CURRENT AFFAIRS – 24/08/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 24/08/2024
- Not neutral, India on the side of peace, says Modi in Ukraine / यूक्रेन में मोदी ने कहा, भारत तटस्थ नहीं, शांति का पक्षधर
- ‘Space sector contributed ₹20,000 crore to India’s GDP over the last decade’ / ‘अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र ने पिछले दशक में भारत के सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में ₹20,000 करोड़ का योगदान दिया’
- Chandrayaan-4/ चंद्रयान-4
- Botswana discovers the world’s second largest diamond / बोत्सवाना ने दुनिया का दूसरा सबसे बड़ा हीरा खोजा
- Gumti River / गुमटी नदी
- The road to 2047 for Indian agriculture / भारतीय कृषि के लिए 2047 का रास्ता
- Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) : International Organizations / इस्लामिक सहयोग संगठन (OIC) : International Organizations
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 24/08/2024
Not neutral, India on the side of peace, says Modi in Ukraine / यूक्रेन में मोदी ने कहा, भारत तटस्थ नहीं, शांति का पक्षधर
Syllabus : GS 2 : International Relations
Source : The Hindu
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Ukraine, the first by an Indian leader since its independence, highlights India’s balancing role in the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- The visit focused on peace efforts, humanitarian cooperation, and strengthening bilateral relations, amidst concerns over India’s trade with Russia and its global influence on the crisis.
- Peace Efforts: Prime Minister Modi emphasised India’s commitment to supporting peace efforts, underlining India’s stance on the need for dialogue and diplomacy to resolve the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Humanitarian Focus: Four key agreements were signed, focusing on:
- Humanitarian assistance by India for high-capacity development projects.
- Cooperation in agriculture and the food industry.
- Cultural cooperation.
- Agreement on drug quality and regulation.
- Support for Sovereignty: PM Modi reaffirmed India’s respect for the sovereignty and territorial integrity of nations, stressing that India has chosen the “side of peace” from the start of the conflict.
- Ukraine’s Concerns: Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy raised concerns about India’s purchase of Russian oil, highlighting India’s influence on Russia’s economy.
How can India mediate between Russia – Ukraine conflict?
- Ways for India to Mediate Between Russia and Ukraine
- Diplomatic Engagement: Leverage India’s non-aligned stance and strong diplomatic relations with both Russia and Ukraine to facilitate dialogue and propose peace talks.
- Humanitarian Assistance: Increase humanitarian aid to affected regions, showing commitment to alleviating human suffering and building goodwill with both sides.
- International Forums: Utilise platforms like the United Nations and BRICS to advocate for peaceful resolutions and support conflict de-escalation measures.
- Neutral Mediator: Offer to host peace negotiations or act as a neutral intermediary to bridge gaps between the conflicting parties.
- Economic Leverage: Use India’s growing economic influence to encourage economic incentives or sanctions adjustments that might appeal to both sides.
- Potential Implications for India
- Enhanced Global Standing: Successfully mediating could bolster India’s reputation as a responsible global actor and enhance its standing in international diplomacy.
- Strategic Partnerships: Strengthening ties with both Russia and Ukraine could open up new avenues for trade, defence, and technology collaborations.
- Geopolitical Risks: Engaging in mediation could lead to geopolitical risks, including potential backlash from global powers with vested interests in the conflict.
- Domestic Reactions: Balancing relationships with both Russia and Ukraine may cause domestic political challenges and public scrutiny.
- Economic Impact: Increased involvement might affect India’s trade relationships or energy imports from Russia, necessitating careful management of economic impacts.
यूक्रेन में मोदी ने कहा, भारत तटस्थ नहीं, शांति का पक्षधर
प्रधानमंत्री नरेंद्र मोदी की यूक्रेन यात्रा, जो कि स्वतंत्रता के बाद किसी भारतीय नेता की पहली यूक्रेन यात्रा है, रूस-यूक्रेन संघर्ष में भारत की संतुलनकारी भूमिका को उजागर करती है।
- यह यात्रा शांति प्रयासों, मानवीय सहयोग और द्विपक्षीय संबंधों को मजबूत करने पर केंद्रित थी, जबकि रूस के साथ भारत के व्यापार और संकट पर इसके वैश्विक प्रभाव को लेकर चिंताएं थीं।
- शांति प्रयास: प्रधानमंत्री मोदी ने शांति प्रयासों का समर्थन करने के लिए भारत की प्रतिबद्धता पर जोर दिया, रूस-यूक्रेन संघर्ष को हल करने के लिए बातचीत और कूटनीति की आवश्यकता पर भारत के रुख को रेखांकित किया।
- मानवीय फोकस: चार प्रमुख समझौतों पर हस्ताक्षर किए गए, जो निम्न पर केंद्रित थे:
- उच्च क्षमता वाली विकास परियोजनाओं के लिए भारत द्वारा मानवीय सहायता।
- कृषि और खाद्य उद्योग में सहयोग।
- सांस्कृतिक सहयोग।
- दवा की गुणवत्ता और विनियमन पर समझौता।
- संप्रभुता के लिए समर्थन: प्रधानमंत्री मोदी ने राष्ट्रों की संप्रभुता और क्षेत्रीय अखंडता के लिए भारत के सम्मान की पुष्टि की, इस बात पर जोर दिया कि भारत ने संघर्ष की शुरुआत से ही “शांति का पक्ष” चुना है।
- यूक्रेन की चिंताएँ: यूक्रेन के राष्ट्रपति वोलोडिमिर ज़ेलेंस्की ने भारत द्वारा रूसी तेल की खरीद पर चिंता जताई, जिसमें रूस की अर्थव्यवस्था पर भारत के प्रभाव को उजागर किया गया।
भारत रूस-यूक्रेन संघर्ष के बीच मध्यस्थता कैसे कर सकता है?
