CURRENT AFFAIRS – 17/10/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 17/10/2024
- Army to commemorate 62 years of the Battle of Walong with China / सेना चीन के साथ वालोंग की लड़ाई की 62वीं वर्षगांठ मनाएगी
- Manufacture, marketing of antibiotics may be regulated; prescription to be mandatory / एंटीबायोटिक्स के निर्माण और विपणन को विनियमित किया जा सकता है; प्रिस्क्रिप्शन अनिवार्य होगा
- Climate change impact harsher on poorer farmers in India FAO report / भारत में गरीब किसानों पर जलवायु परिवर्तन का अधिक प्रभाव FAO रिपोर्ट
- Astronauts to wear Prada as Axiom unveils new suit / एक्सिओम द्वारा नए सूट के अनावरण के साथ अंतरिक्ष यात्री प्रादा पहनेंगे
- Tensions between North and South Korea / उत्तर और दक्षिण कोरिया के बीच तनाव
- Reimagining access to justice / न्याय तक पहुँच की पुनर्कल्पना
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 17/10/2024
Army to commemorate 62 years of the Battle of Walong with China / सेना चीन के साथ वालोंग की लड़ाई की 62वीं वर्षगांठ मनाएगी
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
The Battle of Walong during the 1962 Indo-China war is remembered for the Indian Army’s fierce defence in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Vastly outnumbered, Indian soldiers held their ground for 27 days.A month-long commemoration honours Indian soldiers’ bravery and sacrifice.
Battle of Walong:
- The Battle of Walong occurred during the 1962 Indo-China war in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Indian troops, comprising units like 6 Kumaon, 4 Sikh, 3 Gorkha Rifles, and 4 Dogra, fiercely defended the region.
- Despite being vastly outnumbered (800 Indian soldiers vs 4,000 Chinese troops), the Indian Army held its ground for 27 days.
- The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) was forced to deploy an additional 15,000 troops from the Tawang Sector to break the stalemate.
- Indian soldiers fought until they ran out of ammunition and resources, showcasing immense bravery.
- The Time magazine praised their courage in 1963, stating, “At Walong, Indian troops lacked everything. The only thing they did not lack was guts.”
सेना चीन के साथ वालोंग की लड़ाई की 62वीं वर्षगांठ मनाएगी
1962 के भारत-चीन युद्ध के दौरान वालोंग की लड़ाई को अरुणाचल प्रदेश में भारतीय सेना की ज़बरदस्त रक्षा के लिए याद किया जाता है।
- संख्या में काफ़ी कम होने के बावजूद भारतीय सैनिकों ने 27 दिनों तक अपनी ज़मीन पर डटे रहे। एक महीने तक चलने वाला स्मरणोत्सव भारतीय सैनिकों की बहादुरी और बलिदान का सम्मान करता है।
वालोंग की लड़ाई:
- वालोंग की लड़ाई 1962 के भारत-चीन युद्ध के दौरान अरुणाचल प्रदेश में हुई थी।
- 6 कुमाऊं, 4 सिख, 3 गोरखा राइफल्स और 4 डोगरा जैसी इकाइयों वाली भारतीय सेना ने इस क्षेत्र की जमकर रक्षा की।
- संख्या में बहुत कम होने के बावजूद (800 भारतीय सैनिक बनाम 4,000 चीनी सैनिक), भारतीय सेना ने 27 दिनों तक अपनी जमीन पर डटे रहे।
- पीपुल्स लिबरेशन आर्मी (PLA) को गतिरोध को तोड़ने के लिए तवांग सेक्टर से अतिरिक्त 15,000 सैनिकों को तैनात करने के लिए मजबूर होना पड़ा।
- भारतीय सैनिकों ने तब तक लड़ाई लड़ी जब तक उनके पास गोला-बारूद और संसाधन खत्म नहीं हो गए, उन्होंने बहुत बहादुरी दिखाई।
- टाइम पत्रिका ने 1963 में उनके साहस की प्रशंसा करते हुए कहा, “वालोंग में, भारतीय सैनिकों के पास हर चीज की कमी थी। केवल एक चीज की कमी नहीं थी, वह थी हिम्मत।”
Manufacture, marketing of antibiotics may be regulated; prescription to be mandatory / एंटीबायोटिक्स के निर्माण और विपणन को विनियमित किया जा सकता है; प्रिस्क्रिप्शन अनिवार्य होगा
Syllabus : GS 2 : Social Justice
Source : The Hindu
The Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB) has recommended that all antibiotics be included in the definition of “new drug” under the New Drugs and Clinical Trial (NDCT) Rules, 2019.
- This recommendation has been made to the Drugs Consultative Committee (DCC) to address the rising threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Reasons for the Step
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is recognized as a global public health threat.
- Misuse of antibiotics, antivirals, and antifungals has contributed to rising drug resistance.
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) report highlights drug resistance in diseases like urinary tract infections, bloodstream infections, pneumonia, and typhoid.
- This move aims to curb misuse of antibiotics and promote their responsible use to prevent further escalation of drug-resistant infections.
