CURRENT AFFAIRS – 13/08/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 13/08/2024
- IIT-Madras retains top spot in NIRF ranking for sixth consecutive year / आईआईटी-मद्रास ने लगातार छठे साल एनआईआरएफ रैंकिंग में शीर्ष स्थान बरकरार रखा
- Centre and States are in for a confrontation over redistribution of taxes : Thomas Isaac / करों के पुनर्वितरण को लेकर केंद्र और राज्यों के बीच टकराव: थॉमस इसाक
- Suspected case of Chandipura virus found in M.P.’s Indore / मध्य प्रदेश के इंदौर में चांदीपुरा वायरस का संदिग्ध मामला पाया गया
- On the allegations against the SEBI chief / सेबी प्रमुख के खिलाफ आरोपों पर
- Ukraine’s Kursk Operation in Russia / रूस में यूक्रेन का कुर्स्क ऑपरेशन
- Cold War nuke tests light up a bug in present-day climate models /शीत युद्ध के परमाणु परीक्षणों ने वर्तमान जलवायु मॉडल में एक बग को उजागर किया
- On amendments to the Waqf Act / वक्फ अधिनियम में संशोधन पर
- The top court as custodian of liberties / स्वतंत्रता के संरक्षक के रूप में शीर्ष न्यायालय
- United Nations (UN) / संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन)
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 13/08/2024
IIT-Madras retains top spot in NIRF ranking for sixth consecutive year / आईआईटी-मद्रास ने लगातार छठे साल एनआईआरएफ रैंकिंग में शीर्ष स्थान बरकरार रखा
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) 2024 highlights top Indian educational institutions based on comprehensive parameters.
- IIT-Madras and Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru continued their dominance in engineering and research.
- New categories and increased institutional participation reflect ongoing enhancements in India’s higher education landscape.
About the news:
- IIT-Madras ranked as the best educational institution in India for the sixth time since 2019.
- IIT-Madras also retained the top position in engineering for the ninth consecutive year.
- Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru ranked highest in universities and research categories.
- New NIRF categories: open universities, skill universities, and State public universities.
- IIM-Ahmedabad continued as the top management institute for the fifth year.
- AIIMS, New Delhi remains the best in medical sciences for seven years.
- IIT-Bombay is the top institution for innovation.
- Increased participation in 2024: 6,517 institutions, 10,845 applications.
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)
- The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) is an initiative by the Ministry of Education, launched in 2015 to rank higher education institutions in India.
- It assesses institutions across several parameters, including teaching, learning, and resources, research and professional practices, graduation outcomes, outreach and inclusivity, and perception.
- NIRF publishes annual rankings in various categories such as overall, universities, engineering, management, pharmacy, and colleges, among others.
- The framework aims to promote competitive excellence and enhance the quality of education.
- Participating institutions submit data online, which is then subjected to thorough scrutiny and analysis to ensure accuracy and transparency.
आईआईटी-मद्रास ने लगातार छठे साल एनआईआरएफ रैंकिंग में शीर्ष स्थान बरकरार रखा
राष्ट्रीय संस्थागत रैंकिंग फ्रेमवर्क (NIRF) 2024 व्यापक मापदंडों के आधार पर शीर्ष भारतीय शैक्षणिक संस्थानों को उजागर करता है।
- आईआईटी-मद्रास और भारतीय विज्ञान संस्थान, बेंगलुरु ने इंजीनियरिंग और अनुसंधान में अपना वर्चस्व जारी रखा।
- नई श्रेणियाँ और बढ़ी हुई संस्थागत भागीदारी भारत के उच्च शिक्षा परिदृश्य में चल रही वृद्धि को दर्शाती है।
समाचार के बारे में:
- आईआईटी-मद्रास को 2019 के बाद से छठी बार भारत में सर्वश्रेष्ठ शैक्षणिक संस्थान का दर्जा दिया गया है।
- आईआईटी-मद्रास ने लगातार नौवें साल इंजीनियरिंग में भी शीर्ष स्थान बरकरार रखा है।
- भारतीय विज्ञान संस्थान, बेंगलुरु ने विश्वविद्यालयों और शोध श्रेणियों में सर्वोच्च स्थान प्राप्त किया है।
- नई एनआईआरएफ श्रेणियाँ: मुक्त विश्वविद्यालय, कौशल विश्वविद्यालय और राज्य सार्वजनिक विश्वविद्यालय।
- आईआईएम-अहमदाबाद पांचवें साल भी शीर्ष प्रबंधन संस्थान बना रहा।
- एम्स, नई दिल्ली सात साल से चिकित्सा विज्ञान में सर्वश्रेष्ठ बना हुआ है।
- आईआईटी-बॉम्बे नवाचार के लिए शीर्ष संस्थान है।
- 2024 में भागीदारी में वृद्धि: 6,517 संस्थान, 10,845 आवेदन।
राष्ट्रीय संस्थागत रैंकिंग ढांचा (एनआईआरएफ)
- राष्ट्रीय संस्थागत रैंकिंग ढांचा (एनआईआरएफ) शिक्षा मंत्रालय द्वारा 2015 में भारत में उच्च शिक्षा संस्थानों को रैंक करने के लिए शुरू की गई एक पहल है।
- यह शिक्षण, सीखने और संसाधनों, अनुसंधान और पेशेवर प्रथाओं, स्नातक परिणामों, आउटरीच और समावेशिता और धारणा सहित कई मापदंडों पर संस्थानों का मूल्यांकन करता है।
- एनआईआरएफ विभिन्न श्रेणियों जैसे समग्र, विश्वविद्यालय, इंजीनियरिंग, प्रबंधन, फार्मेसी और कॉलेजों आदि में वार्षिक रैंकिंग प्रकाशित करता है।
- इस ढांचे का उद्देश्य प्रतिस्पर्धी उत्कृष्टता को बढ़ावा देना और शिक्षा की गुणवत्ता को बढ़ाना है।
- भाग लेने वाले संस्थान ऑनलाइन डेटा जमा करते हैं, जिसे सटीकता और पारदर्शिता सुनिश्चित करने के लिए गहन जांच और विश्लेषण के अधीन किया जाता है।
Centre and States are in for a confrontation over redistribution of taxes : Thomas Isaac / करों के पुनर्वितरण को लेकर केंद्र और राज्यों के बीच टकराव: थॉमस इसाक
Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity
Source : The Hindu
The issue revolves around the Union government’s use of cesses and surcharges, which reduce the divisible pool of taxes shared with States.
