CURRENT AFFAIRS – 26/12/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 26/12/2024
- ₹45,000-cr. Ken-Betwa link project launched / ₹45,000 करोड़ की केन-बेतवा लिंक परियोजना शुरू की गई
- ‘We want to be among the top five maritime nations by 2047’ /‘हम 2047 तक शीर्ष पांच समुद्री देशों में शामिल होना चाहते हैं’
- How the 2004 Indian Ocean quake transformed tsunami science /2004 के हिंद महासागर भूकंप ने सुनामी विज्ञान को कैसे बदल दिया
- Scientists find bacteria living on fish brains /वैज्ञानिकों ने मछली के मस्तिष्क पर जीवित बैक्टीरिया पाया
- U.S. and China renew S&T Agreement /अमेरिका और चीन ने विज्ञान और प्रौद्योगिकी समझौते को नवीनीकृत किया
- The lapses in the disaster management Bill /आपदा प्रबंधन विधेयक में खामियाँ
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 26/12/2024
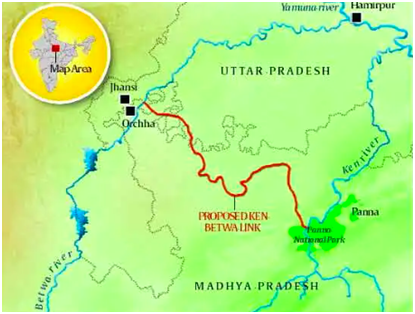
₹45,000-cr. Ken-Betwa link project launched / ₹45,000 करोड़ की केन-बेतवा लिंक परियोजना शुरू की गई
Syllabus : GS 1 & 3 : Geography & Indian Economy
Source : The Hindu
The Ken-Betwa river-linking project aims to address water scarcity in Bundelkhand by linking two rivers, improving irrigation, drinking water supply, and energy generation.
- The project involves building canals, dams, hydropower, and solar energy components.
- It is part of India’s broader water management strategy.

Ken-Betwa River-Linking Project Overview
- Objective:
- The Ken-Betwa river-linking project aims to resolve the long-standing water scarcity issues in the drought-prone Bundelkhand region, spanning parts of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- The project focuses on linking the Ken and Betwa rivers to ensure a stable and reliable water supply to the region.
- Key Components of the Project
- Canal Construction: The primary feature of the project involves constructing a canal to transfer water from the Ken River to the Betwa River. This will ensure water availability for both irrigation and drinking needs in the region.
- Daudhan Dam: The project includes the construction of the Daudhan Dam on the Ken River. The dam will store water, regulate its flow, and supply water for irrigation purposes.
- Hydropower Generation: The project aims to generate over 100 MW of hydropower, which will help meet the region’s electricity demands and contribute to sustainable energy production.
- Solar Power Generation: In addition to hydropower, the project will also generate 27 MW of solar power, promoting clean energy and further supporting the region’s energy needs.
- Benefits of the Project
- Water Supply: The project will significantly improve the drinking water supply to at least 10 districts in Madhya Pradesh and several districts in Uttar Pradesh. It will provide a reliable water source for domestic consumption.
- Irrigation: The canal will provide irrigation facilities to approximately 11 lakh hectares of agricultural land. This will enhance agricultural productivity and improve livelihoods for farmers in the region.
- Economic Development: By addressing water and energy needs, the project is expected to stimulate economic growth in the Bundelkhand region, boosting agriculture, energy production, and local infrastructure.
Environmental and Ecological Considerations
- Wildlife and Habitat Protection: The project passes through ecologically sensitive areas such as the Panna Tiger Reserve. Special measures will be implemented to mitigate any potential negative impact on local wildlife and natural habitats.
- Sustainability: The combination of hydropower generation and solar power aligns with the project’s focus on sustainability, reducing the environmental footprint while addressing the water and energy needs of the region.
Strategic Importance
- River-Linking Initiative: This project is a crucial part of India’s larger river-linking strategy, aimed at resolving inter-state water disputes and ensuring long-term water security for drought-prone regions.
- Regional Transformation: By improving water availability, irrigation, and energy access, the project is expected to bring about significant socio-economic development in the Bundelkhand region, fostering overall regional growth.
