CURRENT AFFAIRS – 28/08/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 28/08/2024
- SC stays AYUSH Ministry’s notification omitting key rule prohibiting misleading advertisements/ सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने भ्रामक विज्ञापनों पर रोक लगाने वाले प्रमुख नियम को हटाने वाली आयुष मंत्रालय की अधिसूचना पर रोक लगाई
- The invisible lives of sanitation workers who clean Mumbai’s drains to keep them functional /मुंबई के नालों को साफ करने वाले सफाई कर्मचारियों की अदृश्य जिंदगी
- On SEBI chairperson’s conflicts of interests / सेबी अध्यक्ष के हितों के टकराव पर
- OPEC+ output cut may push Indian refiners to source oil from Americas / ओपेक+ उत्पादन में कटौती से भारतीय रिफाइनर अमेरिका से तेल मंगाने पर मजबूर हो सकते हैं
- Chile’s Atacama Salt Flat sinking due to Lithium Mining / लिथियम खनन के कारण चिली का अटाकामा साल्ट फ्लैट डूब रहा है
- Advancing equity, from COVID-19 to Mpox / कोविड-19 से लेकर एमपॉक्स तक इक्विटी को आगे बढ़ाना
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations : International Organizations / दक्षिण पूर्व एशियाई राष्ट्र संघ : अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठन
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 28/08/2024
SC stays AYUSH Ministry’s notification omitting key rule prohibiting misleading advertisements/ सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने भ्रामक विज्ञापनों पर रोक लगाने वाले प्रमुख नियम को हटाने वाली आयुष मंत्रालय की अधिसूचना पर रोक लगाई
Syllabus : GS 2 : Social Justice
Source : The Hindu
The Supreme Court of India stayed a notification issued by the Ministry of AYUSH in which Rule 170 of the Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945 was omitted.
- The Rule deals with the power to take action against objectionable or misleading advertisements about Ayurvedic, Siddha, and Unani drugs.
Drug Regulation in India:
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules 1945: These have entrusted various responsibilities to central and state regulators for regulation of drugs and cosmetics.
Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO):
- The CDSCO under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, is the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) of India.
Under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, CDSCO is responsible for –
- Approval of Drugs.
- Conduct of Clinical Trials.
- Laying down the standards for Drugs.
- Control over the quality of imported Drugs in the country.
- Coordination of the activities of State Drug Control Organisations.
- Further CDSCO along with state regulators, is jointly responsible for grant of licences of certain specialised categories of critical Drugs such as vaccine and sera, etc.
- The Indian government has announced plans to subject all medical devices, including implants and contraception, to CDSCO scrutiny.
Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI):
- DCGI is the head of department of the CDSCO responsible for approval of licences of specified categories of drugs such as blood and blood products, vaccines and sera, etc., in India.
- DCGI also sets standards for manufacturing, sales, import, and distribution of drugs in India.
About the Ayurveda, Siddha and Unani Drugs:
- Definition: The Drugs and Cosmetics Act 1940 defines Ayurvedic, Siddha, and Unani drugs as medicines that are used internally or externally to treat, prevent, mitigate, or diagnose diseases or disorders in humans or animals.
- Regulation:
- The act also establishes the Ayurvedic, Siddha, and Unani Drugs Technical Advisory Board (ASUDTAB), which sets the standards for these drugs.
- The Central Government can also make or change rules regarding these drugs after consulting with the board.
- Schedule T under Drugs and Cosmetics Act 1940: Schedule T describes the Good Manufacturing Practice for Ayurvedic, Siddha and Unani Medicines.
The SC’s Efforts to Protect Consumers from Being Trapped by Misleading Ads:
- In a contempt case against Patanjali Ayurved Limited, the SC (on May 7,2024) directed that advertisers should submit self-declarations that they are not misrepresenting or making false claims about products before promoting them in the media.
- However, the Ministry of AYUSH (on July 1, 2024) notified that Rule 170 of the Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945 was no longer operational.
- According to the ministry, the basis of this notification is a recommendation made by the ASUDTAB.
- In its recent order, the SC stays centre’s notification (dated July 1) to omit Rule 170 of the Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945, as it runs contrary to directions issued by this court.
सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने भ्रामक विज्ञापनों पर रोक लगाने वाले प्रमुख नियम को हटाने वाली आयुष मंत्रालय की अधिसूचना पर रोक लगाई
भारत के सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने आयुष मंत्रालय द्वारा जारी अधिसूचना पर रोक लगा दी है, जिसमें औषधि एवं प्रसाधन सामग्री नियम, 1945 के नियम 170 को हटा दिया गया था।
- यह नियम आयुर्वेदिक, सिद्ध और यूनानी दवाओं के बारे में आपत्तिजनक या भ्रामक विज्ञापनों के खिलाफ कार्रवाई करने की शक्ति से संबंधित है।
भारत में औषधि विनियमन:
- औषधि एवं प्रसाधन सामग्री अधिनियम, 1940 तथा नियम 1945: इनमें औषधियों एवं प्रसाधन सामग्री के विनियमन के लिए केंद्रीय एवं राज्य विनियामकों को विभिन्न जिम्मेदारियाँ सौंपी गई हैं।
केंद्रीय औषधि मानक नियंत्रण संगठन (CDSCO):
- स्वास्थ्य एवं परिवार कल्याण मंत्रालय के स्वास्थ्य सेवा महानिदेशालय के अधीन CDSCO भारत का राष्ट्रीय विनियामक प्राधिकरण (NRA) है।
औषधि एवं प्रसाधन सामग्री अधिनियम के अंतर्गत, CDSCO निम्नलिखित के लिए जिम्मेदार है –