- This practice, coupled with perceived discriminatory redistribution, has led to tensions in fiscal federalism, especially affecting the financial autonomy and resource distribution among different Indian States.
Levy of Cesses and Surcharges by the Union Government
- The Union government imposes cesses and surcharges, which are not part of the divisible pool of taxes shared with States.
- Between 2015-16 and 2018-19, States reportedly lost approximately ₹5.26 lakh crore due to these levies, reducing the resources available for distribution.
Discriminatory Redistribution of the Divisible Pool
- The central redistribution of the divisible pool of taxes is perceived as discriminatory, with some States receiving a smaller share compared to others.
- Examples include Tamil Nadu receiving only 29% of its contributions back, Maharashtra 10%, while Kerala gets 57%, compared to higher shares for States like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh.
Challenges in Fiscal Federalism
- Lack of Objective Criteria for Resource Transfer
- There is a need for transparent and objective criteria for transferring resources to ensure fairness and equity among States.
- Current devolution practices are seen as inequitable, leading to fiscal stress for some States.
- Impact on State Finances
- States argue that the current system restricts their financial autonomy and ability to effectively manage their resources.
- The fiscal pressure is particularly acute for States investing heavily in social sectors, facing reduced funding from the Centre.
Implications for Backward States
- Limited Economic Improvement Despite Higher Share
- Despite receiving a higher share from the divisible pool, many backward States have not shown significant improvement in per capita income.
- This raises questions about the effectiveness of the current redistribution model in promoting balanced regional development.
Constraints Post-GST Implementation
- Reduced Taxation Powers for States
- The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) has limited the taxation powers of States, restricting them to levying taxes mainly on petrol, diesel, and alcohol.
- This has further constrained States’ ability to generate revenue independently, increasing reliance on central transfers.
Political Dimensions
- Perceived Discrimination Against Opposition-Ruled States
- There is an allegation that the Union government discriminates against Opposition-ruled States, particularly those investing significantly in social sectors.
- This perceived bias adds a political dimension to the fiscal confrontation, with claims of financial squeezing of these States.
करों के पुनर्वितरण को लेकर केंद्र और राज्यों के बीच टकराव: थॉमस इसाक
यह मुद्दा केंद्र सरकार द्वारा उपकरों और अधिभारों के उपयोग के इर्द-गिर्द घूमता है, जो राज्यों के साथ साझा किए जाने वाले करों के विभाज्य पूल को कम करते हैं।
- इस प्रथा के साथ-साथ कथित भेदभावपूर्ण पुनर्वितरण के कारण राजकोषीय संघवाद में तनाव पैदा हुआ है, विशेष रूप से विभिन्न भारतीय राज्यों के बीच वित्तीय स्वायत्तता और संसाधन वितरण प्रभावित हुआ है।
केंद्र सरकार द्वारा उपकर और अधिभार लगाना
- केंद्र सरकार उपकर और अधिभार लगाती है, जो राज्यों के साथ साझा किए जाने वाले करों के विभाज्य पूल का हिस्सा नहीं हैं।
- 2015-16 और 2018-19 के बीच, राज्यों को इन शुल्कों के कारण लगभग ₹5.26 लाख करोड़ का नुकसान हुआ, जिससे वितरण के लिए उपलब्ध संसाधन कम हो गए।
विभाज्य पूल का भेदभावपूर्ण पुनर्वितरण
- करों के विभाज्य पूल का केंद्रीय पुनर्वितरण भेदभावपूर्ण माना जाता है, जिसमें कुछ राज्यों को दूसरों की तुलना में कम हिस्सा मिलता है।
- उदाहरणों में तमिलनाडु को अपने अंशदान का केवल 29% वापस मिलता है, महाराष्ट्र को 10%, जबकि केरल को 57% मिलता है, जबकि बिहार, उत्तर प्रदेश और छत्तीसगढ़ जैसे राज्यों को अधिक हिस्सा मिलता है।
राजकोषीय संघवाद में चुनौतियाँ
- संसाधन हस्तांतरण के लिए वस्तुनिष्ठ मानदंडों का अभाव
- राज्यों के बीच निष्पक्षता और समानता सुनिश्चित करने के लिए संसाधनों के हस्तांतरण के लिए पारदर्शी और वस्तुनिष्ठ मानदंडों की आवश्यकता है।
- वर्तमान हस्तांतरण प्रथाओं को असमान माना जाता है, जिससे कुछ राज्यों के लिए राजकोषीय तनाव पैदा होता है।
राज्यों के वित्त पर प्रभाव
- राज्यों का तर्क है कि वर्तमान प्रणाली उनकी वित्तीय स्वायत्तता और उनके संसाधनों को प्रभावी ढंग से प्रबंधित करने की क्षमता को सीमित करती है।
- सामाजिक क्षेत्रों में भारी निवेश करने वाले राज्यों के लिए राजकोषीय दबाव विशेष रूप से तीव्र है, जिन्हें केंद्र से कम धन मिल रहा है।