₹45,000 करोड़ की केन-बेतवा लिंक परियोजना शुरू की गई
केन-बेतवा नदी जोड़ो परियोजना का उद्देश्य दो नदियों को जोड़कर बुंदेलखंड में जल की कमी को दूर करना, सिंचाई, पेयजल आपूर्ति और ऊर्जा उत्पादन में सुधार करना है।
- इस परियोजना में नहरें, बांध, जलविद्युत और सौर ऊर्जा घटकों का निर्माण शामिल है।
- यह भारत की व्यापक जल प्रबंधन रणनीति का हिस्सा है।
केन-बेतवा नदी-जोड़ो परियोजना अवलोकन
- उद्देश्य:
- केन-बेतवा नदी-जोड़ो परियोजना का उद्देश्य उत्तर प्रदेश और मध्य प्रदेश के कुछ हिस्सों में फैले सूखाग्रस्त बुंदेलखंड क्षेत्र में लंबे समय से चली आ रही जल की कमी के मुद्दों को हल करना है।
- परियोजना केन और बेतवा नदियों को जोड़ने पर केंद्रित है ताकि क्षेत्र में स्थिर और विश्वसनीय जल आपूर्ति सुनिश्चित की जा सके।
- परियोजना के प्रमुख घटक
- नहर निर्माण: परियोजना की प्राथमिक विशेषता केन नदी से बेतवा नदी में पानी स्थानांतरित करने के लिए एक नहर का निर्माण करना है। इससे क्षेत्र में सिंचाई और पीने की दोनों जरूरतों के लिए पानी की उपलब्धता सुनिश्चित होगी।
- दौधन बांध: इस परियोजना में केन नदी पर दौधन बांध का निर्माण शामिल है। बांध पानी को संग्रहीत करेगा, इसके प्रवाह को नियंत्रित करेगा और सिंचाई के उद्देश्यों के लिए पानी की आपूर्ति करेगा।
- जलविद्युत उत्पादन: इस परियोजना का लक्ष्य 100 मेगावाट से अधिक जलविद्युत उत्पादन करना है, जो क्षेत्र की बिजली की मांग को पूरा करने में मदद करेगा और स्थायी ऊर्जा उत्पादन में योगदान देगा।
- सौर ऊर्जा उत्पादन: जलविद्युत के अलावा, परियोजना 27 मेगावाट सौर ऊर्जा भी उत्पन्न करेगी, जो स्वच्छ ऊर्जा को बढ़ावा देगी और क्षेत्र की ऊर्जा आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करेगी।
- परियोजना के लाभ
- जल आपूर्ति: इस परियोजना से मध्य प्रदेश के कम से कम 10 जिलों और उत्तर प्रदेश के कई जिलों में पेयजल आपूर्ति में उल्लेखनीय सुधार होगा। यह घरेलू खपत के लिए एक विश्वसनीय जल स्रोत प्रदान करेगा।
- सिंचाई: नहर लगभग 11 लाख हेक्टेयर कृषि भूमि को सिंचाई सुविधाएँ प्रदान करेगी। इससे कृषि उत्पादकता बढ़ेगी और क्षेत्र के किसानों की आजीविका में सुधार होगा।
- आर्थिक विकास: जल और ऊर्जा आवश्यकताओं को संबोधित करके, परियोजना से बुंदेलखंड क्षेत्र में आर्थिक विकास को बढ़ावा मिलने की उम्मीद है, जिससे कृषि, ऊर्जा उत्पादन और स्थानीय बुनियादी ढाँचे को बढ़ावा मिलेगा।
पर्यावरण और पारिस्थितिकी संबंधी विचार
- वन्यजीव और पर्यावास संरक्षण: यह परियोजना पन्ना टाइगर रिजर्व जैसे पारिस्थितिक रूप से संवेदनशील क्षेत्रों से होकर गुज़रती है। स्थानीय वन्यजीवों और प्राकृतिक आवासों पर किसी भी संभावित नकारात्मक प्रभाव को कम करने के लिए विशेष उपाय लागू किए जाएंगे।
- स्थायित्व: जलविद्युत उत्पादन और सौर ऊर्जा का संयोजन परियोजना के स्थिरता पर ध्यान केंद्रित करने के साथ संरेखित होता है, जो क्षेत्र की जल और ऊर्जा आवश्यकताओं को संबोधित करते हुए पर्यावरणीय पदचिह्न को कम करता है।
रणनीतिक महत्व
- नदी-जोड़ने की पहल: यह परियोजना भारत की बड़ी नदी-जोड़ने की रणनीति का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है, जिसका उद्देश्य अंतर-राज्यीय जल विवादों को हल करना और सूखाग्रस्त क्षेत्रों के लिए दीर्घकालिक जल सुरक्षा सुनिश्चित करना है।
- क्षेत्रीय परिवर्तन: जल उपलब्धता, सिंचाई और ऊर्जा पहुंच में सुधार करके, इस परियोजना से बुंदेलखंड क्षेत्र में महत्वपूर्ण सामाजिक-आर्थिक विकास लाने और समग्र क्षेत्रीय विकास को बढ़ावा देने की उम्मीद है।
‘We want to be among the top five maritime nations by 2047’ /‘हम 2047 तक शीर्ष पांच समुद्री देशों में शामिल होना चाहते हैं’
Syllabus : GS 3 : Indian Economy
Source : The Hindu
The article discusses the Indian government’s initiatives and targets for the maritime sector.
- This includes Maritime Vision 2047, the development of maritime infrastructure, cruise tourism, and legislative reforms.
- Key reforms like the Coastal Shipping Bill and Merchant Shipping Bill aim to boost India’s maritime capabilities.
Government Initiatives, Missions, and Targets Regarding Maritime Sector
- Maritime Vision 2047
- India aims to become a global leader in maritime sectors such as shipbuilding, ship repair, and ship recycling.
- By 2030, India plans to be among the top 10 maritime nations and top 5 by 2047.
- The country intends to enhance cargo handling capacity from 1,600 million metric tonnes to 10,000 million metric tonnes by 2047.
- The vision includes investment of ₹80 lakh crore in the maritime sector over the next 25 years.
- Infrastructure Development
- Investment will be directed towards the modernisation of ports, development of green ports, and eco-friendly shipping.
- The Ministry plans to develop world-class ecosystems in all verticals, including port management systems, cargo handling, and inland waterways.
- Cruise Tourism Development
- The government has developed six international cruise terminals with facilities comparable to airports.
- Tax exemptions and incentives have been introduced to promote cruise tourism.
- Cruise tourism has been boosted with quality international cruise liners visiting Indian ports.
- Lighthouse tourism has grown by 273% in 10 years, attracting 16.19 lakh visitors.