Implications of the Move
- Antibiotics will require manufacturing, marketing, and sale documentation under the “new drug” category.
- Manufacturers will need to obtain clearance from the Union government instead of State drug administrations.
- Patients will only be able to buy antibiotics with a prescription, limiting over-the-counter access.
- A blue strip or box will be added to the labelling of antimicrobial products under the Drugs Rules, 1945.
Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB)
- The Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB) is a statutory body established under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 in India.
- It advises the Central Government on technical matters related to drugs and cosmetics regulation.
- Comprising experts from various fields, DTAB focuses on ensuring drug safety, efficacy, and quality.
- The board addresses issues related to drug approvals, clinical trials, and amendments to existing drug regulations.
- DTAB plays a crucial role in formulating policies and guidelines to combat public health challenges, such as antimicrobial resistance.
- It conducts meetings to review recommendations from subcommittees and provides insights to improve India’s drug regulatory framework.
एंटीबायोटिक्स के निर्माण और विपणन को विनियमित किया जा सकता है; प्रिस्क्रिप्शन अनिवार्य होगा
औषधि तकनीकी सलाहकार बोर्ड (डीटीएबी) ने सिफारिश की है कि सभी एंटीबायोटिक दवाओं को नई औषधि और क्लिनिकल परीक्षण (एनडीसीटी) नियम, 2019 के तहत “नई दवा” की परिभाषा में शामिल किया जाना चाहिए।
- यह सिफारिश औषधि परामर्शदात्री समिति (DCC) को रोगाणुरोधी प्रतिरोध (AMR) के बढ़ते खतरे से निपटने के लिए की गई है।
इस कदम के कारण
- एंटीमाइक्रोबियल प्रतिरोध (एएमआर) को वैश्विक सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य खतरे के रूप में पहचाना जाता है।
- एंटीबायोटिक, एंटीवायरल और एंटीफंगल के दुरुपयोग ने दवा प्रतिरोध को बढ़ाने में योगदान दिया है।
- भारतीय चिकित्सा अनुसंधान परिषद (ICMR) की रिपोर्ट मूत्र पथ के संक्रमण, रक्तप्रवाह संक्रमण, निमोनिया और टाइफाइड जैसी बीमारियों में दवा प्रतिरोध को उजागर करती है।
- इस कदम का उद्देश्य एंटीबायोटिक दवाओं के दुरुपयोग को रोकना और दवा प्रतिरोधी संक्रमणों को और बढ़ने से रोकने के लिए उनके जिम्मेदार उपयोग को बढ़ावा देना है।
इस कदम के निहितार्थ
- एंटीबायोटिक दवाओं को “नई दवा” श्रेणी के तहत विनिर्माण, विपणन और बिक्री दस्तावेज की आवश्यकता होगी।
- निर्माताओं को राज्य दवा प्रशासन के बजाय केंद्र सरकार से मंजूरी लेनी होगी।
- रोगी केवल डॉक्टर के पर्चे के साथ एंटीबायोटिक खरीद पाएंगे, जिससे ओवर-द-काउंटर पहुंच सीमित हो जाएगी।
- औषधि नियम, 1945 के तहत रोगाणुरोधी उत्पादों की लेबलिंग में एक नीली पट्टी या बॉक्स जोड़ा जाएगा।
औषधि तकनीकी सलाहकार बोर्ड (DTAB)
- औषधि तकनीकी सलाहकार बोर्ड (DTAB) भारत में औषधि और प्रसाधन सामग्री अधिनियम, 1940 के तहत स्थापित एक वैधानिक निकाय है।
- यह केंद्र सरकार को औषधि और प्रसाधन सामग्री विनियमन से संबंधित तकनीकी मामलों पर सलाह देता है।
- विभिन्न क्षेत्रों के विशेषज्ञों से मिलकर बना DTAB औषधि सुरक्षा, प्रभावकारिता और गुणवत्ता सुनिश्चित करने पर ध्यान केंद्रित करता है।
- बोर्ड औषधि अनुमोदन, नैदानिक परीक्षणों और मौजूदा औषधि विनियमों में संशोधन से संबंधित मुद्दों को संबोधित करता है।
- DTAB रोगाणुरोधी प्रतिरोध जैसी सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य चुनौतियों से निपटने के लिए नीतियों और दिशानिर्देशों को तैयार करने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
- यह उपसमितियों की सिफारिशों की समीक्षा करने के लिए बैठकें आयोजित करता है और भारत के औषधि नियामक ढांचे को बेहतर बनाने के लिए अंतर्दृष्टि प्रदान करता है।
Climate change impact harsher on poorer farmers in India FAO report / भारत में गरीब किसानों पर जलवायु परिवर्तन का अधिक प्रभाव FAO रिपोर्ट
Syllabus : GS 3 : Enviroment
Source : The Hindu
The FAO report highlights the disproportionate impact of climate change on India’s rural poor, especially from heat stress and floods.
- It urges policy interventions to strengthen social protection and livelihood support.
Important Highlights Of The Report:
- Poor households lose an average of 5% of income from heat stress and 4.4% from floods annually compared to wealthier families.