पिछड़े राज्यों के लिए निहितार्थ
- उच्च हिस्सेदारी के बावजूद सीमित आर्थिक सुधार
- विभाज्य पूल से उच्च हिस्सेदारी प्राप्त करने के बावजूद, कई पिछड़े राज्यों ने प्रति व्यक्ति आय में महत्वपूर्ण सुधार नहीं दिखाया है।
- यह संतुलित क्षेत्रीय विकास को बढ़ावा देने में वर्तमान पुनर्वितरण मॉडल की प्रभावशीलता के बारे में सवाल उठाता है।
जीएसटी कार्यान्वयन के बाद बाधाएँ
- राज्यों के लिए कम कर लगाने की शक्तियाँ
- वस्तु एवं सेवा कर (जीएसटी) की शुरूआत ने राज्यों की कर लगाने की शक्तियों को सीमित कर दिया है, जिससे उन्हें मुख्य रूप से पेट्रोल, डीजल और शराब पर कर लगाने तक सीमित कर दिया गया है।
- इसने राज्यों की स्वतंत्र रूप से राजस्व उत्पन्न करने की क्षमता को और बाधित किया है, जिससे केंद्रीय हस्तांतरण पर निर्भरता बढ़ गई है।
राजनीतिक आयाम
- विपक्ष शासित राज्यों के खिलाफ कथित भेदभाव
- आरोप है कि केंद्र सरकार विपक्ष शासित राज्यों, खासकर सामाजिक क्षेत्रों में महत्वपूर्ण निवेश करने वाले राज्यों के खिलाफ भेदभाव करती है।
- यह कथित पूर्वाग्रह राजकोषीय टकराव में एक राजनीतिक आयाम जोड़ता है, जिसमें इन राज्यों को वित्तीय रूप से निचोड़ने का दावा किया जाता है।
Suspected case of Chandipura virus found in M.P.’s Indore / मध्य प्रदेश के इंदौर में चांदीपुरा वायरस का संदिग्ध मामला पाया गया
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
In Indore, Madhya Pradesh, a 20-year-old man showing symptoms of the Chandipura virus, such as flu, cold, and cough, had his sample sent to a Pune lab for testing.
- Union Health Minister J.P. Nadda reported 53 confirmed cases in India, with 51 from Gujarat, including 19 deaths.
Chandipura Virus:
- Origin: Chandipura virus was first identified in 1965 in the village of Chandipura in Maharashtra, India.
- Transmission: The virus is primarily transmitted by sandflies, particularly the Phlebotomus species.
- Geographic Distribution: While initially reported in India, outbreaks have also been observed in neighbouring countries like Nepal and Bangladesh.
- Symptoms: The virus can cause an acute encephalitic illness characterised by sudden high fever, convulsions, altered mental status, and sometimes coma. It primarily affects children.
- Outbreaks: Notable outbreaks have occurred in central and western India, with significant mortality rates among children.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis is typically made through serological tests and RT-PCR to detect the virus in blood or cerebrospinal fluid.
- Prevention and Control: Control measures focus on reducing sandfly populations and avoiding exposure, as there is currently no specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for the Chandipura virus.
मध्य प्रदेश के इंदौर में चांदीपुरा वायरस का संदिग्ध मामला पाया गया
मध्य प्रदेश के इंदौर में, 20 वर्षीय एक व्यक्ति में फ्लू, सर्दी और खांसी जैसे चांदीपुरा वायरस के लक्षण दिखे, जिसका नमूना जांच के लिए पुणे की एक प्रयोगशाला में भेजा गया।
- केंद्रीय स्वास्थ्य मंत्री जे.पी. नड्डा ने भारत में 53 पुष्ट मामलों की सूचना दी, जिनमें से 51 गुजरात से थे, जिनमें 19 मौतें शामिल हैं।
चांदीपुरा वायरस:
- उत्पत्ति: चांदीपुरा वायरस की पहचान सबसे पहले 1965 में महाराष्ट्र, भारत के चांदीपुरा गांव में हुई थी।
- संचरण: यह वायरस मुख्य रूप से सैंडफ्लाई, विशेष रूप से फ्लेबोटोमस प्रजाति द्वारा फैलता है।
- भौगोलिक वितरण: हालांकि शुरुआत में भारत में रिपोर्ट किया गया था, लेकिन नेपाल और बांग्लादेश जैसे पड़ोसी देशों में भी इसका प्रकोप देखा गया है।
- लक्षण: यह वायरस एक तीव्र मस्तिष्क संबंधी बीमारी का कारण बन सकता है, जिसमें अचानक तेज बुखार, ऐंठन, मानसिक स्थिति में बदलाव और कभी-कभी कोमा जैसी स्थिति हो सकती है। यह मुख्य रूप से बच्चों को प्रभावित करता है।
- प्रकोप: मध्य और पश्चिमी भारत में उल्लेखनीय प्रकोप हुए हैं, जिसमें बच्चों में मृत्यु दर काफी अधिक है।
- निदान: आमतौर पर रक्त या मस्तिष्कमेरु द्रव में वायरस का पता लगाने के लिए सीरोलॉजिकल परीक्षण और आरटी-पीसीआर के माध्यम से निदान किया जाता है।
- रोकथाम और नियंत्रण: नियंत्रण उपाय सैंडफ्लाई आबादी को कम करने और जोखिम से बचने पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हैं, क्योंकि वर्तमान में चांदीपुरा वायरस के लिए कोई विशिष्ट एंटीवायरल उपचार या टीका नहीं है।
On the allegations against the SEBI chief / सेबी प्रमुख के खिलाफ आरोपों पर
Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity
Source : The Hindu
Hindenburg Research alleges SEBI Chairman Madhabi Puri Buch and her husband had hidden stakes in offshore funds linked to Adani stock manipulation.
