CURRENT AFFAIRS – 10/07/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 10/07/2024
- India, Russia to boost bilateral trade to 0 billion by 2030 / भारत, रूस 2030 तक द्विपक्षीय व्यापार को बढ़ाकर 100 बिलियन डॉलर करेंगे
- The shape of manufacturing 3.0 for Modi 3.0 / मोदी 3.0 के लिए विनिर्माण 3.0 का स्वरूप
- The innate limitations in executing iCET / आईसीईटी को क्रियान्वित करने में अंतर्निहित सीमाएँ
- What is the draft Digital Competition Bill ? / डिजिटल प्रतिस्पर्धा विधेयक का मसौदा क्या है?
- Integrated Tribal Development Programme by NABARD / नाबार्ड द्वारा एकीकृत जनजातीय विकास कार्यक्रम
- A Budget that drives growth with stability / एक ऐसा बजट जो स्थिरता के साथ विकास को बढ़ावा देता है
- Lakes in India [Mapping] / भारत में झीलें [मानचित्र]
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 10/07/2024
India, Russia to boost bilateral trade to 0 billion by 2030 / भारत, रूस 2030 तक द्विपक्षीय व्यापार को बढ़ाकर 100 बिलियन डॉलर करेंगे
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
During the 22nd Annual Summit on Tuesday, both countries agreed to elevate bilateral trade to $100 billion by 2030. This agreement includes the use of national currencies to bypass Western sanctions.
About the News
Key highlights of the 22nd Annual Summit
- Trade and Economic Cooperation: India and Russia have set an ambitious target to increase bilateral trade to $100 billion by 2030. They plan to use national currencies for trade to bypass Western sanctions, reflecting a strategic shift in their economic engagements.
- Defense and Strategic Partnership: The countries discussed delays in defense supplies and committed to enhancing the co-production of defense equipment.
- Response to Ukraine Conflict: Prime Minister Modi made a plea for ending civilian casualties and the conflict in Ukraine. Both countries called for a peaceful resolution to the Ukraine conflict in their joint statement, highlighting mediation efforts and adherence to international law.
- Institutional Agreements and MoUs: Several MoUs were signed on topics including climate change, polar research, legal arbitration, and pharmaceutical certification, demonstrating broad-based cooperation.
- Recognition and Future Engagements: Modi received Russia’s highest civilian honor, the Order of St. Andrew the Apostle. Putin invited Modi to the “Extended BRICS” summit in Kazan in October 2024, emphasizing ongoing and future high-level engagements.
- Russia Offers Compensation and Citizenship to Kin of Indians Killed in War Against Ukraine
- Expedited Discharge of Indian Recruits: President Putin accepted Prime Minister Modi’s request to expedite the discharge of Indian nationals recruited by the Russian military. Approximately 40 Indians, currently at the war front, are to be discharged through diplomatic processes.
- Compensation and Citizenship Offer: Russia has offered compensation and citizenship to the families of Indian nationals who have been killed in the conflict in Ukraine. This move aims to provide support and recognition to the families of the deceased.
New Delhi and Moscow call for ‘zero tolerance’ towards terrorism
- Joint Statement on Terrorism: India and Russia reiterated their strong stance against terrorism, emphasizing the need for “zero tolerance” towards all forms of terrorism.
- Commitment to International Cooperation: Both countries underscored the importance of international cooperation to combat terrorism effectively. They highlighted the necessity for a coordinated global response to address the threat of terrorism.
- Condemnation of Terrorist Acts: The leaders condemned terrorist acts worldwide and stressed that no cause or ideology could justify the killing of innocent people. They called for the strictest measures to combat and eliminate terrorism.
Bilateral ties between India-Russia
- Long-standing strategic partnership: India and Russia have enjoyed a strong strategic partnership since the Cold War era.
- This was further strengthened with the signing of the “Declaration on the India-Russia Strategic Partnership” in 2000, which elevated cooperation in various areas including politics, security, defense, trade, and culture.
- In 2010, the partnership was elevated to a “Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership”.
- Robust defense cooperation: Russia is India’s largest defense partner, accounting for approximately 68% of India’s military hardware imports in 2017.
- The two countries have an Inter-Governmental Commission on Military-Technical Cooperation that meets annually.
- Major defense projects include the MiG-21, Su-30, and the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant.
- Economic and Trade Relations: Russia is India’s 7th largest trading partner, with bilateral trade reaching $45 billion, surpassing the target of $30 billion by 2025.
- Key areas of economic cooperation include energy, nuclear energy, and the North-South Transport Corridor.
- Russia is also an important partner in India’s energy security, with investments in the oil and gas sectors.
- Geopolitical coordination: India and Russia closely collaborate on matters of shared national interest at international forums such as the UN, BRICS, G20, and SCO.
- Russia supports India’s permanent seat on the UN Security Council and its membership in the NSG and APEC.
- The two countries also coordinate on regional issues like Afghanistan and the Indo-Pacific.
भारत, रूस 2030 तक द्विपक्षीय व्यापार को बढ़ाकर 100 बिलियन डॉलर करेंगे
मंगलवार को 22वें वार्षिक शिखर सम्मेलन के दौरान दोनों देशों ने 2030 तक द्विपक्षीय व्यापार को 100 बिलियन डॉलर तक बढ़ाने पर सहमति व्यक्त की। इस समझौते में पश्चिमी प्रतिबंधों को दरकिनार करने के लिए राष्ट्रीय मुद्राओं का उपयोग शामिल है।
समाचार के बारे में
22वें वार्षिक शिखर सम्मेलन की मुख्य बातें
- व्यापार और आर्थिक सहयोग: भारत और रूस ने 2030 तक द्विपक्षीय व्यापार को 100 बिलियन डॉलर तक बढ़ाने का महत्वाकांक्षी लक्ष्य रखा है। वे पश्चिमी प्रतिबंधों को दरकिनार करने के लिए व्यापार के लिए राष्ट्रीय मुद्राओं का उपयोग करने की योजना बना रहे हैं, जो उनके आर्थिक जुड़ाव में एक रणनीतिक बदलाव को दर्शाता है।
- रक्षा और रणनीतिक साझेदारी: देशों ने रक्षा आपूर्ति में देरी पर चर्चा की और रक्षा उपकरणों के सह-उत्पादन को बढ़ाने के लिए प्रतिबद्ध हुए।
