CURRENT AFFAIRS – 17/09/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 17/09/2024
- ‘Renewable energy sector will power India’s growth’ / ‘नवीकरणीय ऊर्जा क्षेत्र भारत के विकास को गति देगा’
- How quantum computing can make large language models even better / क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग किस तरह बड़े भाषा मॉडल को और बेहतर बना सकती है
- How do emergency provisions impact Centre-State relations? / आपातकालीन प्रावधान केंद्र-राज्य संबंधों को कैसे प्रभावित करते हैं?
- What is the current status of the introduction of African cheetahs?/ अफ्रीकी चीतों की शुरूआत की वर्तमान स्थिति क्या है?
- Line of Actual Control (LAC) / वास्तविक नियंत्रण रेखा (LAC)
- Women-led development in the Rajya Sabha / राज्यसभा में महिलाओं के नेतृत्व में विकास
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 17/09/2024
‘Renewable energy sector will power India’s growth’ / ‘नवीकरणीय ऊर्जा क्षेत्र भारत के विकास को गति देगा’
Syllabus : GS 3 : Indian Economy
Source : The Hindu
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the fourth Global Renewable Energy Investors Meet and Expo in Gujarat, highlighting India’s commitment to renewable energy and rapid economic growth.
- He detailed government initiatives, including new industrial cities, high-speed rail, research funding, and renewable energy targets, reinforcing India’s leadership in green technology.
Analysis of the news:
- Steps taken by the Indian government to advance renewable energy and infrastructure development:
- Expansion of Infrastructure: Announced the creation of 12 new industrial cities and eight high-speed road corridors to boost economic growth.
- Railway Upgrades: Launched over 15 semi-high-speed Vande Bharat trains to enhance connectivity.
- Research Funding: Established a ₹1 trillion fund to promote research and development in various sectors.
- E-Mobility Promotion: Initiated various measures to drive the adoption of electric mobility.
- Biomanufacturing: Introduced the Bio-E3 policy to advance high-performance biomanufacturing.
- Offshore Wind Energy: Launched a viability gap funding scheme worth over ₹7,000 crore to support offshore wind projects.
- Renewable Energy Targets: Set a goal to achieve 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030.
- Climate Commitments: Achieved Paris climate goals nine years ahead of schedule.
These initiatives aim to reinforce India’s position as a leader in renewable energy and sustainable development.
‘नवीकरणीय ऊर्जा क्षेत्र भारत के विकास को गति देगा’
प्रधानमंत्री नरेंद्र मोदी ने गुजरात में चौथे वैश्विक अक्षय ऊर्जा निवेशक सम्मेलन और एक्सपो का उद्घाटन किया, जिसमें अक्षय ऊर्जा और तीव्र आर्थिक विकास के प्रति भारत की प्रतिबद्धता पर प्रकाश डाला गया।
- उन्होंने नए औद्योगिक शहरों, हाई-स्पीड रेल, अनुसंधान निधि और अक्षय ऊर्जा लक्ष्यों सहित सरकारी पहलों के बारे में विस्तार से बताया, जिससे हरित प्रौद्योगिकी में भारत के नेतृत्व को मजबूती मिली।
समाचार का विश्लेषण:
- अक्षय ऊर्जा और बुनियादी ढांचे के विकास को आगे बढ़ाने के लिए भारत सरकार द्वारा उठाए गए कदम:
- बुनियादी ढांचे का विस्तार: आर्थिक विकास को बढ़ावा देने के लिए 12 नए औद्योगिक शहरों और आठ हाई-स्पीड रोड कॉरिडोर के निर्माण की घोषणा की गई।
- रेलवे अपग्रेड: कनेक्टिविटी बढ़ाने के लिए 15 से अधिक सेमी-हाई-स्पीड वंदे भारत ट्रेनें शुरू की गईं।
- शोध निधि: विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में अनुसंधान और विकास को बढ़ावा देने के लिए ₹1 ट्रिलियन का कोष स्थापित किया गया।
- ई-मोबिलिटी प्रमोशन: इलेक्ट्रिक मोबिलिटी को अपनाने के लिए विभिन्न उपायों की शुरुआत की गई।
- बायोमैन्युफैक्चरिंग: उच्च प्रदर्शन वाले बायोमैन्युफैक्चरिंग को आगे बढ़ाने के लिए बायो-ई3 नीति की शुरुआत की गई।
- अपतटीय पवन ऊर्जा: अपतटीय पवन परियोजनाओं का समर्थन करने के लिए ₹7,000 करोड़ से अधिक की व्यवहार्यता अंतर निधि योजना शुरू की गई।
- अक्षय ऊर्जा लक्ष्य: 2030 तक 500 गीगावाट अक्षय ऊर्जा प्राप्त करने का लक्ष्य निर्धारित किया गया।
- जलवायु प्रतिबद्धताएँ: पेरिस जलवायु लक्ष्यों को निर्धारित समय से नौ साल पहले हासिल किया गया।
इन पहलों का उद्देश्य नवीकरणीय ऊर्जा और सतत विकास में अग्रणी के रूप में भारत की स्थिति को मजबूत करना है।
How quantum computing can make large language models even better / क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग किस तरह बड़े भाषा मॉडल को और बेहतर बना सकती है
Syllabus : GS 3 : Science and Technology
Source : The Hindu
Advancements in AI and NLP, particularly large language models, have revolutionised human-computer interactions but face challenges like high energy consumption and inaccuracies.
