
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 06/12/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 06/12/2024
- Winged visitors /पंख वाले आगंतुक
- At ICJ, India blames developed nations for the climate crisis /आईसीजे में भारत ने जलवायु संकट के लिए विकसित देशों को दोषी ठहराया
- PSLV-C59 places PROBA-3 satellites into designated orbit with precision/PSLV-C59 ने प्रोबा-3 उपग्रहों को सटीकता के साथ निर्धारित कक्षा में स्थापित किया
- Is Syria’s Assad regime in danger? /क्या सीरिया की असद सरकार खतरे में है?
- North-East Region Development /उत्तर-पूर्व क्षेत्र विकास
- States and the challenge before the Finance Commission /वित्त आयोग के समक्ष राज्य और चुनौतियां
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 06/12/2024
Winged visitors /पंख वाले आगंतुक
Syllabus : Prelims Facts
Source : The Hindu
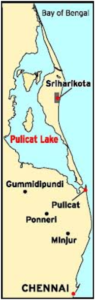
Pulicat Lake near Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, has become a vibrant hub for flamingos and other migratory birds with the onset of the northeast monsoon.
- The brimming lake highlights its ecological significance as a key wintering site for avian species.

About Greater Flamingo:
- Physical Characteristics: Tall wading birds with pinkish plumage, long necks, and legs. The color comes from their diet of algae and crustaceans.
- Conservation Status: Least Concern (IUCN), but face threats like habitat loss and pollution.
- Species Diversity: Six recognized species, with the Greater Flamingo and Lesser Flamingo most commonly found in India.
- Diet: Feed on algae, diatoms, and small aquatic organisms, using their specialized beaks to filter food.
- Habitat: Prefer shallow water bodies like lagoons, estuaries, and salt pans.
- Behavior: Highly social, they form large flocks to feed and breed.
- Breeding: Build mud mound nests and lay a single egg.
- Significance: Indicators of wetland health, they attract ecotourism and contribute to biodiversity.
- Migration to India: Flamingos migrate to India during winter, seeking favorable feeding and breeding conditions in wetlands like Pulicat Lake and Rann of Kutch.
पंख वाले आगंतुक
आंध्र प्रदेश के श्रीहरिकोटा के पास पुलिकट झील, पूर्वोत्तर मानसून की शुरुआत के साथ ही फ्लेमिंगो और अन्य प्रवासी पक्षियों के लिए एक जीवंत केंद्र बन गई है।
- लबालब भरी यह झील पक्षी प्रजातियों के लिए एक प्रमुख शीतकालीन स्थल के रूप में अपने पारिस्थितिक महत्व को उजागर करती है।
ग्रेटर फ्लेमिंगो के बारे में:
- शारीरिक विशेषताएँ: गुलाबी रंग के पंख, लंबी गर्दन और पैरों वाले लंबे जलचर पक्षी। यह रंग शैवाल और क्रस्टेशियन के आहार से आता है।
- संरक्षण स्थिति: कम से कम चिंता (IUCN), लेकिन आवास के नुकसान और प्रदूषण जैसे खतरों का सामना करते हैं।
- प्रजाति विविधता: छह मान्यता प्राप्त प्रजातियाँ, जिनमें ग्रेटर फ्लेमिंगो और लेसर फ्लेमिंगो सबसे अधिक भारत में पाए जाते हैं।
- आहार: शैवाल, डायटम और छोटे जलीय जीवों को खाते हैं, भोजन को छानने के लिए अपनी विशेष चोंच का उपयोग करते हैं।
- निवास स्थान: लैगून, मुहाना और नमक के तालाब जैसे उथले जल निकायों को प्राथमिकता देते हैं।
- व्यवहार: अत्यधिक सामाजिक, वे भोजन और प्रजनन के लिए बड़े झुंड बनाते हैं।
- प्रजनन: मिट्टी के टीले के घोंसले बनाते हैं और एक अंडा देते हैं।
- महत्व: आर्द्रभूमि के स्वास्थ्य के संकेतक, वे इकोटूरिज्म को आकर्षित करते हैं और जैव विविधता में योगदान करते हैं।
- भारत की ओर प्रवास: राजहंस सर्दियों के दौरान भारत की ओर प्रवास करते हैं, तथा पुलिकट झील और कच्छ के रण जैसे आर्द्रभूमि में अनुकूल भोजन और प्रजनन की स्थिति की तलाश करते हैं।
At ICJ, India blames developed nations for the climate crisis /आईसीजे में भारत ने जलवायु संकट के लिए विकसित देशों को दोषी ठहराया
Syllabus : GS 2 & 3 : International Relations & Environment
Source : The Hindu
The news discusses India’s position during a landmark hearing at the International Court of Justice, where it criticized developed nations for causing the climate crisis and failing to meet climate finance commitments.