- Hindenburg Research also raised concerns about Buch’s continued involvement with Agora Partners and Blackstone.
- SEBI denies bias and maintains the integrity of its policies and recusal procedures.
Accusations Against SEBI Chairman Madhabi Puri Buch
- Offshore Fund Connections: Hindenburg Research alleges that Madhabi Puri Buch and her husband, Dhaval Buch, held stakes in offshore funds based in Bermuda and Mauritius, which are linked to the Adani Group.
- These funds are purportedly used by Vinod Adani, brother of Gautam Adani, raising concerns about a conflict of interest.
- Financial Opacity: The report highlights that Mr. Buch fully owned a consulting firm, Agora Partners, during her tenure at SEBI.
- Hindenburg asserts that she transferred ownership of this firm to her husband shortly after her appointment as SEBI Chairperson, which raises questions about financial transparency.
- Conflict of Interest with Blackstone: Hindenburg alleges that Dhaval Buch was appointed as a senior advisor at Blackstone, a major player in the Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) market, while Madhabi Puri Buch was leading SEBI.
- The report claims that under her leadership, SEBI approved regulatory changes that favored REITs, benefiting Blackstone.
Status of the Ongoing Investigation by SEBI
- Supreme Court Oversight: The Supreme Court has directed SEBI to investigate the allegations made by Hindenburg Research. The Court has set a timeline for SEBI to complete its investigation into specific allegations, emphasizing the need for accountability in the ongoing inquiry.
- Show Cause Notice by SEBI: In June 2024, SEBI issued a show cause notice to Hindenburg Research, indicating that the regulator is actively pursuing the matter.
Understanding Short Selling
- Definition: Short selling involves profiting from a decline in the price of a stock. It involves selling borrowed shares with the expectation of buying them back at a lower price.
- Example: Selling 10 shares at ₹100 each results in ₹1,000. If the price drops to ₹85, buying back the shares costs ₹850, yielding a profit of ₹150.
- Uses and Risks: While short selling can help address market imbalances and ensure price efficiency, it can also be used for market manipulation, as described by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as a “bear raid”.
Key Takeaways
- Allegations of Conflict of Interest: The core issue is the alleged conflict of interest involving SEBI Chairman Madhabi Puri Buch and her husband’s investments and professional engagements.
- Short Selling and Market Manipulation: Short selling can be a tool for market manipulation, raising concerns about the intentions of short sellers.
- SEBI’s Response and Legal Proceedings: SEBI is defending its actions and the Supreme Court is overseeing the investigation, with ongoing scrutiny of the regulator’s handling of the case.
सेबी प्रमुख के खिलाफ आरोपों पर
हिंडनबर्ग रिसर्च ने आरोप लगाया है कि सेबी की चेयरमैन माधबी पुरी बुच और उनके पति ने अडानी स्टॉक हेरफेर से जुड़े ऑफशोर फंड में अपनी हिस्सेदारी छिपाई है।
- हिंडनबर्ग रिसर्च ने बुच के एगोरा पार्टनर्स और ब्लैकस्टोन के साथ लगातार जुड़े रहने पर भी चिंता जताई है।
- सेबी पक्षपात से इनकार करता है और अपनी नीतियों और अलग होने की प्रक्रियाओं की अखंडता को बनाए रखता है।
सेबी अध्यक्ष माधबी पुरी बुच के खिलाफ आरोप
- ऑफशोर फंड कनेक्शन: हिंडनबर्ग रिसर्च का आरोप है कि माधबी पुरी बुच और उनके पति धवल बुच ने बरमूडा और मॉरीशस में स्थित ऑफशोर फंड में हिस्सेदारी रखी है, जो अडानी समूह से जुड़े हैं।
- इन फंड का कथित तौर पर गौतम अडानी के भाई विनोद अडानी द्वारा उपयोग किया जाता है, जिससे हितों के टकराव की चिंता बढ़ जाती है।
- वित्तीय अस्पष्टता: रिपोर्ट में इस बात पर प्रकाश डाला गया है कि श्री बुच सेबी में अपने कार्यकाल के दौरान एक कंसल्टिंग फर्म, अगोरा पार्टनर्स के पूर्ण मालिक थे।