- Quantum computing, especially QNLP and QGen, offers promising solutions for more efficient, accurate, and sustainable AI systems.
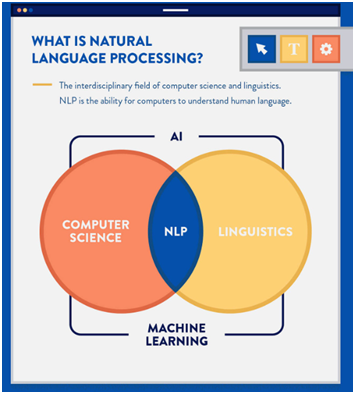
Transformations in AI and NLP:
- The landscape of AI, especially in natural language processing (NLP), has seen remarkable advancements.
- Large language models (LLMs) from OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft have revolutionised human-computer interactions through generative AI.
Problems with Current LLMs:
- High Energy Consumption: LLMs require significant computational power due to their large number of parameters. For instance, GPT-3 consumed 1,287 MWh of electricity for training, equivalent to an average household’s 120-year energy consumption.
- Pre-trained Nature and Hallucinations: LLMs generate contextually coherent but factually incorrect outputs, due to the limitations of their pre-training.
- Syntactic Issues: While LLMs excel in semantic understanding, they struggle with syntax, misinterpreting cues essential for generating accurate text.
Syntactics and Semantics with Quantum NLP:
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing leverages phenomena like superposition and entanglement to reduce energy costs and enhance efficiency.
- Quantum Natural Language Processing (QNLP): QNLP addresses the limitations of current LLMs by integrating syntax and semantics more effectively, lowering hallucinations, and improving context comprehension.
- Improved Language Understanding: QNLP offers a deeper understanding of language by better mapping grammar rules with quantum phenomena.
Time-Series Forecasting:
- Quantum Generative Model (QGen): Quantum computing can handle time-series data, using fewer parameters than classical models.
- Advantages of QGen: It is effective for both stationary (stable) and nonstationary (fluctuating) data, offering more efficient pattern detection and anomaly identification.
- Recent Research: A Japanese study demonstrated that a QGen AI model outperforms classical methods in financial problem-solving with fewer computational resources.
Conclusion:
- Quantum computing, particularly QNLP and QGen, holds significant potential to overcome current LLM challenges, enabling more sustainable, efficient, and powerful AI applications.
क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग किस तरह बड़े भाषा मॉडल को और बेहतर बना सकती है
एआई और एनएलपी में प्रगति, विशेष रूप से बड़े भाषा मॉडल, ने मानव-कंप्यूटर इंटरैक्शन में क्रांति ला दी है, लेकिन उच्च ऊर्जा खपत और अशुद्धि जैसी चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ता है।
- क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग, विशेष रूप से क्यूएनएलपी और क्यूजेन, अधिक कुशल, सटीक और टिकाऊ एआई सिस्टम के लिए आशाजनक समाधान प्रदान करते हैं।
एआई और एनएलपी में परिवर्तन:
- एआई के परिदृश्य में, विशेष रूप से प्राकृतिक भाषा प्रसंस्करण (एनएलपी) में, उल्लेखनीय प्रगति देखी गई है। ओपनएआई, गूगल और माइक्रोसॉफ्ट के बड़े भाषा मॉडल (एलएलएम) ने जनरेटिव एआई के माध्यम से मानव-कंप्यूटर इंटरैक्शन में क्रांति ला दी है।
वर्तमान एलएलएम के साथ समस्याएँ:
- उच्च ऊर्जा खपत: एलएलएम को उनके बड़ी संख्या में मापदंडों के कारण महत्वपूर्ण कम्प्यूटेशनल शक्ति की आवश्यकता होती है। उदाहरण के लिए, GPT-3 ने प्रशिक्षण के लिए 1,287 MWh बिजली की खपत की, जो एक औसत घर की 120 साल की ऊर्जा खपत के बराबर है।
- पूर्व-प्रशिक्षित प्रकृति और मतिभ्रम: एलएलएम अपने पूर्व-प्रशिक्षण की सीमाओं के कारण संदर्भगत रूप से सुसंगत लेकिन तथ्यात्मक रूप से गलत आउटपुट उत्पन्न करते हैं।
- वाक्यगत मुद्दे: जबकि एलएलएम अर्थपूर्ण समझ में उत्कृष्ट हैं, वे वाक्यविन्यास के साथ संघर्ष करते हैं, सटीक पाठ उत्पन्न करने के लिए आवश्यक संकेतों की गलत व्याख्या करते हैं।
क्वांटम एनएलपी के साथ वाक्यविन्यास और शब्दार्थ:
- क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग: क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग ऊर्जा लागत को कम करने और दक्षता बढ़ाने के लिए सुपरपोजिशन और उलझाव जैसी घटनाओं का लाभ उठाती है।
- क्वांटम प्राकृतिक भाषा प्रसंस्करण (QNLP): QNLP वाक्यविन्यास और शब्दार्थ को अधिक प्रभावी ढंग से एकीकृत करके, मतिभ्रम को कम करके और संदर्भ समझ में सुधार करके वर्तमान एलएलएम की सीमाओं को संबोधित करता है।
- बेहतर भाषा समझ: QNLP क्वांटम परिघटनाओं के साथ व्याकरण नियमों को बेहतर तरीके से मैप करके भाषा की गहरी समझ प्रदान करता है।
समय-श्रृंखला पूर्वानुमान:
- क्वांटम जनरेटिव मॉडल (QGen): क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग शास्त्रीय मॉडल की तुलना में कम मापदंडों का उपयोग करके समय-श्रृंखला डेटा को संभाल सकती है।
- QGen के लाभ: यह स्थिर (स्थिर) और गैर-स्थिर (उतार-चढ़ाव वाले) डेटा दोनों के लिए प्रभावी है, जो अधिक कुशल पैटर्न पहचान और विसंगति पहचान प्रदान करता है।
- हाल ही में किए गए शोध: एक जापानी अध्ययन ने प्रदर्शित किया कि QGen AI मॉडल कम कम्प्यूटेशनल संसाधनों के साथ वित्तीय समस्या-समाधान में शास्त्रीय तरीकों से बेहतर प्रदर्शन करता है।
निष्कर्ष:
- क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग, विशेष रूप से QNLP और QGen, वर्तमान LLM चुनौतियों को दूर करने की महत्वपूर्ण क्षमता रखते हैं, जिससे अधिक टिकाऊ, कुशल और शक्तिशाली AI अनुप्रयोग सक्षम होते हैं।
How do emergency provisions impact Centre-State relations? / आपातकालीन प्रावधान केंद्र-राज्य संबंधों को कैसे प्रभावित करते हैं?
Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity
Source : The Hindu
The ongoing violence in Manipur has reignited debates around Centre-State relations and the use of emergency provisions, particularly Articles 355 and 356,
- The news highlights constitutional obligations and the challenges of maintaining law and order in federal governance.
Federal Structure of India:
- India follows a federal system with distinct governments at the Centre and in the States.
- The Seventh Schedule of the Constitution distributes powers between the Union and States, with law and order being the State’s responsibility.
Emergency Provisions:
- Part XVIII of the Constitution outlines emergency provisions, with Articles 355 and 356 focusing on the Centre’s duty towards States.
- Article 355 mandates the Centre to protect States from external aggression and internal disturbances and ensure State governments function according to the Constitution.
- Article 356 allows for the imposition of President’s rule when a State government cannot operate constitutionally.
Purpose of Article 355:
- B.R. Ambedkar incorporated Article 355 to justify the Centre’s intervention under Article 356 only in cases of constitutional obligation, preventing arbitrary use of power.
Judicial Interpretation:
- Article 356 was often misused to dismiss State governments until the Supreme Court’s S.R. Bommai case (1994), which restricted its use to situations where there is a breakdown of constitutional machinery, not merely a law and order issue.
- Article 356 is subject to judicial review and should not be used for political reasons.
- The Supreme Court has broadened the scope of Article 355 in various rulings to permit all actions necessary to protect States and ensure constitutional governance.
Commissions’ Recommendations:
- The Sarkaria Commission (1987), National Commission to Review the Constitution (2002), and Punchhi Commission (2010) recommended using Article 356 as a last resort, emphasizing the Centre’s duty under Article 355.
Manipur Crisis:
- The ongoing violence in Manipur represents a serious constitutional and law-and-order crisis.
- While political considerations may prevent the invocation of Article 356, all actions under Article 355 must continue to restore peace.
आपातकालीन प्रावधान केंद्र-राज्य संबंधों को कैसे प्रभावित करते हैं?
