CURRENT AFFAIRS – 16/05/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 16/05/2024
- Army set to receive next batch of shoulder-fired Igla-S air defence systems / सेना Igla-S वायु रक्षा प्रणालियों का अगला बैच प्राप्त करने के लिए तैयार है
- India records highest number of Internet shutdowns in 2023 / भारत में 2023 में सबसे ज्यादा इंटरनेट शटडाउन दर्ज किए गए
- Social media’s impact on Indian politics / सोशल मीडिया का भारतीय राजनीति पर प्रभाव
- On Delhi’s mounting waste crisis / दिल्ली के बढ़ते अपशिष्ट संकट पर
- 1. Election Commission of India /भारत का चुनाव आयोग 2. India Meteorological Department /भारत मौसम विज्ञान विभाग 3. What is Cancer? / कैंसर क्या है?
- The case for election day as a holiday /चुनाव के दिन छुट्टी का मामला
- Major Physical Divisions of South America / दक्षिण अमेरिका के प्रमुख भौतिक प्रभाग [Mapping]
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 16/05/2024
Army set to receive next batch of shoulder-fired Igla-S air defence systems / सेना Igla-S वायु रक्षा प्रणालियों का अगला बैच प्राप्त करने के लिए तैयार है
Source : The Hindu
- It is a man-portable air defence system (MANPADS) developed by Russia.
- It is known in the West as SA-24 Grinch.
- It entered service with the Russian Army in 2004.
- It can be fired by an individual or crew to bring down an enemy aircraft.
- It has the capability of bringing down low-flying aircraft. It can also identify and neutralise air targets, such as cruise missiles and drones.
Features:
- The Igla-S system comprises of combat equipment, including the 9M342 missile and the 9P522 launching mechanism, along with maintenance equipment, including the 9V866-2 mobile test station and the 9F719-2 test set.
- It has an effective range upto 6 km.
- The limiting altitude of effective target destruction for the “Igla-S” complex is 3.5 km.
- It has a heavier, more powerful warhead to maximize damage capabilities, as well as contact and timed fuzes for increased attack range.
- The warhead is a high-explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) and weighs 2.5 kg.
- Guidance is homing via infrared.
Igla-S के बारे में:
- यह रूस द्वारा विकसित एक मानव-पोर्टेबल वायु रक्षा प्रणाली (MANPADS) है।
- इसे पश्चिम में SA-24 ग्रिंच के नाम से जाना जाता है।
- इसने 2004 में रूसी सेना के साथ सेवा में प्रवेश किया।
- इसे किसी व्यक्ति या चालक दल द्वारा दुश्मन के विमान को गिराने के लिए दागा जा सकता है।
- इसमें कम ऊंचाई पर उड़ रहे विमानों को गिराने की क्षमता है। यह क्रूज़ मिसाइलों और ड्रोन जैसे हवाई लक्ष्यों की भी पहचान कर सकता है और उन्हें निष्क्रिय कर सकता है।
विशेषताएँ:
- इग्ला-एस प्रणाली में लड़ाकू उपकरण शामिल हैं, जिसमें 9M342 मिसाइल और 9P522 लॉन्चिंग तंत्र के साथ-साथ रखरखाव उपकरण शामिल हैं, जिसमें 9V866-2 मोबाइल परीक्षण स्टेशन और 9F719-2 परीक्षण सेट शामिल हैं।
- इसकी प्रभावी रेंज 6 किमी तक है।
- “इगला-एस” कॉम्प्लेक्स के लिए प्रभावी लक्ष्य विनाश की सीमित ऊंचाई 5 किमी है।
- इसमें क्षति क्षमताओं को अधिकतम करने के लिए एक भारी, अधिक शक्तिशाली वारहेड है, साथ ही बढ़ी हुई हमले की सीमा के लिए संपर्क और समयबद्ध फ़्यूज़ भी हैं।
- यह बम उच्च-विस्फोटक विखंडन (HE-FRAG) है और इसका वजन 5 किलोग्राम है।
- इन्फ्रारेड के माध्यम से मार्गदर्शन घर आ रहा है।
India records highest number of Internet shutdowns in 2023 / भारत में 2023 में सबसे ज्यादा इंटरनेट शटडाउन दर्ज किए गए
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
Internet Shutdowns in India:
- India has recorded the highest number of internet shutdowns in the world.
- Such shutdowns are never or almost never implemented in most parts of Europe, North and South America, and Oceania, while they are rampant in Africa and Asia.
Who Governs Internet Shutdowns in India?
- Internet shutdown orders are governed under the Temporary Suspension of Telecom Services (Public Emergency or Public Safety) Rules, 2017, under the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885.
- Using Section 144 of the Code of Criminal Procedure: It justifies the communications blockade and the continuance of it, has been a rising trend.
