CURRENT AFFAIRS – 24/02/2024
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 24/02/2024
ISRO: PAPA detects solar wind impact of coronal mass ejections
(General Studies- Paper III)
Source : The Hindu
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has reported the operational success of the Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA) payload aboard the Aditya-L1 satellite.
- PAPA’s advanced sensors have effectively identified the impact of coronal mass ejections (CMEs), including recent occurrences in February 2024.
Key Highlights
- PAPA is an energy and mass analyzer designed for in-situ measurements of solar wind electrons and ions in the low energy range.
- It comprises two key sensors:
- SWEEP (Solar Wind Electron Energy Probe):
- Measures electrons in the energy range of 10 eV to 3 keV.
- SWICAR (Solar Wind Ion Composition Analyser):
- Measures ions in the energy range of 10 eV to 25 keV.
- Covers a mass range of 1-60 amu.
- Both sensors are equipped to determine the direction of arrival of solar wind particles.
- SWEEP (Solar Wind Electron Energy Probe):
- Operational Success and Observations:
- PAPA has been operational since December 12, 2023, and its SWEEP and SWICAR sensors are continuously observing solar wind electrons and ions in the default mode.
- The observations highlight the payload’s effectiveness in monitoring space weather conditions and its ability to detect and analyze solar phenomena.
- The PAPA payload is a collaborative effort of the Space Physics Laboratory and Avionics Entity of the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC)/ISRO.
- The successful performance of PAPA underscores India’s growing capabilities in space research and technology.
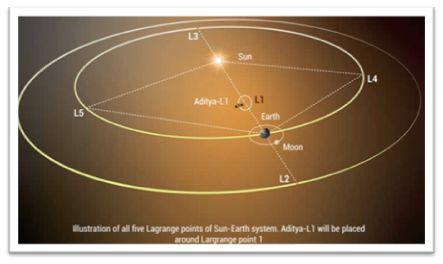
About the Aditya-L1 satellite
- Aditya-L1 is India’s first dedicated solar observatory mission, aimed at comprehensively studying the Sun.
- The satellite was launched on September 2, 2023, and successfully reached its destination, the Lagrangian Point 1 (L1), on January 6, 2024.
- At L1, Aditya-L1 maintains a continuous view of the Sun without any occlusion or eclipses due to its unique orbit.
- Key Features
- Location: Orbited around L1, approximately 1.5 million km from Earth, allowing for a constant view of the Sun.
- Orbit: An irregularly shaped orbit in a plane roughly perpendicular to the line connecting Earth and the Sun.
- Payloads: Seven scientific instruments focused on observing the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona, as well as conducting in-situ measurements of particles and fields.
- Operational Life: Expected to operate for five years.
- Aditya-L1 aims to address critical questions related to the Sun’s behavior, particularly concerning coronal heating, coronal mass ejections, pre-flares, flares, and space weather effects.
- By studying these phenomena, researchers hope to better predict and mitigate potential impacts on Earth and space technology.
Understanding the terminologies
- Solar Flares:
- These are sudden and intense bursts of energy and radiation from the Sun’s surface. They are often associated with sunspots and can precede CMEs.
- Sunspots:
- Dark, cooler areas on the Sun’s surface caused by strong magnetic activity. Sunspots are often associated with increased solar activity and the potential for CMEs.
- Solar Wind:
- A stream of charged particles, mainly electrons and protons, continuously flowing outward from the Sun. CMEs are significant disturbances in the solar wind.
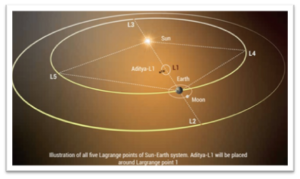
- Solar Corona:
- The outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, visible during a total solar eclipse. It is extremely hot, and its behavior is influenced by the Sun’s magnetic field.
- Geomagnetic Storms:
- Disturbances in Earth’s magnetosphere caused by interactions with solar wind or CMEs.