- यूक्रेन संघर्ष पर प्रतिक्रिया: प्रधानमंत्री मोदी ने यूक्रेन में नागरिक हताहतों और संघर्ष को समाप्त करने की अपील की। दोनों देशों ने अपने संयुक्त वक्तव्य में यूक्रेन संघर्ष के शांतिपूर्ण समाधान का आह्वान किया, जिसमें मध्यस्थता प्रयासों और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय कानून के पालन पर प्रकाश डाला गया।
- संस्थागत समझौते और समझौता ज्ञापन: जलवायु परिवर्तन, ध्रुवीय अनुसंधान, कानूनी मध्यस्थता और दवा प्रमाणन सहित कई विषयों पर कई समझौता ज्ञापनों पर हस्ताक्षर किए गए, जो व्यापक सहयोग को प्रदर्शित करते हैं।
- मान्यता और भविष्य की भागीदारी: मोदी को रूस का सर्वोच्च नागरिक सम्मान, ऑर्डर ऑफ सेंट एंड्रयू द एपोस्टल मिला। पुतिन ने अक्टूबर 2024 में कज़ान में होने वाले “विस्तारित ब्रिक्स” शिखर सम्मेलन में मोदी को आमंत्रित किया, जिसमें चल रहे और भविष्य के उच्च-स्तरीय जुड़ावों पर जोर दिया गया।
- भारतीय भर्ती करने वालों की शीघ्र रिहाई: राष्ट्रपति पुतिन ने रूसी सेना द्वारा भर्ती किए गए भारतीय नागरिकों की रिहाई में तेजी लाने के प्रधानमंत्री मोदी के अनुरोध को स्वीकार कर लिया। वर्तमान में युद्ध के मोर्चे पर मौजूद लगभग 40 भारतीयों को कूटनीतिक प्रक्रियाओं के माध्यम से रिहा किया जाना है।
- मुआवजा और नागरिकता की पेशकश: रूस ने यूक्रेन में संघर्ष में मारे गए भारतीय नागरिकों के परिवारों को मुआवजा और नागरिकता की पेशकश की है। इस कदम का उद्देश्य मृतकों के परिवारों को सहायता और मान्यता प्रदान करना है।
नई दिल्ली और मॉस्को ने आतंकवाद के प्रति ‘शून्य सहनशीलता’ का आह्वान किया
- आतंकवाद पर संयुक्त वक्तव्य: भारत और रूस ने आतंकवाद के खिलाफ अपने कड़े रुख को दोहराया, आतंकवाद के सभी रूपों के प्रति “शून्य सहनशीलता” की आवश्यकता पर जोर दिया।
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग के लिए प्रतिबद्धता: दोनों देशों ने आतंकवाद से प्रभावी ढंग से निपटने के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग के महत्व को रेखांकित किया। उन्होंने आतंकवाद के खतरे से निपटने के लिए समन्वित वैश्विक प्रतिक्रिया की आवश्यकता पर प्रकाश डाला।
- आतंकवादी कृत्यों की निंदा: नेताओं ने दुनिया भर में आतंकवादी कृत्यों की निंदा की और इस बात पर जोर दिया कि कोई भी कारण या विचारधारा निर्दोष लोगों की हत्या को उचित नहीं ठहरा सकती। उन्होंने आतंकवाद से निपटने और उसे खत्म करने के लिए सख्त कदम उठाने का आह्वान किया।
भारत-रूस के बीच द्विपक्षीय संबंध
- दीर्घकालिक रणनीतिक साझेदारी: भारत और रूस ने शीत युद्ध के समय से ही मजबूत रणनीतिक साझेदारी का आनंद लिया है।
- 2000 में “भारत-रूस रणनीतिक साझेदारी पर घोषणा” पर हस्ताक्षर करने के साथ ही यह साझेदारी और मजबूत हुई, जिसने राजनीति, सुरक्षा, रक्षा, व्यापार और संस्कृति सहित विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में सहयोग को बढ़ाया।
- 2010 में, साझेदारी को “विशेष और विशेषाधिकार प्राप्त रणनीतिक साझेदारी” के रूप में उन्नत किया गया।
- मजबूत रक्षा सहयोग: रूस भारत का सबसे बड़ा रक्षा साझेदार है, जिसने 2017 में भारत के सैन्य हार्डवेयर आयात का लगभग 68% हिस्सा खरीदा।
- दोनों देशों के बीच सैन्य-तकनीकी सहयोग पर एक अंतर-सरकारी आयोग है, जिसकी सालाना बैठक होती है।
- प्रमुख रक्षा परियोजनाओं में मिग-21, एसयू-30 और कुडनकुलम परमाणु ऊर्जा संयंत्र शामिल हैं।
- आर्थिक और व्यापारिक संबंध: रूस भारत का 7वां सबसे बड़ा व्यापारिक साझेदार है, जिसका द्विपक्षीय व्यापार 45 बिलियन डॉलर तक पहुंच गया है, जो 2025 तक 30 बिलियन डॉलर के लक्ष्य को पार कर गया है।
- आर्थिक सहयोग के प्रमुख क्षेत्रों में ऊर्जा, परमाणु ऊर्जा और उत्तर-दक्षिण परिवहन गलियारा शामिल हैं।
- रूस भारत की ऊर्जा सुरक्षा में भी एक महत्वपूर्ण साझेदार है, जिसका तेल और गैस क्षेत्रों में निवेश है।
- भू-राजनीतिक समन्वय: भारत और रूस संयुक्त राष्ट्र, ब्रिक्स, जी-20 और एससीओ जैसे अंतर्राष्ट्रीय मंचों पर साझा राष्ट्रीय हित के मामलों पर निकटता से सहयोग करते हैं।
- रूस संयुक्त राष्ट्र सुरक्षा परिषद में भारत की स्थायी सीट और एनएसजी और एपीईसी में इसकी सदस्यता का समर्थन करता है।
- दोनों देश अफगानिस्तान और हिंद-प्रशांत जैसे क्षेत्रीय मुद्दों पर भी समन्वय करते हैं।
The shape of manufacturing 3.0 for Modi 3.0 / मोदी 3.0 के लिए विनिर्माण 3.0 का स्वरूप
(General Studies- Paper III)
Source : The Hindu
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s coalition government emphasises boosting India’s manufacturing sector to address urbanisation, employment shifts from agriculture, trade deficits, and national security concerns amid geopolitical dynamics, including China’s assertiveness.
Government’s Manufacturing Goals
- Since 2014, the central government has aimed to increase manufacturing as a percentage of GDP from 15% to 25% by 2025.
- Despite reforms like GST, India’s manufacturing contribution declined to 13% of GDP by 2022, contrasting unfavourably with other countries like China, Vietnam, and Bangladesh.
Importance of Boosting Manufacturing
- Employment Generation: Shift from low-productivity agriculture necessitates creating employment in manufacturing, catering to half of India’s workforce.
- Trade Deficit: India faces a significant goods trade deficit, with substantial imports of manufactured goods like electronics, alongside a surplus in services trade.
Strategic Importance for India and U.S.
- National Security: Strengthening India’s manufacturing supports its regional security role amidst rising geopolitical tensions, particularly concerning China.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Building manufacturing capabilities in India enhances supply chain reliability for U.S. interests, reducing offshore dependencies.
Challenges and Considerations
- State-Level Governance: Most factors influencing manufacturing—electric power, water, labour regulations—are controlled by State governments, requiring enhanced policy attention from the central government.
- Business Environment: Initiatives like BRAP for state competitiveness have been inconsistent, lacking updated assessments post-COVID-19 and reliant on self-reported data.
- Sector Focus: Advocacy for job-intensive sectors like textiles and furniture is proposed over capital-intensive sectors to stimulate broader employment growth.
U.S. Role and Engagement
- Supportive Engagement:S. involvement in enhancing Indian state governance and economic policies could improve investment attractiveness and supply chain integration.
- Regional Engagement: Suggestions for U.S. officials to extend engagements beyond major cities like Delhi-Mumbai-Bengaluru to include key manufacturing states, fostering deeper economic ties.
Conclusion
- Policy Realignment: The central government’s renewed focus on manufacturing post-election underscores persistent needs for job creation, trade balance, and security enhancement.
- Path Forward: While India’s market size and growth potential remain attractive, achieving “Make in India” success hinges on comprehensive reforms at both central and state levels to accelerate manufacturing growth.