- औषधियों की स्वीकृति।
- नैदानिक परीक्षणों का संचालन।
- औषधियों के लिए मानक निर्धारित करना।
- देश में आयातित औषधियों की गुणवत्ता पर नियंत्रण।
- राज्य औषधि नियंत्रण संगठनों की गतिविधियों का समन्वय।
- इसके अलावा, CDSCO राज्य विनियामकों के साथ मिलकर वैक्सीन और सीरम जैसी महत्वपूर्ण औषधियों की कुछ विशेष श्रेणियों के लाइसेंस प्रदान करने के लिए संयुक्त रूप से जिम्मेदार है।
- भारत सरकार ने प्रत्यारोपण और गर्भनिरोधक सहित सभी चिकित्सा उपकरणों को CDSCO जांच के दायरे में लाने की योजना की घोषणा की है।
भारतीय औषधि महानियंत्रक (DCGI):
- DCGI CDSCO का विभागाध्यक्ष है, जो भारत में रक्त और रक्त उत्पादों, टीकों और सीरम आदि जैसी दवाओं की निर्दिष्ट श्रेणियों के लाइसेंसों के अनुमोदन के लिए जिम्मेदार है।
- DCGI भारत में दवाओं के निर्माण, बिक्री, आयात और वितरण के लिए मानक भी निर्धारित करता है।
आयुर्वेद, सिद्ध और यूनानी दवाओं के बारे में:
- परिभाषा: औषधि और प्रसाधन सामग्री अधिनियम 1940 आयुर्वेदिक, सिद्ध और यूनानी दवाओं को ऐसी दवाओं के रूप में परिभाषित करता है, जिनका उपयोग मनुष्यों या पशुओं में बीमारियों या विकारों के उपचार, रोकथाम, शमन या निदान के लिए आंतरिक या बाह्य रूप से किया जाता है।
- विनियमन:
- अधिनियम आयुर्वेदिक, सिद्ध और यूनानी औषधि तकनीकी सलाहकार बोर्ड (ASUDTAB) की भी स्थापना करता है, जो इन दवाओं के लिए मानक निर्धारित करता है।
- केंद्र सरकार बोर्ड से परामर्श के बाद इन दवाओं के संबंध में नियम बना या बदल भी सकती है।
- औषधि और प्रसाधन सामग्री अधिनियम 1940 के तहत अनुसूची टी: अनुसूची टी आयुर्वेदिक, सिद्ध और यूनानी दवाओं के लिए अच्छे विनिर्माण अभ्यास का वर्णन करती है।
उपभोक्ताओं को भ्रामक विज्ञापनों के जाल में फंसने से बचाने के लिए सुप्रीम कोर्ट के प्रयास:
- पतंजलि आयुर्वेद लिमिटेड के खिलाफ अवमानना मामले में, सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने (7 मई, 2024 को) निर्देश दिया कि विज्ञापनदाताओं को मीडिया में उत्पादों का प्रचार करने से पहले स्व-घोषणा प्रस्तुत करनी चाहिए कि वे उत्पादों के बारे में गलत जानकारी नहीं दे रहे हैं या झूठे दावे नहीं कर रहे हैं।
- हालांकि, आयुष मंत्रालय ने (1 जुलाई, 2024 को) अधिसूचित किया कि औषधि और प्रसाधन सामग्री नियम, 1945 का नियम 170 अब लागू नहीं है।
- मंत्रालय के अनुसार, इस अधिसूचना का आधार ASUDTAB द्वारा की गई सिफारिश है।
- अपने हालिया आदेश में, सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने औषधि और प्रसाधन सामग्री नियम, 1945 के नियम 170 को हटाने के लिए केंद्र की अधिसूचना (दिनांक 1 जुलाई) पर रोक लगा दी, क्योंकि यह इस अदालत द्वारा जारी निर्देशों के विपरीत है।
The invisible lives of sanitation workers who clean Mumbai’s drains to keep them functional /मुंबई के नालों को साफ करने वाले सफाई कर्मचारियों की अदृश्य जिंदगी
Syllabus : GS 2 : Social Justice
Source : The Hindu
Sanitation workers in Mumbai face dangerous conditions cleaning stormwater drains, often manually handling sewage.
- Despite regulations against manual scavenging, workers remain unprotected due to gaps in recognition and enforcement.
- Seasonal migration and child labour further complicate their situation, with inadequate infrastructure and safety measures exacerbating their vulnerability.
Issues faced by sanitation workers:
- Hazardous Conditions: Sanitation workers are often required to clean stormwater drains and sewers manually, exposing them to toxic substances and unsafe conditions, including direct contact with sewage.
- Lack of Recognition: Manual scavenging in stormwater drains is not officially recognized, which prevents workers from receiving proper protections and benefits under laws prohibiting manual scavenging.
- Regulatory Gaps: Inadequate separation of sewers from stormwater drains results in the discharge of sewage into drains, increasing the risk and difficulty of sanitation work.
- Temporary Employment: Workers are often seasonal migrants, with unstable income and limited job security, exacerbating their vulnerability and lack of access to social protections.
- Inadequate Safety Measures: Despite regulations mandating safety gear, workers frequently work without proper protection, as enforcement of safety standards is insufficient.
- Generational Poverty: The sanitation work is often inherited across generations, trapping families in a cycle of poverty and limiting opportunities for upward mobility.
- Child Labour: Children from these communities are often involved in hazardous work, impacting their education and future prospects.
- Lack of Accountability: There is a lack of proper tracking and record-keeping, which hinders efforts to ensure fair treatment and rehabilitation of workers.
Way Forward:
- Enforce Safety Regulations: Strictly implement and monitor adherence to safety standards and provide necessary protective gear for workers.
- Acknowledge Manual Scavenging: Officially recognize manual scavenging in stormwater drains to ensure workers receive appropriate benefits and protections.
- Improve Infrastructure: Upgrade drainage systems to separate sewage from stormwater, reducing the risk and difficulty of cleaning tasks.
- Support Stable Employment: Provide stable and secure employment opportunities to migrant workers to reduce their economic vulnerability.
- Enhance Child Protection: Implement measures to prevent child labour and ensure access to education and support for affected children.
- Strengthen Record-Keeping: Establish comprehensive tracking systems for workers to ensure fair treatment and facilitate rehabilitation efforts.
मुंबई के नालों को साफ करने वाले सफाई कर्मचारियों की अदृश्य जिंदगी
मुंबई में सफाई कर्मचारियों को बरसाती नालों की सफाई करते समय खतरनाक परिस्थितियों का सामना करना पड़ता है, अक्सर उन्हें सीवेज को हाथ से साफ करना पड़ता है।
- हाथ से मैला ढोने के खिलाफ़ नियमों के बावजूद, मान्यता और प्रवर्तन में अंतराल के कारण कर्मचारी असुरक्षित रहते हैं।