- India highlighted the unequal responsibility for climate degradation and its own climate goals.
- The country also raised concerns about the burden on its citizens in addressing climate change.
India’s Stance at the ICJ on Climate Crisis
Developed Countries’ Role in the Crisis
- India criticized developed countries for their historical contribution to the climate crisis.
- India stated that these countries exploited the global carbon budget and failed to fulfill their climate finance promises.
- Despite their minimal contribution to global emissions, developing countries are bearing the brunt of climate change impacts.
Unequal Responsibility for Climate Degradation
- India emphasized that responsibility for climate change should be distributed equally, considering the unequal contribution to global degradation.
- India stressed that those who have benefited the most from fossil fuel usage are now discouraging developing nations from utilizing their own energy resources for growth.
Climate Finance Commitments Unfulfilled
- India highlighted the failure of developed countries to honor climate finance commitments, particularly the $100 billion pledge made at the Copenhagen COP in 2009.
- The new climate finance package from COP29 was criticized as insufficient and distant, failing to address the immediate needs of the Global South.
Commitment to Climate Targets with Caution
- India reaffirmed its commitment to the Paris Agreement but expressed concerns about overburdening its citizens.
- The country emphasized the need to balance climate action with the socio-economic realities of sustaining one-sixth of the global population while pursuing Sustainable Development Goals.
International Court of Justice
- Principal judicial organ of the United Nations: Settles legal disputes between states and gives advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by authorized UN organs and specialized agencies.
- Located in The Hague, Netherlands: Known as the “World Court,” it is the successor to the Permanent Court of International Justice.
- 15 Judges: Elected to nine-year terms by the UN General Assembly and Security Council.
- Two types of cases: Contentious cases between states and advisory proceedings on legal questions.
- Judgments are binding: However, the ICJ has no way to enforce its decisions.
- Official languages: English and French. These languages are used for the court’s proceedings, documents, and communications.
आईसीजे में भारत ने जलवायु संकट के लिए विकसित देशों को दोषी ठहराया
समाचार में अंतर्राष्ट्रीय न्यायालय में एक ऐतिहासिक सुनवाई के दौरान भारत की स्थिति पर चर्चा की गई है, जहाँ उसने जलवायु संकट पैदा करने और जलवायु वित्त प्रतिबद्धताओं को पूरा करने में विफल रहने के लिए विकसित देशों की आलोचना की।
- भारत ने जलवायु क्षरण और अपने स्वयं के जलवायु लक्ष्यों के लिए असमान जिम्मेदारी पर प्रकाश डाला।
- देश ने जलवायु परिवर्तन से निपटने में अपने नागरिकों पर पड़ने वाले बोझ के बारे में भी चिंता जताई।
जलवायु संकट पर ICJ में भारत का रुख
संकट में विकसित देशों की भूमिका
- भारत ने जलवायु संकट में उनके ऐतिहासिक योगदान के लिए विकसित देशों की आलोचना की।
- भारत ने कहा कि इन देशों ने वैश्विक कार्बन बजट का दोहन किया और अपने जलवायु वित्त वादों को पूरा करने में विफल रहे।
- वैश्विक उत्सर्जन में उनके न्यूनतम योगदान के बावजूद, विकासशील देश जलवायु परिवर्तन के प्रभावों का खामियाजा भुगत रहे हैं।