मोदी 3.0 के लिए विनिर्माण 3.0 का स्वरूप
प्रधानमंत्री नरेंद्र मोदी की गठबंधन सरकार शहरीकरण, कृषि से रोजगार में बदलाव, व्यापार घाटे और चीन की आक्रामकता सहित भू-राजनीतिक गतिशीलता के बीच राष्ट्रीय सुरक्षा चिंताओं को दूर करने के लिए भारत के विनिर्माण क्षेत्र को बढ़ावा देने पर जोर दे रही है।
सरकार के विनिर्माण लक्ष्य
- वर्ष 2014 से, केंद्र सरकार ने वर्ष 2025 तक सकल घरेलू उत्पाद के प्रतिशत के रूप में विनिर्माण को 15% से बढ़ाकर 25% करने का लक्ष्य रखा है।
- जीएसटी जैसे सुधारों के बावजूद, भारत का विनिर्माण योगदान वर्ष 2022 तक सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में घटकर 13% रह गया, जो चीन, वियतनाम और बांग्लादेश जैसे अन्य देशों के साथ प्रतिकूल है।
विनिर्माण को बढ़ावा देने का महत्व
- रोजगार सृजन: कम उत्पादकता वाली कृषि से हटकर विनिर्माण में रोजगार सृजन की आवश्यकता है, जो भारत के आधे कार्यबल की जरूरतों को पूरा करेगा।
- व्यापार घाटा: भारत को एक महत्वपूर्ण वस्तु व्यापार घाटे का सामना करना पड़ रहा है, जिसमें इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स जैसे विनिर्मित वस्तुओं का पर्याप्त आयात होता है, साथ ही सेवा व्यापार में अधिशेष भी है।
भारत और अमेरिका के लिए रणनीतिक महत्व
- राष्ट्रीय सुरक्षा: भारत के विनिर्माण को मजबूत करना बढ़ते भू-राजनीतिक तनावों, विशेष रूप से चीन के संबंध में, के बीच इसकी क्षेत्रीय सुरक्षा भूमिका का समर्थन करता है।
- आपूर्ति श्रृंखला लचीलापन: भारत में विनिर्माण क्षमताओं का निर्माण अमेरिकी हितों के लिए आपूर्ति श्रृंखला विश्वसनीयता को बढ़ाता है, जिससे अपतटीय निर्भरता कम होती है।
चुनौतियाँ और विचार
- राज्य-स्तरीय शासन: विनिर्माण को प्रभावित करने वाले अधिकांश कारक- बिजली, पानी, श्रम विनियमन- राज्य सरकारों द्वारा नियंत्रित होते हैं, जिसके लिए केंद्र सरकार से नीतिगत ध्यान बढ़ाने की आवश्यकता होती है।
- व्यावसायिक वातावरण: राज्य प्रतिस्पर्धात्मकता के लिए BRAP जैसी पहल असंगत रही है, COVID-19 के बाद अद्यतन मूल्यांकन की कमी है और स्व-रिपोर्ट किए गए डेटा पर निर्भर है।
- क्षेत्रीय फोकस: व्यापक रोजगार वृद्धि को प्रोत्साहित करने के लिए पूंजी-गहन क्षेत्रों की तुलना में कपड़ा और फर्नीचर जैसे नौकरी-गहन क्षेत्रों की वकालत प्रस्तावित है।
अमेरिका की भूमिका और जुड़ाव
- सहायक जुड़ाव: भारतीय राज्य शासन और आर्थिक नीतियों को बढ़ाने में अमेरिका की भागीदारी निवेश आकर्षण और आपूर्ति श्रृंखला एकीकरण में सुधार कर सकती है।
- क्षेत्रीय जुड़ाव: अमेरिकी अधिकारियों के लिए सुझाव कि वे दिल्ली-मुंबई-बेंगलुरु जैसे प्रमुख शहरों से आगे बढ़कर प्रमुख विनिर्माण राज्यों को शामिल करें, जिससे गहरे आर्थिक संबंधों को बढ़ावा मिले।
निष्कर्ष
- नीति पुनर्संरेखण: चुनाव के बाद विनिर्माण पर केंद्र सरकार का नया ध्यान रोजगार सृजन, व्यापार संतुलन और सुरक्षा वृद्धि की निरंतर आवश्यकताओं को रेखांकित करता है।
- आगे की राह: यद्यपि भारत का बाजार आकार और विकास क्षमता आकर्षक बनी हुई है, फिर भी “मेक इन इंडिया” की सफलता विनिर्माण विकास में तेजी लाने के लिए केंद्र और राज्य दोनों स्तरों पर व्यापक सुधारों पर निर्भर है।
The innate limitations in executing iCET / आईसीईटी को क्रियान्वित करने में अंतर्निहित सीमाएँ
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
The Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET) between India and the US faces structural challenges in its execution, particularly regarding technology transfer and autonomy of US defense companies.
Challenges in Technology Transfer:
- IPR and Export Control Hurdles: US defense companies are reluctant to share military technologies due to strict export control laws and intellectual property rights concerns.
- Partial Technology Transfer: General Electric’s F-414INS6 engine deal with India involves transferring about 80% technology, but excludes critical know-how related to forging metallurgy discs for turbines.
- Limited UAV Technology Sharing: Technology transfer from General Atomics for MQ-9 UAVs is limited to around 10-15%, primarily focused on establishing a domestic maintenance facility.
Limitations of US Defense Industry Cooperation:
- Commercial Interests vs. Strategic Goals: US government does not act on behalf of defense companies owning IPRs, as these companies are primarily driven by commercial interests.
- Historical Precedent: Failure of the 2012 Defense Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI) due to technology transfer issues highlights persistent challenges.
- Restrictions on ‘Jugaad’: Complex ‘enabling’ protocols and strict end-use monitoring programs like ‘Golden Sentry’ restrict India’s ability to apply ‘jugaad’ (innovative adaptations) to US-origin platforms.
Strategic Implications and Future Prospects:
- Shifting Defense Partnerships: iCET is part of US strategy to reduce India’s dependency on Russian arms, as outlined in a recent Senate Foreign Relations Committee report.
- Multi-organizational Approach: The initiative involves multiple organizations like INDUS-X, Joint IMPACT, and ADDD to facilitate cooperation.
- Balancing Act: Success of iCET depends on overcoming bureaucratic hurdles and aligning US commercial interests with broader strategic goals in the India-US partnership.
आईसीईटी को क्रियान्वित करने में अंतर्निहित सीमाएँ
भारत और अमेरिका के बीच महत्वपूर्ण एवं उभरती प्रौद्योगिकियों पर पहल (ICET) को अपने क्रियान्वयन में संरचनात्मक चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ रहा है, विशेष रूप से प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण और अमेरिकी रक्षा कंपनियों की स्वायत्तता के संबंध में।
प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण में चुनौतियाँ:
- आई.पी.आर. और निर्यात नियंत्रण बाधाएँ: अमेरिकी रक्षा कंपनियाँ सख्त निर्यात नियंत्रण कानूनों और बौद्धिक संपदा अधिकारों की चिंताओं के कारण सैन्य प्रौद्योगिकियों को साझा करने में अनिच्छुक हैं।
- आंशिक प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण: भारत के साथ जनरल इलेक्ट्रिक के F-414 I.N.S.6 इंजन सौदे में लगभग 80% प्रौद्योगिकी का हस्तांतरण शामिल है, लेकिन टर्बाइनों के लिए धातुकर्म डिस्क बनाने से संबंधित महत्वपूर्ण जानकारी को इसमें शामिल नहीं किया गया है।
- सीमित यू.ए.वी. प्रौद्योगिकी साझाकरण: एम.क्यू.-9 यू.ए.वी. के लिए जनरल एटॉमिक्स से प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण लगभग 10-15% तक सीमित है, जो मुख्य रूप से घरेलू रखरखाव सुविधा स्थापित करने पर केंद्रित है।
अमेरिकी रक्षा उद्योग सहयोग की सीमाएँ:
- वाणिज्यिक हित बनाम रणनीतिक लक्ष्य: अमेरिकी सरकार आई.पी.आर. रखने वाली रक्षा कंपनियों की ओर से कार्य नहीं करती है, क्योंकि ये कंपनियाँ मुख्य रूप से वाणिज्यिक हितों से प्रेरित होती हैं।
- ऐतिहासिक मिसाल: प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण मुद्दों के कारण 2012 रक्षा प्रौद्योगिकी और व्यापार पहल (डी.टी.टी.आई.) की विफलता लगातार चुनौतियों को उजागर करती है।
- ‘जुगाड़’ पर प्रतिबंध: जटिल ‘सक्षम’ प्रोटोकॉल और ‘गोल्डन सेंट्री’ जैसे सख्त अंतिम-उपयोग निगरानी कार्यक्रम भारत की अमेरिकी मूल के प्लेटफॉर्म पर ‘जुगाड़’ (अभिनव अनुकूलन) लागू करने की क्षमता को प्रतिबंधित करते हैं।
रणनीतिक निहितार्थ और भविष्य की संभावनाएँ:
- रक्षा साझेदारी में बदलाव: iCET, रूसी हथियारों पर भारत की निर्भरता को कम करने की अमेरिकी रणनीति का हिस्सा है, जैसा कि हाल ही में सीनेट की विदेश संबंध समिति की रिपोर्ट में बताया गया है।
- बहु-संगठनात्मक दृष्टिकोण: इस पहल में सहयोग को सुविधाजनक बनाने के लिए INDUS-X, संयुक्त IMPACT और ADDD जैसे कई संगठन शामिल हैं।
- संतुलन अधिनियम: iCET की सफलता नौकरशाही बाधाओं को दूर करने और भारत-अमेरिका साझेदारी में व्यापक रणनीतिक लक्ष्यों के साथ अमेरिकी वाणिज्यिक हितों को संरेखित करने पर निर्भर करती है।
What is the draft Digital Competition Bill ? / डिजिटल प्रतिस्पर्धा विधेयक का मसौदा क्या है?
Syllabus : Governance
Source : The Hindu
In February 2023, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) established a Committee on Digital Competition Law (CDCL) to assess the necessity for distinct legislation concerning competition within digital markets.
What is an ex-post framework?
- An ex-post framework refers to a regulatory approach where authorities intervene and enforce regulations after potentially harmful activities or behaviors have already occurred.
- In the context of competition law, it means that enforcement actions are taken against anti-competitive practices only after they have been observed or reported.
How is an ex-post framework different from an ex-ante framework?