- भारत के लिए रूस और यूक्रेन के बीच मध्यस्थता करने के तरीके
- कूटनीतिक जुड़ाव: संवाद को सुविधाजनक बनाने और शांति वार्ता का प्रस्ताव करने के लिए रूस और यूक्रेन दोनों के साथ भारत के गुटनिरपेक्ष रुख और मजबूत कूटनीतिक संबंधों का लाभ उठाएँ।
- मानवीय सहायता: प्रभावित क्षेत्रों में मानवीय सहायता बढ़ाएँ, मानवीय पीड़ा को कम करने और दोनों पक्षों के साथ सद्भावना बनाने की प्रतिबद्धता दिखाएँ।
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय मंच: शांतिपूर्ण समाधानों की वकालत करने और संघर्ष को कम करने के उपायों का समर्थन करने के लिए संयुक्त राष्ट्र और ब्रिक्स जैसे मंचों का उपयोग करें।
- तटस्थ मध्यस्थ: संघर्षरत पक्षों के बीच मतभेदों को पाटने के लिए शांति वार्ता की मेजबानी करने या तटस्थ मध्यस्थ के रूप में कार्य करने की पेशकश करें।
- आर्थिक लाभ: आर्थिक प्रोत्साहन या प्रतिबंध समायोजन को प्रोत्साहित करने के लिए भारत के बढ़ते आर्थिक प्रभाव का उपयोग करें जो दोनों पक्षों को आकर्षित कर सकते हैं।
- भारत के लिए संभावित निहितार्थ
- वैश्विक प्रतिष्ठा में वृद्धि: सफलतापूर्वक मध्यस्थता करने से भारत की एक जिम्मेदार वैश्विक अभिनेता के रूप में प्रतिष्ठा बढ़ सकती है और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय कूटनीति में इसकी प्रतिष्ठा बढ़ सकती है।
- रणनीतिक साझेदारी: रूस और यूक्रेन दोनों के साथ संबंधों को मजबूत करने से व्यापार, रक्षा और प्रौद्योगिकी सहयोग के लिए नए रास्ते खुल सकते हैं।
- भू-राजनीतिक जोखिम: मध्यस्थता में शामिल होने से भू-राजनीतिक जोखिम हो सकते हैं, जिसमें संघर्ष में निहित स्वार्थों वाली वैश्विक शक्तियों से संभावित प्रतिक्रिया भी शामिल है।
- घरेलू प्रतिक्रियाएँ: रूस और यूक्रेन दोनों के साथ संबंधों को संतुलित करने से घरेलू राजनीतिक चुनौतियाँ और सार्वजनिक जाँच हो सकती है।
- आर्थिक प्रभाव: बढ़ी हुई भागीदारी भारत के व्यापार संबंधों या रूस से ऊर्जा आयात को प्रभावित कर सकती है, जिससे आर्थिक प्रभावों का सावधानीपूर्वक प्रबंधन करना आवश्यक हो जाता है।
‘Space sector contributed ₹20,000 crore to India’s GDP over the last decade’ / ‘अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र ने पिछले दशक में भारत के सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में ₹20,000 करोड़ का योगदान दिया’
Syllabus : GS 3 : Economy and Science & Tech
Source : The Hindu
India’s space sector contributed $24 billion to the GDP and supported 96,000 jobs over the last decade, with a significant multiplier effect of $2.54 on the economy.
- These findings were presented during National Space Day, based on a report commissioned by ISRO and conducted by econONE and Novaspace from 2014 to 2023.
Key highlights of the report
- About the report
- The report was initiated” by ISRO to evaluate the socio-economic impact of the space sector from 2014-2023.
- The study was conducted by Indian economics research firm econONE and Novaspace.
- It was presented during the National Space Day celebrations in New Delhi on August 23, 2024.
- The Space Day celebrations are to commemorate the first anniversary of the successful landing of the Chandrayaan-3 on August 23 last year.
Key findings
- Impact on Indian Economy
- India’s space sector has directly contributed about $24 billion (₹20,000 crore) to India’s GDP over the last decade.
- It has directly supported 96,000 jobs in the public and private sector.
- For every dollar produced by the space sector, there was a multiplier effect of $2.54 to the Indian economy.
- India’s space force was 2.5 times more productive than the country’s broader industrial workforce.
- 8th largest space economy (in terms of funding) in the world
- With $13 billion invested in the last decade it is the 8th largest space economy (in terms of funding) in the world.
- Satellite communications contributed 54% to the space economy, followed by navigation (26%) and launches (11%).
- Diversified space sector
- The Indian space sector was diversifying and now had 700 companies including 200 start-ups.
- It had seen revenues grow to $6.3 billion in 2023, which was about 1.5% of the global space market.
Way ahead
- India’s space sector has significantly enhanced the nation’s prestige, sovereignty, and global leadership, but its impact on the profitability and competitiveness of companies within the country has been limited.
- According to industry stakeholders, this is because the space program over the past decade has been primarily driven by political considerations.
- However, there is a shift occurring as commercial space is becoming a priority.
- Regulatory reforms have been introduced but have yet to fully take effect, and an under-developed venture capital ecosystem is hindering space technology start-ups from accessing necessary capital.