- The report, titled “The Unjust Climate,” emphasises that the farming population in India is highly vulnerable to climate stressors, such as droughts and floods.
- During droughts, poor households dedicate more resources to agriculture due to fewer off-farm job opportunities.
- Structural inequalities exacerbate the vulnerability of these households, leading to reduced total incomes.
- The report calls for policy measures, including expanding social security and implementing anticipatory social protection programs.
- It recommends scaling up livelihood support ahead of extreme weather events and promoting workforce diversification to reduce poverty.
- In response NITI Aayog highlighted India’s efforts through National Innovations on Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) and the employment guarantee scheme to combat climate change.
भारत में गरीब किसानों पर जलवायु परिवर्तन का अधिक प्रभाव FAO रिपोर्ट
FAO की रिपोर्ट में भारत के ग्रामीण गरीबों पर जलवायु परिवर्तन के असमान प्रभाव को उजागर किया गया है, खासकर गर्मी के तनाव और बाढ़ से।
- इसमें सामाजिक सुरक्षा और आजीविका समर्थन को मजबूत करने के लिए नीतिगत हस्तक्षेप का आग्रह किया गया है।
रिपोर्ट की महत्वपूर्ण झलकियाँ:
- गरीब परिवारों को गर्मी के कारण होने वाले तनाव से सालाना औसतन 5% और बाढ़ के कारण होने वाली आय में 4% की हानि होती है, जबकि अमीर परिवारों को यह हानि नहीं होती।
- “अन्यायपूर्ण जलवायु” शीर्षक वाली रिपोर्ट में इस बात पर जोर दिया गया है कि भारत में खेती करने वाली आबादी सूखे और बाढ़ जैसे जलवायु तनावों के प्रति अत्यधिक संवेदनशील है।
- सूखे के दौरान, गरीब परिवार कम कृषि-बाह्य रोजगार अवसरों के कारण कृषि के लिए अधिक संसाधन समर्पित करते हैं।
- संरचनात्मक असमानताएँ इन परिवारों की भेद्यता को बढ़ाती हैं, जिससे कुल आय में कमी आती है।
- रिपोर्ट में नीतिगत उपायों की मांग की गई है, जिसमें सामाजिक सुरक्षा का विस्तार और पूर्वानुमानित सामाजिक सुरक्षा कार्यक्रमों को लागू करना शामिल है।
- यह चरम मौसम की घटनाओं से पहले आजीविका समर्थन को बढ़ाने और गरीबी को कम करने के लिए कार्यबल विविधीकरण को बढ़ावा देने की सिफारिश करता है।
- इसके जवाब में नीति आयोग ने जलवायु परिवर्तन से निपटने के लिए जलवायु अनुकूल कृषि (एनआईसीआरए) और रोजगार गारंटी योजना पर राष्ट्रीय नवाचारों के माध्यम से भारत के प्रयासों पर प्रकाश डाला।
Astronauts to wear Prada as Axiom unveils new suit / एक्सिओम द्वारा नए सूट के अनावरण के साथ अंतरिक्ष यात्री प्रादा पहनेंगे
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
Axiom Space has teamed up with Prada to design lunar suits for NASA’s Artemis 3 mission, set for September 2026.
- The suits will be used by astronauts exploring the lunar South Pole.
Analysis of the news:
- Axiom Space has collaborated with Prada to create lunar suits for NASA’s Artemis 3 mission, planned for September 2026.
- These lunar suits are designed for safety and comfort, allowing astronauts to perform tasks effectively in challenging conditions.
- They are unisex and adjustable to accommodate different sizes, ensuring inclusivity as the mission aims to include the first woman on the moon.
NASA’s Artemis 3 Mission
- NASA’s Artemis 3 mission aims to land astronauts on the lunar South Pole in September 2026, marking the first crewed moon landing since Apollo 17 in 1972.
- The mission will include the first woman and a man on the lunar surface, focusing on exploring the region’s resources, particularly water ice.
- Artemis 3 will utilise advanced technologies, including the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft, to transport astronauts to lunar orbit.
- The mission is part of NASA’s broader Artemis program, which seeks to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon and prepare for future missions to Mars.