जलवायु क्षरण के लिए असमान जिम्मेदारी
- भारत ने इस बात पर जोर दिया कि वैश्विक क्षरण में असमान योगदान को देखते हुए जलवायु परिवर्तन के लिए जिम्मेदारी समान रूप से वितरित की जानी चाहिए।
- भारत ने इस बात पर जोर दिया कि जीवाश्म ईंधन के उपयोग से सबसे अधिक लाभ उठाने वाले लोग अब विकासशील देशों को विकास के लिए अपने स्वयं के ऊर्जा संसाधनों का उपयोग करने से हतोत्साहित कर रहे हैं।
जलवायु वित्त प्रतिबद्धताएँ पूरी नहीं हुईं
- भारत ने जलवायु वित्त प्रतिबद्धताओं, विशेष रूप से 2009 में कोपेनहेगन COP में किए गए 100 बिलियन डॉलर के वादे को पूरा करने में विकसित देशों की विफलता को उजागर किया।
- COP29 के नए जलवायु वित्त पैकेज की आलोचना अपर्याप्त और दूरगामी होने के कारण की गई, जो वैश्विक दक्षिण की तत्काल आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने में विफल रहा।
जलवायु लक्ष्यों के प्रति सावधानी से प्रतिबद्धता
- भारत ने पेरिस समझौते के प्रति अपनी प्रतिबद्धता की पुष्टि की, लेकिन अपने नागरिकों पर अत्यधिक बोझ डालने के बारे में चिंता व्यक्त की।
- देश ने सतत विकास लक्ष्यों का अनुसरण करते हुए वैश्विक आबादी के छठे हिस्से को बनाए रखने की सामाजिक-आर्थिक वास्तविकताओं के साथ जलवायु कार्रवाई को संतुलित करने की आवश्यकता पर जोर दिया।
अंतर्राष्ट्रीय न्यायालय
- संयुक्त राष्ट्र का प्रमुख न्यायिक अंग: राज्यों के बीच कानूनी विवादों का निपटारा करता है और अधिकृत संयुक्त राष्ट्र अंगों और विशेष एजेंसियों द्वारा संदर्भित कानूनी प्रश्नों पर सलाहकार राय देता है।
- नीदरलैंड के हेग में स्थित: “विश्व न्यायालय” के रूप में जाना जाता है, यह अंतर्राष्ट्रीय न्याय के स्थायी न्यायालय का उत्तराधिकारी है।
- 15 न्यायाधीश: संयुक्त राष्ट्र महासभा और सुरक्षा परिषद द्वारा नौ साल के कार्यकाल के लिए चुने गए।
- दो प्रकार के मामले: राज्यों के बीच विवादास्पद मामले और कानूनी प्रश्नों पर सलाहकार कार्यवाही।
- निर्णय बाध्यकारी हैं: हालाँकि, ICJ के पास अपने निर्णयों को लागू करने का कोई तरीका नहीं है।
- आधिकारिक भाषाएँ: अंग्रेजी और फ्रेंच। इन भाषाओं का उपयोग न्यायालय की कार्यवाही, दस्तावेजों और संचार के लिए किया जाता है।
PSLV-C59 places PROBA-3 satellites into designated orbit with precision/PSLV-C59 ने प्रोबा-3 उपग्रहों को सटीकता के साथ निर्धारित कक्षा में स्थापित किया
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
The PROBA-3 mission, launched aboard ISRO’s PSLV-C59, showcases ESA’s breakthrough in precise formation flying using twin spacecraft.
- It aims to study the Sun’s corona through artificial eclipses, marking a milestone in advanced space mission capabilities.
PROBA-3: Key Information
- Purpose: Designed to create artificial solar eclipses, enabling prolonged studies of the Sun’s corona, the outermost layer of its atmosphere.
- Agency: The European Space Agency (ESA) oversees PROBA-3.
- Spacecraft Configuration: Comprises two spacecraft launched together that separate in orbit to function as a single unit through coordinated flying.
- Technological Advancement: Demonstrates formation flying with millimeter precision, a significant step for future multi-satellite missions.
- Launch Details: Successfully launched aboard ISRO’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle-C59 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- Orbit Operations: Initial commissioning will last several months, with operational observations expected to begin in about four months.
- Significance: Paves the way for advanced in-orbit demonstrations, enhancing capabilities for astronomical studies and future space missions.