‘अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र ने पिछले दशक में भारत के सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में ₹20,000 करोड़ का योगदान दिया’
भारत के अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र ने पिछले दशक में सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में 24 बिलियन डॉलर का योगदान दिया और 96,000 नौकरियों का समर्थन किया, जिसका अर्थव्यवस्था पर 2.54 डॉलर का महत्वपूर्ण गुणक प्रभाव पड़ा।
- ये निष्कर्ष राष्ट्रीय अंतरिक्ष दिवस के दौरान प्रस्तुत किए गए, जो इसरो द्वारा कमीशन की गई और 2014 से 2023 तक इकॉनवन और नोवास्पेस द्वारा संचालित एक रिपोर्ट पर आधारित है।
रिपोर्ट के मुख्य अंश रिपोर्ट के बारे में
- इसरो द्वारा 2014-2023 तक अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र के सामाजिक-आर्थिक प्रभाव का मूल्यांकन करने के लिए रिपोर्ट शुरू की गई थी।
- अध्ययन भारतीय अर्थशास्त्र अनुसंधान फर्म इकॉनवन और नोवास्पेस द्वारा किया गया था।
- इसे 23 अगस्त, 2024 को नई दिल्ली में राष्ट्रीय अंतरिक्ष दिवस समारोह के दौरान प्रस्तुत किया गया था।
- अंतरिक्ष दिवस समारोह पिछले साल 23 अगस्त को चंद्रयान-3 की सफल लैंडिंग की पहली वर्षगांठ मनाने के लिए है।
मुख्य निष्कर्ष
- भारतीय अर्थव्यवस्था पर प्रभाव
- भारत के अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र ने पिछले दशक में भारत के सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में लगभग 24 बिलियन डॉलर (₹20,000 करोड़) का प्रत्यक्ष योगदान दिया है।
- इसने सार्वजनिक और निजी क्षेत्र में 96,000 नौकरियों को प्रत्यक्ष रूप से समर्थन दिया है।
- अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र द्वारा उत्पादित प्रत्येक डॉलर के लिए, भारतीय अर्थव्यवस्था पर $2.54 का गुणक प्रभाव पड़ा।
- भारत का अंतरिक्ष बल देश के व्यापक औद्योगिक कार्यबल की तुलना में 5 गुना अधिक उत्पादक था।
- दुनिया में 8वीं सबसे बड़ी अंतरिक्ष अर्थव्यवस्था (वित्त पोषण के मामले में)
- पिछले दशक में 13 बिलियन डॉलर के निवेश के साथ यह दुनिया में 8वीं सबसे बड़ी अंतरिक्ष अर्थव्यवस्था (वित्त पोषण के मामले में) है।
- उपग्रह संचार ने अंतरिक्ष अर्थव्यवस्था में 54% योगदान दिया, इसके बाद नेविगेशन (26%) और प्रक्षेपण (11%) का स्थान रहा।
- विविधतापूर्ण अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र
- भारतीय अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र में विविधता आ रही थी और अब इसमें 200 स्टार्ट-अप सहित 700 कंपनियाँ थीं।
- इसने 2023 में राजस्व में 3 बिलियन डॉलर की वृद्धि देखी, जो वैश्विक अंतरिक्ष बाजार का लगभग 1.5% था।
आगे का रास्ता
- भारत के अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र ने देश की प्रतिष्ठा, संप्रभुता और वैश्विक नेतृत्व को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से बढ़ाया है, लेकिन देश के भीतर कंपनियों की लाभप्रदता और प्रतिस्पर्धात्मकता पर इसका प्रभाव सीमित रहा है।
- उद्योग के हितधारकों के अनुसार, ऐसा इसलिए है क्योंकि पिछले एक दशक में अंतरिक्ष कार्यक्रम मुख्य रूप से राजनीतिक विचारों से प्रेरित रहा है।
- हालाँकि, एक बदलाव हो रहा है क्योंकि वाणिज्यिक स्थान प्राथमिकता बन रहा है।
- विनियामक सुधार पेश किए गए हैं, लेकिन अभी तक पूरी तरह से प्रभावी नहीं हुए हैं, और एक अविकसित उद्यम पूंजी पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र अंतरिक्ष प्रौद्योगिकी स्टार्ट-अप को आवश्यक पूंजी तक पहुँचने में बाधा डाल रहा है।
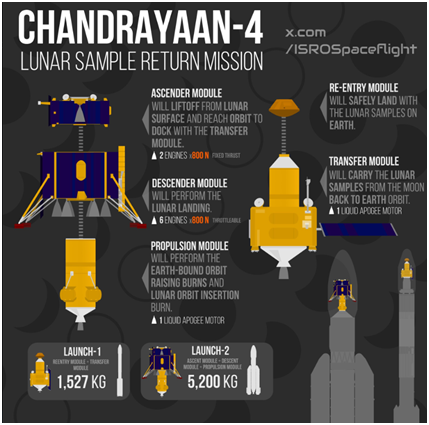
Chandrayaan-4/ चंद्रयान-4
Syllabus : GS 3 : Science & Tech
Source : The Hindu
Chandrayaan-4, India’s upcoming Moon mission scheduled for 2027, aims to bring rock and soil samples back to Earth.
- The mission’s designs have been finalized and await government approval.

About the News:
- Mission Structure
- Modules: The Chandrayaan-4 spacecraft will consist of five separate modules, unlike Chandrayaan-3, which had three. The mission involves complex stages, including landing, sample collection, and returning the samples to Earth.
- Docking Operations: The mission will require docking space modules twice—a new capability for ISRO that will be first demonstrated in the upcoming Spadex mission.
- Technological Advancements
- Previous Demonstrations: Key capabilities, such as lifting off from the lunar surface and bringing a spacecraft back from lunar orbit, were successfully demonstrated during Chandrayaan-3. This sets the foundation for the Chandrayaan-4 mission.
- Scientific Importance
- Sample Return: Bringing lunar samples back to Earth will enable more detailed analysis with advanced instruments, facilitating significant scientific discoveries. The samples will be distributed across various scientific laboratories in India.