- National Maritime Heritage Complex
- A major project located in Lothal, Gujarat, this complex will be the world’s largest maritime museum.
- Phase-1A will open to the public in September 2025, with full completion expected by 2029.
- The project will include international collaborations for research, preservation, and exchange of maritime knowledge.
- It is expected to attract 25,000 daily visitors and create 22,000 jobs.
- Recent Legislative Reforms
- The Major Port Authority Act, National Waterways Act, Inland Vessel Act, and Recycling of Ships Act have been enacted to streamline growth in the port, waterways, and ship recycling sectors.
- The Coastal Shipping Bill and Merchant Shipping Bill are set to be enacted to boost coastal shipping, promote shipbuilding, enhance Indian ship ownership, improve coastal security, and ensure seafarer welfare.
‘हम 2047 तक शीर्ष पांच समुद्री देशों में शामिल होना चाहते हैं’
लेख में समुद्री क्षेत्र के लिए भारत सरकार की पहलों और लक्ष्यों पर चर्चा की गई है।
- इसमें मैरीटाइम विजन 2047, समुद्री बुनियादी ढांचे का विकास, क्रूज पर्यटन और विधायी सुधार शामिल हैं।
- तटीय नौवहन विधेयक और मर्चेंट नौवहन विधेयक जैसे प्रमुख सुधारों का उद्देश्य भारत की समुद्री क्षमताओं को बढ़ावा देना है।
समुद्री क्षेत्र के संबंध में सरकारी पहल, मिशन और लक्ष्य
- समुद्री विजन 2047
- भारत का लक्ष्य जहाज निर्माण, जहाज मरम्मत और जहाज पुनर्चक्रण जैसे समुद्री क्षेत्रों में वैश्विक नेता बनना है।
- 2030 तक, भारत की योजना शीर्ष 10 समुद्री देशों में और 2047 तक शीर्ष 5 में शामिल होने की है।
- देश का इरादा 2047 तक कार्गो हैंडलिंग क्षमता को 1,600 मिलियन मीट्रिक टन से बढ़ाकर 10,000 मिलियन मीट्रिक टन करने का है।
- इस विजन में अगले 25 वर्षों में समुद्री क्षेत्र में ₹80 लाख करोड़ का निवेश शामिल है।
- अवसंरचना विकास
- निवेश बंदरगाहों के आधुनिकीकरण, हरित बंदरगाहों के विकास और पर्यावरण के अनुकूल शिपिंग की ओर निर्देशित किया जाएगा।
- मंत्रालय बंदरगाह प्रबंधन प्रणाली, कार्गो हैंडलिंग और अंतर्देशीय जलमार्गों सहित सभी क्षेत्रों में विश्व स्तरीय पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र विकसित करने की योजना बना रहा है।
- क्रूज पर्यटन विकास
- सरकार ने हवाई अड्डों के बराबर सुविधाओं वाले छह अंतरराष्ट्रीय क्रूज टर्मिनल विकसित किए हैं।
- क्रूज पर्यटन को बढ़ावा देने के लिए कर छूट और प्रोत्साहन शुरू किए गए हैं।
- भारतीय बंदरगाहों पर आने वाले गुणवत्तापूर्ण अंतरराष्ट्रीय क्रूज लाइनरों से क्रूज पर्यटन को बढ़ावा मिला है।
- लाइटहाउस पर्यटन में 10 वर्षों में 273% की वृद्धि हुई है, जिसने 16.19 लाख आगंतुकों को आकर्षित किया है।
- राष्ट्रीय समुद्री विरासत परिसर
- गुजरात के लोथल में स्थित एक प्रमुख परियोजना, यह परिसर दुनिया का सबसे बड़ा समुद्री संग्रहालय होगा।
- चरण-1ए सितंबर 2025 में जनता के लिए खुलेगा, जिसके 2029 तक पूर्ण रूप से पूरा होने की उम्मीद है।
- परियोजना में अनुसंधान, संरक्षण और समुद्री ज्ञान के आदान-प्रदान के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग शामिल होंगे।
- इससे प्रतिदिन 25,000 आगंतुकों के आकर्षित होने और 22,000 नौकरियों के सृजन की उम्मीद है।
- हालिया विधायी सुधार
- बंदरगाह, जलमार्ग और जहाज पुनर्चक्रण क्षेत्रों में विकास को सुव्यवस्थित करने के लिए प्रमुख बंदरगाह प्राधिकरण अधिनियम, राष्ट्रीय जलमार्ग अधिनियम, अंतर्देशीय पोत अधिनियम और जहाजों के पुनर्चक्रण अधिनियम को अधिनियमित किया गया है।
- तटीय नौवहन को बढ़ावा देने, जहाज निर्माण को बढ़ावा देने, भारतीय जहाज स्वामित्व को बढ़ाने, तटीय सुरक्षा में सुधार करने और नाविकों का कल्याण सुनिश्चित करने के लिए तटीय नौवहन विधेयक और व्यापारिक नौवहन विधेयक को अधिनियमित किया जाना है।
How the 2004 Indian Ocean quake transformed tsunami science /2004 के हिंद महासागर भूकंप ने सुनामी विज्ञान को कैसे बदल दिया
Syllabus : GS 3 : Disaster & Disaster Management
Source : The Hindu
The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, one of the deadliest natural disasters in history, highlighted the vulnerability of coastal regions to massive seismic events.
- It spurred advancements in tsunami warning systems and scientific research. Lessons learned from this disaster continue to shape global disaster management strategies.