PSLV-C59 ने प्रोबा-3 उपग्रहों को सटीकता के साथ निर्धारित कक्षा में स्थापित किया
इसरो के PSLV-C59 से प्रक्षेपित प्रोबा-3 मिशन, जुड़वां अंतरिक्ष यान का उपयोग करके सटीक संरचना उड़ान में ईएसए की सफलता को दर्शाता है।
- इसका उद्देश्य कृत्रिम ग्रहणों के माध्यम से सूर्य के कोरोना का अध्ययन करना है, जो उन्नत अंतरिक्ष मिशन क्षमताओं में एक मील का पत्थर है।
प्रोबा-3: मुख्य जानकारी
- उद्देश्य: कृत्रिम सौर ग्रहण बनाने के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया, जिससे सूर्य के वायुमंडल की सबसे बाहरी परत, कोरोना का लंबे समय तक अध्ययन किया जा सके।
- एजेंसी: यूरोपीय अंतरिक्ष एजेंसी (ESA) प्रोबा-3 की देखरेख करती है।
- अंतरिक्ष यान विन्यास: इसमें एक साथ प्रक्षेपित किए गए दो अंतरिक्ष यान शामिल हैं जो समन्वित उड़ान के माध्यम से एकल इकाई के रूप में कार्य करने के लिए कक्षा में अलग हो जाते हैं।
- तकनीकी उन्नति: मिलीमीटर परिशुद्धता के साथ गठन उड़ान का प्रदर्शन करता है, जो भविष्य के बहु-उपग्रह मिशनों के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण कदम है।
- प्रक्षेपण विवरण: श्रीहरिकोटा के सतीश धवन अंतरिक्ष केंद्र से इसरो के ध्रुवीय उपग्रह प्रक्षेपण यान-सी59 पर सफलतापूर्वक प्रक्षेपित किया गया।
- कक्षा संचालन: प्रारंभिक कमीशनिंग कई महीनों तक चलेगी, परिचालन अवलोकन लगभग चार महीनों में शुरू होने की उम्मीद है।
- महत्व: उन्नत इन-ऑर्बिट प्रदर्शनों का मार्ग प्रशस्त करता है, खगोलीय अध्ययनों और भविष्य के अंतरिक्ष मिशनों के लिए क्षमताओं को बढ़ाता है।
Is Syria’s Assad regime in danger? /क्या सीरिया की असद सरकार खतरे में है?
GS 2 – International Relations
Source : The Hindu
TheThe Syrian civil war, which began in 2011, has seen intermittent phases of conflict and relative calm.
- Recently, Islamist militants launched an offensive, capturing significant territories, including Aleppo and Hama, destabilizing the Assad regime’s control.
- Geopolitical shifts, including Russia’s preoccupation with Ukraine, have contributed to the regime’s vulnerabilities.
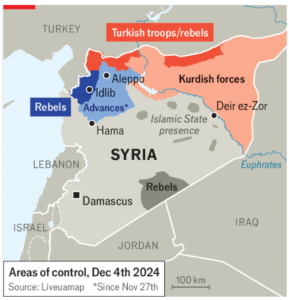
Renewed Conflict in Syria
- Islamist militants launched a surprise offensive in northwest Syria, capturing key territories, including Aleppo.
- This marks the resumption of active conflict after a relative calm since 2016.
Shift in Territorial Control
- Prior to Russia’s intervention in 2015, the Assad regime controlled only Damascus and coastal cities.
- Post-2016, the regime regained territories with Russian and Iranian support, pushing militants into Idlib.
- Last week’s offensive allowed militants to more than double their territorial holdings, including Aleppo and parts of Hama.
Key Actors in the Conflict
- The Regime: Backed by Russia, Iran, and Shia militias, it seeks to retain control.
- Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF): Kurdish militias backed by the U.S., controlling northeast Syria.
- Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS): A jihadist group leading the current offensive, along with the Syrian National Army (SNA).
HTS: A Leading Militant Group
- HTS evolved from al-Qaeda’s Syrian branch, led by a U.S.-designated terrorist.
- It controls Idlib and has declared its fight against the Assad regime, not the U.S.
Geopolitical Factors Driving the Offensive
- Russia’s focus on Ukraine and reduced presence in Syria weakened regime support.
- Iran and Hezbollah, key allies of Assad, are overstretched or weakened due to external conflicts and airstrikes.
- Turkey reportedly backed the militants, exploiting the regime’s vulnerabilities.
Implications for the Future
- Rebel advances signal a potential resurgence of civil war across Syria.
- Regime forces are regrouping with reinforcements from Iraqi militias, but prolonged bloodshed is likely.
क्या सीरिया की असद सरकार खतरे में है?