- हिंडनबर्ग का दावा है कि उन्होंने सेबी अध्यक्ष के रूप में अपनी नियुक्ति के तुरंत बाद इस फर्म का स्वामित्व अपने पति को हस्तांतरित कर दिया, जिससे वित्तीय पारदर्शिता पर सवाल उठते हैं।
- ब्लैकस्टोन के साथ हितों का टकराव: हिंडनबर्ग का आरोप है कि धवल बुच को रियल एस्टेट इन्वेस्टमेंट ट्रस्ट (आरईआईटी) बाजार में एक प्रमुख खिलाड़ी ब्लैकस्टोन में वरिष्ठ सलाहकार के रूप में नियुक्त किया गया था, जबकि माधबी पुरी बुच सेबी का नेतृत्व कर रही थीं।
- रिपोर्ट में दावा किया गया है कि उनके नेतृत्व में, सेबी ने नियामक परिवर्तनों को मंजूरी दी जो REITs के पक्ष में थे, जिससे ब्लैकस्टोन को लाभ हुआ।
सेबी द्वारा चल रही जांच की स्थिति
- सुप्रीम कोर्ट की निगरानी: सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने सेबी को हिंडनबर्ग रिसर्च द्वारा लगाए गए आरोपों की जांच करने का निर्देश दिया है। कोर्ट ने सेबी को विशिष्ट आरोपों की जांच पूरी करने के लिए एक समयसीमा निर्धारित की है, जिसमें चल रही जांच में जवाबदेही की आवश्यकता पर जोर दिया गया है।
- सेबी द्वारा कारण बताओ नोटिस: जून 2024 में, सेबी ने हिंडनबर्ग रिसर्च को कारण बताओ नोटिस जारी किया, जो दर्शाता है कि नियामक सक्रिय रूप से मामले को आगे बढ़ा रहा है।
शॉर्ट सेलिंग को समझना
- परिभाषा: शॉर्ट सेलिंग में स्टॉक की कीमत में गिरावट से लाभ कमाना शामिल है। इसमें कम कीमत पर उन्हें वापस खरीदने की उम्मीद के साथ उधार लिए गए शेयरों को बेचना शामिल है।
- उदाहरण: 10 शेयर ₹100 पर बेचने पर ₹1,000 मिलते हैं। यदि कीमत ₹85 तक गिर जाती है, तो शेयर वापस खरीदने पर ₹850 का खर्च आएगा, जिससे ₹150 का लाभ होगा।
- उपयोग और जोखिम: जबकि शॉर्ट सेलिंग बाजार असंतुलन को दूर करने और मूल्य दक्षता सुनिश्चित करने में मदद कर सकती है, इसका उपयोग बाजार में हेरफेर के लिए भी किया जा सकता है, जैसा कि यू.एस. सिक्योरिटीज एंड एक्सचेंज कमीशन (एसईसी) द्वारा “बेयर रेड” के रूप में वर्णित किया गया है।
मुख्य बातें
- हितों के टकराव के आरोप: मुख्य मुद्दा सेबी की अध्यक्ष माधबी पुरी बुच और उनके पति के निवेश और पेशेवर जुड़ाव से जुड़े कथित हितों के टकराव का है।
- शॉर्ट सेलिंग और बाजार में हेरफेर: शॉर्ट सेलिंग बाजार में हेरफेर करने का एक साधन हो सकता है, जिससे शॉर्ट सेलर्स के इरादों के बारे में चिंता बढ़ जाती है।
- सेबी की प्रतिक्रिया और कानूनी कार्यवाही: सेबी अपने कार्यों का बचाव कर रहा है और सुप्रीम कोर्ट मामले की नियामक द्वारा की जा रही हैंडलिंग की निरंतर जांच के साथ जांच की निगरानी कर रहा है।
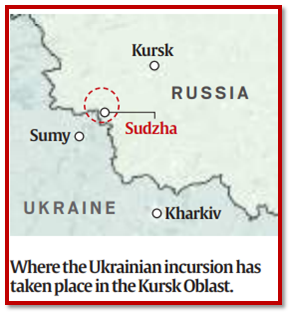
Ukraine’s Kursk Operation in Russia / रूस में यूक्रेन का कुर्स्क ऑपरेशन
Location In News
Ukrainian troops have advanced up to 35 kilometers into Russian territory in the Kursk region.
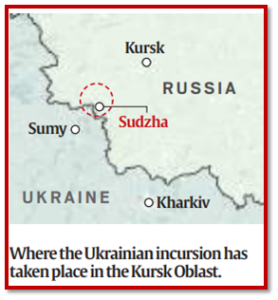
What is the Kursk Operation?
- The Kursk operation marks a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict between Ukraine and Russia.
- The operation has been characterized by intense fighting, with reports of casualties.
About Kursk Region:
- It is located in the western part of Russia, bordering Ukraine to the southwest.
- The region holds historical significance Battle of Kursk as the site of the, which took place from July to August 1943 and is recognized as the largest tank battle in history during World War II.
- The Kursk region is rich in iron ore, which has led to substantial mining operations in the area.
- The region experiences a continental climate, with cold winters and warm summers.
Significance of the Kursk Operation for Ukraine
- Strategic Leverage: Strengthens Ukraine’s position in future negotiations by capturing Russian territory for potential land exchanges.
- Buffer Zone Creation: Enhances security for contested Ukrainian areas by establishing a protective buffer on Russian soil.
- Military Diversion: Forces Russia to redeploy troops, weakening their main front lines and easing pressure on Ukrainian forces.
रूस में यूक्रेन का कुर्स्क ऑपरेशन
यूक्रेनी सैनिक कुर्स्क क्षेत्र में रूसी क्षेत्र में 35 किलोमीटर तक आगे बढ़ गए हैं।
कुर्स्क ऑपरेशन क्या है?