मणिपुर में जारी हिंसा ने केंद्र-राज्य संबंधों और आपातकालीन प्रावधानों, विशेष रूप से अनुच्छेद 355 और 356 के उपयोग के बारे में बहस को फिर से हवा दे दी है।
- यह खबर संवैधानिक दायित्वों और संघीय शासन में कानून और व्यवस्था बनाए रखने की चुनौतियों पर प्रकाश डालती है।
भारत की संघीय संरचना:
- भारत एक संघीय प्रणाली का पालन करता है जिसमें केंद्र और राज्यों में अलग-अलग सरकारें हैं।
- संविधान की सातवीं अनुसूची संघ और राज्यों के बीच शक्तियों का वितरण करती है, जिसमें कानून और व्यवस्था राज्य की जिम्मेदारी है।
आपातकालीन प्रावधान:
- संविधान के भाग XVIII में आपातकालीन प्रावधानों की रूपरेखा दी गई है, जिसमें अनुच्छेद 355 और 356 राज्यों के प्रति केंद्र के कर्तव्य पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हैं।
- अनुच्छेद 355 केंद्र को राज्यों को बाहरी आक्रमण और आंतरिक अशांति से बचाने और राज्य सरकारों को संविधान के अनुसार काम करने के लिए बाध्य करता है।
- अनुच्छेद 356 राष्ट्रपति शासन लगाने की अनुमति देता है जब कोई राज्य सरकार संवैधानिक रूप से काम नहीं कर सकती है।
अनुच्छेद 355 का उद्देश्य:
- डॉ. बी.आर. अंबेडकर ने अनुच्छेद 356 के तहत केंद्र के हस्तक्षेप को केवल संवैधानिक दायित्व के मामलों में उचित ठहराने के लिए अनुच्छेद 355 को शामिल किया, जिससे शक्ति के मनमाने इस्तेमाल को रोका जा सके।
न्यायिक व्याख्या:
- अनुच्छेद 356 का अक्सर राज्य सरकारों को बर्खास्त करने के लिए दुरुपयोग किया जाता था जब तक कि सुप्रीम कोर्ट के एस.आर. बोम्मई केस (1994) में इसका इस्तेमाल केवल कानून और व्यवस्था के मुद्दे तक ही सीमित रखा गया था, न कि संवैधानिक तंत्र के टूटने की स्थिति में।
- अनुच्छेद 356 न्यायिक समीक्षा के अधीन है और इसका इस्तेमाल राजनीतिक कारणों से नहीं किया जाना चाहिए।
- उच्चतम न्यायालय ने राज्यों की रक्षा करने और संवैधानिक शासन सुनिश्चित करने के लिए आवश्यक सभी कार्रवाइयों की अनुमति देने के लिए विभिन्न फैसलों में अनुच्छेद 355 के दायरे को व्यापक बनाया है।
आयोगों की सिफारिशें:
- सरकारिया आयोग (1987), संविधान की समीक्षा के लिए राष्ट्रीय आयोग (2002), और पुंछी आयोग (2010) ने अनुच्छेद 356 को अंतिम उपाय के रूप में इस्तेमाल करने की सिफारिश की, जिसमें अनुच्छेद 355 के तहत केंद्र के कर्तव्य पर जोर दिया गया।
मणिपुर संकट:
- मणिपुर में चल रही हिंसा एक गंभीर संवैधानिक और कानून-व्यवस्था संकट का प्रतिनिधित्व करती है।
- जबकि राजनीतिक विचार अनुच्छेद 356 के इस्तेमाल को रोक सकते हैं, अनुच्छेद 355 के तहत सभी कार्रवाइयां शांति बहाल करने के लिए जारी रहनी चाहिए।
What is the current status of the introduction of African cheetahs?/ अफ्रीकी चीतों की शुरूआत की वर्तमान स्थिति क्या है?
Syllabus : GS 3 : Environment
Source : The Hindu
The Cheetah Action Plan (CAP) aims to introduce African cheetahs into India to restore ecosystems and boost eco-tourism.
- However, challenges include extended captivity, high cheetah mortality, and habitat concerns, raising doubts about the project’s long-term success.
Project Cheetah Overview
- Cheetah Action Plan (CAP): India’s initiative to introduce African cheetahs into its ecosystems, aiming to conserve the species and restore savanna habitats. It also supports future collaboration with Iran on Asiatic cheetah conservation.
- Project Management And Stakeholders: The NTCA, MoEFCC, Wildlife Institute of India, and Madhya Pradesh Forest Department oversee the project, with guidance from an expert committee.
- Eco-tourism: Cheetahs are intended to be a flagship species, promoting the restoration of dry-open forest ecosystems and benefiting local communities through eco-tourism.
Challenges of Long-Term Captivity
- Extended Captivity: The 12 surviving adult cheetahs have spent most of their time in captivity, contradicting the plan’s objective to release them into the wild. Prolonged captivity renders cheetahs unfit for release.
- International Standards: Namibian policy limits captivity for wild carnivores to three months, after which they are either euthanized or held permanently.
Cheetah Deaths
- Mortality Issues: Several cheetahs have died due to pre-existing conditions, poor management, or environmental factors like heatstroke. There are concerns about their suitability for survival in the Indian climate.
Location and Habitat
- Kuno National Park: Chosen as the most suitable site for cheetahs, although the animals have largely been held in captivity. Plans to release cheetahs in Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary and Banni grasslands are delayed.
- Habitat Concerns: Doubts remain about the availability of sufficient high-quality habitat (4,000-8,000 sq. km) needed to sustain a viable cheetah population.
Measurable Outcomes
- Short-term Goals: Cheetah survival, home range establishment, reproduction, and eco-tourism have not been met due to extended captivity.
- Long-term Goals: Establishing a stable metapopulation and improving local economies through conservation efforts are the project’s ultimate aims, with a timeline extending up to 40 years.
अफ्रीकी चीतों की शुरूआत की वर्तमान स्थिति क्या है?