- Timing of Intervention:
- Ex-post framework: Intervenes after anti-competitive conduct has occurred and its effects are observed. It relies on retrospective enforcement based on complaints or identified issues.
- Ex-ante framework: Proactively sets rules and obligations before anti-competitive behavior happens, aiming to prevent market distortions and protect competition from potential harms.
- Nature of Regulation:
- Ex-post framework: Reactive in nature, focusing on remedial measures and enforcement actions against established instances of anti-competitive behavior.
- Ex-ante framework: Proactive in nature, establishing upfront rules and obligations to guide behavior and prevent market abuses by dominant players before they occur.
- Focus and Objectives:
- Ex-post framework: Focuses on addressing past harms to competition, ensuring fair market practices, and correcting market distortions post-occurrence.
- Ex-ante framework: Focuses on maintaining competitive markets, promoting innovation, and protecting consumer choice by setting clear rules and preventing anti-competitive behavior from developing in the first place.
Why does the draft Bill encourage an ex-ante competition regulation?
- Proactive Prevention: Digital markets exhibit characteristics such as rapid growth, network effects, and economies of scale that can lead to quick and irreversible market dominance. An ex-ante framework allows regulatory authorities to preemptively set rules and obligations to prevent anti-competitive practices before they occur, thereby maintaining market competition and ensuring consumer choice.
- Timely Intervention: The existing ex-post framework under the Competition Act, 2002 is considered inadequate for digital markets, where traditional enforcement mechanisms may be too slow to effectively address evolving market dynamics and prevent potential harms to competition. An ex-ante approach enables timely intervention and regulatory oversight to curb monopolistic tendencies and promote a level playing field for all market participants.
Digital Competition Bill
- Drafting Process: The Bill was drafted by a 16-member committee on digital competition law after a year of deliberation.
- Target Group: It focuses on regulating “systemically significant digital enterprises” (SSDEs), which are large tech firms with major revenue and user base in India. SSDEs are identified by having at least ₹4,000 crore in Indian revenue and $30 billion globally.
- Bill’s Aims: Designed to prevent anti-competitive practices, ensure transparency, and curb unfair favoritism in the digital sector.
- Current Status: The Bill is open for public comment and may require further adjustments before being finalized.
What are the benefits of the Digital Competition Bill?
- Increases Transparency: Requires tech companies to be more transparent in their operations and dealings.
- Protects Innovators and Startups: Exempts smaller companies and startups from stringent rules, encouraging innovation.
- Aligns with Global Standards: Follows a similar approach to the EU’s Digital Markets Act, showing an effort to align with international regulatory frameworks.
- Boosts Digital Economy: By regulating effectively, it supports the growth of India’s digital market, expected to reach $800 billion by 2030.
How is the bill intended to regulate big tech companies?
- The Digital Competition Bill intends to regulate big tech companies by requiring them to operate in a fair, transparent manner, and establish clear complaint-handling mechanisms.
- It specifically prohibits these companies from unfairly favoring their own products or those of related parties.
- Additionally, the Bill restricts the misuse of non-public data of business users and prevents the restriction of third-party apps.
- It also bans practices like “steering” or “self-referencing” and predatory pricing.
- These regulations apply alongside compliance with the existing Competition Act and the Digital Personal Data Protection Act.
Criticism of the digital competition Bill 2024
- Significant compliance burden
- An ex-ante framework with its strict prescriptive norms could lead to significant compliance burden for big tech companies.
- It may lead to shift of focus from innovation and research to ensuring that companies do not presumptively engage in an anti-competitive practice.
- Stringent requirements of the EU’s DMA and associated impact
- Experts have highlighted that there has been a significant increase in the time it takes to find things via Google search.
- Broad definition of who a significant platform
- Companies are concerned about the broad definition — both quantitative and qualitative — of who a significant platform could be.
- Unlike EU’s DMA which specifically names the ‘gatekeeper’ entities, that decision in India’s draft law has been left to the discretion of the CCI.
- Companies believe that could lead to arbitrary decision making, which could potentially also impact start-ups.
- May affect smaller businesses
- Companies are claiming that the bill would force them to make the changes to their platform and cut down on data sharing.
- It could also impact smaller businesses who rely on their platforms to reach a big target audience.
डिजिटल प्रतिस्पर्धा विधेयक का मसौदा क्या है?
फरवरी 2023 में, कॉर्पोरेट मामलों के मंत्रालय (एमसीए) ने डिजिटल बाजारों में प्रतिस्पर्धा के संबंध में अलग कानून की आवश्यकता का आकलन करने के लिए डिजिटल प्रतिस्पर्धा कानून (सीडीसीएल) पर एक समिति की स्थापना की।
एक्स-पोस्ट फ्रेमवर्क क्या है?
- एक्स-पोस्ट फ्रेमवर्क एक विनियामक दृष्टिकोण को संदर्भित करता है, जहाँ अधिकारी संभावित रूप से हानिकारक गतिविधियों या व्यवहारों के घटित होने के बाद हस्तक्षेप करते हैं और विनियमन लागू करते हैं।
- प्रतिस्पर्धा कानून के संदर्भ में, इसका अर्थ है कि प्रतिस्पर्धा-विरोधी प्रथाओं के विरुद्ध प्रवर्तन कार्रवाई केवल उनके देखे जाने या रिपोर्ट किए जाने के बाद ही की जाती है।
एक्स-पोस्ट फ्रेमवर्क, एक्स-एंटे फ्रेमवर्क से किस प्रकार भिन्न है?
- हस्तक्षेप का समय:
- एक्स-पोस्ट फ्रेमवर्क: प्रतिस्पर्धा-विरोधी आचरण के घटित होने और उसके प्रभावों के देखे जाने के बाद हस्तक्षेप करता है। यह शिकायतों या पहचाने गए मुद्दों के आधार पर पूर्वव्यापी प्रवर्तन पर निर्भर करता है।
- एक्स-एंटे फ्रेमवर्क: प्रतिस्पर्धा-विरोधी व्यवहार होने से पहले सक्रिय रूप से नियम और दायित्व निर्धारित करता है, जिसका उद्देश्य बाजार में विकृतियों को रोकना और प्रतिस्पर्धा को संभावित नुकसान से बचाना है।
विनियमन की प्रकृति:
- एक्स-पोस्ट फ्रेमवर्क: प्रकृति में प्रतिक्रियाशील, प्रतिस्पर्धा-विरोधी व्यवहार के स्थापित उदाहरणों के विरुद्ध उपचारात्मक उपायों और प्रवर्तन कार्रवाइयों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करता है।
- एक्स-एंटे फ्रेमवर्क: प्रकृति में सक्रिय, व्यवहार को निर्देशित करने और प्रमुख खिलाड़ियों द्वारा बाजार में दुरुपयोग को रोकने के लिए पहले से नियम और दायित्व स्थापित करता है।
फोकस और उद्देश्य:
- पूर्व-पश्चात रूपरेखा: प्रतिस्पर्धा को होने वाले पिछले नुकसानों को संबोधित करने, निष्पक्ष बाजार प्रथाओं को सुनिश्चित करने और घटना के बाद बाजार विकृतियों को ठीक करने पर ध्यान केंद्रित करती है।
- पूर्व-पश्चात रूपरेखा: प्रतिस्पर्धी बाजारों को बनाए रखने, नवाचार को बढ़ावा देने और स्पष्ट नियम निर्धारित करके और प्रतिस्पर्धा-विरोधी व्यवहार को पहले स्थान पर विकसित होने से रोककर उपभोक्ता की पसंद की रक्षा करने पर ध्यान केंद्रित करती है।
मसौदा विधेयक पूर्व-पश्चात प्रतिस्पर्धा विनियमन को क्यों प्रोत्साहित करता है?