एक्सिओम द्वारा नए सूट के अनावरण के साथ अंतरिक्ष यात्री प्रादा पहनेंगे
एक्सिओम स्पेस ने प्रादा के साथ मिलकर नासा के आर्टेमिस 3 मिशन के लिए चंद्र सूट डिजाइन किया है, जिसे सितंबर 2026 में लॉन्च किया जाना है।
- इन सूट का इस्तेमाल अंतरिक्ष यात्री चांद के दक्षिणी ध्रुव की खोज में करेंगे।
समाचार का विश्लेषण:
- एक्सिओम स्पेस ने नासा के आर्टेमिस 3 मिशन के लिए चंद्र सूट बनाने के लिए प्रादा के साथ मिलकर काम किया है, जिसे सितंबर 2026 में लॉन्च किया जाना है।
- इन चंद्र सूट को सुरक्षा और आराम के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया है, जिससे अंतरिक्ष यात्री चुनौतीपूर्ण परिस्थितियों में भी प्रभावी ढंग से काम कर सकते हैं।
- ये यूनिसेक्स हैं और अलग-अलग साइज़ के हिसाब से एडजस्ट किए जा सकते हैं, जिससे समावेशिता सुनिश्चित होती है क्योंकि मिशन का लक्ष्य चांद पर पहली महिला को शामिल करना है।
नासा का आर्टेमिस 3 मिशन
- नासा के आर्टेमिस 3 मिशन का लक्ष्य सितंबर 2026 में चांद के दक्षिणी ध्रुव पर अंतरिक्ष यात्रियों को उतारना है, जो 1972 में अपोलो 17 के बाद पहली क्रू मून लैंडिंग होगी।
- इस मिशन में चांद की सतह पर पहली महिला और एक पुरुष शामिल होंगे, जो इस क्षेत्र के संसाधनों, खास तौर पर पानी की बर्फ की खोज पर ध्यान केंद्रित करेंगे।
- आर्टेमिस 3 अंतरिक्ष यात्रियों को चंद्र की कक्षा में ले जाने के लिए स्पेस लॉन्च सिस्टम (SLS) रॉकेट और ओरियन अंतरिक्ष यान सहित उन्नत तकनीकों का उपयोग करेगा।
- यह मिशन नासा के व्यापक आर्टेमिस कार्यक्रम का हिस्सा है, जिसका उद्देश्य चंद्रमा पर एक स्थायी मानव उपस्थिति स्थापित करना और मंगल ग्रह के भविष्य के मिशनों के लिए तैयारी करना है।
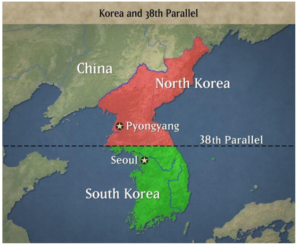
Tensions between North and South Korea / उत्तर और दक्षिण कोरिया के बीच तनाव
In News
Tensions between North and South Korea have escalated recently, with North Korea claiming over 1.4 million citizens applied to join the army.
- This followed the North’s destruction of roads and railways on its southern border, allegedly in retaliation for South Korea sending anti-Pyongyang propaganda via drones.
Analysis of News:
- Historical Context
- The Korean Peninsula was divided after Japan’s surrender in 1945, with the Soviet Union and China supporting North Korea and the U.S. backing South Korea.
- The Korean War (1950-1953) resulted in an armistice but no peace treaty, leaving both nations technically at war.
- Over the decades, reunification efforts were made, but progress was minimal, especially as North Korea developed nuclear weapons, facing sanctions from the UN and the West.
- Genesis of Current Tensions
- The breakdown of U.S.-North Korea talks in 2019, particularly after the failed Hanoi summit between Donald Trump and Kim Jong Un, was a turning point. Kim viewed the collapse of negotiations as a significant loss, leading North Korea to renew its nuclear program.
- In 2024, Kim declared South Korea as the North’s “primary foe,” officially abandoning hopes for peaceful reunification, culminating in recent border tensions.
- Potential for War
- While tensions are at their highest since 1950, experts believe that war is unlikely.
- North Korea’s actions are seen as tactics to strengthen internal unity by emphasizing external threats, rather than actual preparation for a large-scale conflict.
What about India’s Position in Korean Conflict?
- India’s Stand: India has consistently voiced its opposition to North Korean nuclear and missile tests. However, it has maintained a neutral stance regarding sanctions.
- Earlier, during the Korean War (1950- 53), India played a major role in a cease-fire agreement signed between both the warring sides.
- India’s Relations with North and South Korea: In May 2015, the bilateral relationship with South Korea was upgraded to ‘special strategic partnership’.
- India has a major role to play in South Korea’s Southern Policy under which the latter is looking at expanding relations beyond its immediate region.
- Similarly, South Korea is a major player in India’s Act East Policy under which India aims to promote economic cooperation, cultural ties and develop strategic relationships with countries in the Asia-Pacific.
- India has diplomatic relations with North Korea for over 47 years, which reflects the legacy of India’s commitment to the Non-Alignment Movement.