How does it violate fundamental Rights?
- The Internet plays a crucial role in realizing numerous Fundamental Rights beyond Freedom of Speech and Expression.
- Article 19 of the Constitution mentions freedom of speech and freedom to practise any profession.
- Article 21 protects the right to life and liberty, which also encompasses the right to education and the right to exercise one’s freedom to access the Internet.
- In the digital age, people utilize it for essential activities such as accessing rations, conducting card transactions, communicating with relatives, managing healthcare, and more, all of which are vital for their daily functioning.
Supreme Court’s View on Internet Shutdown
- The Supreme Court has held in various decisions, including in Anuradha Bhasinand Faheema Shirin, that access to the Internethas to be preserved.
- Shutdowns should be exercised only in situations which require exceptional control and surveillance.
- The Court has said a shutdown needs to be temporary, limited in scope, lawful and proportionate.
भारत में इंटरनेट शटडाउन:
- दुनिया में सबसे ज्यादा इंटरनेट शटडाउन भारत में दर्ज किया गया है।
- यूरोप, उत्तर और दक्षिण अमेरिका और ओशिनिया के अधिकांश हिस्सों में ऐसे शटडाउन कभी या लगभग कभी लागू नहीं किए जाते हैं, जबकि वे अफ्रीका और एशिया में बड़े पैमाने पर होते हैं।
भारत में इंटरनेट शटडाउन को कौन नियंत्रित करता है?
- इंटरनेट शटडाउन आदेश भारतीय टेलीग्राफ अधिनियम, 1885 के तहत दूरसंचार सेवाओं के अस्थायी निलंबन (सार्वजनिक आपातकाल या सार्वजनिक सुरक्षा) नियम, 2017 के तहत नियंत्रित होते हैं।
- दंड प्रक्रिया संहिता की धारा 144 का उपयोग करना: यह संचार नाकाबंदी को उचित ठहराता है और इसे जारी रखना एक बढ़ती प्रवृत्ति रही है।
यह मौलिक अधिकारों का उल्लंघन कैसे करता है?
- बोलने और अभिव्यक्ति की स्वतंत्रता से परे कई मौलिक अधिकारों को साकार करने में इंटरनेट महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
- संविधान के अनुच्छेद 19 में अभिव्यक्ति की स्वतंत्रता और कोई भी पेशा अपनाने की स्वतंत्रता का उल्लेख है।
- अनुच्छेद 21 जीवन और स्वतंत्रता के अधिकार की रक्षा करता है, जिसमें शिक्षा का अधिकार और इंटरनेट तक पहुंच की स्वतंत्रता का प्रयोग करने का अधिकार भी शामिल है।
- डिजिटल युग में, लोग इसका उपयोग आवश्यक गतिविधियों जैसे राशन तक पहुंच, कार्ड लेनदेन करना, रिश्तेदारों के साथ संवाद करना, स्वास्थ्य देखभाल का प्रबंधन और बहुत कुछ के लिए करते हैं, जो उनके दैनिक कामकाज के लिए महत्वपूर्ण हैं।
इंटरनेट शटडाउन पर सुप्रीम कोर्ट का नजरिया
- सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने अनुराधा भसीन और फहीमा शिरीन सहित विभिन्न फैसलों में कहा है कि इंटरनेट तक पहुंच को संरक्षित किया जाना चाहिए।
- शटडाउन केवल उन स्थितियों में किया जाना चाहिए जिनमें असाधारण नियंत्रण और निगरानी की आवश्यकता होती है।
- कोर्ट ने कहा है कि शटडाउन अस्थायी, सीमित दायरे वाला, वैध और आनुपातिक होना चाहिए।
Social media’s impact on Indian politics / सोशल मीडिया का भारतीय राजनीति पर प्रभाव
(General Studies- Paper I, II & III)
Source : The Hindu
Potential Impact of Social Media On Election Process
Pros of Social Media on Election Process:
- Increased Voter Engagement: Social media platforms provide opportunities for political parties and candidates to engage directly with voters, encouraging participation and awareness.
- Wider Reach: Social media enables political campaigns to reach a broader audience, including young voters and those in remote areas, enhancing political communication and outreach.
- Transparency: Real-time updates and information sharing on social media promote transparency in the electoral process, allowing voters to access news and updates easily.
- Cost-Effective Campaigning: Social media campaigns are often more cost-effective than traditional advertising methods, levelling the playing field for candidates with limited resources.
- Political Discourse: Social media facilitates political discourse and debate, allowing citizens to discuss issues, share opinions, and participate in democratic dialogue.
Cons of Social Media on Election Process:
- Spread of Misinformation: Social media can be a breeding ground for the spread of fake news, rumours, and misinformation, influencing voter perceptions and decision-making.