सीरियाई गृहयुद्ध, जो 2011 में शुरू हुआ था, में संघर्ष और सापेक्ष शांति के बीच-बीच में चरण देखे गए हैं।
- हाल ही में, इस्लामी आतंकवादियों ने एक आक्रामक अभियान शुरू किया, जिसमें अलेप्पो और हामा सहित महत्वपूर्ण क्षेत्रों पर कब्ज़ा कर लिया, जिससे असद शासन का नियंत्रण अस्थिर हो गया।
- यूक्रेन के साथ रूस की व्यस्तता सहित भू-राजनीतिक बदलावों ने शासन की कमज़ोरियों में योगदान दिया है।
सीरिया में फिर से संघर्ष
- इस्लामी आतंकवादियों ने उत्तर-पश्चिमी सीरिया में एक आश्चर्यजनक हमला किया, जिसमें अलेप्पो सहित प्रमुख क्षेत्रों पर कब्ज़ा कर लिया।
- यह 2016 के बाद से अपेक्षाकृत शांत रहने के बाद सक्रिय संघर्ष की बहाली को दर्शाता है।
क्षेत्रीय नियंत्रण में बदलाव
- 2015 में रूस के हस्तक्षेप से पहले, असद शासन केवल दमिश्क और तटीय शहरों को नियंत्रित करता था।
- 2016 के बाद, शासन ने रूसी और ईरानी समर्थन के साथ क्षेत्रों को पुनः प्राप्त किया, जिससे आतंकवादियों को इदलिब में धकेल दिया गया।
- पिछले सप्ताह के हमले ने आतंकवादियों को अलेप्पो और हमा के कुछ हिस्सों सहित अपने क्षेत्रीय कब्ज़े को दोगुना करने की अनुमति दी।
संघर्ष में मुख्य अभिनेता
- शासन: रूस, ईरान और शिया मिलिशिया द्वारा समर्थित, यह नियंत्रण बनाए रखना चाहता है।
- सीरियन डेमोक्रेटिक फोर्सेस (एसडीएफ): अमेरिका द्वारा समर्थित कुर्द मिलिशिया, पूर्वोत्तर सीरिया को नियंत्रित कर रहे हैं।
- हयात तहरीर अल-शाम (एचटीएस): सीरियाई राष्ट्रीय सेना (एसएनए) के साथ वर्तमान आक्रमण का नेतृत्व करने वाला एक जिहादी समूह।
HTS: एक प्रमुख उग्रवादी समूह
- HTS अल-कायदा की सीरियाई शाखा से विकसित हुआ, जिसका नेतृत्व अमेरिका द्वारा नामित आतंकवादी कर रहा है।
- यह इदलिब को नियंत्रित करता है और इसने अमेरिका के खिलाफ नहीं, बल्कि असद शासन के खिलाफ अपनी लड़ाई की घोषणा की है।
आक्रमण को प्रेरित करने वाले भू-राजनीतिक कारक
- रूस का यूक्रेन पर ध्यान और सीरिया में कम उपस्थिति ने शासन के समर्थन को कमजोर कर दिया।
- ईरान और हिजबुल्लाह, असद के प्रमुख सहयोगी, बाहरी संघर्षों और हवाई हमलों के कारण बहुत अधिक तनावग्रस्त या कमजोर हो गए हैं।
- तुर्की ने कथित तौर पर शासन की कमजोरियों का फायदा उठाते हुए उग्रवादियों का समर्थन किया।
भविष्य के लिए निहितार्थ
- विद्रोहियों की बढ़त सीरिया में गृहयुद्ध के संभावित पुनरुत्थान का संकेत है।
- शासन बल इराकी मिलिशिया से सुदृढीकरण के साथ फिर से संगठित हो रहे हैं, लेकिन लंबे समय तक रक्तपात की संभावना है।
North-East Region Development /उत्तर-पूर्व क्षेत्र विकास
In News
Source : The Hindu
The PM-DevINE scheme focuses on infrastructure and social development in the Northeast Region (NER), promoting holistic growth through Central funding.
- Complementing it, the UNNATI initiative supports industrialization, employment generation, and resilience, fostering inclusive development in the region.

PM-DevINE Scheme Overview
- Announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 as a Central Sector Scheme with 100% Central funding.
- Initial outlay of ₹1,500 crore, later increased to ₹6,600 crore for FY 2022-23 to FY 2025-26.
- Objectives:
- Funds infrastructure projects aligned with PM Gati Shakti.
- Supports social development initiatives based on the needs of the North East Region (NER).
- Promotes livelihood activities for youth and women.
- Addresses development gaps in various sectors.
- Progress:
- 35 projects worth ₹4,857.11 crore sanctioned as of November 2024.
Industrialization Initiatives in NER
- North East Industrial Development Scheme (NEIDS):
- Launched in 2017 and ended on March 31, 2022.