उत्तर और दक्षिण कोरिया के बीच तनाव
उत्तर कोरिया और दक्षिण कोरिया के बीच तनाव हाल ही में बढ़ गया है, उत्तर कोरिया ने दावा किया है कि उसके 1.4 मिलियन से अधिक नागरिकों ने सेना में शामिल होने के लिए आवेदन किया है।
- इसके बाद उत्तर कोरिया ने अपनी दक्षिणी सीमा पर सड़कों और रेलमार्गों को नष्ट कर दिया, कथित तौर पर दक्षिण कोरिया द्वारा ड्रोन के माध्यम से प्योंगयांग विरोधी प्रचार भेजने के प्रतिशोध में।
समाचार का विश्लेषण:
- ऐतिहासिक संदर्भ
- 1945 में जापान के आत्मसमर्पण के बाद कोरियाई प्रायद्वीप विभाजित हो गया था, सोवियत संघ और चीन ने उत्तर कोरिया का समर्थन किया और अमेरिका ने दक्षिण कोरिया का समर्थन किया।
- कोरियाई युद्ध (1950-1953) के परिणामस्वरूप युद्धविराम हुआ, लेकिन कोई शांति संधि नहीं हुई, जिससे दोनों देश तकनीकी रूप से युद्ध में थे।
- दशकों से, एकीकरण के प्रयास किए गए, लेकिन प्रगति बहुत कम थी, खासकर जब उत्तर कोरिया ने परमाणु हथियार विकसित किए, संयुक्त राष्ट्र और पश्चिम से प्रतिबंधों का सामना करना पड़ा।
- वर्तमान तनाव की उत्पत्ति
- 2019 में अमेरिका-उत्तर कोरिया वार्ता का टूटना, विशेष रूप से डोनाल्ड ट्रम्प और किम जोंग उन के बीच हनोई शिखर सम्मेलन के विफल होने के बाद, एक महत्वपूर्ण मोड़ था। किम ने वार्ता के टूटने को एक महत्वपूर्ण नुकसान के रूप में देखा, जिसके कारण उत्तर कोरिया ने अपने परमाणु कार्यक्रम को नवीनीकृत किया।
- 2024 में, किम ने दक्षिण कोरिया को उत्तर का “प्राथमिक दुश्मन” घोषित किया, आधिकारिक तौर पर शांतिपूर्ण एकीकरण की उम्मीदों को त्याग दिया, जिसका समापन हाल ही में सीमा तनाव में हुआ।
- युद्ध की संभावना
- 1950 के बाद से तनाव अपने उच्चतम स्तर पर है, लेकिन विशेषज्ञों का मानना है कि युद्ध की संभावना नहीं है।
- उत्तर कोरिया की कार्रवाइयों को बड़े पैमाने पर संघर्ष की वास्तविक तैयारी के बजाय बाहरी खतरों पर जोर देकर आंतरिक एकता को मजबूत करने की रणनीति के रूप में देखा जाता है।
- कोरियाई संघर्ष में भारत की स्थिति के बारे में क्या?
- भारत का रुख: भारत ने उत्तर कोरिया के परमाणु और मिसाइल परीक्षणों के प्रति लगातार अपना विरोध जताया है। हालांकि, प्रतिबंधों के संबंध में इसने तटस्थ रुख बनाए रखा है।
- इससे पहले, कोरियाई युद्ध (1950-53) के दौरान, भारत ने दोनों युद्धरत पक्षों के बीच हस्ताक्षरित युद्ध विराम समझौते में एक प्रमुख भूमिका निभाई थी।
- उत्तर और दक्षिण कोरिया के साथ भारत के संबंध: मई 2015 में, दक्षिण कोरिया के साथ द्विपक्षीय संबंधों को ‘विशेष रणनीतिक साझेदारी’ में अपग्रेड किया गया था।
- दक्षिण कोरिया की दक्षिणी नीति में भारत की प्रमुख भूमिका है, जिसके तहत कोरिया अपने तत्काल क्षेत्र से परे संबंधों का विस्तार करने पर विचार कर रहा है।
- इसी तरह, दक्षिण कोरिया भारत की एक्ट ईस्ट नीति में एक प्रमुख खिलाड़ी है जिसके तहत भारत का लक्ष्य एशिया-प्रशांत क्षेत्र के देशों के साथ आर्थिक सहयोग, सांस्कृतिक संबंधों को बढ़ावा देना और रणनीतिक संबंध विकसित करना है।
- भारत के उत्तर कोरिया के साथ 47 वर्षों से अधिक समय से राजनयिक संबंध हैं, जो गुटनिरपेक्ष आंदोलन के प्रति भारत की प्रतिबद्धता की विरासत को दर्शाता है।
Reimagining access to justice / न्याय तक पहुँच की पुनर्कल्पना
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity – Judiciary
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- Third-Party Litigation Funding (TPLF) is gaining prominence in India’s legal system as a tool to enhance access to justice for financially disadvantaged individuals.
- While supported by the Supreme Court, the lack of comprehensive regulation raises concerns over funder influence and ethical considerations.
- A national framework is necessary for effective implementation.
Introduction
- In the heart of India’s legal system, from the Supreme Court in Delhi to modest district courts in rural Bihar, a quiet revolution has been in the making for decades. This revolution is not about abrogating colonial laws, drafting new laws, or ensuring speedier verdicts.
- Instead, it centres on the question — who foots the bill for justice? In this context, the idea of Third-Party Litigation Funding (TPLF) has quickly emerged as a game-changer, potentially opening courtroom doors for many who felt they had been shut out.
What are the real-life struggles?
- A small shopkeeper from Pune’s markets, waging a lonely battle against a deep-pocketed e-commerce behemoth, or tribal villagers from Odisha challenging a polluting industrial giant — these are not just David and Goliath tales but real-life legal struggles that often end before they begin, not because of weak cases, but empty wallets.