- Polarisation: Echo chambers and filter bubbles on social media platforms can reinforce existing biases and polarise political discourse, leading to increased divisiveness.
- Manipulation: Social media can be exploited for political manipulation, including the spread of propaganda, disinformation campaigns, and foreign interference.
- Privacy Concerns: The collection and use of personal data on social media raise privacy concerns, particularly regarding targeted advertising and micro-targeting of voters.
Digital Divide: Not all citizens have equal access to social media platforms, creating a digital divide that may exclude certain demographics from participating fully in the electoral process.
चुनाव प्रक्रिया पर सोशल मीडिया का संभावित प्रभाव
चुनाव प्रक्रिया पर सोशल मीडिया के फायदे:
- मतदाता जुड़ाव में वृद्धि: सोशल मीडिया प्लेटफ़ॉर्म राजनीतिक दलों और उम्मीदवारों को मतदाताओं से सीधे जुड़ने, भागीदारी और जागरूकता को प्रोत्साहित करने के अवसर प्रदान करते हैं।
- व्यापक पहुंच: सोशल मीडिया राजनीतिक अभियानों को व्यापक दर्शकों तक पहुंचने में सक्षम बनाता है, जिसमें युवा मतदाता और दूरदराज के इलाकों के मतदाता भी शामिल हैं, जिससे राजनीतिक संचार और पहुंच बढ़ती है।
- पारदर्शिता: सोशल मीडिया पर वास्तविक समय के अपडेट और जानकारी साझा करने से चुनावी प्रक्रिया में पारदर्शिता को बढ़ावा मिलता है, जिससे मतदाताओं को समाचार और अपडेट आसानी से मिल पाते हैं।
- लागत-प्रभावी प्रचार: सोशल मीडिया अभियान अक्सर पारंपरिक विज्ञापन तरीकों की तुलना में अधिक लागत-प्रभावी होते हैं, जो सीमित संसाधनों वाले उम्मीदवारों के लिए समान अवसर प्रदान करते हैं।
- राजनीतिक विमर्श: सोशल मीडिया राजनीतिक विमर्श और बहस को सुविधाजनक बनाता है, जिससे नागरिकों को मुद्दों पर चर्चा करने, राय साझा करने और लोकतांत्रिक संवाद में भाग लेने की अनुमति मिलती है।
चुनाव प्रक्रिया पर सोशल मीडिया के नुकसान:
- गलत सूचना का प्रसार: सोशल मीडिया फर्जी खबरों, अफवाहों और गलत सूचनाओं के प्रसार के लिए प्रजनन स्थल बन सकता है, जो मतदाताओं की धारणाओं और निर्णय लेने को प्रभावित करता है।
- ध्रुवीकरण: सोशल मीडिया प्लेटफॉर्म पर इको चैंबर और फिल्टर बबल मौजूदा पूर्वाग्रहों को मजबूत कर सकते हैं और राजनीतिक प्रवचन का ध्रुवीकरण कर सकते हैं, जिससे विभाजन बढ़ सकता है।
- हेरफेर: सोशल मीडिया का उपयोग राजनीतिक हेरफेर के लिए किया जा सकता है, जिसमें प्रचार प्रसार, दुष्प्रचार अभियान और विदेशी हस्तक्षेप शामिल हैं।
- गोपनीयता संबंधी चिंताएँ: सोशल मीडिया पर व्यक्तिगत डेटा का संग्रह और उपयोग गोपनीयता संबंधी चिंताओं को बढ़ाता है, विशेष रूप से लक्षित विज्ञापन और मतदाताओं के सूक्ष्म-लक्ष्यीकरण के संबंध में।
डिजिटल विभाजन: सभी नागरिकों के पास सोशल मीडिया प्लेटफ़ॉर्म तक समान पहुंच नहीं है, जिससे एक डिजिटल विभाजन पैदा होता है जो कुछ जनसांख्यिकी को चुनावी प्रक्रिया में पूरी तरह से भाग लेने से बाहर कर सकता है।
On Delhi’s mounting waste crisis / दिल्ली के बढ़ते अपशिष्ट संकट पर
(General Studies- Paper II & III)
Source : The Hindu
What is the status of Delhi’s SWM system?
- Population Growth and Waste Generation:
- According to the 2011 Census Data, New Delhi’s population was approximately 1.7 crore. However, this Population is expected to increase to around 2.32 crore.
- This increase will lead to a significant rise in waste generation, estimated at approximately 13,000 tonnes per day (TPD), which equates to roughly 1,400 truckloads daily.
- Presently, this daily waste generation accumulates to about 42 lakh tonnes per annum. The population is anticipated to reach 2.85 crore by 2031 due to which the waste generation could increase to 17,000 TPD.