- These can affect radio communication, satellite operations, and power grids on Earth.
- Auroras:
- Beautiful displays of light in the Earth’s Polar Regions caused by charged particles from the Sun interacting with the Earth’s magnetosphere.
- CMEs can enhance auroras by increasing the intensity and extent of these displays.
- Solar Maximum and Minimum:
- The solar cycle, approximately 11 years in duration, during which the Sun’s activity fluctuates.
- Solar maximum is the period of increased solar activity, including a higher frequency of CMEs, while solar minimum is a period of decreased activity.
- Heliosphere:
- The region of space influenced by the solar wind and the Sun’s magnetic field, extending far beyond the orbit of Pluto.
- Solar Prominences
- Solar prominences are large, bright, gaseous features that extend outward from the Sun’s surface into its outer atmosphere, the corona
The NB8 visit to India focuses on cooperation and trust
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
Representatives from the Nordic-Baltic countries, collectively known as NB8, are participating in the Raisina Dialogue in New Delhi.
- Two years post-Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, these eight nations stress the significance of global collaboration.
- The joint message revolves around the urgent need for trust, dialogue, and cooperation amid global turmoil.
- The primary objectives include protecting peace and stability, opposing aggression, upholding a rules-based world order, and fostering a world economy grounded in free trade, sustainability, and enduring partnerships.
Key Highlights
- The Nordic-Baltic Alliance:
- The participating countries, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, and Sweden, share geographical proximity, deep historical ties, and strong economic and cultural connections.
- Their advanced, outward-looking economies are integrated into the European Common Market, collectively possessing economic influence equivalent to the G-20 and G-10.
- The NB8 nations are committed to democracy and human rights, advocating for an international order based on multilateralism and adherence to international law.
- They highlight a fruitful cooperation with India, emphasizing the alignment of core values and a longstanding democratic tradition.
- The Nordic-Baltic countries also maintain enduring ties with India and the wider Indo-Pacific region.
- Diverse Collaboration: Nordic-Baltic Countries Strengthen Ties with India
- The Nordic-Baltic cooperation with India spans a wide array of fields, including innovation, green transition, maritime affairs, health, intellectual property rights, new technologies, space cooperation, artificial intelligence, student exchanges, culture, and tourism.
- The trade and investment relationship between the Nordic-Baltic region and India is steadily growing, reflecting a collaborative pursuit of common goals.
- Amid geopolitical shifts, the security of both the Nordic-Baltic region and the Indo-Pacific becomes interlinked.
- The Nordic-Baltic countries emphasize the need to work collectively to uphold international law, build capacity to address security threats, and tackle both traditional and non-traditional challenges.
- Recognizing India’s growing role in international politics, the Nordic-Baltic nations appreciate India’s leadership, particularly in its successfully concluded G-20 presidency.
- Shared Objectives in an Interconnected World:
- In a more interconnected world, challenges are shared, necessitating collaborative efforts.
- The Nordic-Baltic countries and India have faced global health, climate-related, and geopolitical shocks in recent years.
- Acknowledging the urgent need to return to a positive agenda for global cooperation, the cooperative efforts aim to make a positive impact on international relations and address common challenges.
- The NB8 delegation’s visit to India marks the first high-level joint venture outside Europe, underscoring the commitment to multilateralism.
- Choosing India as the inaugural destination, the delegation aims to foster dialogue and cooperation on issues crucial to India and global partners.
- The focus is on forging partnerships for development and health, green transition, digitalization, and peace and stability.
About the Nordic-Baltic countries
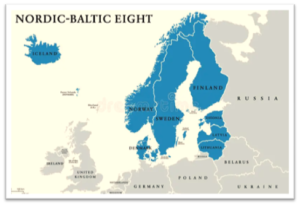
- The Nordic-Baltic region refers to a geopolitical and cultural grouping of countries in Northern Europe, encompassing both the Nordic countries and the Baltic states.