What is the idea behind TPLF?
- The idea behind TPLF is to rope investors in that would bankroll such legal battles in exchange for a cut of the winnings.
- The need for such an idea in India is painfully clear, given the massive pendency and skyrocketing litigation expenses.
- Unfortunately, we have reached a stage where justice is increasingly becoming a luxury only a few can afford.
‘Potential equaliser’
- The Supreme Court in a landmark judgment: Bar Council of India v. A.K. Balaji cautiously gave a green signal to TPLF.
- It has viewed it as ‘a potential equaliser in the courtroom’ and categorically holding that TPLF was not off-limits as long as lawyers were not the ones bankrolling such cases.
- This stance is built on solid historical foundations from the 1876 Privy Council judgment Ram Coomar Coondoo v. Chunder Canto Mookerjee, which held that old English laws on champerty against such funding would not apply to India.
What are the potential ripple effects of TPLF?
- Broader reach: at every corner of India. In fact, we may witness situations with consumer groups in Mumbai possibly banding together against food adulterators,
- Bengaluru’s tech startups withstanding pressure against industry giants,
- tribes supported by NGOs taking on mining mafias without fear of financial ruin, and
- workers in textile mills facing unfair treatment being able to seek justice.
- In specialised fields such as medical malpractice or IPR, which heavily depend on expert testimonies, TPLF could honestly turn out to be the difference between a case being heard or silenced.
- TPLF might breathe new air into Public Interest Litigation, a powerful tool for social change since the 1980s.
What are the concerns and why is there the need for regulation?
- Any novel concept cannot evolve without thorough analysis and criticism.
- funders will cherry-pick only the most profitable cases, leaving socially crucial but less lucrative claims in the dust.
- how much say a funder should ordinarily be granted in matters of case strategy.
- Need for careful regulation: States such as Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, and Gujarat have dipped their toes by amending their civil procedure codes to accord recognition to ‘third-party financier of litigation’
- Need for framework: India still lacks a comprehensive national framework for TPLF.
- Such a regulatory framework is needed to ensure funders are both financially sound and ethically upright, to mandate transparency in funding deals, to protect clients’ decision-making rights, and to cap funders’ profits reasonably.
What are the broader implications of TPLF?
- A more accessible legal system should also bring about
- stronger consumer safeguards in a country plagued by fake products,
- better environmental protection in rapidly-industrialising regions, and
- more accountable institutions across the board.
- High Pendancy: With over ±80,000 cases pending at the top court and ±40 million pending cases across the nation, TPLF does offer more than a ray of hope.
- Scope of TPLF: In a nation where ‘justice for all’ has long been a constitutional dream, TPLF might help turn it into reality — one funded lawsuit at a time.
What are the considerations for structuring a regulatory framework?
- As we turn to the question of structuring a regulatory framework governing TPLF, several significant issues crop up.
- Licensing to be done or not: One crucial consideration is whether litigation funders should be licensed as financial service providers.
- Its suitability pertaining to India requires careful assessment.
- Establishing a dedicated oversight body: to monitor funders and regulate such funding is a topic that requires thoughtful deliberation and discussion.
- Capital adequacy: is another critical concern in TPLF regulation.
- For instance, Hong Kong’s Code of Practice for Third Party Funding in Arbitration 2019 mandates disclosure of financing details, information on adverse costs, liability for costs, and the extent of funder control.
- Addressing the costs concerns: India must evaluate if its mechanism of ordering security for costs addresses similar risks in the broader litigation context.
Way Forward
- Determining the appropriate level of court involvement and the extent of court approval in TPLF arrangements is a complex question that requires resolution.
- Identifying the right degree of court intervention and recognising specific arrangements that necessitate such oversight will become foundational pillars in shaping a well-defined regulatory framework. This must reconcile access to justice with preserving judicial integrity.
Conclusion
- TPLF presents both challenges and opportunities for India’s legal system.
- With well-designed regulations tailored to India’s legal landscape, the country could foster a thriving legal funding ecosystem while protecting all parties involved.
न्याय तक पहुँच की पुनर्कल्पना
संदर्भ:
- भारत की कानूनी प्रणाली में थर्ड पार्टी लिटिगेशन फंडिंग (TPLF) आर्थिक रूप से वंचित व्यक्तियों के लिए न्याय तक पहुँच बढ़ाने के साधन के रूप में प्रमुखता प्राप्त कर रही है।
- हालाँकि सर्वोच्च न्यायालय द्वारा इसका समर्थन किया जाता है, लेकिन व्यापक विनियमन की कमी से फंडर के प्रभाव और नैतिक विचारों पर चिंताएँ पैदा होती हैं।
- प्रभावी कार्यान्वयन के लिए एक राष्ट्रीय ढाँचा आवश्यक है।
परिचय
- भारत की कानूनी प्रणाली के केंद्र में, दिल्ली में सर्वोच्च न्यायालय से लेकर ग्रामीण बिहार में मामूली जिला न्यायालयों तक, दशकों से एक शांत क्रांति चल रही है। यह क्रांति औपनिवेशिक कानूनों को निरस्त करने, नए कानूनों का मसौदा तैयार करने या त्वरित निर्णय सुनिश्चित करने के बारे में नहीं है।
- इसके बजाय, यह इस सवाल पर केंद्रित है – न्याय का बिल कौन चुकाएगा?