- Waste Collection: Around 90% of the waste generated in the city is collected by three municipal corporations:
- Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD)
- Delhi Cantonment Board
- New Delhi Municipal Corporation
- Waste Composition is of major types – Biodegradable Wet Waste (50-55%), Non-Biodegradable Dry Waste (around 35%), and Inert Waste (10% that does not decompose). The total collective capacity of these facilities is about 9,200 tonnes per day (TPD).
Challenges to waste management in Municipal Corporation of Delhi
- Lack of Waste Segregation at Source: Many households and commercial establishments do not segregate waste. Unprocessed mixed waste enters landfills as a result.
- Land Availability for Waste Processing Plants: Waste processing plants require large land parcels (30-40 acres each). Securing such large tracts of land is challenging in Delhi.
- Public Awareness and Practices: There is a lack of public awareness regarding proper waste management practices. This leads to littering and improper disposal habits. MCD’s focus shifts to clearing open points rather than processing wet waste.
- Inadequate Waste Collection Services: Some areas suffer from irregular waste collection services. This contributes to waste buildup and increased littering.
Illegal Dumping: Waste is often illegally dumped in open areas and water bodies. This increases the pressure on the MCD and requires additional resources for cleanup.
दिल्ली के SWM सिस्टम की क्या स्थिति है?
- जनसंख्या वृद्धि और अपशिष्ट सृजन:
- 2011 की जनगणना के आंकड़ों के अनुसार, नई दिल्ली की जनसंख्या लगभग 7 करोड़ थी। हालाँकि, यह जनसंख्या बढ़कर लगभग 2.32 करोड़ होने की उम्मीद है।
- इस वृद्धि से अपशिष्ट उत्पादन में उल्लेखनीय वृद्धि होगी, जिसका अनुमान लगभग 13,000 टन प्रति दिन (टीपीडी) है, जो प्रतिदिन लगभग 1,400 ट्रक लोड के बराबर है।
- वर्तमान में, यह दैनिक अपशिष्ट उत्पादन लगभग 42 लाख टन प्रति वर्ष जमा होता है। 2031 तक जनसंख्या 85 करोड़ तक पहुंचने का अनुमान है जिसके कारण अपशिष्ट उत्पादन 17,000 टीपीडी तक बढ़ सकता है।
- अपशिष्ट संग्रहण: शहर में उत्पन्न लगभग 90% कचरा तीन नगर निगमों द्वारा एकत्र किया जाता है:
- दिल्ली नगर निगम (एमसीडी)
- दिल्ली छावनी बोर्ड
- नई दिल्ली नगर निगम
- अपशिष्ट संरचना प्रमुख प्रकार की होती है – बायोडिग्रेडेबल गीला कचरा (50-55%), गैर-बायोडिग्रेडेबल सूखा कचरा (लगभग 35%), और निष्क्रिय अपशिष्ट (10% जो विघटित नहीं होता है)। इन सुविधाओं की कुल सामूहिक क्षमता लगभग 9,200 टन प्रति दिन (टीपीडी) है।
दिल्ली नगर निगम में अपशिष्ट प्रबंधन की चुनौतियाँ
- स्रोत पर अपशिष्ट पृथक्करण का अभाव: कई घर और व्यावसायिक प्रतिष्ठान अपशिष्ट पृथक्करण नहीं करते हैं। परिणामस्वरूप असंसाधित मिश्रित कचरा लैंडफिल में प्रवेश करता है।
- अपशिष्ट प्रसंस्करण संयंत्रों के लिए भूमि की उपलब्धता: अपशिष्ट प्रसंस्करण संयंत्रों के लिए बड़े भूमि पार्सल (प्रत्येक 30-40 एकड़) की आवश्यकता होती है। दिल्ली में जमीन के इतने बड़े हिस्से को सुरक्षित रखना चुनौतीपूर्ण है।
- सार्वजनिक जागरूकता और प्रथाएँ: उचित अपशिष्ट प्रबंधन प्रथाओं के संबंध में सार्वजनिक जागरूकता की कमी है। इससे कूड़ा-कचरा फैलाया जाता है और निपटान की गलत आदतें पैदा होती हैं। एमसीडी का ध्यान गीले कचरे के प्रसंस्करण के बजाय खुले स्थानों को साफ करने पर केंद्रित है।
- अपर्याप्त अपशिष्ट संग्रहण सेवाएँ: कुछ क्षेत्र अनियत अपशिष्ट संग्रहण सेवाओं से पीड़ित हैं। यह अपशिष्ट संचय और कूड़े-कचरे में वृद्धि में योगदान देता है।
- अवैध डंपिंग: कचरे को अक्सर खुले क्षेत्रों और जल निकायों में अवैध रूप से डंप किया जाता है। इससे एमसीडी पर दबाव बढ़ता है और सफाई के लिए अतिरिक्त संसाधनों की आवश्यकता होती है।
1. Election Commission of India /भारत का चुनाव आयोग 2. India Meteorological Department /भारत मौसम विज्ञान विभाग 3. What is Cancer? / कैंसर क्या है?