चंद्रयान-4
भारत का आगामी चंद्र मिशन चंद्रयान-4, जो 2027 में निर्धारित है, का लक्ष्य चट्टान और मिट्टी के नमूने वापस धरती पर लाना है।
- मिशन के डिजाइन को अंतिम रूप दे दिया गया है और सरकार की मंजूरी का इंतजार है।
समाचार के बारे में:
- मिशन संरचना
- मॉड्यूल: चंद्रयान-4 अंतरिक्ष यान में चंद्रयान-3 के विपरीत पाँच अलग-अलग मॉड्यूल होंगे, जिसमें तीन मॉड्यूल थे। मिशन में लैंडिंग, नमूना संग्रह और नमूनों को धरती पर वापस लाने सहित जटिल चरण शामिल हैं।
- डॉकिंग ऑपरेशन: मिशन में अंतरिक्ष मॉड्यूल को दो बार डॉक करने की आवश्यकता होगी – इसरो के लिए एक नई क्षमता जिसे पहली बार आगामी स्पैडेक्स मिशन में प्रदर्शित किया जाएगा।
- तकनीकी प्रगति
- पिछले प्रदर्शन: चंद्र सतह से उड़ान भरने और चंद्र कक्षा से अंतरिक्ष यान को वापस लाने जैसी प्रमुख क्षमताओं का चंद्रयान-3 के दौरान सफलतापूर्वक प्रदर्शन किया गया था। यह चंद्रयान-4 मिशन की नींव रखता है।
- वैज्ञानिक महत्व
- नमूना वापसी: चंद्र नमूनों को वापस धरती पर लाने से उन्नत उपकरणों के साथ अधिक विस्तृत विश्लेषण संभव होगा, जिससे महत्वपूर्ण वैज्ञानिक खोजों में मदद मिलेगी। ये नमूने भारत की विभिन्न वैज्ञानिक प्रयोगशालाओं में वितरित किये जायेंगे।
Botswana discovers the world’s second largest diamond / बोत्सवाना ने दुनिया का दूसरा सबसे बड़ा हीरा खोजा
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
A 2,492-carat diamond, the second largest ever, was discovered in Botswana’s Karowe Diamond Mine using X-ray technology by Lucara Diamond Corp.
- The massive stone, second only to the Cullinan Diamond, was presented to President Mokgweetsi Masisi, highlighting Botswana’s significance as one of the top diamond producers globally.
About the news:
- A 2,492-carat diamond, the second largest in the world, was discovered in Botswana’s Karowe Diamond Mine.
- The diamond was found using X-ray detection technology developed by Lucara Diamond Corp.
- It is second in size only to the 3,016-carat Cullinan Diamond found in South Africa in 1905.
- The diamond was presented to Botswana’s President Mokgweetsi Masisi by Lucara’s managing director.
- Botswana is a leading global producer of diamonds, and this discovery is the largest ever found in the country.
X-ray Detection Technology
- X-ray detection technology in diamond mining uses X-rays to identify diamonds based on their unique atomic structure.
- When exposed to X-rays, diamonds emit a distinctive light, which machines detect and separate from other materials.
- This method is highly efficient, preserving large, high-value diamonds during extraction and minimising damage compared to traditional methods, making it ideal for detecting valuable stones in mines.
बोत्सवाना ने दुनिया का दूसरा सबसे बड़ा हीरा खोजा
लुकारा डायमंड कॉर्प द्वारा एक्स-रे तकनीक का उपयोग करके बोत्सवाना की कारोवे डायमंड माइन में 2,492 कैरेट का हीरा खोजा गया, जो अब तक का दूसरा सबसे बड़ा हीरा है।
- कुलिनन डायमंड के बाद दूसरा सबसे बड़ा हीरा, राष्ट्रपति मोकग्वेत्सी मासीसी को भेंट किया गया, जो वैश्विक स्तर पर शीर्ष हीरा उत्पादकों में से एक के रूप में बोत्सवाना के महत्व को दर्शाता है।
समाचार के बारे में:
- बोत्सवाना की कारोवे डायमंड माइन में 2,492 कैरेट का हीरा खोजा गया, जो दुनिया का दूसरा सबसे बड़ा हीरा है।
- लुकारा डायमंड कॉर्प द्वारा विकसित एक्स-रे डिटेक्शन तकनीक का उपयोग करके हीरा खोजा गया।
- यह आकार में 1905 में दक्षिण अफ्रीका में पाए गए 3,016 कैरेट के कुलिनन डायमंड के बाद दूसरे स्थान पर है।
- लुकारा के प्रबंध निदेशक द्वारा हीरा बोत्सवाना के राष्ट्रपति मोकग्वेत्सी मासीसी को भेंट किया गया।
- बोत्सवाना हीरे का एक अग्रणी वैश्विक उत्पादक है, और यह खोज देश में अब तक की सबसे बड़ी खोज है।
एक्स-रे डिटेक्शन तकनीक
- हीरे के खनन में एक्स-रे डिटेक्शन तकनीक हीरे की पहचान करने के लिए उनकी अनूठी परमाणु संरचना के आधार पर एक्स-रे का उपयोग करती है।
- जब एक्स-रे के संपर्क में आते हैं, तो हीरे एक विशिष्ट प्रकाश उत्सर्जित करते हैं, जिसे मशीनें पहचान लेती हैं और अन्य सामग्रियों से अलग कर देती हैं।
- यह विधि अत्यधिक कुशल है, निष्कर्षण के दौरान बड़े, उच्च-मूल्य वाले हीरों को संरक्षित करती है और पारंपरिक तरीकों की तुलना में नुकसान को कम करती है, जिससे यह खदानों में मूल्यवान पत्थरों का पता लगाने के लिए आदर्श बन जाती है।
Gumti River / गुमटी नदी
Term In News
India has refuted allegations that the recent floods in eastern Bangladesh were caused by the opening of the Dumbur dam over Gumti River in Tripura.
