देखा गया है।
FTA 3.0
- भारत को एक स्पष्ट एफटीए नीति की आवश्यकता है, विशेष रूप से अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार और विदेशी निवेश कानूनों से निपटने में।
- मान लीजिए कि भारत न केवल व्यापार बल्कि किसी विशेष देश से उच्च निवेश प्रवाह की भी उम्मीद करता है, जो निस्संदेह उसके अधिकांश एफटीए-वार्तालाप भागीदारों के साथ सच है।
- उस स्थिति में, दो महत्वपूर्ण तत्वों को इसकी एफटीए नीति में शामिल किया जाना चाहिए। सबसे पहले, भारत को एक व्यापक आर्थिक संधि के हिस्से के रूप में व्यापार और निवेश पर बातचीत करनी चाहिए। व्यापार को निवेश से अलग करना कोई अच्छा विचार नहीं है। दोनों को मिलाने से भारत को एक लाभकारी सौदा करने के लिए स्पष्ट बातचीत का लाभ मिलेगा।
- दूसरा, भारत को अंतरराष्ट्रीय कानून के तहत एक प्रभावशाली विवाद निपटान तंत्र के साथ, निवेश के मुद्दों के दायरे को केवल सुविधा से प्रभावी सुरक्षा तक विस्तारित करने पर विचार करना चाहिए। अंतरराष्ट्रीय कानून के तहत विदेशी निवेशकों को प्रवर्तनीय कानूनी सुरक्षा प्रदान करने से उनका आत्मविश्वास बढ़ेगा।
निष्कर्ष
- यह ऐसे समय में महत्वपूर्ण है जब भारत में प्रत्यक्ष विदेशी निवेश का स्तर गिर गया है। भारत को उच्च आर्थिक विकास पथ पर ले जाने के लिए एक स्पष्ट और व्यापक एफटीए नीति आवश्यक है।
भारत-EFTA समझौता: व्यापार और आर्थिक साझेदारी समझौता (TEPA)
- हस्ताक्षरित: 10 मार्च, 2024
- शामिल हैं: भारत और ईएफटीए सदस्य देश: आइसलैंड, लिकटेंस्टीन, नॉर्वे और स्विट्जरलैंड।
- लक्ष्य: निवेश और निर्यात को बढ़ावा देना, विशेष रूप से भारत के आईटी, दृश्य-श्रव्य क्षेत्रों और कुशल पेशेवर आंदोलन में।
- निवेश लक्ष्य: ईएफटीए राज्यों का लक्ष्य 10 वर्षों के भीतर भारत में एफडीआई को 50 बिलियन डॉलर और उसके बाद के पांच वर्षों में 50 बिलियन डॉलर तक बढ़ाना होगा।
- अतिरिक्त प्रावधान: पहली बार, एफटीए में मानवाधिकारों और सतत विकास के प्रति प्रतिबद्धताओं पर एक अध्याय भी शामिल किया गया है।
- समझौता ईएफटीए राज्यों द्वारा अनुसमर्थन के बाद लागू होगा, संभवतः वर्ष के अंत तक।
भारत के लिए संभावित लाभ
- टैरिफ में कमी: संधि लागू होने के बाद, ईएफटीए देशों को भारत में निर्यात होने वाले अधिकांश औद्योगिक सामानों, जैसे फार्मास्युटिकल उत्पाद, मशीनरी, घड़ियां, उर्वरक, दवा, रासायनिक उत्पाद और अन्य पर टैरिफ में कमी देखने को मिलेगी।
- बढ़ा हुआ व्यापार और निवेश: 2022 में ईएफटीए निवेश पहले से ही 7 बिलियन डॉलर था और देशों के इस समूह में स्विट्जरलैंड भारत का सबसे बड़ा व्यापारिक भागीदार है, इसके बाद नॉर्वे है।
- रोजगार सृजन: नए हस्ताक्षरित समझौते के अनुसार, ईएफटीए राज्यों का लक्ष्य 15 वर्षों के भीतर भारत में एफडीआई को 1o0 बिलियन डॉलर तक बढ़ाने का होगा। इससे देश में दस लाख प्रत्यक्ष रोजगार पैदा करने में मदद मिल सकती है।
- ईएफटीए बाजारों तक पहुंच: इन चार देशों के बाजार भारतीय उत्पादों के लिए खोले जाएंगे, जिससे भारतीय उत्पादों के लिए निर्यात के रास्ते बढ़ेंगे।
- सेवा क्षेत्र: सेवा क्षेत्र भी इस व्यापार समझौते का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है। यह समझौता सूचना प्रौद्योगिकी जैसे क्षेत्रों में सेवाओं के निर्यात को प्रोत्साहित करने और प्रमुख कुशल कर्मियों की आवाजाही को सुविधाजनक बनाने में मदद करेगा।
भारत के लिए चुनौतियाँ
- स्विस के साथ व्यापार: CY2023 में EFTA को कुल 87 बिलियन डॉलर के भारतीय निर्यात में स्विट्जरलैंड का योगदान 1.38 बिलियन डॉलर था।
- लेकिन, स्विट्जरलैंड को भारत का 98% निर्यात पहले से ही शून्य टैरिफ पर आने वाले औद्योगिक सामान हैं और उन्हें एफटीए से कोई लाभ नहीं होगा।