Source : The Hindu
- Election Commission of India
- Election Commission is a permanent and independent body.
- By Article 324 of the Constitution of India, it is vested with the power of conducting elections to –
- Parliament,
- State Legislatures,
- Office of President and Vice-President of India.
- Appointment : Article 324(2) says appointment of CEC and other ECs shall be subject to provisions of any law made by the Parliament.
- Tenure : They have tenure of six years, or up to the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- They enjoy the same status and receive salary and perks as available to Judges of the Supreme Court of India.
- Removal : The proviso to Article 324 (5) of the Constitution says that a CEC can only be removed in a manner similar to that of a SC judge.
- Composition: Since the inceptions and till 15th October 1989, the EC functioned as a single member body consisting of the CEC.
- On 16th October 1989, the President appointed two more commissioners to cope with the increased work of the EC, on account of lowering of the voting age from 21 to 18 years.
2.India Meteorological Department (IMD):
- IMD was established in 1875. It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- The Director General of Meteorology is the Head of the India Meteorological Department.
- There are 6 Regional Meteorological Centres, each under a Deputy Director General with headquarters at Mumbai, Chennai, New Delhi, Calcutta, Nagpur and Guwahati.
- Its headquarter is in New Delhi.
- At present IMD is under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
3.What is Cancer?
- Cancer is a disease in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body.
- Cancer can start almost anywhere in the human body, which is made up of trillions of cells.
- Normally, human cells grow and multiply through a process called cell division, to form new cells as the body needs them.
- When cells grow old or become damaged, they die, and new cells take their place. Sometimes this orderly process breaks down, and abnormal or damaged cells grow and multiply when they shouldn’t.
- These cells may form tumours, which are lumps of tissue and can be cancerous or not cancerous.
- भारत का चुनाव आयोग
- चुनाव आयोग एक स्थायी एवं स्वतंत्र निकाय है।
- भारत के संविधान के अनुच्छेद 324 द्वारा, चुनाव कराने की शक्ति निहित है –
- संसद,
- राज्य विधानमंडल,
- भारत के राष्ट्रपति और उपराष्ट्रपति का कार्यालय।
- नियुक्ति: अनुच्छेद 324(2) कहता है कि सीईसी और अन्य ईसी की नियुक्ति संसद द्वारा बनाए गए किसी भी कानून के प्रावधानों के अधीन होगी।
- कार्यकाल: उनका कार्यकाल छह वर्ष या 65 वर्ष की आयु तक, जो भी पहले हो, होता है।
- उन्हें वही दर्जा प्राप्त है और वे भारत के सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के न्यायाधीशों के समान वेतन और भत्ते प्राप्त करते हैं।
- हटाना: संविधान के अनुच्छेद 324 (5) के प्रावधान में कहा गया है कि सीईसी को केवल एससी न्यायाधीश के समान तरीके से ही हटाया जा सकता है।
- संरचना: स्थापना के बाद से और 15 अक्टूबर 1989 तक, EC ने CEC सहित एकल सदस्य निकाय के रूप में कार्य किया।
- 16 अक्टूबर 1989 को राष्ट्रपति ने मतदान की उम्र 21 से घटाकर 18 वर्ष करने के कारण चुनाव आयोग के बढ़ते काम से निपटने के लिए दो और आयुक्तों की नियुक्ति की।
2.भारत मौसम विज्ञान विभाग (IMD):
- आईएमडी की स्थापना 1875 में हुई थी। यह देश की राष्ट्रीय मौसम विज्ञान सेवा है और मौसम विज्ञान और संबद्ध विषयों से संबंधित सभी मामलों में प्रमुख सरकारी एजेंसी है।
- मौसम विज्ञान महानिदेशक भारत मौसम विज्ञान विभाग के प्रमुख हैं।
- 6 क्षेत्रीय मौसम विज्ञान केंद्र हैं, प्रत्येक का मुख्यालय एक उप महानिदेशक के अधीन है, जिनका मुख्यालय मुंबई, चेन्नई, नई दिल्ली, कलकत्ता, नागपुर और गुवाहाटी में है।
- इसका मुख्यालय नई दिल्ली में है।
- वर्तमान में IMD पृथ्वी विज्ञान मंत्रालय (MoES) के अधीन है।
3.कैंसर क्या है?