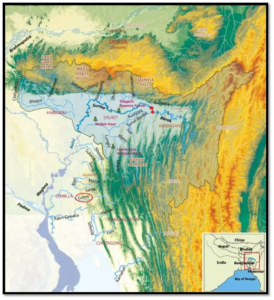
About Gumti River
| Origin | Dumboor Lake, Tripura, India |
| Length | Approximately 150 kilometers |
| Course | · Flows southward through Tripura, India, and then into Bangladesh;· Joins the Meghna River. |
| Tributaries | · Left: Raima, Manu· Right: Deo, Khowai |
| Terrain | Hilly terrain in upper course, fertile plains in lower course |
| Biodiversity | Supports diverse flora and fauna |
| Projects Installed | · Gumti Hydroelectric Project: Located near Dumbur; Generates hydroelectric power in Tripura; Bangladesh also receives 40 MW.· Gumti Irrigation Project: Supports irrigation for agriculture in Tripura, India |
गुमटी नदी
भारत ने उन आरोपों का खंडन किया है कि पूर्वी बांग्लादेश में हाल ही में आई बाढ़ का कारण त्रिपुरा में गुमती नदी पर डंबूर बांध को खोलना था।
गुमटी नदी के बारे में
| उद्गम | डुम्बूर झील, त्रिपुरा, भारत |
| लंबाई | लगभग 150 किलोमीटर |
| पाठ्यक्रम | · त्रिपुरा, भारत से होकर दक्षिण की ओर बहती है, और फिर बांग्लादेश में प्रवेश करती है;· मेघना नदी में मिलती है। |
| सहायक नदियाँ | · बाएं: राइमा, मनु· दाएं: देव, खोवाई |
| भूभाग | ऊपरी भाग में पहाड़ी इलाका, निचले भाग में उपजाऊ मैदान |
| जैव विविधता | विविध वनस्पतियों और जीवों को सहारा देता है |
| स्थापित परियोजनाएँ | · गुमटी जलविद्युत परियोजना: डंबूर के पास स्थित; त्रिपुरा में जलविद्युत शक्ति उत्पन्न करती है; बांग्लादेश को भी 40 मेगावाट प्राप्त होती है।· गुमटी सिंचाई परियोजना: भारत के त्रिपुरा में कृषि के लिए सिंचाई का समर्थन करती है |
The road to 2047 for Indian agriculture / भारतीय कृषि के लिए 2047 का रास्ता
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 3 : Economy- Agriculture
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- India’s goal of becoming a developed nation by 2047 hinges on transforming its agricultural sector through sustainable practices, technological innovations, and strategic government initiatives.
- Addressing challenges like climate change and food demand, the government is prioritising agricultural innovation, infrastructure, and credit to ensure inclusive, long-term growth.
Road to sustainable agriculture
- Transforming Indian agriculture depends on adopting sustainable practices that ensure long-term productivity and environmental health.
- Precision farming, genetically modified crops, and advanced irrigation techniques such as drip and sprinkler systems are leading this transformation.
- The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) has covered 78 lakh hectares, promoting water-use efficiency through micro-irrigation. The scheme’s ₹93,068 crore allocation for 2021-26 underscores the government’s commitment to sustainable water management.
Challenges and Solutions to issues in Indian Agriculture
- India’s agricultural sector faces challenges, including climate change, land degradation, and market access issues.
- The Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): introduced in 2016, provides financial assistance for crop losses. With 49.5 crore farmers enrolled and claims totalling over ₹1.45 lakh crore, the scheme is a cornerstone of agricultural risk management.
- The Electronic National Agriculture Market (eNAM): launched in 2016, integrates existing markets through an electronic platform. By September 2023, 1,361 mandis had been integrated, benefiting 1.76 million farmers and recording trade worth ₹2.88 lakh crore. This initiative improves market access and ensures better price realisation for farmers.
An imbalance in Indian Agriculture
- Limited contribution in GDP: Despite agriculture engaging nearly 46% of the workforce, agriculture’s contribution to GDP is about 18%, highlighting a stark imbalance.
- Agriculture GDP: Agricultural GDP lags at 3.3%. Under the Narendra Modi administration, overall GDP growth was 5.9%, and agriculture grew at 3.6%. However, this is insufficient for a sector so critical to the nation’s socioeconomic fabric.
- Bleak Future of agriculture growth: By 2047, agriculture’s share in GDP might shrink to 7%-8%, yet, it could still employ over 30% of the workforce if significant structural changes are not implemented.
- Unpredictability of monsoons: The expected 7.6% overall GDP growth for 2023-24 is promising. However, the agri-GDP’s anaemic growth of 0.7%, primarily due to unseasonal rains, is alarming.
- Rising population and demands: Further, according to United Nations projections, India’s population is expected to reach 1.5 billion by 2030 and 1.59 billion by 2040. And meeting the food requirements of this burgeoning population will be imperative.
- Food price and demands will be impacted: With an estimated expenditure elasticity of food at 0.45, the demand for food is expected to grow by approximately 2.85% annually, considering the population growth rate of 0.85%.
- India’s real per capita income and expenditure dynamics: Increased by 41% from 2011-12 to 2021-22 and is projected to accelerate further. However, the expenditure elasticity post-2023 is anticipated to be lower.
Some initiatives to help agriculture progress
- Several initiatives have been rolled out to bolster farmer prosperity and sustainable agricultural growth.
- Rationalising food and fertilizer subsidies and redirecting savings towards agricultural research and development innovation and extension services are crucial.
- The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): launched in 2019, disburses ₹6,000 annually to farmers in three instalments. This scheme has already benefited over 11.8 crore farmers, offering much-neededfinancial support.
- The Soil Health Card (SHC) scheme: aims to optimise soil nutrient use, thereby enhancing agricultural productivity. Over 23 crore SHCs have been distributed, providing farmers with crucial insights into soil health and nutrient management.
- Millets support: The government also championed the International Year of Millets in 2023, promoting nutritious coarse grains, both domestically and internationally.
- The Agriculture Infrastructure Fund: with a ₹1 lakh crore financing facility, supports the development andmodernisation of post-harvest management infrastructure.
- Employment opportunities: These projects have created employment for more than 5.8 lakh individuals and improved farmer incomes by 20%-25% through better price realisation.
- SVAMITVA initiative: aims to ensure transparent property ownership in rural areas. As of September 2023, over 1.6 crore property cards have been generated, enhancing land security and facilitating credit access for farmers.
Strategic planning to boost Agricultural Growth
- The government’s strategic planning for agriculture, leading up to 2047, focuses on several key areas:
- Anticipated future demand for agricultural products
- Insights from past growth catalysts, existing challenges, and potential opportunities in the agricultural landscape.
- Projections indicate that the total demand for food grains in 2047-48 will rise.
Way Forward:
- Investment in R&D: To meet future demands sustainably, significant investments in agricultural research, infrastructure, and policy support are necessary.