चीता एक्शन प्लान (CAP) का उद्देश्य पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र को बहाल करने और इको-टूरिज्म को बढ़ावा देने के लिए अफ्रीकी चीतों को भारत में लाना है।
- हालांकि, चुनौतियों में लंबे समय तक कैद में रखना, चीतों की उच्च मृत्यु दर और आवास संबंधी चिंताएँ शामिल हैं, जिससे परियोजना की दीर्घकालिक सफलता पर संदेह पैदा होता है।
प्रोजेक्ट चीता अवलोकन
- चीता कार्य योजना (CAP): अफ्रीकी चीतों को अपने पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र में शामिल करने की भारत की पहल, जिसका उद्देश्य प्रजातियों का संरक्षण करना और सवाना आवासों को बहाल करना है। यह एशियाई चीता संरक्षण पर ईरान के साथ भविष्य के सहयोग का भी समर्थन करता है।
- परियोजना प्रबंधन और हितधारक: NTCA, MoEFCC, भारतीय वन्यजीव संस्थान और मध्य प्रदेश वन विभाग एक विशेषज्ञ समिति के मार्गदर्शन में परियोजना की देखरेख करते हैं।
- पारिस्थितिकी पर्यटन: चीतों को एक प्रमुख प्रजाति माना जाता है, जो शुष्क-खुले वन पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र की बहाली को बढ़ावा देता है और पारिस्थितिकी पर्यटन के माध्यम से स्थानीय समुदायों को लाभान्वित करता है।
दीर्घकालिक कैद की चुनौतियाँ
- विस्तारित कैद: 12 जीवित वयस्क चीतों ने अपना अधिकांश समय कैद में बिताया है, जो उन्हें जंगल में छोड़ने की योजना के उद्देश्य के विपरीत है। लंबे समय तक कैद में रहने से चीते रिहाई के लिए अयोग्य हो जाते हैं।
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय मानक: नामीबिया की नीति जंगली मांसाहारियों के लिए कैद को तीन महीने तक सीमित करती है, जिसके बाद उन्हें या तो मार दिया जाता है या स्थायी रूप से रखा जाता है।
- चीता की मृत्यु
- मृत्यु दर के मुद्दे: कई चीते पहले से मौजूद स्थितियों, खराब प्रबंधन या हीटस्ट्रोक जैसे पर्यावरणीय कारकों के कारण मर चुके हैं। भारतीय जलवायु में उनके जीवित रहने की उपयुक्तता के बारे में चिंताएँ हैं।
- स्थान और आवास
- कुनो राष्ट्रीय उद्यान: चीतों के लिए सबसे उपयुक्त स्थल के रूप में चुना गया है, हालाँकि जानवरों को बड़े पैमाने पर कैद में रखा गया है। गांधी सागर वन्यजीव अभयारण्य और बन्नी घास के मैदानों में चीतों को छोड़ने की योजना में देरी हो रही है।
- आवास संबंधी चिंताएँ: व्यवहार्य चीता आबादी को बनाए रखने के लिए आवश्यक पर्याप्त उच्च गुणवत्ता वाले आवास (4,000-8,000 वर्ग किमी) की उपलब्धता के बारे में संदेह बना हुआ है।
मापनीय परिणाम
- अल्पकालिक लक्ष्य: लंबे समय तक कैद में रहने के कारण चीता का अस्तित्व, घरेलू सीमा की स्थापना, प्रजनन और इको-टूरिज्म को पूरा नहीं किया जा सका है।
- दीर्घकालिक लक्ष्य: एक स्थिर मेटापॉपुलेशन की स्थापना करना और संरक्षण प्रयासों के माध्यम से स्थानीय अर्थव्यवस्थाओं में सुधार करना परियोजना का अंतिम लक्ष्य है, जिसकी समयसीमा 40 वर्ष तक है।
Line of Actual Control (LAC) / वास्तविक नियंत्रण रेखा (LAC)
Term In News
The Union Ministry of External Affairs recently said that about 75% of the “disengagement problems” with China on the military standoff along the Line of Actual Control in eastern Ladakh have been “sorted out”.

About Line of Actual Control (LAC):
- The LAC is the demarcation that separates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory.
- Although not recognised as an official border, it serves as a de facto border between India and China.
- India considers the LAC to be 3,488 km long, while the Chinese consider it to be only around 2,000 km.
- It is divided into three sectors:
- the eastern sector which spans Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim
- the middle sector, in Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh, and
- the western sector in Ladakh.
- It runs along Tibet and Xinjiang on the Chinese side.
- The LAC has always remained a major cause of tension between India and China. There are areas along the border where India and China have differing perceptions of the LAC.
- Due to both sides undertaking patrolling upto their respective perceptions of the LAC, transgressions do occur.
- India’s claim line is the line seen in the official boundary marked on the maps as released by the Survey of India, including both Aksai Chin and Gilgit-Baltistan. This means LAC is not the claim line for India.
- In China’s case, LAC is the claim line except in the eastern sector, where it claims the entire Arunachal Pradesh as South Tibet.