- कैंसर एक ऐसी बीमारी है जिसमें शरीर की कुछ कोशिकाएं अनियंत्रित रूप से बढ़ती हैं और शरीर के अन्य हिस्सों में फैल जाती हैं।
- कैंसर मानव शरीर में लगभग कहीं भी शुरू हो सकता है, जो खरबों कोशिकाओं से बना होता है।
- आम तौर पर, मानव कोशिकाएं कोशिका विभाजन नामक प्रक्रिया के माध्यम से बढ़ती और गुणा होती हैं, ताकि शरीर को उनकी आवश्यकता के अनुसार नई कोशिकाएं बनाई जा सकें।
- जब कोशिकाएं पुरानी हो जाती हैं या क्षतिग्रस्त हो जाती हैं, तो वे मर जाती हैं और नई कोशिकाएं उनकी जगह ले लेती हैं। कभी-कभी यह व्यवस्थित प्रक्रिया टूट जाती है, और असामान्य या क्षतिग्रस्त कोशिकाएँ बढ़ती और बढ़ती हैं जबकि ऐसा नहीं होना चाहिए।
- ये कोशिकाएं ट्यूमर बना सकती हैं, जो ऊतक की गांठें होती हैं और कैंसरयुक्त या गैर-कैंसरयुक्त भी हो सकती हैं।
The case for election day as a holiday /चुनाव के दिन छुट्टी का मामला
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : The Hindu
Context:
- The debate over whether employers, especially Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs), should declare a holiday on election day in India has sparked discussions on the balance between civic responsibility and personal freedoms.
- Article seeks to draw comparisons with global practices and proposes innovative solutions to encourage voter participation.
- In a vibrant democracy such as India, the right to vote is not just a privilege but also a fundamental duty enshrined in the Constitution.
- Several countries around the world such as Australia (where voting is mandatory), South Africa, South Korea, France provide a holiday on election day to facilitate voter participation.
Introduction
- The right to vote in India is not just a privilege but a constitutional right outlined in the Constitution.
- Many democracies worldwide provide a holiday on election day to facilitate voter participation.
Effects on Private sector
- Recent discussions revolve around whether employers, especially SMEs, should declare a holiday on election day.
- Some argue for this practice, citing constitutional principles, while others question its necessity and potential infringement on individual liberties.
Trends in Other Countries
- Some countries like Australia mandate voting and provide a holiday, while others, like the United States, don’t.
- A study from Princeton University suggests that having an election holiday doesn’t significantly increase voter turnout.
The issue of a balance
- Advocates argue that the Constitution upholds voting as a right, hence employers should grant a day off.
- Business organisations like FICCI, ASSOCHAM, and NASSCOM are expected to align with societal goals.
- The counterargument emphasises individual freedom and the principles of a free market economy.
- Mandating a holiday may be seen as an infringement on employer autonomy, especially for smaller businesses.
Comparative Analysis with the U.S.
- In the U.S., election day isn’t a national holiday, and individuals manage their schedules to vote.
- Some states offer paid time off to vote, but it’s not universally mandated at the federal level.
Recommendations for India
- The proposal to link paid leave to proof of voting suggests a middle ground.
- This incentivizes voter turnout while allowing employer discretion, addressing both civic engagement and business concerns.
Perspective
- The issue transcends legalities and delves into democracy’s essence, fostering civic engagement while respecting diverse needs.
- Policymakers should explore innovative solutions to encourage voting without burdening employers.
- Future technological advancements may enable voting from home without undue influence.
Conclusion
- The debate on employer obligations on election day is nuanced, touching upon democracy, individual freedoms, and economic realities.
- Striking a balance between civic obligations and business autonomy is essential for upholding India’s democratic ethos.
- Flexible solutions can accommodate the dynamic needs of society while promoting voter participation.