- Budget Allocation: The Budget for 2024-25 includes ₹20 lakh crore for targeted agricultural credit and the launch of the Agriculture Accelerator Fund, highlighting a proactive approach to fostering agricultural innovation and growth.
- Enhance Digital Infrastructure: Support and expand digital platforms like eNAM to improve market access, provide real-time data, and facilitate better price realization for farmers.
Goals of Indian Agriculture by Vision 2047:
- Comprehensive Goal: India’s centennial year of independence requires a six-fold increase in per capita Gross National Income (GNI), emphasizing the need for comprehensive development, especially in agriculture.
- Trade Goal: India’s agricultural and processed food exports have gone up to more than USD 50 billion in 2022-23.
- The Vision 2047 aims to improve the availability of nutritious foods by enhancing the processing of fruits and vegetables, and augment the proportion of value-added products in India’s export portfolio.
- Sustainable Goal: Transforming Indian agriculture will hinge on adopting sustainable practices such as precision farming, genetically modified crops, and advanced irrigation techniques (e.g., drip and sprinkler systems).
भारतीय कृषि के लिए 2047 का रास्ता
Context :
- 2047 तक विकसित राष्ट्र बनने का भारत का लक्ष्य संधारणीय प्रथाओं, तकनीकी नवाचारों और रणनीतिक सरकारी पहलों के माध्यम से अपने कृषि क्षेत्र को बदलने पर टिका है।
- जलवायु परिवर्तन और खाद्य मांग जैसी चुनौतियों का समाधान करते हुए, सरकार समावेशी, दीर्घकालिक विकास सुनिश्चित करने के लिए कृषि नवाचार, बुनियादी ढाँचे और ऋण को प्राथमिकता दे रही है।
संधारणीय कृषि का मार्ग
- भारतीय कृषि में परिवर्तन संधारणीय प्रथाओं को अपनाने पर निर्भर करता है जो दीर्घकालिक उत्पादकता और पर्यावरणीय स्वास्थ्य सुनिश्चित करते हैं।
- सटीक खेती, आनुवंशिक रूप से संशोधित फसलें और ड्रिप और स्प्रिंकलर सिस्टम जैसी उन्नत सिंचाई तकनीकें इस परिवर्तन का नेतृत्व कर रही हैं।
- प्रधानमंत्री कृषि सिंचाई योजना (PMKSY) ने 78 लाख हेक्टेयर को कवर किया है, जो सूक्ष्म सिंचाई के माध्यम से जल-उपयोग दक्षता को बढ़ावा देती है। 2021-26 के लिए योजना का ₹93,068 करोड़ का आवंटन संधारणीय जल प्रबंधन के लिए सरकार की प्रतिबद्धता को रेखांकित करता है।
भारतीय कृषि में चुनौतियों और मुद्दों के समाधान
- भारत का कृषि क्षेत्र जलवायु परिवर्तन, भूमि क्षरण और बाजार पहुंच के मुद्दों सहित चुनौतियों का सामना कर रहा है।
- प्रधानमंत्री फसल बीमा योजना (PMFBY): 2016 में शुरू की गई, जो फसल के नुकसान के लिए वित्तीय सहायता प्रदान करती है। 49.5 करोड़ किसानों के नामांकन और ₹1.45 लाख करोड़ से अधिक के दावों के साथ, यह योजना कृषि जोखिम प्रबंधन की आधारशिला है।
- इलेक्ट्रॉनिक राष्ट्रीय कृषि बाजार (eNAM): 2016 में शुरू किया गया, जो एक इलेक्ट्रॉनिक प्लेटफ़ॉर्म के माध्यम से मौजूदा बाज़ारों को एकीकृत करता है। सितंबर 2023 तक, 1,361 मंडियों को एकीकृत किया गया था, जिससे 1.76 मिलियन किसानों को लाभ हुआ और ₹2.88 लाख करोड़ का व्यापार दर्ज किया गया। यह पहल बाजार तक पहुँच में सुधार करती है और किसानों के लिए बेहतर मूल्य प्राप्ति सुनिश्चित करती है।
भारतीय कृषि में असंतुलन
- जीडीपी में सीमित योगदान: कृषि में लगभग 46% कार्यबल लगे होने के बावजूद, जीडीपी में कृषि का योगदान लगभग 18% है, जो एक गंभीर असंतुलन को दर्शाता है।
- कृषि जीडीपी: कृषि जीडीपी 3.3% पर पिछड़ गई। नरेंद्र मोदी प्रशासन के तहत, कुल जीडीपी वृद्धि 5.9% थी, और कृषि 3.6% की दर से बढ़ी। हालांकि, देश के सामाजिक-आर्थिक ताने-बाने के लिए इतने महत्वपूर्ण क्षेत्र के लिए यह अपर्याप्त है।
- कृषि विकास का निराशाजनक भविष्य: 2047 तक, सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में कृषि का हिस्सा 7%-8% तक कम हो सकता है, फिर भी, यदि महत्वपूर्ण संरचनात्मक परिवर्तन लागू नहीं किए जाते हैं, तो यह अभी भी 30% से अधिक कार्यबल को रोजगार दे सकता है।
- मानसून की अप्रत्याशितता: 2023-24 के लिए अपेक्षित 7.6% समग्र सकल घरेलू उत्पाद की वृद्धि आशाजनक है। हालांकि, मुख्य रूप से बेमौसम बारिश के कारण कृषि-जीडीपी की 0.7% की कमजोर वृद्धि चिंताजनक है।
- बढ़ती जनसंख्या और मांग: इसके अलावा, संयुक्त राष्ट्र के अनुमानों के अनुसार, भारत की जनसंख्या 2030 तक 1.5 बिलियन और 2040 तक 1.59 बिलियन तक पहुँचने की उम्मीद है। और इस बढ़ती आबादी की खाद्य आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करना अनिवार्य होगा।