- Nordic Countries:
- Denmark: A constitutional monarchy comprising Denmark, Greenland, and the Faroe Islands.
- Finland: A Nordic country with a parliamentary republic.
- Iceland: A North Atlantic island nation.
- Norway: A constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system.
- Sweden: A constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system.
- Baltic States:
- Estonia: A Baltic country on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea.
- Latvia: A Baltic country situated between Estonia and Lithuania.
- Lithuania: A Baltic country on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea.
- Geography:
- The Nordic-Baltic region is located in Northern Europe and encompasses countries with diverse landscapes, including fjords, islands, forests, and coastlines along the Baltic Sea.
- History:
- While the Nordic countries share historical and cultural ties, the Baltic states have a distinct history influenced by various empires and geopolitical shifts.
- All the countries in the region have experienced significant changes in the 20th century, including periods of independence, occupation, and re-establishment.
- Economy:
- The Nordic-Baltic countries generally have well-developed and highly industrialized economies.
- They engage in regional cooperation to strengthen economic ties, trade, and innovation.
- Security Cooperation:
- The region collaborates on security matters, particularly within the framework of the Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8) initiative, which includes the Nordic Council countries and the Baltic states.
- Security challenges, including regional defense and cooperation with NATO, are key areas of focus.
- European Union and NATO:
- Many of the Nordic-Baltic countries are members of the European Union (EU) and NATO, contributing to the broader European and transatlantic cooperation.
What is Raisina Dialogue?
- The Raisina Dialogue is an annual multilateral conference held in New Delhi, India, focusing on geopolitical and geo-economic matters.
- Initiated in 2016, the event brings together leaders from various sectors such as politics, business, media, and civil society to discuss pressing global issues and foster cooperation between nations.
- The conference features high-profile participants, including heads of state, cabinet ministers, and local government officials, along with representatives from the private sector, media, and academia.
- Key aspects of the Raisina Dialogue include:
- Annual conference since 2016
- Addresses complex international topics through multi-stakeholder, cross-sectoral discussions
- Hosted by the Observer Research Foundation in collaboration with the Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India
- Supported by numerous organizations and individuals
- Held in New Delhi, India, on Raisina Hill, which is home to the Government of India and the Presidential Palace of India, RashtrapatiBhavan
- Ninth edition took place from February 21 to 23, 2024, with the theme being “Chaturanga: Conflict, Cooperation, Competition, and Change”.
Grey-zone warfare latest entry in lexicon of warfare, says CDS
(General Studies- Paper III)
Source : The Hindu
During the Raisina Dialogue, Chief of Defence Staff Gen. Anil Chauhan highlighted the emergence of “grey-zone” warfare, referencing China’s actions in the South China Sea and along India’s northern borders.
- He explained that grey-zone warfare involves military actions below a specific threshold that avoids immediate retaliation, with the benefits of such actions becoming apparent only over an extended period.
- Chauhan noted that historical disputes often serve as the origins for launching such strategies.
What is grey-zone warfare?
- Grey-zone warfare refers to a form of conflict that operates in the space between peace and open warfare.
- In this type of warfare, aggressive actions are taken by a state or non-state actor to achieve strategic objectives, but they often fall below the threshold that would traditionally warrant a full-scale military response.
- Grey-zone tactics typically involve the use of unconventional methods, such as cyber attacks, disinformation campaigns, economic coercion, and proxy forces, to gain an advantage without directly engaging in overt hostilities.
- Grey-zone warfare is characterized by ambiguity and deniability, making it challenging for targeted nations to respond effectively.
- It exploits the “grey areas” in international law and norms, allowing actors to pursue their goals while avoiding clear violations that could trigger a forceful counter-response.
Centre amends surrogacy rules, allows couples to use donor gametes
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
In response to Supreme Court scrutiny, the Central government in India has amended the Surrogacy (Regulation) Rules, 2022, introducing significant changes in the surrogacy process.
- The latest modifications address key aspects, allowing more flexibility for intending couples and single women.