- कृषि उत्पाद सौदे से बाहर हैं: भारत अपनी टैरिफ लाइनों का 7 प्रतिशत पेश कर रहा है जो समूह के निर्यात का 95.3 प्रतिशत कवर करता है। हालाँकि, अधिकांश कृषि वस्तुओं को कथित तौर पर इस सौदे के दायरे से बाहर रखा गया है।
- पहुंच की कम गुंजाइश: ईएफटीए में वस्तुओं के लिए बाजार पहुंच बढ़ाने की कम गुंजाइश चिंता का विषय हो सकती है क्योंकि भारत को CY23 में ब्लॉक के साथ 58 बिलियन डॉलर का व्यापार घाटा हुआ था, जबकि इसका आयात 20.45 बिलियन डॉलर था।
- इसमें से स्विट्जरलैंड से आयातित सोना और अन्य कीमती धातुएं, पत्थर और सिक्के, 16.7 बिलियन डॉलर के थे। सोना, जो स्विट्जरलैंड से भारत के आयात का 80% हिस्सा बनाता है, एक महत्वपूर्ण कारक है।
- कम प्रतिस्पर्धा: देशों ने जिन संयुक्त उद्यम क्षेत्रों को शॉर्टलिस्ट किया है, जहां निवेश किया जाना है, उनमें से अधिकांश में भारत से प्रतिस्पर्धा नहीं है।
आगे की राह
- भारत सरकार ने 2030 तक वस्तुओं और सेवाओं के निर्यात में 2 ट्रिलियन डॉलर का महत्वाकांक्षी लक्ष्य रखा था। इसे प्राप्त करने के लिए कई मुद्दों पर नीतिगत कार्रवाई की आवश्यकता होगी – टैरिफ कम करने से लेकर देश की सुरक्षा करते हुए गहरे, अधिक व्यापक मुक्त व्यापार समझौतों में प्रवेश करना।
- इसमें यह सुनिश्चित करने का भी आह्वान किया गया है कि ऐसे उपाय किए जाएं ताकि इन व्यापार समझौतों से लाभ पूरी तरह से प्राप्त हो सके।
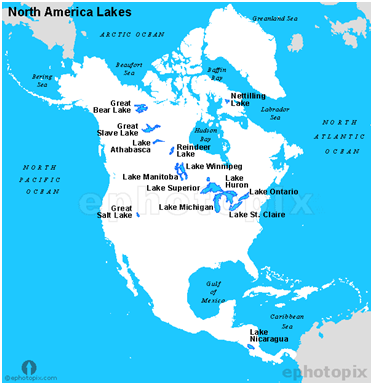
North America : Inland Drainage System and Lakes / उत्तरी अमेरिका: अंतर्देशीय जल निकासी प्रणाली और झीलें [Mapping]
- The Great Basin area in the Rocky Mountains (Middle) has rivers which do not reach the coast, but terminate in the land. This is the Inland Drainage System.
- The rivers are small, seasonal and end up in saline lakes.

Lakes in North America
- The Lakes of the Canadian Shield are freshwater bodies.
- The Great Salt Lake between the Rockies and the Sierra Nevada has a high salt content and is an area of ‘Inland drainage’.
- Lake Erie in Ontario, Canada, and Michigan, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania in the USA.
- Lake Huron in Ontario, Canada, and Michigan in the USA.
- Lake Ontario in Ontario, and New York in the USA.
- Lake St Clair in Ontario, and Michigan in the USA.
- Lake Superior in Michigan, Minnesota, Wisconsin in the USA.

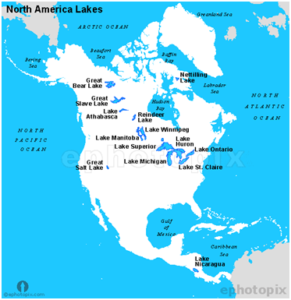
- रॉकी पर्वत (मध्य) में ग्रेट बेसिन क्षेत्र में नदियाँ हैं जो तट तक नहीं पहुँचती हैं, बल्कि भूमि में समाप्त हो जाती हैं। यह अंतर्देशीय जल निकासी प्रणाली है।
- नदियाँ छोटी, मौसमी हैं और खारे झीलों में समाप्त होती हैं।
उत्तरी अमेरिका में झीलें
- कैनेडियन शील्ड की झीलें मीठे पानी की झीलें हैं।
- रॉकीज़ और सिएरा नेवादा के बीच ग्रेट साल्ट लेक में नमक की मात्रा अधिक है और यह ‘अंतर्देशीय जल निकासी’ का क्षेत्र है।
- ओंटारियो, कनाडा में एरी झील और संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका में मिशिगन, न्यूयॉर्क, ओहियो, पेंसिल्वेनिया।
- कनाडा के ओन्टारियो में ह्यूरन झील और संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका में मिशिगन।
- ओंटारियो में ओंटारियो झील और संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका में न्यूयॉर्क।
- ओंटारियो में लेक सेंट क्लेयर और संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका में मिशिगन।
- संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका में मिशिगन, मिनेसोटा, विस्कॉन्सिन में सुपीरियर झील।