- मौसमी प्रवास और बाल श्रम उनकी स्थिति को और जटिल बनाते हैं, अपर्याप्त बुनियादी ढाँचा और सुरक्षा उपाय उनकी कमज़ोरी को और बढ़ा देते हैं।
सफाई कर्मचारियों के सामने आने वाली समस्याएँ:
- खतरनाक परिस्थितियाँ: सफाई कर्मचारियों को अक्सर स्टॉर्मवॉटर नालियों और सीवरों को हाथ से साफ करना पड़ता है, जिससे उन्हें ज़हरीले पदार्थों और असुरक्षित परिस्थितियों का सामना करना पड़ता है, जिसमें सीवेज के साथ सीधा संपर्क भी शामिल है।
- मान्यता का अभाव: स्टॉर्मवॉटर नालियों में हाथ से मैला ढोने को आधिकारिक तौर पर मान्यता नहीं दी गई है, जो कर्मचारियों को हाथ से मैला ढोने पर रोक लगाने वाले कानूनों के तहत उचित सुरक्षा और लाभ प्राप्त करने से रोकता है।
- नियामक अंतराल: स्टॉर्मवॉटर नालियों से सीवरों के अपर्याप्त पृथक्करण के परिणामस्वरूप सीवेज नालियों में गिर जाता है, जिससे सफाई कार्य का जोखिम और कठिनाई बढ़ जाती है।
- अस्थायी रोजगार: कर्मचारी अक्सर मौसमी प्रवासी होते हैं, जिनकी आय अस्थिर होती है और नौकरी की सुरक्षा सीमित होती है, जिससे उनकी भेद्यता और सामाजिक सुरक्षा तक पहुँच की कमी बढ़ जाती है।
- अपर्याप्त सुरक्षा उपाय: सुरक्षा गियर को अनिवार्य करने वाले नियमों के बावजूद, कर्मचारी अक्सर उचित सुरक्षा के बिना काम करते हैं, क्योंकि सुरक्षा मानकों का प्रवर्तन अपर्याप्त है।
- पीढ़ीगत गरीबी: सफाई का काम अक्सर पीढ़ियों से विरासत में मिलता है, जिससे परिवार गरीबी के चक्र में फंस जाते हैं और ऊपर की ओर बढ़ने के अवसर सीमित हो जाते हैं।
- बाल श्रम: इन समुदायों के बच्चे अक्सर खतरनाक कामों में लगे रहते हैं, जिससे उनकी शिक्षा और भविष्य की संभावनाएं प्रभावित होती हैं।
- उत्तरदायित्व का अभाव: उचित ट्रैकिंग और रिकॉर्ड रखने का अभाव है, जो श्रमिकों के साथ उचित व्यवहार और पुनर्वास सुनिश्चित करने के प्रयासों में बाधा डालता है।
आगे का रास्ता:
- सुरक्षा विनियमन लागू करें: सुरक्षा मानकों के पालन को सख्ती से लागू करें और निगरानी करें तथा श्रमिकों के लिए आवश्यक सुरक्षात्मक गियर प्रदान करें।
- मैनुअल स्कैवेंजिंग को मान्यता दें: यह सुनिश्चित करने के लिए कि श्रमिकों को उचित लाभ और सुरक्षा मिले, तूफानी नालों में मैनुअल स्कैवेंजिंग को आधिकारिक रूप से मान्यता दें।
- बुनियादी ढांचे में सुधार करें: सीवेज को तूफानी पानी से अलग करने के लिए जल निकासी प्रणालियों को अपग्रेड करें, जिससे सफाई कार्यों के जोखिम और कठिनाई को कम किया जा सके।
- स्थिर रोजगार का समर्थन करें: प्रवासी श्रमिकों को उनकी आर्थिक कमजोरी को कम करने के लिए स्थिर और सुरक्षित रोजगार के अवसर प्रदान करें।
- बाल संरक्षण को बढ़ावा दें: बाल श्रम को रोकने के उपायों को लागू करें और प्रभावित बच्चों के लिए शिक्षा और सहायता तक पहुँच सुनिश्चित करें।
- रिकॉर्ड-कीपिंग को मजबूत करें: श्रमिकों के लिए उचित व्यवहार सुनिश्चित करने और पुनर्वास प्रयासों को सुविधाजनक बनाने के लिए व्यापक ट्रैकिंग सिस्टम स्थापित करें।
On SEBI chairperson’s conflicts of interests / सेबी अध्यक्ष के हितों के टकराव पर
Syllabus : GS 2 & 4 : Governance & Ethics
Source : The Hindu
Hindenburg Research’s report exposed conflicts of interest involving SEBI Chairperson Madhabi Buch, including investments in an offshore fund linked to Adani Enterprises and ownership of a consulting firm active during her SEBI tenure.
- These revelations raise concerns about SEBI’s integrity and its handling of investigations, notably into the Adani group.
Conflict of Interest for SEBI Chief:
- Investment in Offshore Fund: Madhabi Buch and Dhaval Buch invested over ₹5.6 crore in Bermuda-based Global Dynamic Opportunities Fund in 2015, managed by Anil Ahuja, an Adani Enterprises director at the time. Buch redeemed this investment in 2018 while serving as a SEBI member.
- Undisclosed Holdings: Madhabi Buch owned 99% of Agora Advisory Private Limited, which remained active and profitable during her SEBI tenure, violating SEBI’s conflict of interest code.
- Promotion of REITs: Buch’s husband works for Blackstone, benefiting from SEBI’s favourable decisions on Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), raising concerns about preferential treatment.
Issues:
- Potential lack of transparency and regulatory integrity.
- Questions on SEBI’s role in the Adani group investigation.
- Violation of SEBI’s conflict of interest rules by the chairperson.
Conflict Of Interest In Governance:
- Definition: Conflict of interest in governance occurs when an individual’s personal interests or relationships could improperly influence their official duties, leading to biassed decisions or actions.
Importance for Civil Servants to Avoid:
- Maintains Integrity: Ensures that decisions are made based on fairness and merit, not personal gain or relationships.
- Builds Public Trust: Upholds the credibility and trustworthiness of public institutions and their representatives.
- Prevents Corruption: Reduces the risk of corrupt practices and unfair advantages in public administration.
- Legal Compliance: Adheres to ethical standards and legal requirements set for public servants.
- Promotes Accountability: Facilitates a clear accountability mechanism, where actions and decisions can be scrutinised without bias or personal interest.
Ways to Avoid Conflict of Interest in Civil Service:
- Disclosure: Regularly disclose any personal, financial, or familial interests that might influence decision-making.
- Recusal: Abstain from participating in decisions or processes where a conflict of interest is present.
- Ethics Training: Participate in ongoing ethics and compliance training to understand and manage potential conflicts.
- Transparency: Ensure all decisions and actions are transparent and well-documented to prevent perceptions of bias.
- Clear Guidelines: Follow established codes of conduct and conflict-of-interest guidelines specific to the civil service.
- Third-Party Review: Seek advice from ethics committees or independent reviewers to handle potential conflicts appropriately.