Context:
- इस बात पर बहस छिड़ गई है कि क्या नियोक्ताओं, विशेष रूप से छोटे और मध्यम आकार के उद्यमों (SME) को भारत में चुनाव के दिन छुट्टी घोषित करनी चाहिए, ने नागरिक जिम्मेदारी और व्यक्तिगत स्वतंत्रता के बीच संतुलन पर चर्चा शुरू कर दी है।
- लेख वैश्विक प्रथाओं के साथ तुलना करने का प्रयास करता है और मतदाता भागीदारी को प्रोत्साहित करने के लिए नवीन समाधान प्रस्तावित करता है।
- भारत जैसे जीवंत लोकतंत्र में, वोट देने का अधिकार न केवल एक विशेषाधिकार है बल्कि संविधान में निहित एक मौलिक कर्तव्य भी है।
- दुनिया भर के कई देश जैसे ऑस्ट्रेलिया (जहां मतदान अनिवार्य है), दक्षिण अफ्रीका, दक्षिण कोरिया, फ्रांस मतदाताओं की भागीदारी को सुविधाजनक बनाने के लिए चुनाव के दिन छुट्टी प्रदान करते हैं।
परिचय
- भारत में वोट देने का अधिकार सिर्फ एक विशेषाधिकार नहीं है बल्कि संविधान में उल्लिखित एक संवैधानिक अधिकार है।
- दुनिया भर में कई लोकतंत्र मतदाताओं की भागीदारी को सुविधाजनक बनाने के लिए चुनाव के दिन छुट्टी प्रदान करते हैं।
निजी क्षेत्र पर प्रभाव
- हाल की चर्चाएँ इस बात पर केंद्रित हैं कि क्या नियोक्ताओं, विशेष रूप से एसएमई को, चुनाव के दिन छुट्टी की घोषणा करनी चाहिए।
- कुछ लोग संवैधानिक सिद्धांतों का हवाला देते हुए इस प्रथा के पक्ष में तर्क देते हैं, जबकि अन्य इसकी आवश्यकता और व्यक्तिगत स्वतंत्रता पर संभावित उल्लंघन पर सवाल उठाते हैं।
अन्य देशों में रुझान
- ऑस्ट्रेलिया जैसे कुछ देश मतदान अनिवार्य करते हैं और छुट्टी प्रदान करते हैं, जबकि संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका जैसे अन्य देश ऐसा नहीं करते हैं।
- प्रिंसटन यूनिवर्सिटी के एक अध्ययन से पता चलता है कि चुनावी छुट्टी होने से मतदान प्रतिशत में उल्लेखनीय वृद्धि नहीं होती है।
संतुलन का मुद्दा
- अधिवक्ताओं का तर्क है कि संविधान मतदान को अधिकार मानता है, इसलिए नियोक्ताओं को एक दिन की छुट्टी देनी चाहिए।
- फिक्की, एसोचैम और नैसकॉम जैसे व्यापारिक संगठनों से सामाजिक लक्ष्यों के साथ जुड़ने की उम्मीद की जाती है।
- प्रतिवाद व्यक्तिगत स्वतंत्रता और मुक्त बाजार अर्थव्यवस्था के सिद्धांतों पर जोर देता है।
- छुट्टी अनिवार्य करना नियोक्ता की स्वायत्तता के उल्लंघन के रूप में देखा जा सकता है, खासकर छोटे व्यवसायों के लिए।
अमेरिका के साथ तुलनात्मक विश्लेषण
- अमेरिका में, चुनाव के दिन राष्ट्रीय अवकाश नहीं होता है, और व्यक्ति मतदान करने के लिए अपने कार्यक्रम का प्रबंधन करते हैं।
- कुछ राज्य मतदान के लिए सवैतनिक अवकाश की पेशकश करते हैं, लेकिन यह संघीय स्तर पर सार्वभौमिक रूप से अनिवार्य नहीं है।
भारत के लिए सिफ़ारिशें
- सवैतनिक अवकाश को मतदान के प्रमाण से जोड़ने का प्रस्ताव बीच का रास्ता सुझाता है।
- यह नागरिक सहभागिता और व्यावसायिक चिंताओं दोनों को संबोधित करते हुए नियोक्ता को विवेकाधिकार की अनुमति देते हुए मतदाता मतदान को प्रोत्साहित करता है।
परिप्रेक्ष्य
- यह मुद्दा कानूनीताओं से परे है और लोकतंत्र के सार में गहराई से उतरता है, विभिन्न आवश्यकताओं का सम्मान करते हुए नागरिक जुड़ाव को बढ़ावा देता है।
- नीति निर्माताओं को नियोक्ताओं पर बोझ डाले बिना मतदान को प्रोत्साहित करने के लिए नवीन समाधान तलाशने चाहिए।
- भविष्य की तकनीकी प्रगति से अनुचित प्रभाव के बिना घर से मतदान करना संभव हो सकता है।
निष्कर्ष
- चुनाव के दिन नियोक्ता के दायित्वों पर बहस सूक्ष्म होती है, जो लोकतंत्र, व्यक्तिगत स्वतंत्रता और आर्थिक वास्तविकताओं को छूती है।
- भारत के लोकतांत्रिक लोकाचार को बनाए रखने के लिए नागरिक दायित्वों और व्यावसायिक स्वायत्तता के बीच संतुलन बनाना आवश्यक है।
- लचीले समाधान मतदाता भागीदारी को बढ़ावा देते हुए समाज की गतिशील आवश्यकताओं को समायोजित कर सकते हैं।
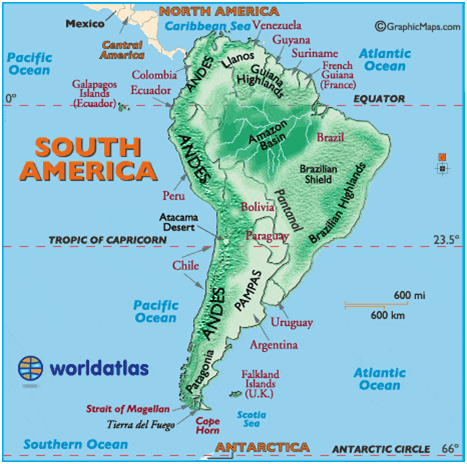
Major Physical Divisions of South America / दक्षिण अमेरिका के प्रमुख भौतिक प्रभाग [Mapping]
- The Pacific coastal strip
- Mountain Ranges
- The Central Lowlands
- The Eastern Highlands

The Pacific coastal strip
- It lies in the west, between the ocean and the Andes. It is the longest coastal plain in the Atlantic world.