- कुर्स्क ऑपरेशन यूक्रेन और रूस के बीच चल रहे संघर्ष में एक महत्वपूर्ण वृद्धि को दर्शाता है।
- इस ऑपरेशन में भीषण लड़ाई हुई है, जिसमें हताहतों की रिपोर्ट भी आई है।
कुर्स्क क्षेत्र के बारे में:
- यह रूस के पश्चिमी भाग में स्थित है, जो दक्षिण-पश्चिम में यूक्रेन की सीमा से लगा हुआ है।
- इस क्षेत्र का ऐतिहासिक महत्व है, कुर्स्क की लड़ाई यहीं हुई थी, जो जुलाई से अगस्त 1943 तक चली थी और इसे द्वितीय विश्व युद्ध के दौरान इतिहास की सबसे बड़ी टैंक लड़ाई के रूप में मान्यता प्राप्त है।
- कुर्स्क क्षेत्र लौह अयस्क से समृद्ध है, जिसके कारण इस क्षेत्र में पर्याप्त खनन कार्य हुए हैं।
- इस क्षेत्र में महाद्वीपीय जलवायु है, जिसमें सर्दियाँ ठंडी और गर्मियाँ गर्म होती हैं।
यूक्रेन के लिए कुर्स्क ऑपरेशन का महत्व
- रणनीतिक लाभ: संभावित भूमि विनिमय के लिए रूसी क्षेत्र पर कब्जा करके भविष्य की वार्ता में यूक्रेन की स्थिति को मजबूत करता है।
- बफर जोन निर्माण: रूसी धरती पर सुरक्षात्मक बफर स्थापित करके विवादित यूक्रेनी क्षेत्रों की सुरक्षा बढ़ाता है।
- सैन्य विचलन: रूस को सैनिकों को पुनः तैनात करने के लिए मजबूर किया जाता है, जिससे उनकी मुख्य अग्रिम पंक्तियां कमजोर हो जाती हैं और यूक्रेनी सेना पर दबाव कम हो जाता है।
Cold War nuke tests light up a bug in present-day climate models /शीत युद्ध के परमाणु परीक्षणों ने वर्तमान जलवायु मॉडल में एक बग को उजागर किया
Syllabus : GS 3 : Environment
Source : The Hindu
Recent research reveals that plants absorb more CO2 and store it for shorter periods than previously thought.Using radiocarbon from Cold War nuclear tests, scientists found that plants cycle carbon faster than estimated.
- This finding challenges existing climate models and highlights the need for better integration of radiocarbon data in climate projections to improve accuracy.
Study by an International Team of Researchers:
- A recent study published in Science by an international research team suggests that plants absorb more CO2 from the atmosphere than previously thought but release it back into their surroundings sooner than expected.
- Researchers utilized climate models to analyze the impact of radiocarbon (carbon-14) from nuclear bomb tests on the carbon cycle. They tracked changes in radiocarbon levels in the atmosphere and how it was absorbed by plants during photosynthesis.
- The study estimates that plants store around 80 billion tonnes of carbon per year, primarily in leaves and finer roots, which is higher than previous estimates of 43-76 billion tonnes. This indicates that plants may be cycling carbon through the atmosphere and soil more rapidly than previously thought.
Study from the Relics of the Cold War:
- The nuclear bomb tests conducted during the Cold War inadvertently provided scientists with valuable data for climate research.
- The tests released significant amounts of radiocarbon into the atmosphere, allowing researchers to study its movement and absorption by vegetation.
- The presence of radiocarbon in the atmosphere serves as a marker for understanding carbon dynamics.
- The study analyzed the radiocarbon levels before and after the 1963 Limited Test Ban Treaty, which halted atmospheric nuclear testing, providing insights into how carbon is cycled between the atmosphere and vegetation.
- The study highlights that many climate models have not incorporated radiocarbon data, which could lead to inaccuracies in predicting carbon cycling and its impact on climate change.
- Only one model, the Community Earth System Model 2, has accounted for radiocarbon, but it predicted lower absorption levels than the study found.
How the Whole System is Cycling Faster?
- Accelerated Carbon Exchange: The researchers concluded that the entire carbon cycle is operating faster than previously understood.
- This means that while plants absorb more CO2, they also release it back into the atmosphere more quickly, leading to a more dynamic and less stable carbon storage system.
- Implications for Climate Mitigation: The findings suggest that strategies relying on plant carbon sequestration to offset fossil fuel emissions may need to be reevaluated.
- If plants are releasing carbon sooner than expected, the potential for mitigating climate change through natural carbon sinks could be less effective than previously thought.
Way forward:
- Incorporate Radiocarbon Data: Integrate radiocarbon data into existing and future climate models to more accurately predict carbon cycling and the role of vegetation in carbon sequestration. This will lead to more reliable forecasts of climate change impacts and inform better policy decisions.
- Develop Dynamic Carbon Cycle Models: Improve models to account for the faster carbon cycling observed, ensuring they reflect the actual pace at which carbon is absorbed and released by plants. This will help in refining strategies for climate mitigation.