20th Anniversary of the 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake and Tsunami
Overview of the 2004 Disaster
- On December 26, 2004, a magnitude 9.1 earthquake struck off the coast of Sumatra, triggering one of the deadliest tsunamis in recorded history.
- The earthquake originated 30 km below the ocean floor in the Sunda Trench, where the Indo-Australian plate subducts beneath the Burma microplate.
- The rupture extended over a 1,300 km stretch of the plate boundary, affecting Indonesia, Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and other nations.
- The tsunami impacted 17 countries along the Indian Ocean, causing over 227,000 deaths and displacing 1.7 million people.
Subsequent Disasters and Lessons Learned
- In March 2011, a magnitude 9.1 earthquake off Japan triggered a tsunami and the Fukushima nuclear disaster, showing the ongoing vulnerability to natural disasters.
- The 2004 tsunami highlighted the unpredictability of such events and underscored the necessity for disaster preparedness and resilience.
Scientific Advancements Post-Tsunami
- The 2004 tsunami was a shock to researchers, as it was the first recorded massive tsunami along India’s eastern seaboard.
- The Indian Tsunami Early Warning Centre (ITEWC) was set up in 2007, improving earthquake and tsunami monitoring.
- ITEWC operates seismological stations and ocean monitoring systems to issue early warnings for the Indian Ocean region, with alerts sent within 10 minutes of detecting potential tsunami-producing earthquakes.
Impact on Tsunami Research
- The tsunami prompted the development of tsunami geology, with significant findings in India and other countries.
- Excavations in Mahabalipuram uncovered evidence of a tsunami from the same period as the 2004 disaster.
- Researchers studied sedimentary deposits along the coast, discovering more ancient tsunamis and establishing a new scientific field focused on tsunami research.
Nuclear Vulnerabilities and Future Risks
- The 2004 tsunami revealed vulnerabilities in nuclear power plants along India’s coast.
- Though the Kalpakkam nuclear power plant withstood the tsunami, it was automatically shut down due to rising water levels, highlighting potential risks to nuclear facilities.
- Following the Fukushima disaster, the risks to nuclear plants from tsunamis became clearer, spurring calls for increased safety measures.
Emerging Tsunami Risks
- The Makran Coast, spanning Iran and Pakistan, poses a potential tsunami threat to India’s west coast, including Mumbai, where nuclear reactors are located.
- Research has also identified other seismic risks, including slow seismic slips that could provide clues about impending earthquakes and tsunamis, enhancing predictive capabilities.
Ongoing Research and Seismological Milestones
- The 2004 event marked a significant milestone in seismological research, offering valuable data on earthquake generation and related hazards.
- Studies on seismic slips at plate boundaries and pre-earthquake phenomena have advanced, offering new insights into earthquake prediction and risk mitigation strategies.
2004 के हिंद महासागर भूकंप ने सुनामी विज्ञान को कैसे बदल दिया
2004 में हिंद महासागर में आए भूकंप और सुनामी, जो इतिहास की सबसे घातक प्राकृतिक आपदाओं में से एक थी, ने विशाल भूकंपीय घटनाओं के प्रति तटीय क्षेत्रों की संवेदनशीलता को उजागर किया।
- इसने सुनामी चेतावनी प्रणालियों और वैज्ञानिक अनुसंधान में प्रगति को बढ़ावा दिया। इस आपदा से सीखे गए सबक वैश्विक आपदा प्रबंधन रणनीतियों को आकार देते हैं।
2004 के हिंद महासागर भूकंप और सुनामी की 20वीं वर्षगांठ
- 2004 की आपदा का अवलोकन
- 26 दिसंबर, 2004 को सुमात्रा के तट पर 1 तीव्रता का भूकंप आया, जिसने इतिहास में दर्ज सबसे घातक सुनामी में से एक को जन्म दिया।
- भूकंप समुद्र तल से 30 किमी नीचे सुंडा ट्रेंच में उत्पन्न हुआ, जहाँ इंडो-ऑस्ट्रेलियाई प्लेट बर्मा माइक्रोप्लेट के नीचे धंस जाती है।