- In most places, it is about 80 kilometers wide but in some, it is as narrow as 8 meters. The coastline of South America is smooth and regular. At the river mouths, there are inlets that are used as harbors.
- The south-western coast of the continent has fiords or deep inlets of the sea.
Andes Mountains:
- Forms the second-highest mountain systems in the world and is next to the Himalayas
- Mount Aconcagua is the extinct volcano lies in Argentina
- Mount Ojas del Salado is the highest active volcano in the world of Argentina
- Andes Mountains – A part of seven countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Bolivia, Peru, Chile, Argentina.
Mountain Ranges
- The Andes stretches through the entire continent, running in the north-south direction from Isthmus of Panama to Strait of Magellan.
- They are the continuous range of folded mountain systems that cover the entire western coast of South America.
- The Andes is the longest mountain range in the world. The highest mountain of this mountain range is Aconcagua, which stands at 6,962 meters (22,841 feet) and straddles the Argentina-Chile border.
- They form a chain of ranges and knots with enclosed intermontane plateaus namely in Ecuador and Bolivia.
- Being part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, there are many volcanoes and frequent earthquakes in this region. Mount Cotopaxi and Mount Chimborazo are active volcanic peak, which is the highest peak in South America.
- प्रशांत तटीय पट्टी
- पर्वत श्रृंखलाएँ
- केन्द्रीय तराई क्षेत्र
- पूर्वी हाइलैंड्स
प्रशांत तटीय पट्टी
- यह पश्चिम में, महासागर और एंडीज़ के बीच स्थित है। यह अटलांटिक विश्व का सबसे लंबा तटीय मैदान है।
- अधिकांश स्थानों पर, यह लगभग 80 किलोमीटर चौड़ा है, लेकिन कुछ में, यह 8 मीटर तक संकीर्ण है। दक्षिण अमेरिका की तटरेखा चिकनी और नियमित है। नदी के मुहाने पर प्रवेश द्वार हैं जिनका उपयोग बंदरगाह के रूप में किया जाता है।
- महाद्वीप के दक्षिण-पश्चिमी तट पर समुद्र के फ़ॉर्ड या गहरे प्रवेश द्वार हैं।
एंडीज पर्वत:
- यह दुनिया की दूसरी सबसे ऊंची पर्वत प्रणाली है और हिमालय के बगल में है
- माउंट एकॉनकागुआ अर्जेंटीना में स्थित विलुप्त ज्वालामुखी है
- माउंट ओजस डेल सालाडो अर्जेंटीना का विश्व का सबसे ऊंचा सक्रिय ज्वालामुखी है
- एंडीज़ पर्वत – सात देशों का हिस्सा: वेनेजुएला, कोलंबिया, इक्वाडोर, बोलीविया, पेरू, चिली, अर्जेंटीना।
पर्वत श्रृंखलाएं
- एंडीज़ पूरे महाद्वीप में फैला है, जो उत्तर-दक्षिण दिशा में पनामा के इस्तमुस से लेकर मैगलन जलडमरूमध्य तक फैला हुआ है।
- वे वलित पर्वत प्रणालियों की निरंतर श्रृंखला हैं जो दक्षिण अमेरिका के पूरे पश्चिमी तट को कवर करती हैं।
- एंडीज़ विश्व की सबसे लंबी पर्वत श्रृंखला है। इस पर्वत श्रृंखला का सबसे ऊँचा पर्वत एकॉनकागुआ है, जो 6,962 मीटर (22,841 फीट) ऊँचा है और अर्जेंटीना-चिली सीमा तक फैला हुआ है।
- वे इक्वाडोर और बोलीविया में घिरे हुए अंतरपर्वतीय पठारों के साथ श्रेणियों और गांठों की एक श्रृंखला बनाते हैं।
- पैसिफिक रिंग ऑफ फायर का हिस्सा होने के कारण इस क्षेत्र में कई ज्वालामुखी और अक्सर भूकंप आते रहते हैं। माउंट कोटोपैक्सी और माउंट चिम्बोराजो सक्रिय ज्वालामुखी शिखर हैं, जो दक्षिण अमेरिका की सबसे ऊंची चोटी है।