सेबी अध्यक्ष के हितों के टकराव पर
हिंडनबर्ग रिसर्च की रिपोर्ट ने सेबी की चेयरपर्सन माधबी बुच से जुड़े हितों के टकराव को उजागर किया है, जिसमें अडानी एंटरप्राइजेज से जुड़े एक ऑफशोर फंड में निवेश और सेबी में उनके कार्यकाल के दौरान सक्रिय एक कंसल्टिंग फर्म का स्वामित्व शामिल है।
- ये खुलासे सेबी की ईमानदारी और जांच के संचालन, खासकर अडानी समूह के बारे में चिंता पैदा करते हैं।
सेबी प्रमुख के लिए हितों का टकराव:
- ऑफशोर फंड में निवेश: माधबी बुच और धवल बुच ने 2015 में बरमूडा स्थित ग्लोबल डायनेमिक ऑपर्च्युनिटीज फंड में 6 करोड़ रुपये से अधिक का निवेश किया था, जिसका प्रबंधन उस समय अदानी एंटरप्राइजेज के निदेशक अनिल आहूजा द्वारा किया जाता था। बुच ने सेबी सदस्य के रूप में कार्य करते हुए 2018 में इस निवेश को भुनाया।
- अघोषित होल्डिंग्स: माधबी बुच के पास अगोरा एडवाइजरी प्राइवेट लिमिटेड का 99% स्वामित्व था, जो सेबी के हितों के टकराव कोड का उल्लंघन करते हुए सेबी के उनके कार्यकाल के दौरान सक्रिय और लाभदायक रहा।
- आरईआईटी का प्रचार: बुच के पति ब्लैकस्टोन के लिए काम करते हैं, जो रियल एस्टेट इन्वेस्टमेंट ट्रस्ट (आरईआईटी) पर सेबी के अनुकूल निर्णयों से लाभान्वित होते हैं, जिससे तरजीही उपचार के बारे में चिंताएँ बढ़ जाती हैं।
मुद्दे:
- पारदर्शिता और विनियामक अखंडता की संभावित कमी।
- अडानी समूह की जाँच में सेबी की भूमिका पर सवाल।
- अध्यक्ष द्वारा सेबी के हितों के टकराव के नियमों का उल्लंघन।
शासन में हितों का टकराव:
- परिभाषा: शासन में हितों का टकराव तब होता है जब किसी व्यक्ति के व्यक्तिगत हित या संबंध उसके आधिकारिक कर्तव्यों को अनुचित तरीके से प्रभावित कर सकते हैं, जिससे पक्षपातपूर्ण निर्णय या कार्य हो सकते हैं।
सिविल सेवकों के लिए बचने का महत्व:
- ईमानदारी बनाए रखना: यह सुनिश्चित करना कि निर्णय निष्पक्षता और योग्यता के आधार पर किए जाएं, न कि व्यक्तिगत लाभ या संबंधों के आधार पर।
- सार्वजनिक विश्वास का निर्माण: सार्वजनिक संस्थानों और उनके प्रतिनिधियों की विश्वसनीयता और भरोसेमंदता को बनाए रखना।
- भ्रष्टाचार को रोकना: सार्वजनिक प्रशासन में भ्रष्ट प्रथाओं और अनुचित लाभों के जोखिम को कम करना।
- कानूनी अनुपालन: लोक सेवकों के लिए निर्धारित नैतिक मानकों और कानूनी आवश्यकताओं का पालन करना।
- जवाबदेही को बढ़ावा देना: एक स्पष्ट जवाबदेही तंत्र की सुविधा प्रदान करना, जहाँ बिना किसी पक्षपात या व्यक्तिगत हित के कार्यों और निर्णयों की जाँच की जा सकती है।
सिविल सेवा में हितों के टकराव से बचने के तरीके:
- प्रकटीकरण: नियमित रूप से किसी भी व्यक्तिगत, वित्तीय या पारिवारिक हितों का खुलासा करें जो निर्णय लेने को प्रभावित कर सकते हैं।
- अलग होना: ऐसे निर्णयों या प्रक्रियाओं में भाग लेने से दूर रहें जहाँ हितों का टकराव मौजूद हो।
- नैतिकता प्रशिक्षण: संभावित संघर्षों को समझने और प्रबंधित करने के लिए चल रहे नैतिकता और अनुपालन प्रशिक्षण में भाग लें।
- पारदर्शिता: सुनिश्चित करें कि सभी निर्णय और कार्य पारदर्शी हों और पक्षपात की धारणा को रोकने के लिए अच्छी तरह से प्रलेखित हों।
- स्पष्ट दिशा-निर्देश: सिविल सेवा के लिए विशिष्ट आचार संहिता और हितों के टकराव संबंधी दिशा-निर्देशों का पालन करें।
- तीसरे पक्ष की समीक्षा: संभावित संघर्षों को उचित तरीके से संभालने के लिए नैतिकता समितियों या स्वतंत्र समीक्षकों से सलाह लें।
OPEC+ output cut may push Indian refiners to source oil from Americas / ओपेक+ उत्पादन में कटौती से भारतीय रिफाइनर अमेरिका से तेल मंगाने पर मजबूर हो सकते हैं
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
India’s rising liquid fuel consumption, expected to reach 6.6 million barrels per day by 2028.
- Alongside the decrease in crude oil exports from West Asia due to OPEC+ production cuts, Indian refiners might turn to alternative sources from the Americas.
- With West Asia’s share of imports dropping and increasing non-OPEC+ production from countries like the U.S., Brazil, Guyana, and Canada, India is likely to diversify its crude oil sources.
Key Differences Between OPEC and OPEC+:
- Formation: OPEC was formed in 1960 by Iraq, Iran, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela. OPEC+ was established in 2016, including 10 non-OPEC oil producers such as Russia.
- Members: OPEC has 13 member countries. OPEC+ extends beyond OPEC to include additional countries like Russia, expanding its influence.
- Objectives: OPEC’s primary goal is to coordinate petroleum policies among member countries. OPEC+ aims to include both OPEC and non-OPEC producers in managing oil production and prices.
- Production Control: OPEC sets production targets solely for its members. OPEC+ coordinates production targets among both OPEC and non-OPEC countries, including major producers like Russia.
- Market Influence: OPEC+ controls a larger share of global oil production (about 59% in 2022) compared to OPEC alone, enhancing its impact on global oil prices.
ओपेक+ उत्पादन में कटौती से भारतीय रिफाइनर अमेरिका से तेल मंगाने पर मजबूर हो सकते हैं
- भारत में तरल ईंधन की खपत बढ़ रही है, जिसके 2028 तक 6 मिलियन बैरल प्रतिदिन तक पहुंचने की उम्मीद है।
- ओपेक+ के उत्पादन में कटौती के कारण पश्चिम एशिया से कच्चे तेल के निर्यात में कमी के साथ-साथ, भारतीय रिफाइनर अमेरिका से वैकल्पिक स्रोतों की ओर रुख कर सकते हैं।
- पश्चिम एशिया के आयात में हिस्सेदारी घटने और अमेरिका, ब्राजील, गुयाना और कनाडा जैसे देशों से गैर-ओपेक+ उत्पादन बढ़ने के साथ, भारत अपने कच्चे तेल के स्रोतों में विविधता लाने की संभावना है।
ओपेक और ओपेक+ के बीच मुख्य अंतर:
- गठन: ओपेक का गठन 1960 में इराक, ईरान, कुवैत, सऊदी अरब और वेनेजुएला द्वारा किया गया था। ओपेक+ की स्थापना 2016 में हुई थी, जिसमें रूस जैसे 10 गैर-ओपेक तेल उत्पादक शामिल थे।
- सदस्य: ओपेक के 13 सदस्य देश हैं। ओपेक+ ओपेक से आगे बढ़कर रूस जैसे अतिरिक्त देशों को शामिल करता है, जिससे इसका प्रभाव बढ़ता है।
- उद्देश्य: ओपेक का प्राथमिक लक्ष्य सदस्य देशों के बीच पेट्रोलियम नीतियों का समन्वय करना है। ओपेक+ का लक्ष्य तेल उत्पादन और कीमतों के प्रबंधन में ओपेक और गैर-ओपेक दोनों उत्पादकों को शामिल करना है।
- उत्पादन नियंत्रण: ओपेक केवल अपने सदस्यों के लिए उत्पादन लक्ष्य निर्धारित करता है। ओपेक+ रूस जैसे प्रमुख उत्पादकों सहित ओपेक और गैर-ओपेक दोनों देशों के बीच उत्पादन लक्ष्यों का समन्वय करता है।
- बाजार प्रभाव: ओपेक+ अकेले ओपेक की तुलना में वैश्विक तेल उत्पादन (2022 में लगभग 59%) का बड़ा हिस्सा नियंत्रित करता है, जिससे वैश्विक तेल कीमतों पर इसका प्रभाव बढ़ता है।
Chile’s Atacama Salt Flat sinking due to Lithium Mining / लिथियम खनन के कारण चिली का अटाकामा साल्ट फ्लैट डूब रहा है
Location In News
A recent study published in journal IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing has found that Chile’s Atacama salt flat (Salar de Atacama) is sinking at a rate of 1 to 2 centimetres per year due to lithium brine extraction.
- Lithium brine extraction involves pumping salt-rich water to the surface and letting it evaporate in ponds to collect lithium.