- यह दरार प्लेट सीमा के 1,300 किमी क्षेत्र में फैली, जिसने इंडोनेशिया, बांग्लादेश, भारत, श्रीलंका, थाईलैंड और अन्य देशों को प्रभावित किया।
- सुनामी ने हिंद महासागर के किनारे 17 देशों को प्रभावित किया, जिससे 227,000 से अधिक लोगों की मृत्यु हुई और 7 मिलियन लोग विस्थापित हुए।
बाद की आपदाएँ और सीखे गए सबक
- मार्च 2011 में, जापान के तट पर 1 तीव्रता के भूकंप ने सुनामी और फुकुशिमा परमाणु आपदा को जन्म दिया, जिससे प्राकृतिक आपदाओं के प्रति निरंतर संवेदनशीलता का पता चलता है।
- 2004 की सुनामी ने ऐसी घटनाओं की अप्रत्याशितता को उजागर किया और आपदा की तैयारी और लचीलेपन की आवश्यकता को रेखांकित किया।
सुनामी के बाद वैज्ञानिक प्रगति
- 2004 की सुनामी शोधकर्ताओं के लिए एक झटका थी, क्योंकि यह भारत के पूर्वी समुद्र तट पर पहली दर्ज की गई विशाल सुनामी थी।
- भारतीय सुनामी प्रारंभिक चेतावनी केंद्र (ITEWC) की स्थापना 2007 में की गई थी, जिससे भूकंप और सुनामी निगरानी में सुधार हुआ।
- ITEWC भारतीय महासागर क्षेत्र के लिए प्रारंभिक चेतावनी जारी करने के लिए भूकंपीय स्टेशन और महासागर निगरानी प्रणाली संचालित करता है, जिसमें संभावित सुनामी पैदा करने वाले भूकंपों का पता लगाने के 10 मिनट के भीतर अलर्ट भेजे जाते हैं।
सुनामी अनुसंधान पर प्रभाव
- सुनामी ने सुनामी भूविज्ञान के विकास को प्रेरित किया, जिसमें भारत और अन्य देशों में महत्वपूर्ण निष्कर्ष शामिल हैं।
- महाबलीपुरम में उत्खनन से 2004 की आपदा के समान अवधि की सुनामी के साक्ष्य मिले।
- शोधकर्ताओं ने तट के किनारे तलछटी जमा का अध्ययन किया, और अधिक प्राचीन सुनामी की खोज की तथा सुनामी अनुसंधान पर केंद्रित एक नया वैज्ञानिक क्षेत्र स्थापित किया।
परमाणु भेद्यताएँ और भविष्य के जोखिम
- 2004 की सुनामी ने भारत के तट पर परमाणु ऊर्जा संयंत्रों में कमजोरियों को उजागर किया।
- हालांकि कलपक्कम परमाणु ऊर्जा संयंत्र ने सुनामी को झेला, लेकिन बढ़ते जल स्तर के कारण इसे स्वचालित रूप से बंद कर दिया गया, जिससे परमाणु सुविधाओं के लिए संभावित जोखिम उजागर हुए।
- फुकुशिमा आपदा के बाद, सुनामी से परमाणु संयंत्रों के लिए जोखिम स्पष्ट हो गए, जिससे सुरक्षा उपायों को बढ़ाने की मांग उठने लगी।
उभरते सुनामी जोखिम
- ईरान और पाकिस्तान तक फैला मकरान तट भारत के पश्चिमी तट पर संभावित सुनामी खतरा पैदा करता है, जिसमें मुंबई भी शामिल है, जहाँ परमाणु रिएक्टर स्थित हैं।
- शोध में अन्य भूकंपीय जोखिमों की भी पहचान की गई है, जिसमें धीमी भूकंपीय फिसलन शामिल है जो आसन्न भूकंप और सुनामी के बारे में सुराग दे सकती है, जिससे पूर्वानुमान लगाने की क्षमता बढ़ जाती है।
चल रहे शोध और भूकंपीय मील के पत्थर
- 2004 की घटना ने भूकंपीय अनुसंधान में एक महत्वपूर्ण मील का पत्थर साबित किया, जिससे भूकंप निर्माण और संबंधित खतरों पर मूल्यवान डेटा मिला।
- प्लेट सीमाओं पर भूकंपीय फिसलन और भूकंप-पूर्व घटनाओं पर अध्ययन आगे बढ़े हैं, जिससे भूकंप की भविष्यवाणी और जोखिम शमन रणनीतियों में नई अंतर्दृष्टि मिली है।
Scientists find bacteria living on fish brains /वैज्ञानिकों ने मछली के मस्तिष्क पर जीवित बैक्टीरिया पाया
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
A new study challenges the long-held belief that the brain is sterile by revealing that bacteria can thrive in fish brains.
- This discovery suggests the possibility of a brain microbiome in vertebrates, including humans.
Analysis of the news:
- A study by the University of New Mexico challenges the belief that the brain is sterile, showing bacteria can thrive in fish brains.
- Researchers identified living bacteria in fish olfactory bulbs and other brain regions using DNA extraction and microscopic imaging.
Origins of Brain Microbes:
- Some bacteria may have colonized the brain before the evolution of the blood-brain barrier, while others likely entered via the gut or bloodstream, continuously infiltrating the brain.
- The brain’s microbial community appears dynamic, shaped by both early colonization and ongoing interaction with other bodily systems.
Implications for Humans:
- While fish are different from humans, the findings raise questions about whether a similar brain microbiome might exist in humans and other vertebrates.
- The study may also reveal potential roles for microbes in brain processes, similar to the gut-brain axis.