- सक्रिय रोकथाम: डिजिटल बाजार तेजी से विकास, नेटवर्क प्रभाव और पैमाने की अर्थव्यवस्थाओं जैसी विशेषताओं को प्रदर्शित करते हैं जो त्वरित और अपरिवर्तनीय बाजार प्रभुत्व को जन्म दे सकते हैं। पूर्व-पश्चात रूपरेखा नियामक अधिकारियों को प्रतिस्पर्धा-विरोधी प्रथाओं को होने से पहले रोकने के लिए नियमों और दायित्वों को पहले से ही निर्धारित करने की अनुमति देती है, जिससे बाजार में प्रतिस्पर्धा बनी रहती है और उपभोक्ता की पसंद सुनिश्चित होती है।
- समय पर हस्तक्षेप: प्रतिस्पर्धा अधिनियम, 2002 के तहत मौजूदा पूर्व-पश्चात रूपरेखा को डिजिटल बाजारों के लिए अपर्याप्त माना जाता है, जहां पारंपरिक प्रवर्तन तंत्र विकसित बाजार गतिशीलता को प्रभावी ढंग से संबोधित करने और प्रतिस्पर्धा को संभावित नुकसान को रोकने के लिए बहुत धीमा हो सकता है। एक पूर्व-पूर्व दृष्टिकोण एकाधिकारवादी प्रवृत्तियों पर अंकुश लगाने और सभी बाजार प्रतिभागियों के लिए समान अवसर को बढ़ावा देने के लिए समय पर हस्तक्षेप और विनियामक निरीक्षण को सक्षम बनाता है।
- डिजिटल प्रतिस्पर्धा विधेयक
- मसौदा प्रक्रिया: एक वर्ष के विचार-विमर्श के बाद डिजिटल प्रतिस्पर्धा कानून पर 16-सदस्यीय समिति द्वारा विधेयक का मसौदा तैयार किया गया था।
- लक्ष्य समूह: यह “व्यवस्थित रूप से महत्वपूर्ण डिजिटल उद्यमों” (SSDE) को विनियमित करने पर केंद्रित है, जो भारत में प्रमुख राजस्व और उपयोगकर्ता आधार वाली बड़ी तकनीकी फर्म हैं। SSDE की पहचान भारत में कम से कम ₹4,000 करोड़ और वैश्विक स्तर पर $30 बिलियन के राजस्व से की जाती है।
- बिल का उद्देश्य: डिजिटल क्षेत्र में प्रतिस्पर्धा-विरोधी प्रथाओं को रोकने, पारदर्शिता सुनिश्चित करने और अनुचित पक्षपात को रोकने के लिए बनाया गया है।
- वर्तमान स्थिति: बिल सार्वजनिक टिप्पणी के लिए खुला है और इसे अंतिम रूप दिए जाने से पहले और समायोजन की आवश्यकता हो सकती है।
डिजिटल प्रतिस्पर्धा विधेयक के क्या लाभ हैं?
- पारदर्शिता बढ़ाता है: तकनीकी कंपनियों को अपने संचालन और व्यवहार में अधिक पारदर्शी होने की आवश्यकता है।
- नवप्रवर्तकों और स्टार्टअप की सुरक्षा करता है: छोटी कंपनियों और स्टार्टअप को कड़े नियमों से छूट देता है, जिससे नवाचार को बढ़ावा मिलता है।
- वैश्विक मानकों के साथ संरेखित: यूरोपीय संघ के डिजिटल बाजार अधिनियम के समान दृष्टिकोण का अनुसरण करता है, जो अंतर्राष्ट्रीय नियामक ढांचे के साथ संरेखित करने का प्रयास दर्शाता है।
- डिजिटल अर्थव्यवस्था को बढ़ावा देता है: प्रभावी रूप से विनियमित करके, यह भारत के डिजिटल बाजार के विकास का समर्थन करता है, जिसके 2030 तक $800 बिलियन तक पहुँचने की उम्मीद है।
बिल का उद्देश्य बड़ी तकनीकी कंपनियों को कैसे विनियमित करना है?
- डिजिटल प्रतिस्पर्धा विधेयक का उद्देश्य बड़ी तकनीकी कंपनियों को निष्पक्ष, पारदर्शी तरीके से काम करने और स्पष्ट शिकायत-निपटान तंत्र स्थापित करने की आवश्यकता के द्वारा विनियमित करना है।
- यह विशेष रूप से इन कंपनियों को अपने स्वयं के उत्पादों या संबंधित पक्षों के उत्पादों को अनुचित रूप से लाभ पहुँचाने से रोकता है।
- इसके अतिरिक्त, विधेयक व्यावसायिक उपयोगकर्ताओं के गैर-सार्वजनिक डेटा के दुरुपयोग को प्रतिबंधित करता है और तृतीय-पक्ष ऐप्स के प्रतिबंध को रोकता है।
- यह “स्टीयरिंग” या “स्व-संदर्भ” और शिकारी मूल्य निर्धारण जैसी प्रथाओं पर भी प्रतिबंध लगाता है।
- ये विनियमन मौजूदा प्रतिस्पर्धा अधिनियम और डिजिटल व्यक्तिगत डेटा संरक्षण अधिनियम के अनुपालन के साथ-साथ लागू होते हैं।
डिजिटल प्रतिस्पर्धा विधेयक 2024 की आलोचना
- अनुपालन का महत्वपूर्ण बोझ
- सख्त निर्देशात्मक मानदंडों के साथ एक पूर्व-पूर्व रूपरेखा बड़ी तकनीकी कंपनियों के लिए अनुपालन का महत्वपूर्ण बोझ पैदा कर सकती है।
- इससे नवाचार और अनुसंधान से ध्यान हटाकर यह सुनिश्चित करने पर ध्यान केंद्रित हो सकता है कि कंपनियाँ संभावित रूप से प्रतिस्पर्धा-विरोधी व्यवहार में शामिल न हों।
- EU के DMA की सख्त आवश्यकताएँ और संबंधित प्रभाव
- विशेषज्ञों ने इस बात पर प्रकाश डाला है कि Google खोज के माध्यम से चीज़ों को खोजने में लगने वाले समय में उल्लेखनीय वृद्धि हुई है।
- महत्वपूर्ण प्लेटफॉर्म की व्यापक परिभाषा
- कंपनियाँ इस बात को लेकर चिंतित हैं कि महत्वपूर्ण प्लेटफॉर्म की व्यापक परिभाषा – मात्रात्मक और गुणात्मक दोनों – कौन हो सकता है।
- यूरोपीय संघ के डीएमए के विपरीत, जिसमें विशेष रूप से ‘गेटकीपर’ संस्थाओं का नाम दिया गया है, भारत के मसौदा कानून में यह निर्णय सीसीआई के विवेक पर छोड़ दिया गया है।
- कंपनियों का मानना है कि इससे मनमाने ढंग से निर्णय लेने की प्रवृत्ति बढ़ सकती है, जिसका संभावित रूप से स्टार्ट-अप पर भी असर पड़ सकता है।
- छोटे व्यवसायों को प्रभावित कर सकता है
- कंपनियाँ दावा कर रही हैं कि बिल उन्हें अपने प्लेटफॉर्म में बदलाव करने और डेटा शेयरिंग में कटौती करने के लिए मजबूर करेगा।
- यह छोटे व्यवसायों को भी प्रभावित कर सकता है जो बड़े लक्षित दर्शकों तक पहुँचने के लिए अपने प्लेटफॉर्म पर निर्भर हैं।
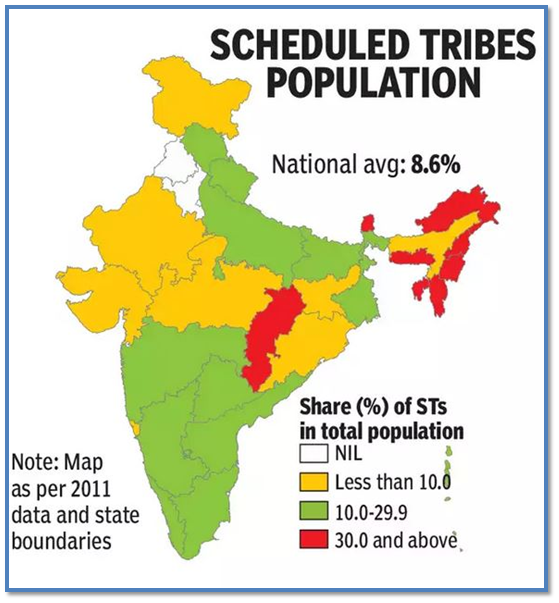
Integrated Tribal Development Programme by NABARD / नाबार्ड द्वारा एकीकृत जनजातीय विकास कार्यक्रम
Programme In News
Source : The Hindu
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) is set to launch an integrated tribal development programme in Kulathupuzha grama panchayat, Kollam.

About ITDP
- Thanal, an environment organisation, will be the implementing agency of the project that aims to transform livelihoods of tribal families over the next five years.
- The five-year initiative targets the sustainable livelihood and agricultural enhancement of 413 families residing in eight hamlets.
- The programme focuses on promoting diverse agricultural crops such as pepper, arecanut, coconut, ginger, Thai ginger, turmeric, and plantain.