- इस संदर्भ में, थर्ड पार्टी लिटिगेशन फंडिंग (TPLF) का विचार जल्दी ही एक गेम-चेंजर के रूप में उभरा है, जो संभावित रूप से उन लोगों के लिए अदालत के दरवाज़े खोल रहा है, जिन्हें लगता था कि उन्हें बाहर रखा गया था।
वास्तविक जीवन के संघर्ष क्या हैं?
- पुणे के बाजारों का एक छोटा दुकानदार, एक अमीर ई-कॉमर्स दिग्गज के खिलाफ अकेले लड़ाई लड़ रहा है, या ओडिशा के आदिवासी ग्रामीण प्रदूषण फैलाने वाली औद्योगिक दिग्गज को चुनौती दे रहे हैं – ये सिर्फ डेविड और गोलियत की कहानियां नहीं हैं, बल्कि वास्तविक जीवन की कानूनी लड़ाइयाँ हैं जो अक्सर कमज़ोर मामलों के कारण नहीं, बल्कि खाली जेबों के कारण शुरू होने से पहले ही खत्म हो जाती हैं।
TPLF के पीछे क्या विचार है?
- टीपीएलएफ के पीछे का विचार निवेशकों को आकर्षित करना है जो जीत के हिस्से के बदले में ऐसी कानूनी लड़ाइयों को वित्तपोषित करेंगे।
- भारत में इस तरह के विचार की आवश्यकता स्पष्ट रूप से स्पष्ट है, क्योंकि बहुत अधिक लंबित मामले और मुकदमेबाजी का खर्च आसमान छू रहा है।
- दुर्भाग्य से, हम एक ऐसे चरण में पहुँच गए हैं जहाँ न्याय तेजी से एक विलासिता बनता जा रहा है जिसे केवल कुछ ही लोग वहन कर सकते हैं।
‘संभावित तुल्यकारक’
- एक ऐतिहासिक फैसले में सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने: बार काउंसिल ऑफ इंडिया बनाम ए.के. बालाजी ने सावधानीपूर्वक टीपीएलएफ को हरी झंडी दी।
- इसने इसे ‘अदालत में संभावित बराबरी लाने वाले’ के रूप में देखा है और स्पष्ट रूप से माना है कि जब तक वकील ऐसे मामलों को वित्तपोषित नहीं करते, तब तक टीपीएलएफ को प्रतिबंधित नहीं किया जा सकता।
- यह रुख 1876 के प्रिवी काउंसिल के फैसले राम कुमार कूंडू बनाम चंदर कैंटो मुखर्जी से ठोस ऐतिहासिक नींव पर बना है, जिसमें कहा गया था कि इस तरह के वित्तपोषण के खिलाफ चैंपर्टी पर पुराने अंग्रेजी कानून भारत पर लागू नहीं होंगे।
TPLF के संभावित प्रभाव क्या हैं?
- व्यापक पहुंच: भारत के हर कोने में। वास्तव में, हम मुंबई में उपभोक्ता समूहों द्वारा खाद्य पदार्थों में मिलावट करने वालों के खिलाफ एकजुट होने की स्थिति देख सकते हैं,
- बेंगलुरु के तकनीकी स्टार्टअप उद्योग के दिग्गजों के खिलाफ दबाव का सामना कर सकते हैं,
- एनजीओ द्वारा समर्थित जनजातियाँ वित्तीय बर्बादी के डर के बिना खनन माफियाओं से लड़ सकती हैं, और
- कपड़ा मिलों में अनुचित व्यवहार का सामना करने वाले श्रमिक न्याय की मांग करने में सक्षम हो सकते हैं।
- विशेष क्षेत्रों जैसे चिकित्सा कदाचार या आईपीआर में, जो विशेषज्ञों की गवाही पर बहुत अधिक निर्भर करता है, टीपीएलएफ ईमानदारी से मामले की सुनवाई या चुप्पी के बीच अंतर साबित हो सकता है।
- टीपीएलएफ 1980 के दशक से सामाजिक परिवर्तन के लिए एक शक्तिशाली उपकरण, जनहित याचिका में नई जान फूंक सकता है।
चिंताएँ क्या हैं और विनियमन की आवश्यकता क्यों है?