- Aims at promoting industrialization in NER.
- Uttar Poorva Transformative Industrialization Scheme (UNNATI) Scheme:
- Launched on March 9, 2024.
- Focuses on enhancing infrastructure, employment, and regional prosperity.
- Incentives provided:
- Capital Investment Incentive.
- Capital Interest Subvention.
- Manufacturing & Services Linked Incentive.
Budgetary Allocation for NER Development
- Non-exempt Union Ministries/Departments are required to allocate 10% of their Gross Budgetary Allocation for NER.
- Provisional expenditure of ₹3,53,412 crore incurred between 2019-20 and 2023-24.
उत्तर-पूर्व क्षेत्र विकास
पीएम-देवाइन योजना पूर्वोत्तर क्षेत्र (एनईआर) में बुनियादी ढांचे और सामाजिक विकास पर ध्यान केंद्रित करती है, जो केंद्रीय वित्त पोषण के माध्यम से समग्र विकास को बढ़ावा देती है।
- इसके पूरक के रूप में, उन्नति पहल औद्योगीकरण, रोजगार सृजन और लचीलेपन का समर्थन करती है, जिससे क्षेत्र में समावेशी विकास को बढ़ावा मिलता है।
पीएम-देवाइन योजना अवलोकन
- केंद्रीय बजट 2022-23 में 100% केंद्रीय वित्त पोषण के साथ एक केंद्रीय क्षेत्र योजना के रूप में घोषित किया गया।
- शुरुआती परिव्यय ₹1,500 करोड़ था, जिसे बाद में वित्त वर्ष 2022-23 से वित्त वर्ष 2025-26 के लिए बढ़ाकर ₹6,600 करोड़ कर दिया गया।
- उद्देश्य:
- पीएम गति शक्ति के साथ संरेखित बुनियादी ढांचा परियोजनाओं को निधि प्रदान करना।
- पूर्वोत्तर क्षेत्र (एनईआर) की जरूरतों के आधार पर सामाजिक विकास पहलों का समर्थन करता है।
- युवाओं और महिलाओं के लिए आजीविका गतिविधियों को बढ़ावा देता है।
- विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में विकास अंतराल को संबोधित करता है।
- प्रगति:
- नवंबर 2024 तक ₹4,857.11 करोड़ की 35 परियोजनाओं को मंजूरी दी गई।
एनईआर में औद्योगिकीकरण पहल
- पूर्वोत्तर औद्योगिक विकास योजना (NIDS):
- 2017 में शुरू की गई और 31 मार्च, 2022 को समाप्त हुई।
- इसका उद्देश्य एनईआर में औद्योगीकरण को बढ़ावा देना है।
- उत्तर पूर्व परिवर्तनकारी औद्योगिकीकरण योजना (उन्नति) योजना:
- 9 मार्च, 2024 को शुरू की गई।
- बुनियादी ढांचे, रोजगार और क्षेत्रीय समृद्धि को बढ़ाने पर ध्यान केंद्रित करती है।
- दिए गए प्रोत्साहन:
- पूंजी निवेश प्रोत्साहन।
- पूंजी ब्याज अनुदान।
- विनिर्माण और सेवा से जुड़े प्रोत्साहन।
एनईआर विकास के लिए बजटीय आवंटन
- गैर-छूट वाले केंद्रीय मंत्रालयों/विभागों को अपने सकल बजटीय आवंटन का 10% एनईआर के लिए आवंटित करना आवश्यक है।
- 2019-20 और 2023-24 के बीच ₹3,53,412 करोड़ का अनंतिम व्यय हुआ।
States and the challenge before the Finance Commission /वित्त आयोग के समक्ष राज्य और चुनौतियां
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity – Constitutional Bodies
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- The article discusses the Sixteenth Finance Commission and its role in addressing fiscal challenges and resource distribution between States and the Union.
- It also focuses on the global economic shifts, challenges faced by progressive States like Tamil Nadu, and the need for a balanced fiscal approach.
Overview of the Commission’s Mandate
- The Sixteenth Finance Commission, chaired by Arvind Panagariya, was recently hosted by the Government of Tamil Nadu.
- This Commission is tasked with addressing critical fiscal challenges and ensuring a fair relationship between States and the Union.
- Its decisions will significantly influence India’s fiscal policies for the next five years and shape the country’s long-term economic trajectory.