वैज्ञानिकों ने मछली के मस्तिष्क पर जीवित बैक्टीरिया पाया
एक नए अध्ययन ने इस लंबे समय से चली आ रही धारणा को चुनौती दी है कि मस्तिष्क बाँझ होता है, यह खुलासा करके कि मछली के मस्तिष्क में बैक्टीरिया पनप सकते हैं।
- यह खोज मनुष्यों सहित कशेरुकियों में मस्तिष्क माइक्रोबायोम की संभावना का सुझाव देती है।
समाचार का विश्लेषण:
- न्यू मैक्सिको विश्वविद्यालय द्वारा किए गए एक अध्ययन ने इस धारणा को चुनौती दी है कि मस्तिष्क बाँझ होता है, यह दिखाते हुए कि मछली के मस्तिष्क में बैक्टीरिया पनप सकते हैं।
- शोधकर्ताओं ने डीएनए निष्कर्षण और सूक्ष्म इमेजिंग का उपयोग करके मछली के घ्राण बल्ब और अन्य मस्तिष्क क्षेत्रों में जीवित बैक्टीरिया की पहचान की।
मस्तिष्क सूक्ष्मजीवों की उत्पत्ति:
- कुछ बैक्टीरिया ने रक्त-मस्तिष्क अवरोध के विकास से पहले मस्तिष्क में उपनिवेश स्थापित किया हो सकता है, जबकि अन्य संभवतः आंत या रक्तप्रवाह के माध्यम से प्रवेश करते हैं, लगातार मस्तिष्क में घुसपैठ करते हैं।
- मस्तिष्क का सूक्ष्मजीव समुदाय गतिशील प्रतीत होता है, जो प्रारंभिक उपनिवेशीकरण और अन्य शारीरिक प्रणालियों के साथ चल रही बातचीत दोनों द्वारा आकार लेता है।
मनुष्यों के लिए निहितार्थ:
- जबकि मछलियाँ मनुष्यों से भिन्न होती हैं, निष्कर्ष इस बारे में प्रश्न उठाते हैं कि क्या मनुष्यों और अन्य कशेरुकियों में एक समान मस्तिष्क माइक्रोबायोम मौजूद हो सकता है।
- अध्ययन से मस्तिष्क प्रक्रियाओं में सूक्ष्मजीवों की संभावित भूमिका का भी पता चल सकता है, जो आंत-मस्तिष्क अक्ष के समान है।
U.S. and China renew S&T Agreement /अमेरिका और चीन ने विज्ञान और प्रौद्योगिकी समझौते को नवीनीकृत किया
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
The U.S. and China extended their 1979 science and technology cooperation agreement for five more years, emphasizing basic research and mutual benefits.
- The renewal seeks to address concerns about technology exports and intellectual property.
- The agreement continues to shape bilateral scientific relations.
Initial Agreement:
- Signed on January 31, 1979, by U.S. President Jimmy Carter and Chinese leader Deng Xiaoping.
- Established during the early days of U.S.-China diplomatic relations.
- Focused initially on agricultural research and technology.
Renewal and Extension:
- Renewed every five years, with the most recent extension on December 13, 2024.
- The renewed agreement includes a protocol to amend it, reflecting current concerns.
Purpose and Scope:
- Promotes scientific collaboration between the U.S. and China.
- Encourages joint research, mobility for students and scientists, and institutional cooperation.
- Governed by the U.S.-PRC Joint Commission on Scientific and Technological Cooperation.
Recent Amendments:
- The collaboration will be confined to basic research and areas of mutual benefit.
- Excludes critical and emerging technologies to prevent disproportionate benefits to China.
- Includes provisions to enhance researcher safety and data reciprocity.
Significance for U.S. and China:
- Both nations have benefited from the Agreement, with China significantly advancing its scientific position.
- U.S. gains in terms of collaboration and retaining leverage over China’s technological rise.
अमेरिका और चीन ने विज्ञान और प्रौद्योगिकी समझौते को नवीनीकृत किया
अमेरिका और चीन ने 1979 के विज्ञान और प्रौद्योगिकी सहयोग समझौते को पाँच और वर्षों के लिए बढ़ा दिया है, जिसमें बुनियादी अनुसंधान और पारस्परिक लाभों पर जोर दिया गया है।
- नवीनीकरण का उद्देश्य प्रौद्योगिकी निर्यात और बौद्धिक संपदा के बारे में चिंताओं को दूर करना है।
- यह समझौता द्विपक्षीय वैज्ञानिक संबंधों को आकार देना जारी रखता है।
प्रारंभिक समझौता:
- 31 जनवरी, 1979 को अमेरिकी राष्ट्रपति जिमी कार्टर और चीनी नेता देंग शियाओपिंग द्वारा हस्ताक्षरित।
- यू.एस.-चीन राजनयिक संबंधों के शुरुआती दिनों में स्थापित।
- शुरू में कृषि अनुसंधान और प्रौद्योगिकी पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया गया।
नवीनीकरण और विस्तार:
- हर पाँच साल में नवीनीकृत, 13 दिसंबर, 2024 को सबसे हालिया विस्तार के साथ।
- नवीनीकृत समझौते में वर्तमान चिंताओं को दर्शाते हुए इसे संशोधित करने के लिए एक प्रोटोकॉल शामिल है।
उद्देश्य और दायरा:
- यू.एस. और चीन के बीच वैज्ञानिक सहयोग को बढ़ावा देता है।
- संयुक्त अनुसंधान, छात्रों और वैज्ञानिकों के लिए गतिशीलता और संस्थागत सहयोग को प्रोत्साहित करता है।
- वैज्ञानिक और तकनीकी सहयोग पर यू.एस.-पीआरसी संयुक्त आयोग द्वारा शासित।
हाल के संशोधन:
- सहयोग बुनियादी अनुसंधान और पारस्परिक लाभ के क्षेत्रों तक ही सीमित रहेगा।
- चीन को असंगत लाभ से बचाने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण और उभरती हुई प्रौद्योगिकियों को शामिल नहीं किया गया है।
- शोधकर्ता सुरक्षा और डेटा पारस्परिकता को बढ़ाने के प्रावधान शामिल हैं।
अमेरिका और चीन के लिए महत्व:
- दोनों देशों को समझौते से लाभ हुआ है, चीन ने अपनी वैज्ञानिक स्थिति को काफी आगे बढ़ाया है।
- अमेरिका को सहयोग के मामले में लाभ हुआ है और चीन के तकनीकी विकास पर उसका दबदबा बना हुआ है।
The lapses in the disaster management Bill /आपदा प्रबंधन विधेयक में खामियाँ
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 3 : Disaster & Disaster Management
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- The Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill, 2024, modifies the Disaster Management Act, 2005, but has raised concerns about its top-down approach, lack of inclusivity, and accountability.