- खाद्य मूल्य और मांग पर असर पड़ेगा: खाद्य की अनुमानित व्यय लोच 0.45 पर है, जनसंख्या वृद्धि दर 0.85% को देखते हुए खाद्य की मांग में सालाना लगभग 2.85% की वृद्धि होने की उम्मीद है।
- भारत की वास्तविक प्रति व्यक्ति आय और व्यय की गतिशीलता: 2011-12 से 2021-22 तक 41% की वृद्धि हुई है और इसमें और तेजी आने का अनुमान है। हालांकि, 2023 के बाद व्यय लोच कम होने का अनुमान है।
कृषि की प्रगति में मदद करने के लिए कुछ पहल
- किसानों की समृद्धि और सतत कृषि विकास को बढ़ावा देने के लिए कई पहल की गई हैं।
- खाद्य और उर्वरक सब्सिडी को युक्तिसंगत बनाना और बचत को कृषि अनुसंधान और विकास नवाचार और विस्तार सेवाओं की ओर पुनर्निर्देशित करना महत्वपूर्ण है।
- प्रधानमंत्री किसान सम्मान निधि (पीएम-किसान): 2019 में शुरू की गई, किसानों को तीन किस्तों में सालाना ₹6,000 वितरित करती है। इस योजना से पहले ही 11.8 करोड़ से अधिक किसानों को लाभ मिल चुका है, जिससे उन्हें बहुत जरूरी वित्तीय सहायता मिली है।
- मृदा स्वास्थ्य कार्ड (SHC) योजना: इसका उद्देश्य मृदा पोषक तत्वों के उपयोग को अनुकूलित करना है, जिससे कृषि उत्पादकता में वृद्धि हो। 23 करोड़ से अधिक SHC वितरित किए गए हैं, जो किसानों को मृदा स्वास्थ्य और पोषक तत्व प्रबंधन के बारे में महत्वपूर्ण जानकारी प्रदान करते हैं।
- बाजरा समर्थन: सरकार ने 2023 में अंतर्राष्ट्रीय बाजरा वर्ष मनाने का भी समर्थन किया, जिससे घरेलू और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर पौष्टिक मोटे अनाज को बढ़ावा मिला।
- कृषि अवसंरचना कोष: ₹1 लाख करोड़ की वित्तपोषण सुविधा के साथ, फसल कटाई के बाद के प्रबंधन अवसंरचना के विकास और आधुनिकीकरण का समर्थन करता है।
- रोजगार के अवसर: इन परियोजनाओं ने 5.8 लाख से अधिक व्यक्तियों के लिए रोजगार सृजित किए हैं और बेहतर मूल्य प्राप्ति के माध्यम से किसानों की आय में 20%-25% की वृद्धि की है।
- स्वामित्व पहल: इसका उद्देश्य ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में पारदर्शी संपत्ति स्वामित्व सुनिश्चित करना है। सितंबर 2023 तक, 6 करोड़ से अधिक संपत्ति कार्ड बनाए जा चुके हैं, जिससे भूमि सुरक्षा में वृद्धि हुई है और किसानों के लिए ऋण पहुँच में सुविधा हुई है।
कृषि विकास को बढ़ावा देने के लिए रणनीतिक योजना
- 2047 तक कृषि के लिए सरकार की रणनीतिक योजना कई प्रमुख क्षेत्रों पर केंद्रित है:
- कृषि उत्पादों की अनुमानित भावी मांग
- कृषि परिदृश्य में पिछले विकास उत्प्रेरकों, मौजूदा चुनौतियों और संभावित अवसरों से अंतर्दृष्टि।
- अनुमानों से संकेत मिलता है कि 2047-48 में खाद्यान्नों की कुल मांग बढ़ेगी।
आगे की राह:
- आरएंडडी में निवेश: भविष्य की मांगों को स्थायी रूप से पूरा करने के लिए, कृषि अनुसंधान, बुनियादी ढांचे और नीति समर्थन में महत्वपूर्ण निवेश आवश्यक है।
- बजट आवंटन: 2024-25 के बजट में लक्षित कृषि ऋण के लिए ₹20 लाख करोड़ और कृषि त्वरक निधि की शुरूआत शामिल है, जो कृषि नवाचार और विकास को बढ़ावा देने के लिए एक सक्रिय दृष्टिकोण पर प्रकाश डालती है।
- डिजिटल बुनियादी ढांचे को बढ़ावा दें: बाजार पहुंच में सुधार, वास्तविक समय के डेटा प्रदान करने और किसानों के लिए बेहतर मूल्य प्राप्ति की सुविधा के लिए ईएनएएम जैसे डिजिटल प्लेटफार्मों का समर्थन और विस्तार करें।
विज़न 2047 के अनुसार भारतीय कृषि के लक्ष्य:
- व्यापक लक्ष्य: भारत की स्वतंत्रता के शताब्दी वर्ष के लिए प्रति व्यक्ति सकल राष्ट्रीय आय (जीएनआई) में छह गुना वृद्धि की आवश्यकता है, जो विशेष रूप से कृषि में व्यापक विकास की आवश्यकता पर बल देता है।
- व्यापार लक्ष्य: भारत का कृषि और प्रसंस्कृत खाद्य निर्यात 2022-23 में 50 बिलियन अमरीकी डॉलर से अधिक हो गया है।
- विज़न 2047 का उद्देश्य फलों और सब्जियों के प्रसंस्करण को बढ़ाकर पौष्टिक खाद्य पदार्थों की उपलब्धता में सुधार करना और भारत के निर्यात पोर्टफोलियो में मूल्यवर्धित उत्पादों के अनुपात को बढ़ाना है।
- स्थायी लक्ष्य: भारतीय कृषि में बदलाव सटीक खेती, आनुवंशिक रूप से संशोधित फसलों और उन्नत सिंचाई तकनीकों (जैसे, ड्रिप और स्प्रिंकलर सिस्टम) जैसी टिकाऊ प्रथाओं को अपनाने पर निर्भर करेगा।
Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) : International Organizations / इस्लामिक सहयोग संगठन (OIC) : International Organizations
About:
- The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) is the second largest organization after the United Nations with a membership of 57 states spread over four continents.