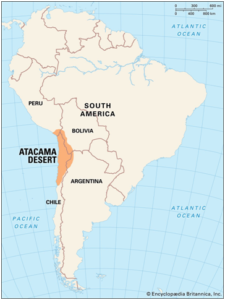
About Salar de Atacama
- The Salar de Atacama in Chile boasts the highest lithium concentration (0.15% by weight) among all brine sources worldwide.
- Argentina boasts more than half of the world’s total lithium resources.
- It holds the distinction of having the 2nd-largest lithium resources, the 3rd-largest lithium reserves, and the 4th-largest lithium production in the world.
- It is a part of the Lithium Triangle comprising of Uyuni (Bolivia) and Hombre Muerto (Argentina).
Key Findings of the Study:
- Researchers analyzed satellite data from 2020 to 2023 to observe deformations in the Earth’s crust in the salt flat.
- The area experiencing subsidence measures approximately 8 km north to south and 5 km east to west.
- The study indicates that subsidence occurs because the rate of lithium brine pumping is faster than the recharge rate of aquifers, leading to the ground sinking.
What is Lithium?
- Lithium is an alkali metal, often referred to as ‘white gold’ due to its value and color.
- It is a soft, silvery-white metal, and notably, it is the lightest metal on the periodic table.
- It is typically found in various minerals like spodumene, petalite, and lepidolite, from which it is extracted and refined.
- The leading producers of lithium are Australia, Chile, China, and Argentina.
Effects of Lithium Mining on Environment:
- Water Use: Lithium mining, especially from salt flats and brine pools, requires substantial water usage, which can deplete local water resources in arid areas.
- Ecological Disruption: The extraction process can alter the chemical balance of the natural environment, affecting local flora and fauna.
- Pollution: Mining and processing lithium can release harmful chemicals into the environment, impacting air and water quality.
लिथियम खनन के कारण चिली का अटाकामा साल्ट फ्लैट डूब रहा है
जर्नल IEEE ट्रांजेक्शन ऑन जियोसाइंस एंड रिमोट सेंसिंग में प्रकाशित एक हालिया अध्ययन में पाया गया है कि चिली का अटाकामा साल्ट फ्लैट (सालार डी अटाकामा) लिथियम ब्राइन निष्कर्षण के कारण प्रति वर्ष 1 से 2 सेंटीमीटर की दर से डूब रहा है।
- लिथियम ब्राइन निष्कर्षण में नमक युक्त पानी को सतह पर पंप करना और लिथियम एकत्र करने के लिए तालाबों में वाष्पित होने देना शामिल है।
सालार डी अटाकामा के बारे में
- चिली में सालार डी अटाकामा दुनिया भर के सभी ब्राइन स्रोतों में सबसे अधिक लिथियम सांद्रता (वजन के हिसाब से 15%) का दावा करता है।
- अर्जेंटीना में दुनिया के कुल लिथियम संसाधनों का आधे से अधिक हिस्सा है।
- यह दुनिया में दूसरे सबसे बड़े लिथियम संसाधन, तीसरे सबसे बड़े लिथियम भंडार और चौथे सबसे बड़े लिथियम उत्पादन का गौरव रखता है।
- यह उयूनी (बोलीविया) और होम्ब्रे मुएर्टो (अर्जेंटीना) से मिलकर बने लिथियम त्रिभुज का एक हिस्सा है।
अध्ययन के मुख्य निष्कर्ष:
- शोधकर्ताओं ने नमक के मैदान में पृथ्वी की पपड़ी में विकृतियों का निरीक्षण करने के लिए 2020 से 2023 तक के उपग्रह डेटा का विश्लेषण किया।
- अवसादन का अनुभव करने वाला क्षेत्र उत्तर से दक्षिण तक लगभग 8 किमी और पूर्व से पश्चिम तक 5 किमी तक फैला हुआ है।
- अध्ययन से संकेत मिलता है कि अवसादन इसलिए होता है क्योंकि लिथियम ब्राइन पंपिंग की दर एक्वीफ़र्स की रिचार्ज दर से तेज़ होती है, जिससे ज़मीन धंस जाती है।
लिथियम क्या है?
- लिथियम एक क्षारीय धातु है, जिसे अक्सर इसके मूल्य और रंग के कारण ‘सफेद सोना’ कहा जाता है।
- यह एक नरम, चांदी जैसी सफ़ेद धातु है और विशेष रूप से, यह आवर्त सारणी की सबसे हल्की धातु है।
- यह आमतौर पर स्पोड्यूमिन, पेटालाइट और लेपिडोलाइट जैसे विभिन्न खनिजों में पाया जाता है, जिनसे इसे निकाला और परिष्कृत किया जाता है।
- लिथियम के प्रमुख उत्पादक ऑस्ट्रेलिया, चिली, चीन और अर्जेंटीना हैं।
पर्यावरण पर लिथियम खनन के प्रभाव:
- जल उपयोग: लिथियम खनन, विशेष रूप से नमक के मैदानों और नमकीन पानी के तालाबों से, पानी के पर्याप्त उपयोग की आवश्यकता होती है, जो शुष्क क्षेत्रों में स्थानीय जल संसाधनों को समाप्त कर सकता है।
- पारिस्थितिक व्यवधान: निष्कर्षण प्रक्रिया प्राकृतिक पर्यावरण के रासायनिक संतुलन को बदल सकती है, जिससे स्थानीय वनस्पतियों और जीवों पर असर पड़ सकता है।
- प्रदूषण: लिथियम का खनन और प्रसंस्करण पर्यावरण में हानिकारक रसायन छोड़ सकता है, जिससे हवा और पानी की गुणवत्ता प्रभावित होती है।
Advancing equity, from COVID-19 to Mpox / कोविड-19 से लेकर एमपॉक्स तक इक्विटी को आगे बढ़ाना
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 : Social Justice
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- This article discusses the global response to the mpox (formerly monkeypox) outbreak, which has been declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) by the WHO.
- It emphasises the importance of international cooperation, vaccine production, equitable access, and the role of technology transfers to address the crisis effectively.
Public Health Emergency
- Less than five years after the COVID-19 pandemic, the world faces a new threat as the World Health Organization (WHO) declares mpox (formerly monkeypox) a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC).
- The outbreak began in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and has spread to over a dozen African countries. Cases have also been reported in Sweden, Pakistan, and the Philippines, indicating global transmission.
- This declaration follows the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention’s (AfricaCDC) declaration of a Public Health Emergency of Continental Security (PHECS), marking the first instance where both regional and global health emergencies have been declared for the same disease.
Role of WHO in Post-2024 IHR Amendments
- This is the first PHEIC declared since the May 2024 amendments to the International Health Regulations (IHR), emphasising equity as a core principle, although these reforms take effect in 2025.
- WHO’s role as a facilitator of essential medical products during emergencies will be expanded, and the global response to mpox must align with these values.
Significance of International Cooperation
- A PHEIC declaration is meant to foster collaboration among countries, international organisations, and non-governmental entities.
- This triggers the rapid mobilisation of financial and technical resources, including emergency funding, medical supplies, and deployment of health-care workers.
Vaccine Availability and the Mpox Response
- One critical difference between the mpox outbreak and COVID-19 is the availability of a vaccine.