- It excludes key provisions for relief measures and ignores the role of local communities.
- The Bill also misses opportunities for regional and international collaboration.
Key Concerns Raised
- Shift from Participatory Governance
- The Bill replaces inclusive governance under the Disaster Management Act (DMA), 2005, with a top-down approach.
- It uses terms like “monitor” and “guidelines” instead of fostering trust with local communities through “supervision” and “direction.”
- Undermining Local Communities
- Global frameworks like the Yokohama Strategy, Hyogo Framework, and Sendai Framework highlight local communities as “first responders.”
- The Bill ignores the vital roles of local communities, panchayats, and NGOs, which have historically been at the forefront of disaster response (e.g., Kerala floods, Kedarnath disaster).
Gaps in Inclusivity and Evaluation
- Intersectional Discrimination
- The Bill lacks provisions addressing vulnerabilities of women, disabled individuals, marginalized castes, and LGBTQIA communities.
- Ignoring intersectional challenges reduces its claim to inclusiveness.
- Performance Evaluation
- No mechanisms exist for evaluating district authorities’ disaster preparedness.
- Failure to address accountability fosters opportunities for political exploitation.
- Key Highlights of the Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill, 2024
- Preparation of Plans: Disaster management plans will now be prepared by NDMA and SDMA, instead of the National and State Executive Committees.
- Enhanced Functions: NDMA and SDMA will periodically assess disaster risks, provide technical assistance, recommend relief standards, and prepare disaster databases.
- Disaster Database: Mandates comprehensive national and state-level disaster databases.
- Urban Disaster Management Authorities: State governments can establish Urban Disaster Management Authorities for state capitals and cities with municipal corporations.
- State Disaster Response Force (SDRF): States can constitute SDRFs with defined functions and terms of service.
- Statutory Status: National Crisis Management Committee (NCMC) and High-Level Committee (HLC) are given statutory status.
- Appointments: NDMA can specify staff and appoint experts with central government approval.
Omission of Key Provisions
- Accountability and Relief Measures
- Sections 12, 13, and 19 of the DMA, which mandated minimum standards for relief and special provisions for widows, orphans, and the homeless, have been removed.
- Provisions ensuring loan repayment relief and ex gratia assistance are missing without replacements.
Preparedness and Integration
- Sections 35(2b) and 35(2d), ensuring integration and preparedness in disaster management plans, have been omitted.
- State Executive Committees (SECs) are no longer required to prepare for disasters effectively, as Sections 22(2a) and 22(2b) are deleted.
Flaws in Good Governance and Speciesism
- Neglect of Animals
- The Bill fails to address disaster-related deaths of animals.
- It overlooks implementing the Animal Birth Control (ABC) Rules, 2023, for disaster preparedness.
- Urban Disaster Management Authority (UDMA)
- The creation of UDMA lacks clarity in its purpose.
- Municipal Corporations, responsible for urban development, often exacerbate flooding through encroachments on natural resources.
Missed Opportunities in Regional Collaboration
- Global and Regional Synergy
- The Bill fails to incorporate international collaboration mechanisms, ignoring groupings like SAARC, BIMSTEC, and BRICS.
- The absence of references to the 2011 SAARC Agreement on Rapid Response to Natural Disasters highlights its oversight of regional disaster strategies.
Conclusion
- The Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill, 2024, weakens the foundational principles of participatory governance, inclusivity, accountability, and preparedness established by the DMA, 2005.
- Its omissions and top-down approach limit its effectiveness in addressing disaster management comprehensively.
आपदा प्रबंधन विधेयक में खामियाँ
संदर्भ :