- The Organization is the collective voice of the Muslim world. It endeavors to safeguard and protect the interests of the Muslim world in the spirit of promoting international peace and harmony among various people of the world.
Background:
- The Organization was established upon a decision of the historical summit which took place in Rabat, Kingdom of Morocco on 25th September, 1969 following the criminal arson of Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem.
- In 1970, the inaugural Islamic Conference of Foreign Ministers (ICFM) resulted in establishment of a permanent secretariat in Jeddah, headed by organization’s secretary general.
Major Objectives:
- The OIC endeavours to establish solidarity among member states.
- To support restoration of complete sovereignty and territorial integrity of any member state under occupation.
- To protect, defend and combat defamation of Islam.
- To prevent growing dissention in Muslim societies and work to ensure that member states take a united stand at the U. N. General Assembly, Human Rights Council and other international fora.
Charter:
- The organisation adheres to a charter that lays out its objectives, principles and operating mechanism.
- First adopted in 1972, the charter has been revised multiple times in line with emerging conditions in the developing world.
- The present charter was adopted in March 2008 at Dakar in Senegal.
- It enshrines that all members be guided and inspired by the noble Islamic teachings and values alongside committing themselves to the purposes and principles of the U. N. charter.
Membership:
- Permanent members:
- The member states include Afghanistan, Algeria, Bangladesh, Brunei Darussalam, Burkina Faso,Djibouti, Egypt, Gabon, Gambia, Guinea, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Morocco, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Oman, Pakistan, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Senegal, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Turkey, Tunisia, Turkmenistan, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Yemen, and others.
- Observer Members
- States: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Central African Republic, Kingdom of Thailand, The Russian Federation, Turkish Cypriot State.
- International Organisations: United Nations (UN), Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), League of Arab States (LAS), African Union (AU), Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO).
इस्लामिक सहयोग संगठन (OIC) : International Organizations
ओआईसी के बारे में:
- इस्लामिक सहयोग संगठन (ओआईसी) संयुक्त राष्ट्र के बाद दूसरा सबसे बड़ा संगठन है, जिसके चार महाद्वीपों में फैले 57 देश सदस्य हैं।
- यह संगठन मुस्लिम दुनिया की सामूहिक आवाज़ है। यह दुनिया के विभिन्न लोगों के बीच अंतर्राष्ट्रीय शांति और सद्भाव को बढ़ावा देने की भावना से मुस्लिम दुनिया के हितों की रक्षा और सुरक्षा करने का प्रयास करता है।
पृष्ठभूमि:
- यह संगठन 25 सितंबर, 1969 को मोरक्को के रबात में हुए ऐतिहासिक शिखर सम्मेलन के निर्णय पर स्थापित किया गया था, जो यरूशलेम में अल-अक्सा मस्जिद में आपराधिक आगजनी के बाद हुआ था।
- 1970 में, विदेश मंत्रियों के उद्घाटन इस्लामी सम्मेलन (ICFM) के परिणामस्वरूप जेद्दा में संगठन के महासचिव की अध्यक्षता में एक स्थायी सचिवालय की स्थापना हुई।
मुख्य उद्देश्य:
- ओआईसी सदस्य राज्यों के बीच एकजुटता स्थापित करने का प्रयास करता है।
- कब्जे के तहत किसी भी सदस्य राज्य की पूर्ण संप्रभुता और क्षेत्रीय अखंडता की बहाली का समर्थन करना।
- इस्लाम की बदनामी की रक्षा, बचाव और मुकाबला करना।
- मुस्लिम समाजों में बढ़ते मतभेद को रोकना और यह सुनिश्चित करना कि सदस्य देश संयुक्त राष्ट्र महासभा, मानवाधिकार परिषद और अन्य अंतर्राष्ट्रीय मंचों पर एकजुट रुख अपनाएं।
चार्टर:
- संगठन एक चार्टर का पालन करता है जो इसके उद्देश्यों, सिद्धांतों और संचालन तंत्र को निर्धारित करता है।
- पहली बार 1972 में अपनाए गए इस चार्टर को विकासशील देशों में उभरती परिस्थितियों के अनुरूप कई बार संशोधित किया गया है।
- वर्तमान चार्टर को मार्च 2008 में सेनेगल के डकार में अपनाया गया था।
- इसमें यह सुनिश्चित किया गया है कि सभी सदस्य संयुक्त राष्ट्र चार्टर के उद्देश्यों और सिद्धांतों के प्रति खुद को प्रतिबद्ध करने के साथ-साथ महान इस्लामी शिक्षाओं और मूल्यों से निर्देशित और प्रेरित हों।
सदस्यता:
- स्थायी सदस्य:
- सदस्य राज्यों में अफगानिस्तान, अल्जीरिया, बांग्लादेश, ब्रुनेई दारुस्सलाम, बुर्किना फासो, जिबूती, मिस्र, गैबॉन, गाम्बिया, गिनी, इंडोनेशिया, ईरान, इराक, जॉर्डन, मोरक्को, मोजाम्बिक, नाइजर, नाइजीरिया, ओमान, पाकिस्तान, फिलिस्तीन, कतर, सऊदी अरब, सेनेगल, सोमालिया, सूडान, सीरिया, ताजिकिस्तान, तुर्की, ट्यूनीशिया, तुर्कमेनिस्तान, संयुक्त अरब अमीरात, उज्बेकिस्तान, यमन और अन्य शामिल हैं।
- पर्यवेक्षक सदस्य
- राज्य: बोस्निया और हर्जेगोविना, मध्य अफ्रीकी गणराज्य, थाईलैंड साम्राज्य, रूसी संघ, तुर्की साइप्रस राज्य।
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठन: संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन), गुटनिरपेक्ष आंदोलन (एनएएम), अरब राज्यों का संघ (एलएएस), अफ्रीकी संघ (एयू), आर्थिक सहयोग संगठन (ईसीओ)।