वास्तविक नियंत्रण रेखा (LAC)
केंद्रीय विदेश मंत्रालय ने हाल ही में कहा कि पूर्वी लद्दाख में वास्तविक नियंत्रण रेखा पर चीन के साथ सैन्य गतिरोध पर लगभग 75% “विघटन समस्याओं” को “सुलझा लिया गया है”।
वास्तविक नियंत्रण रेखा (LAC) के बारे में:
- LAC वह सीमांकन है जो भारतीय-नियंत्रित क्षेत्र को चीनी-नियंत्रित क्षेत्र से अलग करता है।
- हालाँकि इसे आधिकारिक सीमा के रूप में मान्यता नहीं दी गई है, लेकिन यह भारत और चीन के बीच एक वास्तविक सीमा के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- भारत LAC को 3,488 किलोमीटर लंबा मानता है, जबकि चीनी इसे केवल 2,000 किलोमीटर के आसपास मानते हैं।
- इसे तीन सेक्टरों में विभाजित किया गया है:
- पूर्वी सेक्टर जो अरुणाचल प्रदेश और सिक्किम तक फैला है
- मध्य सेक्टर, उत्तराखंड और हिमाचल प्रदेश में, और
- पश्चिमी सेक्टर लद्दाख में।
- यह चीन की तरफ तिब्बत और झिंजियांग से होकर गुजरता है।
- LAC हमेशा से भारत और चीन के बीच तनाव का एक प्रमुख कारण रहा है। सीमा पर ऐसे क्षेत्र हैं जहाँ भारत और चीन की LAC के बारे में अलग-अलग धारणाएँ हैं।
- दोनों पक्षों द्वारा LAC की अपनी-अपनी धारणाओं के अनुसार गश्त करने के कारण, उल्लंघन होते रहते हैं।
- भारत की दावा रेखा वह रेखा है जो सर्वे ऑफ इंडिया द्वारा जारी किए गए मानचित्रों पर आधिकारिक सीमा रेखा के रूप में अंकित है, जिसमें अक्साई चिन और गिलगित-बाल्टिस्तान दोनों शामिल हैं। इसका मतलब है कि LAC भारत के लिए दावा रेखा नहीं है। चीन के मामले में, LAC पूर्वी क्षेत्र को छोड़कर दावा रेखा है, जहाँ वह पूरे अरुणाचल प्रदेश को दक्षिण तिब्बत के रूप में दावा करता है।
Women-led development in the Rajya Sabha / राज्यसभा में महिलाओं के नेतृत्व में विकास
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- Under Vice President Jagdeep Dhankar’s leadership, the Rajya Sabha has introduced progressive measures to empower women in Parliament, symbolised by the reconstitution of the vice-chairpersons panel with women members.
- These initiatives align with the government’s women-led development approach, ensuring women play pivotal roles in decision-making and leadership positions.
What are the women centric measures taken?
- Women inclusive democracy: At a time when women are leading governance and development initiatives across the world, India’s legislature, a pivotal organ of its democracy, cannot afford to be left behind.
- Vice-Presidents women led intervention in the proceedings of house: VP has introduced a slew of progressive measures in the proceedings of the House as well as in the Secretariat.
- Dhankar has always held the view that the role of women in Parliament is enormous.
- He has stated that women are the backbone of Parliament and the country’s economic development.
- The Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam (Women’s Reservation Bill), 2023: Dhankar, in a historic move, reconstituted the panel of vice-chairpersons to include only women.
- Local and global positioning of women: He emphasised that this would “send a powerful message to the world at large and it would symbolise that they held a ‘commanding position’ during this epochal moment of change”.
- Women nomination increased: Dhankar also began the practice of nominating four women members, who constitute 50% of the panel of vice-chairpersons.
- Phangnon Konyak became the first woman Rajya Sabha member from Nagaland to preside over the House.
- Eminent athlete P.T. Usha also created history by becoming the first nominated MP in history to become the Vice Chairperson of the Rajya Sabha.
- Under India’s G20 presidency: The G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration underscored that investing in the empowerment of all women and girls has a multiplier effect in implementing the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- Gender Equality: India is already working tirelessly towards goal 5.5 of the Sustainable Development Goals, which calls for “women’s full and effective participation and equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decision-making in political, economic, and public life.”
- The Rajya Sabha Secretariat is expected to set the highest standards in this direction.
Initiatives in the Secretariat
- With the aim of striking a gender balance at the Rajya Sabha Secretariat, Mr. Dhankar has started many new initiatives.
- Breaking the stereotypes from male focussed to women oriented duties: The sections related to House duty were conventionally considered a male domain because they involved late sittings.
- Now efforts are made that all the gazetted women officers of the Secretariat were trained to perform House-related duties.
- Empowering the women staff: Today, the Table of the House is largely being ‘womanned’ by female officers.
- Accordingly, a duty roster is prepared and women officers are deputed on chamber duty.
- Moreover, an application-based system called ‘Vahan’ was introduced to address the problem of commutation during late sitting hours.
- Through this app, women officers can avail themselves of commutation facilities during odd hours.
- In addition, through a process of selection, some women officials of the Secretariat have been appointed as chamber attendants. This has created a favourable atmosphere even inside the House for women MPs.
- Breaking the stereotypes from male focussed to women oriented duties: The sections related to House duty were conventionally considered a male domain because they involved late sittings.
Women led growth is the future
- Progressive moves in Rajya Sabha: During various interactions with the officers of the Secretariat, Mr. Dhankar has unequivocally stated that women-led development is going to be the future road map of the Rajya Sabha Secretariat.
- Rise in leadership roles for women: Women officers have been appointed in key positions and leading roles in the Rajya Sabha Secretariat.
- Placing trust in women’s capacity: Responsibilities such as human resources, the legislative section, and the capacity-building division have been entrusted to women officers of the Secretariat.
- High skill-based work: Such as officiating in Parliamentary Standing Committees of the Rajya Sabha is being done by women at various levels.