- It encompasses initiatives in goat rearing, poultry, beekeeping, fish farming, and fodder production.
- The establishment of a Tribal Farmer Producer Company (FPO) is also planned to further economically empower the community.
Components of the Programme
- Water Resource Development: Initiatives aimed at enhancing water resources for agricultural purposes.
- Leadership Training: Training sessions to empower local leaders within the tribal communities.
- Awareness Creation: Campaigns to raise awareness about sustainable practices and community development.
- Sanitation and Hygiene Initiatives: Efforts to improve sanitation and hygiene standards among the tribal families.
- Marketing and Branding Training: Training programmes to enhance marketing skills and brand awareness among participants.
- Skill Development Workshops: Workshops focused on enhancing both agricultural and non-agricultural skills among the tribal community.
About NABARD:
- It was established on July 12, 1982, based on the recommendation of the Sivaraman Committee to promote sustainable rural development and agricultural growth in India.
- Aim : To facilitate credit flow for the promotion and development of agriculture, small-scale industries, cottage and village industries, handicrafts, and other rural crafts.
- It operates as a statutory body under the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Act, 1934, with its headquarters located in Mumbai.
- It is governed by a Board of Directors appointed by the GoI:
- Representatives from the RBI;
- Central and state governments;
- Experts from various fields related to Rural Development and Finance.
Functions of NABARD:
- Refinance Support: NABARD provides refinance facilities to banks and financial institutions for agricultural and rural development activities, including crop loans and rural infrastructure projects.
- Financial Inclusion: It promotes financial inclusion by expanding banking services in rural areas, supporting SHGs, FPOs, and MFIs, and facilitating access to credit for rural communities.
- Priority Sector Lending: NABARD plays a crucial role in channelling credit to priority sectors such as agriculture, small-scale industries, and rural infrastructure, in alignment with the Reserve Bank of India’s priority sector lending guidelines.
- Direct Lending: It extends direct loans to institutions for specific rural development projects, such as agricultural production, rural infrastructure development, and agri-processing units.
- Scheme Implementation: The organization administers government schemes and funds like Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF), Watershed Development Fund (WDF) to finance rural infrastructure projects and watershed development activities.
- Credit Planning: NABARD collaborates with central and state governments, RBI, and other stakeholders to formulate credit policies and plans for agriculture and rural sectors.
- Research and Training: NABARD promotes research and development in agriculture, supports capacity building and training programs for rural stakeholders, and facilitates technology transfer initiatives.
नाबार्ड द्वारा एकीकृत जनजातीय विकास कार्यक्रम
राष्ट्रीय कृषि और ग्रामीण विकास बैंक (नाबार्ड) कोल्लम के कुलथुपुझा ग्राम पंचायत में एक एकीकृत जनजातीय विकास कार्यक्रम शुरू करने जा रहा है।
ITDP के बारे में
- थानल नामक एक पर्यावरण संगठन इस परियोजना की कार्यान्वयन एजेंसी होगी, जिसका उद्देश्य अगले पांच वर्षों में आदिवासी परिवारों की आजीविका को बदलना है।
- पांच वर्षीय पहल का लक्ष्य आठ बस्तियों में रहने वाले 413 परिवारों की स्थायी आजीविका और कृषि संवर्धन है।
- कार्यक्रम में मिर्च, सुपारी, नारियल, अदरक, थाई अदरक, हल्दी और केला जैसी विविध कृषि फसलों को बढ़ावा देने पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया गया है।
- इसमें बकरी पालन, मुर्गी पालन, मधुमक्खी पालन, मछली पालन और चारा उत्पादन की पहल शामिल हैं।
- समुदाय को आर्थिक रूप से सशक्त बनाने के लिए एक आदिवासी किसान उत्पादक कंपनी (एफपीओ) की स्थापना की भी योजना बनाई गई है।
कार्यक्रम के घटक
- जल संसाधन विकास: कृषि उद्देश्यों के लिए जल संसाधनों को बढ़ाने के उद्देश्य से पहल।
- नेतृत्व प्रशिक्षण: आदिवासी समुदायों के भीतर स्थानीय नेताओं को सशक्त बनाने के लिए प्रशिक्षण सत्र।
- जागरूकता सृजन: स्थायी प्रथाओं और सामुदायिक विकास के बारे में जागरूकता बढ़ाने के लिए अभियान।
- स्वच्छता और स्वच्छता पहल: आदिवासी परिवारों के बीच स्वच्छता और स्वच्छता मानकों को बेहतर बनाने के प्रयास।
- मार्केटिंग और ब्रांडिंग प्रशिक्षण: प्रतिभागियों के बीच मार्केटिंग कौशल और ब्रांड जागरूकता बढ़ाने के लिए प्रशिक्षण कार्यक्रम।
- कौशल विकास कार्यशालाएँ: आदिवासी समुदाय के बीच कृषि और गैर-कृषि कौशल को बढ़ाने पर केंद्रित कार्यशालाएँ।
नाबार्ड के बारे में:
- इसकी स्थापना 12 जुलाई, 1982 को भारत में सतत ग्रामीण विकास और कृषि वृद्धि को बढ़ावा देने के लिए शिवरामन समिति की सिफारिश के आधार पर की गई थी।
- उद्देश्य: कृषि, लघु उद्योग, कुटीर और ग्रामोद्योग, हस्तशिल्प और अन्य ग्रामीण शिल्प के संवर्धन और विकास के लिए ऋण प्रवाह को सुविधाजनक बनाना।
- यह भारतीय रिजर्व बैंक (RBI) अधिनियम, 1934 के तहत एक वैधानिक निकाय के रूप में कार्य करता है, जिसका मुख्यालय मुंबई में स्थित है।
- यह भारत सरकार द्वारा नियुक्त निदेशक मंडल द्वारा शासित होता है:
- RBI के प्रतिनिधि;
- केंद्र और राज्य सरकारें;
- ग्रामीण विकास और वित्त से संबंधित विभिन्न क्षेत्रों के विशेषज्ञ।
नाबार्ड के कार्य:
- पुनर्वित्त सहायता: नाबार्ड बैंकों और वित्तीय संस्थानों को कृषि और ग्रामीण विकास गतिविधियों, जिसमें फसल ऋण और ग्रामीण अवसंरचना परियोजनाएं शामिल हैं, के लिए पुनर्वित्त सुविधाएं प्रदान करता है।
- वित्तीय समावेशन: यह ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में बैंकिंग सेवाओं का विस्तार करके, एसएचजी, एफपीओ और एमएफआई का समर्थन करके और ग्रामीण समुदायों के लिए ऋण तक पहुंच को सुविधाजनक बनाकर वित्तीय समावेशन को बढ़ावा देता है।
- प्राथमिकता क्षेत्र ऋण: नाबार्ड भारतीय रिजर्व बैंक के प्राथमिकता क्षेत्र ऋण दिशानिर्देशों के अनुरूप कृषि, लघु उद्योग और ग्रामीण अवसंरचना जैसे प्राथमिकता वाले क्षेत्रों को ऋण देने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
- प्रत्यक्ष ऋण: यह कृषि उत्पादन, ग्रामीण अवसंरचना विकास और कृषि प्रसंस्करण इकाइयों जैसी विशिष्ट ग्रामीण विकास परियोजनाओं के लिए संस्थानों को प्रत्यक्ष ऋण प्रदान करता है।
- योजना कार्यान्वयन: संगठन ग्रामीण अवसंरचना परियोजनाओं और वाटरशेड विकास गतिविधियों को वित्तपोषित करने के लिए ग्रामीण अवसंरचना विकास निधि (आरआईडीएफ), वाटरशेड विकास निधि (डब्ल्यूडीएफ) जैसी सरकारी योजनाओं और निधियों का प्रबंधन करता है।
- ऋण योजना: नाबार्ड कृषि और ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों के लिए ऋण नीतियों और योजनाओं को तैयार करने के लिए केंद्र और राज्य सरकारों, आरबीआई और अन्य हितधारकों के साथ सहयोग करता है।
- अनुसंधान एवं प्रशिक्षण: नाबार्ड कृषि में अनुसंधान एवं विकास को बढ़ावा देता है, ग्रामीण हितधारकों के लिए क्षमता निर्माण एवं प्रशिक्षण कार्यक्रमों का समर्थन करता है, तथा प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण पहलों को सुगम बनाता है।
A Budget that drives growth with stability / एक ऐसा बजट जो स्थिरता के साथ विकास को बढ़ावा देता है
(General Studies- Paper III)
Source : The Hindu
Context
The 2024-25 Budget aims to sustain India’s GDP growth at 7%-7.5%, focusing on domestic drivers amidst global economic slowdown.It prioritises reducing the fiscal deficit to 3% of GDP, enhancing investment to 35%, and addressing challenges in exports and employment through strategic fiscal management and infrastructure development.