- कोई भी नवीन अवधारणा गहन विश्लेषण और आलोचना के बिना विकसित नहीं हो सकती।
- वित्तपोषक केवल सबसे अधिक लाभदायक मामलों को ही चुनेंगे, जिससे सामाजिक रूप से महत्वपूर्ण लेकिन कम आकर्षक दावे धूल में मिल जाएँगे।
- मामले की रणनीति के मामलों में एक वित्तपोषक को आम तौर पर कितना अधिकार दिया जाना चाहिए।
- सावधानीपूर्वक विनियमन की आवश्यकता: महाराष्ट्र, मध्य प्रदेश, उड़ीसा और गुजरात जैसे राज्यों ने ‘मुकदमेबाजी के तीसरे पक्ष के वित्तपोषक’ को मान्यता देने के लिए अपने नागरिक प्रक्रिया संहिताओं में संशोधन करके अपने पैर जमा लिए हैं।
- ढांचे की आवश्यकता: भारत में अभी भी टीपीएलएफ के लिए एक व्यापक राष्ट्रीय ढाँचे का अभाव है।
- इस तरह के विनियामक ढांचे की आवश्यकता है ताकि यह सुनिश्चित किया जा सके कि वित्तपोषक वित्तीय रूप से सुदृढ़ और नैतिक रूप से ईमानदार हों, वित्तपोषक सौदों में पारदर्शिता को अनिवार्य बनाया जा सके, ग्राहकों के निर्णय लेने के अधिकारों की रक्षा की जा सके और वित्तपोषकों के मुनाफे को उचित रूप से सीमित किया जा सके।
TPLF के व्यापक निहितार्थ क्या हैं?
- अधिक सुलभ कानूनी प्रणाली को भी लाना चाहिए
- नकली उत्पादों से त्रस्त देश में मजबूत उपभोक्ता सुरक्षा उपाय,
- तेजी से औद्योगिकीकरण वाले क्षेत्रों में बेहतर पर्यावरण संरक्षण, और
- सभी क्षेत्रों में अधिक जवाबदेह संस्थान।
- उच्च लंबितता: शीर्ष न्यायालय में ±80,000 से अधिक लंबित मामलों और पूरे देश में ±40 मिलियन लंबित मामलों के साथ, TPLF आशा की एक किरण से अधिक प्रदान करता है।
- टीपीएलएफ का दायरा: ऐसे राष्ट्र में जहां ‘सभी के लिए न्याय’ लंबे समय से एक संवैधानिक सपना रहा है, टीपीएलएफ एक समय में एक वित्त पोषित मुकदमे के माध्यम से इसे वास्तविकता में बदलने में मदद कर सकता है।
विनियामक ढांचे की संरचना के लिए क्या विचार हैं?
- जब हम TPLF को नियंत्रित करने वाले विनियामक ढांचे की संरचना के प्रश्न की ओर मुड़ते हैं, तो कई महत्वपूर्ण मुद्दे सामने आते हैं।
- लाइसेंस दिया जाना चाहिए या नहीं: एक महत्वपूर्ण विचार यह है कि क्या मुकदमेबाजी के वित्तपोषणकर्ताओं को वित्तीय सेवा प्रदाता के रूप में लाइसेंस दिया जाना चाहिए।
- भारत के लिए इसकी उपयुक्तता का सावधानीपूर्वक मूल्यांकन करने की आवश्यकता है।
- एक समर्पित निरीक्षण निकाय की स्थापना: निधिदाताओं की निगरानी करना और ऐसे वित्तपोषण को विनियमित करना एक ऐसा विषय है जिस पर विचार-विमर्श और चर्चा की आवश्यकता है।
- पूंजी पर्याप्तता: टीपीएलएफ विनियमन में एक और महत्वपूर्ण चिंता है।
- उदाहरण के लिए, मध्यस्थता 2019 में तीसरे पक्ष के वित्तपोषण के लिए हांगकांग की आचार संहिता वित्तपोषण विवरण, प्रतिकूल लागतों की जानकारी, लागतों के लिए देयता और निधिदाता नियंत्रण की सीमा का खुलासा अनिवार्य करती है।
- लागत संबंधी चिंताओं को संबोधित करना: भारत को यह मूल्यांकन करना चाहिए कि लागतों के लिए सुरक्षा आदेश देने का उसका तंत्र व्यापक मुकदमेबाजी संदर्भ में समान जोखिमों को संबोधित करता है या नहीं।
आगे की राह
- टीपीएलएफ व्यवस्थाओं में अदालत की भागीदारी के उचित स्तर और अदालत की मंजूरी की सीमा का निर्धारण एक जटिल प्रश्न है जिसका समाधान आवश्यक है।
- न्यायालय के हस्तक्षेप की सही डिग्री की पहचान करना और ऐसी विशिष्ट व्यवस्थाओं को पहचानना जो इस तरह की निगरानी की आवश्यकता होती है, एक अच्छी तरह से परिभाषित नियामक ढांचे को आकार देने में आधारभूत स्तंभ बन जाएंगे। इसे न्यायिक अखंडता को बनाए रखने के साथ न्याय तक पहुंच को समेटना होगा।
निष्कर्ष
- टीपीएलएफ भारत की कानूनी प्रणाली के लिए चुनौतियां और अवसर दोनों प्रस्तुत करता है।
- भारत के कानूनी परिदृश्य के अनुरूप अच्छी तरह से डिजाइन किए गए विनियमों के साथ, देश सभी संबंधित पक्षों की सुरक्षा करते हुए एक समृद्ध कानूनी वित्तपोषण पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र को बढ़ावा दे सकता है।