- Occupation of senior positions: In security service are being occupied by women officers. Top performing women officers are being recognised and rewarded all across the services.
What are the key outcomes from Nari Shakti Adhiniyam (2023)?
- 33% Reservation for Women in Legislatures: The Bill reserves 33% of seats for women in the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies, aiming to increase women’s participation in governance.
- Long-term Impact on Women’s Representation: The Bill ensures that women are better represented in the political process, potentially reshaping the political landscape by empowering women as decision-makers.
- Women as Key Participants in Development: By providing more opportunities for women in legislatures, it aligns with the goal of women-led development, where women set the agenda for governance and development policies.
Way forward:
- Strengthening Legal Frameworks and Enforcement: Enhancing the implementation of existing laws, along with stricter penalties for gender-based violence, will ensure a safer environment for women.
- Promoting Economic Empowerment and Education: Expanding access to education, financial resources, and skill-building opportunities for women can bridge economic disparities, empowering them to take leadership roles in governance, business, and community development.
राज्यसभा में महिलाओं के नेतृत्व में विकास
Context :
- उपराष्ट्रपति जगदीप धनखड़ के नेतृत्व में, राज्यसभा ने संसद में महिलाओं को सशक्त बनाने के लिए प्रगतिशील उपाय पेश किए हैं, जिसका प्रतीक महिला सदस्यों के साथ उपाध्यक्षों के पैनल का पुनर्गठन है।
- ये पहल सरकार के महिला-नेतृत्व वाले विकास दृष्टिकोण के अनुरूप हैं, जो यह सुनिश्चित करती हैं कि महिलाएँ निर्णय लेने और नेतृत्व के पदों पर महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाएँ।
महिला केंद्रित उपाय क्या हैं?
- महिला समावेशी लोकतंत्र: ऐसे समय में जब महिलाएँ दुनिया भर में शासन और विकास की पहल का नेतृत्व कर रही हैं, भारत की विधायिका, जो लोकतंत्र का एक महत्वपूर्ण अंग है, पीछे नहीं रह सकती।
- उपराष्ट्रपति ने सदन की कार्यवाही में महिलाओं के नेतृत्व में हस्तक्षेप किया: उपराष्ट्रपति ने सदन की कार्यवाही के साथ-साथ सचिवालय में भी कई प्रगतिशील उपाय पेश किए हैं।
- श्री धनखड़ का हमेशा से मानना रहा है कि संसद में महिलाओं की भूमिका बहुत बड़ी है।
- उन्होंने कहा है कि महिलाएँ संसद और देश के आर्थिक विकास की रीढ़ हैं।
- नारी शक्ति वंदन अधिनियम (महिला आरक्षण विधेयक), 2023: श्री धनखड़ ने एक ऐतिहासिक कदम उठाते हुए उपाध्यक्षों के पैनल का पुनर्गठन किया, जिसमें केवल महिलाएं शामिल थीं।
- महिलाओं की स्थानीय और वैश्विक स्थिति: उन्होंने इस बात पर जोर दिया कि इससे “पूरी दुनिया को एक शक्तिशाली संदेश जाएगा और यह इस बात का प्रतीक होगा कि परिवर्तन के इस महत्वपूर्ण क्षण में वे एक ‘कमांडरिंग पोजीशन’ पर हैं”।
- महिलाओं के नामांकन में वृद्धि: श्री धनखड़ ने चार महिला सदस्यों को नामित करने की प्रथा भी शुरू की, जो उपाध्यक्षों के पैनल का 50% हिस्सा हैं।
- फांगनोन कोन्याक सदन की अध्यक्षता करने वाली नागालैंड की पहली महिला राज्यसभा सदस्य बनीं।
- प्रख्यात एथलीट पी.टी. उषा ने भी इतिहास में पहली मनोनीत सांसद बनकर इतिहास रच दिया, जो राज्यसभा की उपाध्यक्ष बनीं।
- भारत की जी-20 अध्यक्षता के तहत: जी-20 नई दिल्ली नेताओं के घोषणापत्र ने इस बात को रेखांकित किया कि सभी महिलाओं और लड़कियों के सशक्तीकरण में निवेश करने से सतत विकास के लिए 2030 एजेंडा को लागू करने में कई गुना प्रभाव पड़ता है।
- लैंगिक समानता: भारत पहले से ही सतत विकास लक्ष्यों के लक्ष्य 5 की दिशा में अथक प्रयास कर रहा है, जिसमें “राजनीतिक, आर्थिक और सार्वजनिक जीवन में निर्णय लेने के सभी स्तरों पर महिलाओं की पूर्ण और प्रभावी भागीदारी और नेतृत्व के लिए समान अवसर” की बात कही गई है।