Introduction
- The new government will present the final budget for 2024-25 on July 23. It provides government with the opportunity to spell out its policy priorities regarding growth and employment.
- With continued global economic shutdown, India will have to rely on domestic growth drivers.
- Short term objective could be to ensure a minimum 7% growth and medium-term objective could be to sustain real GDP growth rate in between 7-7.5%.
- Bringing down the fiscal deficit relative to GDP from the current levels to FRBM consistent level of 3% in next 3-4 years.
- On employment front additional emphasis is to be given on relatively more labour-intensive sectors.
Investment and Savings prospects
- To ensure 7% plus growth on a sustained basis, a real investment rate of 35% is required.
- The real investment rate measured as gross fixed capital formation (GFCF) as percentage of GDP was 33.3 for FY23 and 33.5 for FY24.
- In FY23 the saving to GDP ratio in nominal and real terms were 30.2% and 32.8% respectively.
- If these trends continue then, marginal upward adjustments are required in savings and investment rates to reach the level of 35% of GDP for GFCF.
- The recent fall in household sector financial savings is a cause of concern. It is critical to increase the household financial savings rate to facilitate access to investible surplus at reasonable rates for the private sector because the sector provides investible surplus and inflow of foreign capital.
- Due to subdued export prospects the contribution of net exports to GDP growth has remained low – 0.5% points in FY23 and (-)2.0% points in FY24.
- Until export demand picks up and private investment gathers momentum, India will have to rely on government investment demand to provide support to growth.
Budgetary Options
- Government’s revenue position is expected to improve on account of both higher tax and non-tax revenues.
- A nominal GDP growth for 2024-25 is expected to be 11%, made up of 7% real growth and 3.8% implicit price deflator (IPD) based inflation.
- The rise in IPD based inflation is on account of expected higher Wholesale Price Index (WPI) inflation.
- Tax Revenues: With buoyancy of 1.1 and gross tax revenues (GTR) growth of 12.1%, the GTR is expected to be Rs. 38.8 lakh crore. It will lead to a net tax revenue for the centre at Rs. 26.4 lakh crore after giving the States’ share in central taxes.
- Non-tax Revenues: RBI’s augmented dividends of Rs.2.11 lakh crore will ensure high non-tax revenues. Such a transfer from RBI to government will be expansionary because of liquidity effect and will have implications on monetary policy. But the improved revenue situation of the central government would facilitate meeting the fiscal consolidation target.
- The increased growth will enable the government to accommodate higher revenue expenditures on account of increased subsidies, health expenditures and allocations for MGNREGA to support and provide relief to rural population.
Conclusion
- The 2024-25 Budget signifies a blend of growth imperatives and fiscal prudence, pivotal in navigating global economic challenges while advancing domestic developmental goals.
- The government’s commitment to stability, encompassing price and fiscal stability, underscores its strategic approach in leveraging fiscal policy for sustainable economic expansion.
एक ऐसा बजट जो स्थिरता के साथ विकास को बढ़ावा देता है
संदर्भ
2024-25 के बजट का लक्ष्य वैश्विक आर्थिक मंदी के बीच घरेलू चालकों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हुए भारत की जीडीपी वृद्धि को 7%-7.5% पर बनाए रखना है। इसमें राजकोषीय घाटे को जीडीपी के 3% तक कम करने, निवेश को 35% तक बढ़ाने और रणनीतिक राजकोषीय प्रबंधन और बुनियादी ढांचे के विकास के माध्यम से निर्यात और रोजगार में चुनौतियों का समाधान करने को प्राथमिकता दी गई है।
परिचय
- नई सरकार 23 जुलाई को 2024-25 के लिए अंतिम बजट पेश करेगी। यह सरकार को विकास और रोजगार के संबंध में अपनी नीतिगत प्राथमिकताओं को स्पष्ट करने का अवसर प्रदान करता है।
- निरंतर वैश्विक आर्थिक बंद के साथ, भारत को घरेलू विकास चालकों पर निर्भर रहना होगा।
- अल्पकालिक उद्देश्य न्यूनतम 7% विकास सुनिश्चित करना हो सकता है और मध्यम अवधि का उद्देश्य वास्तविक जीडीपी विकास दर को 7-7.5% के बीच बनाए रखना हो सकता है।
- जीडीपी के सापेक्ष राजकोषीय घाटे को मौजूदा स्तरों से अगले 3-4 वर्षों में एफआरबीएम के सुसंगत स्तर 3% तक लाना।
- रोजगार के मोर्चे पर अपेक्षाकृत अधिक श्रम-गहन क्षेत्रों पर अतिरिक्त जोर दिया जाना है।
निवेश और बचत की संभावनाएँ
- निरंतर आधार पर 7% से अधिक की वृद्धि सुनिश्चित करने के लिए, 35% की वास्तविक निवेश दर की आवश्यकता है।
- जीडीपी के प्रतिशत के रूप में सकल स्थिर पूंजी निर्माण (GFCF) के रूप में मापी गई वास्तविक निवेश दर FY23 के लिए 3 और FY24 के लिए 33.5 थी।
- FY23 में नाममात्र और वास्तविक शर्तों में बचत से जीडीपी अनुपात क्रमशः 2% और 32.8% था।
- यदि ये रुझान जारी रहते हैं, तो GFCF के लिए जीडीपी के 35% के स्तर तक पहुँचने के लिए बचत और निवेश दरों में मामूली वृद्धि की आवश्यकता है।
- घरेलू क्षेत्र की वित्तीय बचत में हाल ही में आई गिरावट चिंता का विषय है। निजी क्षेत्र के लिए उचित दरों पर निवेश योग्य अधिशेष तक पहुँच की सुविधा के लिए घरेलू वित्तीय बचत दर को बढ़ाना महत्वपूर्ण है क्योंकि यह क्षेत्र निवेश योग्य अधिशेष और विदेशी पूंजी का प्रवाह प्रदान करता है।
- निर्यात की कमजोर संभावनाओं के कारण सकल घरेलू उत्पाद की वृद्धि में शुद्ध निर्यात का योगदान कम रहा है – FY23 में 5% अंक और FY24 में (-)2.0% अंक।
- जब तक निर्यात मांग में तेजी नहीं आती और निजी निवेश में तेजी नहीं आती, तब तक भारत को विकास को समर्थन देने के लिए सरकारी निवेश मांग पर निर्भर रहना होगा।
बजटीय विकल्प
- कर और गैर-कर राजस्व दोनों में वृद्धि के कारण सरकार की राजस्व स्थिति में सुधार होने की उम्मीद है।
- वर्ष 2024-25 के लिए नाममात्र जीडीपी वृद्धि 11% रहने की उम्मीद है, जो 7% वास्तविक वृद्धि और 8% निहित मूल्य अपस्फीति (आईपीडी) आधारित मुद्रास्फीति से बनी है।
- आईपीडी आधारित मुद्रास्फीति में वृद्धि अपेक्षित उच्च थोक मूल्य सूचकांक (डब्ल्यूपीआई) मुद्रास्फीति के कारण है।
- कर राजस्व: 1 की उछाल और 12.1% की सकल कर राजस्व (जीटीआर) वृद्धि के साथ, जीटीआर 38.8 लाख करोड़ रुपये होने की उम्मीद है। इससे केंद्रीय करों में राज्यों का हिस्सा देने के बाद केंद्र के लिए शुद्ध कर राजस्व 26.4 लाख करोड़ रुपये हो जाएगा।
- गैर-कर राजस्व: आरबीआई के 11 लाख करोड़ रुपये के संवर्धित लाभांश से उच्च गैर-कर राजस्व सुनिश्चित होगा। आरबीआई से सरकार को इस तरह का हस्तांतरण तरलता प्रभाव के कारण विस्तारवादी होगा और मौद्रिक नीति पर इसका प्रभाव पड़ेगा। लेकिन केंद्र सरकार की बेहतर राजस्व स्थिति राजकोषीय समेकन लक्ष्य को पूरा करने में मदद करेगी।
- बढ़ी हुई वृद्धि सरकार को ग्रामीण आबादी को सहायता और राहत प्रदान करने के लिए बढ़ी हुई सब्सिडी, स्वास्थ्य व्यय और मनरेगा के लिए आवंटन के कारण उच्च राजस्व व्यय को समायोजित करने में सक्षम बनाएगी।
निष्कर्ष
- 2024-25 का बजट विकास अनिवार्यताओं और राजकोषीय विवेक के मिश्रण को दर्शाता है, जो घरेलू विकास लक्ष्यों को आगे बढ़ाते हुए वैश्विक आर्थिक चुनौतियों से निपटने में महत्वपूर्ण है।
- मूल्य और राजकोषीय स्थिरता को शामिल करते हुए स्थिरता के लिए सरकार की प्रतिबद्धता, सतत आर्थिक विस्तार के लिए राजकोषीय नीति का लाभ उठाने में इसके रणनीतिक दृष्टिकोण को रेखांकित करती है।
Lakes in India [Mapping] / भारत में झीलें [मानचित्र]

- A lake is a body of surface water bordered on all sides by land.