Opportunities Arising from Global Changes
- Global shifts in economic trends, including “friendshoring” and “reshoring,” are reshaping international trade and investment.
- These trends present India with a unique opportunity to enhance its economic prospects.
- The Finance Commission’s challenge is to balance equitable redistribution of resources while encouraging growth in high-performing States like Tamil Nadu.
Challenges in Resource Distribution
- Since the establishment of the first Finance Commission in 1951, there has been a consistent attempt to redistribute resources equitably among States.
- However, discrepancies have remained between the Commission’s declared goals and actual outcomes.
- The Fifteenth Finance Commission’s decision to allocate 41% of the divisible pool to States resulted in only 33.16% effective devolution due to the Union’s increasing reliance on cess and surcharges, which hindered devolution.
Increasing State Share and Incentivizing Performance
- States, which manage substantial developmental expenditures, should receive a larger share of the gross central taxes—suggested to be around 50%.
- This would grant States greater fiscal autonomy, enabling them to fund and implement schemes that cater to local needs.
- The current policy of horizontal devolution has limited results in driving growth, and a more balanced approach is necessary to allow both less-developed and high-performing States to thrive.
Challenges in Progressive States
- States like Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra face unique challenges, such as an aging population and increasing urbanisation.
- Tamil Nadu’s aging demographic limits its capacity to generate consumption-based tax revenue, while incurring the costs of supporting an older population rise.
The Commission’s Broader Role
- The Finance Commission’s mandate is not just about fiscal arithmetic but about fostering a future where every State contributes to and benefits from national progress.
- The Commission’s decisions will have far-reaching impacts, including in sectors like manufacturing, urbanisation, and climate resilience, shaping India’s potential as a leading global economy.
Sixteenth Finance Commission:
- Constituted: December 31, 2023
- Chairman: Arvind Panagariya (former Vice-Chairman of NITI Aayog)
- Purpose: To recommend how India’s tax revenue should be shared between the central government and the states.
- Term: 5 years (starting April 1, 2026)
- Key Considerations: Fiscal stability, economic growth, and equity among states.
- Previous Commission: The 15th Finance Commission’s recommendations are in effect until March 31, 2026.
- Important Task: Determining the principles for giving financial aid to states from India’s Consolidated Fund.
- Additional Role: Suggesting measures to increase the resources of the Consolidated Fund to support local governments (Panchayats and Municipalities).
- Current Status: The Commission is in the process of gathering information and conducting consultations with various stakeholders.
वित्त आयोग के समक्ष राज्य और चुनौतियां
संदर्भ :
- लेख में सोलहवें वित्त आयोग और राज्यों तथा संघ के बीच वित्तीय चुनौतियों तथा संसाधन वितरण को संबोधित करने में इसकी भूमिका पर चर्चा की गई है।
- यह वैश्विक आर्थिक बदलावों, तमिलनाडु जैसे प्रगतिशील राज्यों के सामने आने वाली चुनौतियों तथा संतुलित वित्तीय दृष्टिकोण की आवश्यकता पर भी ध्यान केंद्रित करता है।
आयोग के अधिदेश का अवलोकन