- राज्यसभा सचिवालय से इस दिशा में उच्चतम मानक स्थापित करने की अपेक्षा की जाती है।
सचिवालय में पहल
- राज्यसभा सचिवालय में लैंगिक संतुलन बनाने के उद्देश्य से, श्री धनखड़ ने कई नई पहल शुरू की हैं।
- पुरुष केंद्रित से महिला उन्मुख कर्तव्यों की रूढ़िवादिता को तोड़ना: सदन की ड्यूटी से संबंधित अनुभागों को पारंपरिक रूप से पुरुषों का क्षेत्र माना जाता था क्योंकि उनमें देर तक बैठना पड़ता था।
- अब प्रयास किए जा रहे हैं कि सचिवालय की सभी राजपत्रित महिला अधिकारियों को सदन से संबंधित कर्तव्यों का पालन करने के लिए प्रशिक्षित किया जाए।
- महिला कर्मचारियों को सशक्त बनाना: आज सदन की मेज पर मुख्य रूप से महिला अधिकारी ही बैठी हैं।
- तदनुसार, एक ड्यूटी रोस्टर तैयार किया जाता है और महिला अधिकारियों को चैंबर ड्यूटी पर तैनात किया जाता है।
- इसके अलावा, देर रात तक बैठने के दौरान आने-जाने की समस्या को दूर करने के लिए ‘वाहन’ नामक एक एप्लीकेशन-आधारित प्रणाली शुरू की गई है।
- इस ऐप के माध्यम से, महिला अधिकारी विषम घंटों के दौरान आने-जाने की सुविधा का लाभ उठा सकती हैं।
- इसके अलावा, चयन की एक प्रक्रिया के माध्यम से, सचिवालय की कुछ महिला अधिकारियों को चैंबर अटेंडेंट के रूप में नियुक्त किया गया है। इससे महिला सांसदों के लिए सदन के अंदर भी अनुकूल माहौल बना है।
- पुरुष केंद्रित से महिला उन्मुख कर्तव्यों की रूढ़िवादिता को तोड़ना: सदन की ड्यूटी से संबंधित अनुभागों को पारंपरिक रूप से पुरुषों का क्षेत्र माना जाता था क्योंकि उनमें देर तक बैठना पड़ता था।
महिलाओं के नेतृत्व में विकास ही भविष्य है
- राज्यसभा में प्रगतिशील कदम: सचिवालय के अधिकारियों के साथ विभिन्न बातचीत के दौरान, श्री धनखड़ ने स्पष्ट रूप से कहा है कि महिलाओं के नेतृत्व में विकास ही राज्यसभा सचिवालय का भविष्य का रोडमैप होगा।
- महिलाओं के लिए नेतृत्व की भूमिकाओं में वृद्धि: महिला अधिकारियों को राज्यसभा सचिवालय में प्रमुख पदों और अग्रणी भूमिकाओं में नियुक्त किया गया है।
- महिलाओं की क्षमता पर भरोसा: मानव संसाधन, विधायी अनुभाग और क्षमता निर्माण प्रभाग जैसी जिम्मेदारियाँ सचिवालय की महिला अधिकारियों को सौंपी गई हैं।
- उच्च कौशल आधारित कार्य: जैसे कि राज्यसभा की संसदीय स्थायी समितियों में कार्य करना, विभिन्न स्तरों पर महिलाओं द्वारा किया जा रहा है।
- वरिष्ठ पदों पर आसीन होना: सुरक्षा सेवा में महिला अधिकारी आसीन हैं। सभी सेवाओं में सर्वश्रेष्ठ प्रदर्शन करने वाली महिला अधिकारियों को मान्यता दी जा रही है और उन्हें पुरस्कृत किया जा रहा है।
नारी शक्ति अधिनियम (2023) के मुख्य परिणाम क्या हैं?
- विधानसभाओं में महिलाओं के लिए 33% आरक्षण: विधेयक में लोकसभा और राज्य विधानसभाओं में महिलाओं के लिए 33% सीटें आरक्षित की गई हैं, जिसका उद्देश्य शासन में महिलाओं की भागीदारी बढ़ाना है।
- महिलाओं के प्रतिनिधित्व पर दीर्घकालिक प्रभाव: विधेयक यह सुनिश्चित करता है कि महिलाओं को राजनीतिक प्रक्रिया में बेहतर प्रतिनिधित्व मिले, संभावित रूप से महिलाओं को निर्णयकर्ता के रूप में सशक्त बनाकर राजनीतिक परिदृश्य को नया आकार दिया जा सके।
- विकास में प्रमुख भागीदार के रूप में महिलाएँ: विधायिकाओं में महिलाओं के लिए अधिक अवसर प्रदान करके, यह महिलाओं के नेतृत्व वाले विकास के लक्ष्य के साथ संरेखित होता है, जहाँ महिलाएँ शासन और विकास नीतियों का एजेंडा निर्धारित करती हैं।
आगे की राह:
- कानूनी ढाँचे और प्रवर्तन को मज़बूत करना: लिंग आधारित हिंसा के लिए सख्त दंड के साथ-साथ मौजूदा कानूनों के कार्यान्वयन को बढ़ाना महिलाओं के लिए एक सुरक्षित वातावरण सुनिश्चित करेगा।
- आर्थिक सशक्तिकरण और शिक्षा को बढ़ावा देना: महिलाओं के लिए शिक्षा, वित्तीय संसाधनों और कौशल-निर्माण के अवसरों तक पहुँच का विस्तार करके आर्थिक असमानताओं को पाटा जा सकता है, जिससे उन्हें शासन, व्यवसाय और सामुदायिक विकास में नेतृत्व की भूमिका निभाने के लिए सशक्त बनाया जा सकता है।