- The Modified Vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN), also known as Jynneos, is already in production.
- Regulatory authorities in the EU, UK, US, Switzerland, and Canada have approved the MVA-BN vaccine.
- Indian manufacturers are positioned to play a vital role in producing and distributing the vaccine, similar to their contributions during the COVID-19 pandemic with the production of Covishield.
Addressing Vaccine Production Challenges
- The AfricaCDC estimates a need for 10 million doses of the vaccine to combat the outbreak, but only 0.21 million doses are currently available. Bavarian Nordic has the capacity to manufacture 10 million doses by the end of 2025.
- Indian manufacturers like the Serum Institute of India, Bharat Biotech, and Zydus Cadila have the expertise to scale up vaccine production.
- Expanding production will require technology transfers and the sharing of patents, biological resources, and crucial know-how.
The Role of Technology Transfers
- Comprehensive technology transfers are vital for scaling up production, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), ensuring they are not reliant on “charity” from wealthier nations.
- India’s government should negotiate with Bavarian Nordic and collaborate with international organisations like WHO, Gavi, and CEPI to facilitate the transfer of technology and manufacturing capabilities.
- On August 7, India’s drug regulatory agency, CDSCO, waived the requirement for clinical trials for drugs and vaccines approved in countries like the US, UK, and EU, which will expedite the availability of critical vaccines like MVA-BN in India.
Conclusion
- The global response to the mpox outbreak presents an opportunity to demonstrate a commitment to equitable health care by ensuring widespread vaccine access, especially to those most in need.
- Prioritising technology transfers and leveraging India’s manufacturing capabilities will help prevent further outbreaks and strengthen preparedness for future public health emergencies.
Major Learnings from the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Vaccine Manufacturing Capabilities: The COVID-19 pandemic exposed significant gaps in vaccine manufacturing capabilities, particularly in the Global South. This inadequacy was exacerbated by limited technology transfers and a lack of know-how to produce vaccines developed in high-income countries.
- The current response to the Mpox outbreak reflects similar challenges, emphasizing the need for robust local manufacturing capabilities to ensure equitable access to vaccines.
- Global Cooperation: The pandemic underscored the necessity of international collaboration in health emergencies. The WHO’s declaration of Mpox as a PHEIC aims to foster this cooperation, encouraging countries and organizations to share information and resources to combat the outbreak.
- Equity in Health Responses: The recent amendments to the International Health Regulations (IHR) include equity as a core principle, which is crucial for ensuring that all countries, particularly those in lower-middle-income regions, have access to essential medical products during emergencies.
About Mpox
- Mpox, also known as monkeypox, is a DNA virus. It belongs to the family Poxviridae, which consists of large, double-stranded DNA viruses.
- The virus was first identified in monkeys in 1958 but has since been found to infect humans as well.
- Transmission: Mpox is primarily transmitted to humans from animals, particularly rodents and primates, through direct contact or through contaminated objects.
- Symptoms: Mpox infection in humans typically presents with fever, headache, muscle aches, and a characteristic rash that progresses from macules to papules to vesicles and pustules.
- Vaccination: While a vaccine for mpox exists, its availability and effectiveness are limited, highlighting the need for improved prevention and control measures.
Difference Between Small Pox, Chicken Pox, Mpox
| Feature | Smallpox | Monkeypox | Chickenpox |
| Virus | Variola virus | Monkeypox virus | Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) |
| Severity | Highly severe, often fatal | Milder than smallpox, rarely fatal | Mild |
| Status | Eradicated in 1980 | Endemic in Central and West Africa, cases emerging elsewhere | Common childhood illness, less common due to vaccination |
| Transmission | Highly contagious through respiratory droplets and contact with infected lesions | Spread through contact with infected animals, lesions, or bodily fluids | Highly contagious through respiratory droplets and contact with lesions |
| Symptoms | Fever, headache, severe fatigue, vomiting, followed by a deep-seated, pus-filled rash | Fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, followed by a rash that progresses through stages | Fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, followed by an itchy, fluid-filled rash |
| Vaccination | No longer needed | Not routinely recommended, may be given to high-risk individuals | Routine vaccination for children and adults who haven’t had chickenpox |
कोविड-19 से लेकर एमपॉक्स तक इक्विटी को आगे बढ़ाना
संदर्भ:
- यह लेख एमपॉक्स (पूर्व में मंकीपॉक्स) प्रकोप के प्रति वैश्विक प्रतिक्रिया पर चर्चा करता है, जिसे डब्ल्यूएचओ द्वारा अंतर्राष्ट्रीय चिंता का सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य आपातकाल (पीएचईआईसी) घोषित किया गया है।
- यह संकट को प्रभावी ढंग से संबोधित करने के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग, वैक्सीन उत्पादन, न्यायसंगत पहुंच और प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण की भूमिका के महत्व पर जोर देता है।
सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य आपातकाल
- कोविड-19 महामारी के पांच साल से भी कम समय बाद, दुनिया एक नए खतरे का सामना कर रही है क्योंकि विश्व स्वास्थ्य संगठन (डब्ल्यूएचओ) ने एमपॉक्स (पूर्व में मंकीपॉक्स) को अंतर्राष्ट्रीय चिंता का सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य आपातकाल (पीएचईआईसी) घोषित किया है।
- यह प्रकोप कांगो लोकतांत्रिक गणराज्य (डीआरसी) में शुरू हुआ और एक दर्जन से अधिक अफ्रीकी देशों में फैल गया है। स्वीडन, पाकिस्तान और फिलीपींस में भी मामले सामने आए हैं, जो वैश्विक संचरण का संकेत देते हैं।
- यह घोषणा अफ्रीका रोग नियंत्रण और रोकथाम केंद्र (अफ्रीकासीडीसी) द्वारा महाद्वीपीय सुरक्षा के सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य आपातकाल (पीएचईसीएस) की घोषणा के बाद की गई है, जो पहला ऐसा उदाहरण है जहां एक ही बीमारी के लिए क्षेत्रीय और वैश्विक स्वास्थ्य आपातकाल दोनों घोषित किए गए हैं।