शीत युद्ध के परमाणु परीक्षणों ने वर्तमान जलवायु मॉडल में एक बग को उजागर किया
हाल ही में किए गए शोध से पता चला है कि पौधे पहले की अपेक्षा अधिक CO2 अवशोषित करते हैं और इसे कम समय के लिए संग्रहीत करते हैं। शीत युद्ध के परमाणु परीक्षणों से प्राप्त रेडियोकार्बन का उपयोग करते हुए, वैज्ञानिकों ने पाया कि पौधे अनुमान से अधिक तेज़ी से कार्बन का चक्रण करते हैं।
- यह खोज मौजूदा जलवायु मॉडल को चुनौती देती है और सटीकता में सुधार के लिए जलवायु अनुमानों में रेडियोकार्बन डेटा के बेहतर एकीकरण की आवश्यकता पर प्रकाश डालती है।
शोधकर्ताओं की एक अंतरराष्ट्रीय टीम द्वारा अध्ययन:
- विज्ञान में प्रकाशित एक हालिया अध्ययन से पता चलता है कि पौधे पहले की तुलना में वायुमंडल से अधिक CO2 अवशोषित करते हैं, लेकिन इसे अपेक्षा से पहले अपने परिवेश में वापस छोड़ देते हैं।
- शोधकर्ताओं ने कार्बन चक्र पर परमाणु बम परीक्षणों से रेडियोकार्बन (कार्बन-14) के प्रभाव का विश्लेषण करने के लिए जलवायु मॉडल का उपयोग किया। उन्होंने वायुमंडल में रेडियोकार्बन के स्तर में परिवर्तन और प्रकाश संश्लेषण के दौरान पौधों द्वारा इसे कैसे अवशोषित किया गया, इसका पता लगाया।
- अध्ययन का अनुमान है कि पौधे प्रति वर्ष लगभग 80 बिलियन टन कार्बन संग्रहीत करते हैं, मुख्य रूप से पत्तियों और महीन जड़ों में, जो कि 43-76 बिलियन टन के पिछले अनुमानों से अधिक है। यह दर्शाता है कि पौधे पहले की तुलना में अधिक तेज़ी से वायुमंडल और मिट्टी के माध्यम से कार्बन का चक्रण कर रहे हैं।
शीत युद्ध के अवशेषों से अध्ययन:
- शीत युद्ध के दौरान किए गए परमाणु बम परीक्षणों ने अनजाने में वैज्ञानिकों को जलवायु अनुसंधान के लिए मूल्यवान डेटा प्रदान किया।
- परीक्षणों ने वायुमंडल में महत्वपूर्ण मात्रा में रेडियोकार्बन छोड़ा, जिससे शोधकर्ताओं को वनस्पति द्वारा इसकी गति और अवशोषण का अध्ययन करने में मदद मिली।
- वायुमंडल में रेडियोकार्बन की उपस्थिति कार्बन गतिशीलता को समझने के लिए एक मार्कर के रूप में कार्य करती है।
- अध्ययन ने 1963 की सीमित परीक्षण प्रतिबंध संधि से पहले और बाद में रेडियोकार्बन के स्तरों का विश्लेषण किया, जिसने वायुमंडलीय परमाणु परीक्षण को रोक दिया, जिससे वायुमंडल और वनस्पति के बीच कार्बन का चक्रण कैसे होता है, इस बारे में जानकारी मिली।
- अध्ययन में इस बात पर प्रकाश डाला गया है कि कई जलवायु मॉडलों ने रेडियोकार्बन डेटा को शामिल नहीं किया है, जिससे कार्बन चक्रण और जलवायु परिवर्तन पर इसके प्रभाव की भविष्यवाणी करने में अशुद्धियाँ हो सकती हैं।
- केवल एक मॉडल, सामुदायिक पृथ्वी प्रणाली मॉडल 2, ने रेडियोकार्बन को ध्यान में रखा है, लेकिन इसने अध्ययन में पाए गए अवशोषण स्तरों से कम होने की भविष्यवाणी की है।
पूरा सिस्टम किस तरह तेज़ी से चक्रण कर रहा है?
- त्वरित कार्बन विनिमय: शोधकर्ताओं ने निष्कर्ष निकाला कि पूरा कार्बन चक्र पहले से समझे गए चक्रण से अधिक तेज़ी से काम कर रहा है।
- इसका मतलब यह है कि पौधे अधिक CO2 अवशोषित करते हैं, लेकिन वे इसे अधिक तेज़ी से वायुमंडल में वापस छोड़ते हैं, जिससे अधिक गतिशील और कम स्थिर कार्बन भंडारण प्रणाली बनती है।
- जलवायु शमन के लिए निहितार्थ: निष्कर्ष बताते हैं कि जीवाश्म ईंधन उत्सर्जन को कम करने के लिए पौधों द्वारा कार्बन पृथक्करण पर निर्भर रणनीतियों का पुनर्मूल्यांकन करने की आवश्यकता हो सकती है।
- यदि पौधे अपेक्षा से पहले कार्बन छोड़ रहे हैं, तो प्राकृतिक कार्बन सिंक के माध्यम से जलवायु परिवर्तन को कम करने की क्षमता पहले की तुलना में कम प्रभावी हो सकती है।
आगे की राह:
- रेडियोकार्बन डेटा को शामिल करें: कार्बन चक्रण और कार्बन पृथक्करण में वनस्पति की भूमिका का अधिक सटीक रूप से अनुमान लगाने के लिए मौजूदा और भविष्य के जलवायु मॉडल में रेडियोकार्बन डेटा को एकीकृत करें। इससे जलवायु परिवर्तन के प्रभावों का अधिक विश्वसनीय पूर्वानुमान लगाया जा सकेगा और बेहतर नीतिगत निर्णय लिए जा सकेंगे।
- गतिशील कार्बन चक्र मॉडल विकसित करें: देखे गए तेज़ कार्बन चक्रण को ध्यान में रखते हुए मॉडल में सुधार करें, यह सुनिश्चित करते हुए कि वे वास्तविक गति को दर्शाते हैं जिस पर कार्बन अवशोषित होता है और पौधों द्वारा छोड़ा जाता है। इससे जलवायु शमन के लिए रणनीतियों को परिष्कृत करने में मदद मिलेगी।
On amendments to the Waqf Act / वक्फ अधिनियम में संशोधन पर
Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity
Source : The Hindu
The Union government introduced a Bill to amend the 1995 Waqf Act, aiming to enhance regulatory control over waqf properties and include non-Muslims in management boards.