Key Highlights
- The amended rules eliminate the requirement for both gametes in surrogacy procedures to come exclusively from the intending couple.
- Couples certified as suffering from a medical condition can now use at least one gamete from the intending couple.
- Single Women in Surrogacy:
- The updated rules specify that single women, whether widowed or divorced, opting for surrogacy must use their own eggs and donor sperm.
- This marks a shift in the requirements for single women undergoing surrogacy procedures.
- The amendment overturns the previous restriction on using donor eggs for gestational surrogacy by the intending couple.
- District Medical Boards can now certify the need for surrogacy using donor gametes in cases of medical conditions affecting either the husband or wife.
- Supreme Court Inquiry and Government Response:
- The changes follow inquiries from the Supreme Court questioning the government’s delay in addressing surrogacy rules.
- The Union Health Ministry, in response, issued the amendments to provide more inclusive and adaptable regulations for surrogacy.
About the Surrogacy (Regulation) Rules, 2022
- The Surrogacy (Regulation) Act was first introduced in the Lok Sabha on July 15, 2019.
- After being sent to a select committee, the Bill underwent a thorough revision, and the report was presented before the standing committee on February 5, 2020.
- Both houses of Parliament passed the Bill during the 2021 winter session, and it was signed by the President, coming into force in January 2022.
- Definition and Purpose of Surrogacy:
- The Act defines surrogacy as a practice where a woman gives birth to a child for an intending couple with the intention to hand it over to them after birth.
- Surrogacy is permitted only for altruistic purposes or for couples facing proven infertility or disease.
- Commercial purposes of surrogacy, such as sale, prostitution, or exploitation, are strictly prohibited.
- Post-Birth Status and Abortion Provisions:
- After birth, the child born through surrogacy is deemed to be the biological child of the couple.
- Abortion of the fetus is allowed only with the consent of the surrogate mother and authorities, following the provisions of the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act.
- Eligibility Criteria for Couples:
- Couples seeking surrogacy must meet specific eligibility criteria, including having been married for five years.
- The wife should be aged between 25-50 years, and the husband should be between 26-55 years.
- The couple must not have any living child (biological, adopted, or surrogate), except for cases involving a child with mental or physical disabilities or a life-threatening disorder.
- Certificates and Documentation:
- Couples need to obtain certificates of eligibility and essentiality for surrogacy.
- The “essential” certificate requires proof of proven infertility, certified by a District Medical Board.
- An order of parentage and custody of the surrogate child, issued by a Magistrate’s court, is also necessary.
- Insurance coverage for 16 months for the surrogate mother, covering any postpartum complications, is mandatory.
- Surrogate Eligibility Criteria:
- Surrogate mothers must be a close relative of the couple.
- She should be a married woman aged 25-35 with at least one child of her own.
- The woman can be a surrogate only once in her life.
- A certificate of medical and psychological fitness for surrogacy is required.
- Regulatory Bodies:
- The National Surrogacy Board (NSB) and State Surrogacy Boards (SSB) are to be constituted by the Centre and State governments, respectively.
- These boards advise the government on policy, review and monitor law implementation, and formulate a code of conduct for ART clinics and banks.
- These bodies enforce standards for surrogacy clinics, investigate breaches, and recommend modifications.
- Surrogacy clinics must apply for registration within 60 days of the appointment of the appropriate authority.
- Offences and Penalties:
- Offences include commercial surrogacy, selling embryos, and exploiting or abandoning a surrogate child.
- Penalties may include up to 10 years of imprisonment and a fine of up to Rs. 10 lakh.
- ART Act:
- ART encompasses techniques for achieving pregnancy by handling sperm or egg cells outside the human body and transferring embryos into the woman’s reproductive tract.
- Includes sperm donation, in-vitro fertilization (IVF), and gestational surrogacy.
- Registration and Regulations for ART Clinics and Banks:
- Every ART clinic and bank must be registered under the National Registry of Banks and Clinics of India.