2024 के बाद के IHR संशोधनों में WHO की भूमिका
- यह मई 2024 में अंतर्राष्ट्रीय स्वास्थ्य विनियमों (IHR) में संशोधन के बाद घोषित किया गया पहला PHEIC है, जिसमें समानता को एक मुख्य सिद्धांत के रूप में महत्व दिया गया है, हालाँकि ये सुधार 2025 में प्रभावी होंगे।
- आपात स्थितियों के दौरान आवश्यक चिकित्सा उत्पादों के सुविधाकर्ता के रूप में WHO की भूमिका का विस्तार किया जाएगा, और mpox के लिए वैश्विक प्रतिक्रिया को इन मूल्यों के अनुरूप होना चाहिए।
अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग का महत्व
- PHEIC घोषणा का उद्देश्य देशों, अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठनों और गैर-सरकारी संस्थाओं के बीच सहयोग को बढ़ावा देना है।
- इससे आपातकालीन निधि, चिकित्सा आपूर्ति और स्वास्थ्य सेवा कर्मियों की तैनाती सहित वित्तीय और तकनीकी संसाधनों का तेजी से जुटाव होता है।
टीका उपलब्धता और Mpox प्रतिक्रिया
- mpox प्रकोप और COVID-19 के बीच एक महत्वपूर्ण अंतर वैक्सीन की उपलब्धता है।
- संशोधित वैक्सीनिया अंकारा-बवेरियन नॉर्डिक (MVA-BN), जिसे जिनेओस के नाम से भी जाना जाता है, पहले से ही उत्पादन में है।
- यूरोपीय संघ, ब्रिटेन, अमेरिका, स्विटजरलैंड और कनाडा के विनियामक प्राधिकरणों ने एमवीए-बीएन वैक्सीन को मंजूरी दे दी है।
- भारतीय निर्माता वैक्सीन के उत्पादन और वितरण में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाने की स्थिति में हैं, ठीक उसी तरह जैसे कोविड-19 महामारी के दौरान कोविशील्ड के उत्पादन में उनके योगदान ने किया था।
वैक्सीन उत्पादन चुनौतियों का समाधान
- अफ्रीकासीडीसी का अनुमान है कि प्रकोप से निपटने के लिए वैक्सीन की 10 मिलियन खुराक की आवश्यकता है, लेकिन वर्तमान में केवल 21 मिलियन खुराक ही उपलब्ध हैं। बवेरियन नॉर्डिक के पास 2025 के अंत तक 10 मिलियन खुराक बनाने की क्षमता है।
- सीरम इंस्टीट्यूट ऑफ इंडिया, भारत बायोटेक और ज़ाइडस कैडिला जैसे भारतीय निर्माताओं के पास वैक्सीन उत्पादन को बढ़ाने की विशेषज्ञता है।
- उत्पादन का विस्तार करने के लिए प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण और पेटेंट, जैविक संसाधनों और महत्वपूर्ण जानकारी को साझा करने की आवश्यकता होगी।
प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण की भूमिका
- उत्पादन को बढ़ाने के लिए व्यापक प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण महत्वपूर्ण हैं, विशेष रूप से निम्न और मध्यम आय वाले देशों (एलएमआईसी) में, यह सुनिश्चित करते हुए कि वे अमीर देशों से “दान” पर निर्भर न हों।
- भारत सरकार को बवेरियन नॉर्डिक के साथ बातचीत करनी चाहिए और प्रौद्योगिकी और विनिर्माण क्षमताओं के हस्तांतरण को सुविधाजनक बनाने के लिए डब्ल्यूएचओ, गावी और सीईपीआई जैसे अंतरराष्ट्रीय संगठनों के साथ सहयोग करना चाहिए।
- 7 अगस्त को, भारत की दवा नियामक एजेंसी, सीडीएससीओ ने अमेरिका, ब्रिटेन और यूरोपीय संघ जैसे देशों में स्वीकृत दवाओं और टीकों के लिए नैदानिक परीक्षणों की आवश्यकता को माफ कर दिया, जिससे भारत में एमवीए-बीएन जैसे महत्वपूर्ण टीकों की उपलब्धता में तेजी आएगी।
निष्कर्ष
- एमपॉक्स प्रकोप के लिए वैश्विक प्रतिक्रिया व्यापक वैक्सीन पहुंच सुनिश्चित करके न्यायसंगत स्वास्थ्य देखभाल के प्रति प्रतिबद्धता प्रदर्शित करने का अवसर प्रस्तुत करती है, खासकर उन लोगों के लिए जिन्हें इसकी सबसे अधिक आवश्यकता है।
- प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण को प्राथमिकता देना और भारत की विनिर्माण क्षमताओं का लाभ उठाना आगे के प्रकोपों को रोकने और भविष्य की सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य आपात स्थितियों के लिए तैयारियों को मजबूत करने में मदद करेगा।
कोविड-19 महामारी से प्रमुख सीख
- वैक्सीन निर्माण क्षमताएँ: कोविड-19 महामारी ने वैक्सीन निर्माण क्षमताओं में महत्वपूर्ण अंतराल को उजागर किया, विशेष रूप से वैश्विक दक्षिण में। सीमित प्रौद्योगिकी हस्तांतरण और उच्च आय वाले देशों में विकसित टीकों का उत्पादन करने की जानकारी की कमी के कारण यह अपर्याप्तता और बढ़ गई।
- एमपॉक्स प्रकोप के प्रति वर्तमान प्रतिक्रिया समान चुनौतियों को दर्शाती है, जो टीकों तक समान पहुँच सुनिश्चित करने के लिए मजबूत स्थानीय विनिर्माण क्षमताओं की आवश्यकता पर बल देती है।
- वैश्विक सहयोग: महामारी ने स्वास्थ्य आपात स्थितियों में अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग की आवश्यकता को रेखांकित किया है। डब्ल्यूएचओ द्वारा एमपॉक्स को एक पीएचईआईसी के रूप में घोषित करने का उद्देश्य इस सहयोग को बढ़ावा देना है, जिससे देशों और संगठनों को प्रकोप से निपटने के लिए जानकारी और संसाधन साझा करने के लिए प्रोत्साहित किया जा सके।
- स्वास्थ्य प्रतिक्रियाओं में समानता: अंतर्राष्ट्रीय स्वास्थ्य विनियमन (IHR) में हाल ही में किए गए संशोधनों में समानता को एक मुख्य सिद्धांत के रूप में शामिल किया गया है, जो यह सुनिश्चित करने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है कि सभी देश, विशेष रूप से निम्न-मध्यम आय वाले क्षेत्रों में, आपात स्थिति के दौरान आवश्यक चिकित्सा उत्पादों तक पहुँच हो।
Mpox के बारे में
- Mpox, जिसे मंकीपॉक्स के नाम से भी जाना जाता है, एक DNA वायरस है। यह Poxviridae परिवार से संबंधित है, जिसमें बड़े, दोहरे स्ट्रैंड वाले DNA वायरस होते हैं।
- इस वायरस की पहचान सबसे पहले 1958 में बंदरों में की गई थी, लेकिन तब से यह मनुष्यों को भी संक्रमित करता पाया गया है।
- संचरण: Mpox मुख्य रूप से जानवरों, विशेष रूप से कृन्तकों और प्राइमेट्स से, सीधे संपर्क या दूषित वस्तुओं के माध्यम से मनुष्यों में फैलता है।
- लक्षण: मनुष्यों में Mpox संक्रमण आमतौर पर बुखार, सिरदर्द, मांसपेशियों में दर्द और एक विशिष्ट दाने के साथ होता है जो मैक्यूल से पपल्स और फिर पुटिकाओं और फुंसियों में बदल जाता है।
- टीकाकरण: यद्यपि एमपॉक्स के लिए टीका उपलब्ध है, लेकिन इसकी उपलब्धता और प्रभावशीलता सीमित है, जिससे बेहतर रोकथाम और नियंत्रण उपायों की आवश्यकता पर प्रकाश पड़ता है।
स्मॉल पॉक्स, चिकन पॉक्स, एमपॉक्स के बीच अंतर
| विशेषता | चेचक | मंकीपॉक्स | चिकनपॉक्स |
| वायरस | वैरियोला वायरस | मंकीपॉक्स वायरस | वैरिसेला-ज़ोस्टर वायरस (VZV) |
| गंभीरता | अत्यधिक गंभीर, अक्सर घातक | चेचक से हल्का, शायद ही कभी घातक | हल्का |
| स्थिति | 1980 में समाप्त | मध्य और पश्चिमी अफ्रीका में स्थानिक, अन्य जगहों पर मामले सामने आ रहे हैं | बचपन में होने वाली आम बीमारी, टीकाकरण के कारण कम आम |
| संक्रमण | श्वसन की बूंदों और संक्रमित घावों के संपर्क से अत्यधिक संक्रामक | संक्रमित जानवरों, घावों या शारीरिक तरल पदार्थों के संपर्क से फैलता है | सांस की बूंदों और घावों के संपर्क से अत्यधिक संक्रामक |
| लक्षण | बुखार, सिरदर्द, गंभीर थकान, उल्टी, उसके बाद गहरे बैठे, मवाद से भरे दाने | बुखार, सिरदर्द, सूजे हुए लिम्फ नोड्स, उसके बाद दाने जो चरणों में आगे बढ़ते हैं | बुखार, थकान, भूख न लगना, उसके बाद खुजली, तरल पदार्थ से भरा दाने |
| टीकाकरण | अब इसकी ज़रूरत नहीं | नियमित रूप से अनुशंसित नहीं है, उच्च जोखिम वाले व्यक्तियों को दिया जा सकता है | बच्चों और वयस्कों के लिए नियमित टीकाकरण जिन्हें चिकनपॉक्स नहीं हुआ है |
Association of Southeast Asian Nations : International Organizations / दक्षिण पूर्व एशियाई राष्ट्र संघ : अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठन
What is ASEAN?