- Lakes will take water from rivers or function as a source of water since rivers will act as an outlet or inlet to them.
- Lakes may be found in a variety of settings, including hilly areas, plains, plateaus, rift zones, and so on.
- Some lakes are generated by the action of glaciers and ice sheets, while others are formed by wind, river movement, and human activity.
- Lakes are used for a variety of purposes, including drinking water, irrigation, navigation, water storage, livelihood (fishing, for example), and influence on microclimate.
- There are several sorts of lakes that may be classed depending on a variety of factors — these include:
- Freshwater Lakes,
- Salt Water lakes,
- Natural Lakes,
- Artificial Lakes,
- Oxbow lake,
- Crater Lake
Salt Water Lakes
- Due to the endorheic structure of the lake, the water pouring into the lake, which includes salt or minerals, is impossible to depart.
- The water then evaporates, leaving any dissolved salts behind and raising the lake’s salinity, making it a perfect location for salt production.
- High salinity can also result in halophilic flora and fauna in and around the lake; in fact, the salt lake’s lack of multicellular life is sometimes the result.
Important Salt Water lakes in India
| Salt water Lake | Location | Significance |
| Sambhar Lake | Rajasthan |
|
| Lonar Lake | Maharashtra |
|
| Chilka Lake | Odisha |
|
| Pulicat Lake | Andhra Pradesh-Tamil Nadu state border |
|
| Pangong Tso Lake | Ladakh |
|
Natural Lakes in India
- Natural lakes can be found in mountainous locations, rift zones, and areas where glaciers still exist.
- The creation of natural lakes is aided by a number of factors.
- The tectonic movement of a mountain range can create bowl-shaped depressions that collect water and produce lakes.
- Landslides and glacial blocks cause lakes to form. Lagoons are formed by spits and bars along the shore.
Important Natural Lakes
| Natural Lakes | Location | Significance |
| Dal Lake | Srinagar , Kashmir |
|
| Sasthamkotta Lake | Kerala |
|
| Vembanad Lake | Kerala |
|
| Nalsarovar Lake | Gujarat |
|
Oxbow Lakes
- Oxbow Lake is a small lake located in the abandoned meander loop of a river channel.
- A lake is generated by river bends that are U-shaped or curved and are cut off from the main river flow.
- Every river has its own set of twists and bends, also known as meanders, that cut through the landscape in a unique way.
- Due to continual erosion and deposition along the meanders’ borders, the termination of the meander loop becomes closer and closer.
- The river meander loops finally cut themselves off, forming an oxbow lake.
Oxbow Lakes in India
| Oxbow Lakes | Location | Significance |
| Kabar Taal Lake | Bihar |
|
| Vynthala Lake | Kerala |
|
भारत में झीलें [मानचित्र]
- झील सतही जल का एक निकाय है जिसके चारों ओर भूमि होती है।
- झीलें नदियों से पानी लेती हैं या पानी के स्रोत के रूप में कार्य करती हैं क्योंकि नदियाँ उनके लिए आउटलेट या इनलेट का काम करती हैं।
- झीलें विभिन्न प्रकार की सेटिंग्स में पाई जा सकती हैं, जिसमें पहाड़ी क्षेत्र, मैदान, पठार, दरार क्षेत्र आदि शामिल हैं।
- कुछ झीलें ग्लेशियरों और बर्फ की चादरों की क्रिया द्वारा उत्पन्न होती हैं, जबकि अन्य हवा, नदी की गति और मानवीय गतिविधियों से बनती हैं।
- झीलों का उपयोग विभिन्न उद्देश्यों के लिए किया जाता है, जिसमें पीने का पानी, सिंचाई, नेविगेशन, जल भंडारण, आजीविका (उदाहरण के लिए मछली पकड़ना) और माइक्रोक्लाइमेट पर प्रभाव शामिल हैं।
- कई प्रकार की झीलें हैं जिन्हें विभिन्न कारकों के आधार पर वर्गीकृत किया जा सकता है – इनमें शामिल हैं:
- मीठे पानी की झीलें,
- खारे पानी की झीलें,
- प्राकृतिक झीलें,
- कृत्रिम झीलें,
- ऑक्सबो झील,
- एक क्रेटर झील
खारे पानी की झीलें
- झील की एंडोरेइक संरचना के कारण, झील में डाला जाने वाला पानी, जिसमें नमक या खनिज शामिल हैं, बाहर नहीं निकल पाता।
- फिर पानी वाष्पित हो जाता है, जिससे कोई भी घुला हुआ नमक पीछे रह जाता है और झील की लवणता बढ़ जाती है, जिससे यह नमक उत्पादन के लिए एक आदर्श स्थान बन जाता है।
- उच्च लवणता के कारण झील में और उसके आस-पास हेलोफिलिक वनस्पति और जीव भी पैदा हो सकते हैं; वास्तव में, कभी-कभी खारे झील में बहुकोशिकीय जीवन की कमी इसका परिणाम होती है।
भारत में खारे पानी की महत्वपूर्ण झीलें
| खारे पानी की झील | स्थान | महत्व |
| सांभर झील | राजस्थान |
|
| लोनार झील | महाराष्ट्र |
|
| चिल्का झील | ओडिशा |
|
| पुलिकट झील | आंध्र प्रदेश-तमिलनाडु राज्य सीमा |
|
| पैंगोंग त्सो झील | लद्दाख |
|
भारत में प्राकृतिक झीलें
- प्राकृतिक झीलें पहाड़ी स्थानों, दरार क्षेत्रों और उन क्षेत्रों में पाई जा सकती हैं जहाँ ग्लेशियर अभी भी मौजूद हैं।
- प्राकृतिक झीलों के निर्माण में कई कारकों की सहायता मिलती है।
- पर्वत श्रृंखला की टेक्टोनिक हलचल कटोरे के आकार के अवसाद बना सकती है जो पानी इकट्ठा करते हैं और झीलों का निर्माण करते हैं।
- भूस्खलन और हिमनद ब्लॉक झीलों का निर्माण करते हैं। लैगून तट के किनारे थूक और सलाखों से बनते हैं।
महत्वपूर्ण प्राकृतिक झीलें
| प्राकृतिक झीलें | स्थान | महत्व |
| डल झील | श्रीनगर, कश्मीर |
|
| सस्थमकोट्टा झील | केरल |
|
| वेम्बनाड झील | केरल |
|
| नालसरोवर झील | गुजरात |
|
ऑक्सबो झीलें
- ऑक्सबो झील एक छोटी झील है जो नदी चैनल के परित्यक्त मेन्डर लूप में स्थित है।
- झील नदी के उन मोड़ों से बनती है जो यू-आकार के या घुमावदार होते हैं और मुख्य नदी प्रवाह से कटे होते हैं।
- हर नदी के अपने मोड़ और मोड़ होते हैं, जिन्हें मेन्डर भी कहा जाता है, जो एक अनोखे तरीके से परिदृश्य को काटते हैं।
- मेन्डर की सीमाओं के साथ निरंतर कटाव और जमाव के कारण, मेन्डर लूप का अंत और करीब होता जाता है।
- नदी के मेन्डर लूप अंततः खुद को अलग कर लेते हैं, जिससे एक ऑक्सबो झील बन जाती है।
भारत में ऑक्सबो झीलें
| ऑक्सबो झीलें | स्थान | महत्व |
| कबर ताल झील | बिहार |
|
| विंथला झील | केरल |
|