- Registration is valid for five years, renewable for another five years, and may be cancelled or suspended for violations.
- Clinics are prohibited from providing a child of predetermined sex and must screen for genetic diseases before embryo implantation.
- ART procedures require written informed consent from both the couple and the donor.
- The couple must provide insurance coverage for the female donor in case of loss, damage, or death.
- Legal Status of Children:
- A child born via ART procedures is legally deemed the biological child of the couple, with entitlement to all rights.
- The donor retains no parental rights over the child.
- Prohibited Offences:
- Offences include abandoning or exploiting children born through ART, sale, purchase, or trade of embryos, and exploitation of the couple or donor.
- Transfer of an embryo into a male or an animal is also prohibited.
- Penalties:
- First-time offences may attract a fine of Rs 5 to 10 lakhs.
- Subsequent offences are punishable with imprisonment for 8 to 12 years and a fine of Rs 10 to 20 lakhs.
US achieves first moon landing in 50 years
(General Studies- Paper III)
Source : The Indian Express
In a groundbreaking achievement, Texas-based company Intuitive Machines has made history with the successful landing of its spacecraft, Odysseus, near the moon’s south pole.
- This accomplishment stands as the first lunar surface touchdown by the United States in over half a century and represents an unprecedented feat entirely led by the private sector.
Key Highlights
- The six-legged robot lander, Odysseus, executed the historic landing at approximately 6:23 p.m. EST.
- The landing site was near the moon’s South Pole, specifically at the Malapert A crater, as planned.
- The successful touchdown followed Odysseus reaching lunar orbit a week after its launch from Florida.
- The spacecraft was not designed for live video coverage, and the successful event was confirmed through signals.
- The vehicle is carrying a suite of scientific instruments and technology demonstrations for NASA and several commercial customers designed to operate for seven days on solar energy.
- NASA’s Historic Lunar Mission:
- NASA’s uncrewed IM-1 (Intuitive Machines 1) mission has achieved a historic controlled descent to the lunar surface, marking the first such landing by a U.S. spacecraft since Apollo 17 in 1972.
- Launched atop a Falcon 9 rocket by SpaceX, the mission focuses on collecting crucial data on space weather interactions, radio astronomy, and various lunar environment aspects.
- This venture sets the stage for NASA’s planned return of astronauts to the moon later in the decade.
- The successful landing is a significant step in advancing lunar exploration, with the United States standing as the sole country to have sent humans to the lunar surface.
- Dawn of Artemis:
- The successful arrival of the Odysseus spacecraft not only represents the first “soft landing” on the moon by a commercially manufactured and operated vehicle but also signifies a pivotal moment under NASA’s Artemis lunar program.
- This achievement comes as part of the U.S. initiative to return astronauts to the moon, with NASA aiming for the first crewed Artemis mission in late 2026.
- The focus on the moon’s South Pole, rich in frozen water, aligns with plans for sustained lunar exploration and serves as a stepping stone for future human missions to Mars.
- Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) Program:
- NASA’s CLPS program facilitates cost-effective lunar exploration by leveraging smaller, commercially operated landers like Odysseus.
- The program aims to deliver instruments and hardware to the moon through partnerships with private ventures, reducing costs compared to traditional NASA-led missions.
- Challenges and Risks in Commercial Lunar Exploration:
- While smaller landers offer cost advantages, recent setbacks, such as a propulsion system leak on Astrobotic Technology’s Peregrine lander, highlight the risks associated with relying on private ventures.
- Odysseus, part of Intuitive Machines’ mission, navigates the challenges of lunar exploration and sets the stage for future CLPS endeavors.
- Technological Evolution Driving Commercial Space Ventures:
- The proliferation of commercial space ventures is fueled by technological advancements, including modern microchips, electronic sensors, software, and lightweight metal alloys.
- The Apollo program and early lunar missions occurred at the dawn of the computer age, while contemporary innovations drive a new era in space exploration.