- आपदा प्रबंधन (संशोधन) विधेयक, 2024, आपदा प्रबंधन अधिनियम, 2005 को संशोधित करता है, लेकिन इसके शीर्ष-से-नीचे के दृष्टिकोण, समावेशिता की कमी और जवाबदेही के बारे में चिंताएँ जताई हैं।
- इसमें राहत उपायों के लिए मुख्य प्रावधानों को शामिल नहीं किया गया है और स्थानीय समुदायों की भूमिका को अनदेखा किया गया है।
- इस विधेयक में क्षेत्रीय और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग के अवसरों को भी शामिल नहीं किया गया है।
उठाई गई प्रमुख चिंताएँ
- सहभागी शासन से बदलाव
- यह विधेयक आपदा प्रबंधन अधिनियम (डीएमए), 2005 के तहत समावेशी शासन को शीर्ष-से-नीचे के दृष्टिकोण से प्रतिस्थापित करता है।
- यह “पर्यवेक्षण” और “निर्देश” के माध्यम से स्थानीय समुदायों के साथ विश्वास को बढ़ावा देने के बजाय “निगरानी” और “दिशानिर्देश” जैसे शब्दों का उपयोग करता है।
- स्थानीय समुदायों को कमज़ोर करना
- योकोहामा रणनीति, ह्योगो फ्रेमवर्क और सेंडाई फ्रेमवर्क जैसे वैश्विक ढाँचे स्थानीय समुदायों को “प्रथम प्रतिक्रियाकर्ता” के रूप में उजागर करते हैं।
- विधेयक स्थानीय समुदायों, पंचायतों और गैर सरकारी संगठनों की महत्वपूर्ण भूमिकाओं को नज़रअंदाज़ करता है, जो ऐतिहासिक रूप से आपदा प्रतिक्रिया (जैसे, केरल बाढ़, केदारनाथ आपदा) में सबसे आगे रहे हैं।
समावेशीपन और मूल्यांकन में अंतराल
- अंतर्विभागीय भेदभाव
- विधेयक में महिलाओं, विकलांग व्यक्तियों, हाशिए पर पड़ी जातियों और LGBTQIA समुदायों की कमज़ोरियों को संबोधित करने वाले प्रावधानों का अभाव है।
- अंतर्विभागीय चुनौतियों की अनदेखी करने से समावेशिता का दावा कम हो जाता है।
- प्रदर्शन मूल्यांकन
- जिला अधिकारियों की आपदा तैयारियों के मूल्यांकन के लिए कोई तंत्र मौजूद नहीं है।
- जवाबदेही को संबोधित करने में विफलता राजनीतिक शोषण के अवसरों को बढ़ावा देती है।
- आपदा प्रबंधन (संशोधन) विधेयक, 2024 की मुख्य विशेषताएँ
- योजनाओं की तैयारी: आपदा प्रबंधन योजनाएँ अब राष्ट्रीय और राज्य कार्यकारी समितियों के बजाय NDMA और SDMA द्वारा तैयार की जाएँगी।
- बढ़े हुए कार्य: NDMA और SDMA समय-समय पर आपदा जोखिमों का आकलन करेंगे, तकनीकी सहायता प्रदान करेंगे, राहत मानकों की सिफारिश करेंगे और आपदा डेटाबेस तैयार करेंगे।
- आपदा डेटाबेस: व्यापक राष्ट्रीय और राज्य-स्तरीय आपदा डेटाबेस को अनिवार्य बनाता है।
- शहरी आपदा प्रबंधन प्राधिकरण: राज्य सरकारें राज्य की राजधानियों और नगर निगमों वाले शहरों के लिए शहरी आपदा प्रबंधन प्राधिकरण स्थापित कर सकती हैं।
- राज्य आपदा प्रतिक्रिया बल (एसडीआरएफ): राज्य परिभाषित कार्यों और सेवा की शर्तों के साथ एसडीआरएफ का गठन कर सकते हैं।
- वैधानिक स्थिति: राष्ट्रीय संकट प्रबंधन समिति (एनसीएमसी) और उच्च स्तरीय समिति (एचएलसी) को वैधानिक स्थिति दी गई है।
- नियुक्तियाँ: एनडीएमए केंद्र सरकार की मंजूरी से कर्मचारियों को निर्दिष्ट कर सकता है और विशेषज्ञों की नियुक्ति कर सकता है।
मुख्य प्रावधानों की चूक
- जवाबदेही और राहत उपाय
- डीएमए की धारा 12, 13 और 19, जो विधवाओं, अनाथों और बेघरों के लिए राहत और विशेष प्रावधानों के लिए न्यूनतम मानकों को अनिवार्य बनाती हैं, को हटा दिया गया है।
- ऋण चुकौती राहत और अनुग्रह सहायता सुनिश्चित करने वाले प्रावधान प्रतिस्थापन के बिना गायब हैं।
तैयारी और एकीकरण
- आपदा प्रबंधन योजनाओं में एकीकरण और तैयारी सुनिश्चित करने वाली धारा 35 (2 बी) और 35 (2 डी) को हटा दिया गया है।
- राज्य कार्यकारी समितियों (एसईसी) को अब आपदाओं के लिए प्रभावी ढंग से तैयारी करने की आवश्यकता नहीं है, क्योंकि धारा 22 (2 ए) और 22 (2 बी) को हटा दिया गया है।
सुशासन और प्रजातिवाद में खामियाँ
- पशुओं की उपेक्षा
- विधेयक आपदा से संबंधित पशुओं की मौतों को संबोधित करने में विफल रहता है।
- यह आपदा की तैयारी के लिए पशु जन्म नियंत्रण (एबीसी) नियम, 2023 को लागू करने की अनदेखी करता है।
- शहरी आपदा प्रबंधन प्राधिकरण (यूडीएमए)
- यूडीएमए के निर्माण में इसके उद्देश्य में स्पष्टता का अभाव है।
- शहरी विकास के लिए जिम्मेदार नगर निगम अक्सर प्राकृतिक संसाधनों पर अतिक्रमण करके बाढ़ को बढ़ाते हैं।
क्षेत्रीय सहयोग में छूटे अवसर
- वैश्विक और क्षेत्रीय तालमेल
- विधेयक सार्क, बिम्सटेक और ब्रिक्स जैसे समूहों की अनदेखी करते हुए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग तंत्र को शामिल करने में विफल रहता है।
- प्राकृतिक आपदाओं के लिए त्वरित प्रतिक्रिया पर 2011 के सार्क समझौते के संदर्भों की अनुपस्थिति क्षेत्रीय आपदा रणनीतियों की इसकी निगरानी को उजागर करती है।
निष्कर्ष
- आपदा प्रबंधन (संशोधन) विधेयक, 2024, डीएमए, 2005 द्वारा स्थापित भागीदारी शासन, समावेशिता, जवाबदेही और तैयारी के मूलभूत सिद्धांतों को कमजोर करता है।
- इसकी चूक और ऊपर से नीचे का दृष्टिकोण आपदा प्रबंधन को व्यापक रूप से संबोधित करने में इसकी प्रभावशीलता को सीमित करता है।