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a regional association that was founded to maintain social stability and political equilibrium among Asia’s post-colonial states amid escalating conflicts.
- “One Vision, One Identity, One Community” is its motto. The 8th of August is celebrated as the ASEAN Day. The ASEAN Secretariat is based in Jakarta, Indonesia.
Origin of ASEAN
- The ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) was signed by the original members of the organization in 1967.
- Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand are the originating members of ASEAN.
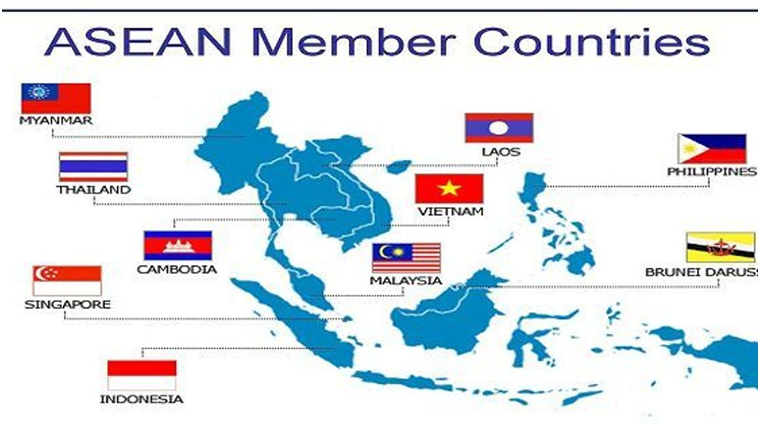
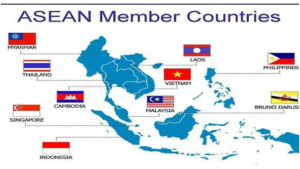
Members of the ASEAN
- ASEAN consists of ten member countries. The ASEAN countries list include the following:
- Thailand
- Singapore
- Vietnam
- Laos
- Indonesia
- Myanmar
- Philippines
- Brunei
- Malaysia
- Cambodia
ASEAN Objectives
- To encourage proactive engagement and reciprocal support in the social, cultural, economic, scientific, administrative and technological spheres on subjects of shared relevance.
- Maintaining strong and mutually advantageous relationships with current global and territorial organizations.
- To work together more efficiently to maximize the use of agriculture and industry, expand commerce, enhance infrastructure and transportation, and raise citizens’ quality of life.
- To encourage the study of Southeast Asian regions.
- To work for a successful and harmonious Southeast Asian neighborhood, to promote economic progress, social improvement, and cultural growth.
- To foster regional harmony and security via an adherence to fairness and by maintaining a system of law, as well as conformity to the United Nations Charter’s ideals.
दक्षिण पूर्व एशियाई राष्ट्र संघ : अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठन
आसियान क्या है?
- दक्षिण-पूर्व एशियाई राष्ट्रों का संगठन (आसियान) एक क्षेत्रीय संघ है जिसकी स्थापना एशिया के उपनिवेशवाद-विरोधी देशों में बढ़ते संघर्षों के बीच सामाजिक स्थिरता और राजनीतिक संतुलन बनाए रखने के लिए की गई थी।
- “एक दृष्टि, एक पहचान, एक समुदाय” इसका आदर्श वाक्य है। 8 अगस्त को आसियान दिवस के रूप में मनाया जाता है। आसियान सचिवालय इंडोनेशिया के जकार्ता में स्थित है।
आसियान की उत्पत्ति
- आसियान घोषणापत्र (बैंकॉक घोषणापत्र) पर संगठन के मूल सदस्यों द्वारा 1967 में हस्ताक्षर किए गए थे।
- इंडोनेशिया, मलेशिया, फिलीपींस, सिंगापुर और थाईलैंड आसियान के मूल सदस्य हैं।
आसियान के सदस्य
- आसियान में दस सदस्य देश शामिल हैं। आसियान देशों की सूची में निम्नलिखित शामिल हैं:
- थाईलैंड
- सिंगापुर
- वियतनाम
- लाओस
- इंडोनेशिया
- म्यांमार
- फिलीपींस
- ब्रुनेई
- मलेशिया
- कंबोडिया
आसियान के उद्देश्य
- साझा प्रासंगिकता के विषयों पर सामाजिक, सांस्कृतिक, आर्थिक, वैज्ञानिक, प्रशासनिक और तकनीकी क्षेत्रों में सक्रिय भागीदारी और पारस्परिक समर्थन को प्रोत्साहित करना।
- वर्तमान वैश्विक और क्षेत्रीय संगठनों के साथ मजबूत और पारस्परिक रूप से लाभप्रद संबंध बनाए रखना।
- कृषि और उद्योग के उपयोग को अधिकतम करने, वाणिज्य का विस्तार करने, बुनियादी ढांचे और परिवहन को बढ़ाने और नागरिकों के जीवन की गुणवत्ता बढ़ाने के लिए अधिक कुशलता से मिलकर काम करना।
- दक्षिण पूर्व एशियाई क्षेत्रों के अध्ययन को प्रोत्साहित करना।
- एक सफल और सामंजस्यपूर्ण दक्षिण-पूर्व एशियाई पड़ोस के लिए काम करना, आर्थिक प्रगति, सामाजिक सुधार और सांस्कृतिक विकास को बढ़ावा देना।
- निष्पक्षता के पालन और कानून की व्यवस्था को बनाए रखने के साथ-साथ संयुक्त राष्ट्र चार्टर के आदर्शों के अनुरूप क्षेत्रीय सद्भाव और सुरक्षा को बढ़ावा देना।