- अरविंद पनगढ़िया की अध्यक्षता में सोलहवें वित्त आयोग की हाल ही में तमिलनाडु सरकार द्वारा मेजबानी की गई थी।
- इस आयोग को महत्वपूर्ण वित्तीय चुनौतियों का समाधान करने तथा राज्यों और संघ के बीच निष्पक्ष संबंध सुनिश्चित करने का कार्य सौंपा गया है।
- इसके निर्णय अगले पाँच वर्षों के लिए भारत की वित्तीय नीतियों को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से प्रभावित करेंगे तथा देश के दीर्घकालिक आर्थिक प्रक्षेपवक्र को आकार देंगे।
वैश्विक परिवर्तनों से उत्पन्न अवसर
- “फ्रेंडशोरिंग” तथा “रीशोरिंग” सहित आर्थिक प्रवृत्तियों में वैश्विक बदलाव, अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार तथा निवेश को नया रूप दे रहे हैं।
- ये प्रवृत्तियाँ भारत को अपनी आर्थिक संभावनाओं को बढ़ाने का एक अनूठा अवसर प्रदान करती हैं।
- वित्त आयोग की चुनौती तमिलनाडु जैसे उच्च प्रदर्शन करने वाले राज्यों में विकास को प्रोत्साहित करते हुए संसाधनों के समान पुनर्वितरण को संतुलित करना है।
संसाधन वितरण में चुनौतियाँ
- 1951 में प्रथम वित्त आयोग की स्थापना के बाद से, राज्यों के बीच संसाधनों को समान रूप से पुनर्वितरित करने का लगातार प्रयास किया गया है।
- हालाँकि, आयोग के घोषित लक्ष्यों और वास्तविक परिणामों के बीच विसंगतियाँ बनी हुई हैं।
- पंद्रहवें वित्त आयोग द्वारा विभाज्य पूल का 41% राज्यों को आवंटित करने के निर्णय के परिणामस्वरूप केवल 16% प्रभावी हस्तांतरण हुआ, क्योंकि संघ की उपकर और अधिभार पर बढ़ती निर्भरता के कारण हस्तांतरण में बाधा उत्पन्न हुई।
राज्यों की हिस्सेदारी बढ़ाना और प्रदर्शन को प्रोत्साहित करना
- जो राज्य पर्याप्त विकास व्यय का प्रबंधन करते हैं, उन्हें सकल केंद्रीय करों का बड़ा हिस्सा मिलना चाहिए – जो लगभग 50% होने का सुझाव दिया गया है।
- इससे राज्यों को अधिक राजकोषीय स्वायत्तता मिलेगी, जिससे वे स्थानीय आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने वाली योजनाओं को निधि देने और लागू करने में सक्षम होंगे।
- क्षैतिज हस्तांतरण की वर्तमान नीति ने विकास को गति देने में सीमित परिणाम दिए हैं, और कम विकसित और उच्च प्रदर्शन करने वाले दोनों राज्यों को फलने-फूलने देने के लिए अधिक संतुलित दृष्टिकोण आवश्यक है।
प्रगतिशील राज्यों में चुनौतियाँ
- तमिलनाडु, महाराष्ट्र जैसे राज्यों को अनूठी चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ रहा है, जैसे कि बढ़ती उम्र की आबादी और बढ़ता शहरीकरण।
- तमिलनाडु की बढ़ती उम्र की जनसांख्यिकी खपत-आधारित कर राजस्व उत्पन्न करने की इसकी क्षमता को सीमित करती है, जबकि बढ़ती उम्र की आबादी को सहारा देने की लागत वहन करती है।
आयोग की व्यापक भूमिका
- वित्त आयोग का अधिदेश केवल राजकोषीय अंकगणित के बारे में नहीं है, बल्कि एक ऐसे भविष्य को बढ़ावा देने के बारे में है, जहाँ हर राज्य राष्ट्रीय प्रगति में योगदान दे और उससे लाभान्वित हो।
- आयोग के निर्णयों का दूरगामी प्रभाव पड़ेगा, जिसमें विनिर्माण, शहरीकरण और जलवायु लचीलापन जैसे क्षेत्र शामिल हैं, जो एक अग्रणी वैश्विक अर्थव्यवस्था के रूप में भारत की क्षमता को आकार देंगे।
सोलहवाँ वित्त आयोग:
- गठन: 31 दिसंबर, 2023
- अध्यक्ष: डॉ. अरविंद पनगढ़िया (नीति आयोग के पूर्व उपाध्यक्ष)
- उद्देश्य: यह सुझाव देना कि भारत के कर राजस्व को केंद्र सरकार और राज्यों के बीच कैसे साझा किया जाना चाहिए।
- कार्यकाल: 5 वर्ष (1 अप्रैल, 2026 से शुरू)
- मुख्य विचार: राजकोषीय स्थिरता, आर्थिक विकास और राज्यों के बीच समानता।
- पिछला आयोग: 15वें वित्त आयोग की सिफारिशें 31 मार्च, 2026 तक प्रभावी हैं।
- महत्वपूर्ण कार्य: भारत की समेकित निधि से राज्यों को वित्तीय सहायता देने के सिद्धांतों का निर्धारण करना।
- अतिरिक्त भूमिका: स्थानीय सरकारों (पंचायतों और नगर पालिकाओं) का समर्थन करने के लिए समेकित निधि के संसाधनों को बढ़ाने के उपाय सुझाना।
- वर्तमान स्थिति: आयोग जानकारी एकत्र करने और विभिन्न हितधारकों के साथ परामर्श करने की प्रक्रिया में है।
- के लिए निरंतर प्रयासों की आवश्यकता है।