- This reform seeks to improve efficiency but faces criticism for potential infringement on religious rights and lack of stakeholder consultation.
Introduction of the Bill
- On August 8, 2024, the Union government introduced a Bill in the Lok Sabha to amend the 1995 Waqf Act.
- The draft legislation, proposed to be renamed the Unified Waqf Management, Empowerment, Efficiency, and Development Act, 2024, seeks to improve the “efficiency of the administration and management of waqf properties.”
- Several Opposition parties have accused the government of introducing the Bill without adequate consultation with stakeholders, claiming it encroaches on the Muslim community’s religious rights.
Understanding Waqf in Islamic Law:
- In Islamic law, waqf refers to property dedicated in the name of God for religious and charitable purposes.
- Waqf properties include movable or immovable assets set aside for the public good, supporting mosques, schools, or the poor.
- Such properties cannot be transferred, sold, or inherited once designated as waqf.Non-Muslims can also create waqfs if they align with Islamic principles.
Regulation of Waqfs in India
- In India, waqfs are governed by the 1995 Waqf Act.
- The Act involves a survey by the State government to identify waqf properties, with a list maintained by the State Waqf Board.
- Each waqf is managed by a mutawalli (custodian), and waqf properties are treated similarly to trusts but cannot be dissolved by a Board.
Role of the Waqf Board
- The 1995 Act establishes State Waqf Boards to oversee waqf property management.
- Boards consist of a chairperson, State government nominees, Muslim legislators, Islamic scholars, and mutawalli.
- A full-time Chief Executive Officer, required to be Muslim, heads each Board.
- The Boards manage waqf properties, can recover lost assets, and sanction property transfers with a two-thirds majority.
- Amendments in 2013 made it nearly impossible to sell waqf properties.
Central Waqf Council
- The Central Waqf Council, under the Ministry of Minority Affairs, ensures uniform administration across the country.
- It advises the Union government on waqf issues and policy development.
Key Changes in the Proposed Law
- Definition of Waqf: The Bill revises the definition to require lawful property owners who have practised Islam for at least five years to create waqf properties through formal deeds. The Bill abolishes the ‘waqf by use’ concept.
- Government Property: Government properties identified or declared as waqf before or after the Act’s commencement will not be recognized as waqf.
- Beneficiaries: The Bill allows widows, divorced women, and orphans to benefit from waqf assets.
- Survey Responsibility: District collectors or equivalent officers will handle the surveying of waqf properties instead of survey commissioners.
- A centralised registration system for waqf properties will be established, and records must be uploaded within six months of the law’s enactment.
- Disputed Properties: The Bill omits section 40, which previously allowed waqf tribunals to determine waqf status. Instead, district collectors will make the final determination and update revenue records. Disputed properties cannot be controlled by Waqf Boards until the final report is submitted.
- Non-Muslim Inclusion: The Bill allows non-Muslims to be included in the Central Waqf Council, State Waqf Boards, and waqf tribunals. It permits the Centre to appoint three Members of Parliament to the Council without religious restrictions and requires State Boards to include two non-Muslims and two women.
- Waqf Tribunals: The Bill changes waqf tribunals from three-member to two-member bodies, consisting of a district judge and a joint secretary rank officer. Tribunals must resolve disputes within six months, with an extension possible.
- Audit and Oversight: The Bill grants the Centre authority to direct the audit of waqfs by auditors appointed by the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India. Waqf Boards must conduct annual audits and face penalties for failing to maintain proper accounts.
- Judicial Intervention: Courts can now intervene in waqf disputes, allowing appeals to the High Court and removing the finality of tribunal decisions.
Potential Implications
- Some scholars have supported the amendments as positive but stress the need for measures protecting waqf properties without infringing on religious freedom under Article 25 of the Constitution.
- Questions whether similar non-Muslim participation would be acceptable in Hindu temple boards and criticises increased government control as contrary to economic liberalisation principles.
- The Bill has been referred to a joint parliamentary panel for further scrutiny after opposition from the Congress-led INDIA bloc.
वक्फ अधिनियम में संशोधन पर
केंद्र सरकार ने 1995 के वक्फ अधिनियम में संशोधन के लिए एक विधेयक पेश किया, जिसका उद्देश्य वक्फ संपत्तियों पर विनियामक नियंत्रण बढ़ाना और प्रबंधन बोर्डों में गैर-मुस्लिमों को शामिल करना है।
- इस सुधार का उद्देश्य कार्यकुशलता में सुधार करना है, लेकिन धार्मिक अधिकारों के संभावित उल्लंघन और हितधारकों के परामर्श की कमी के कारण इसकी आलोचना की जा रही है।
विधेयक का परिचय
- 8 अगस्त, 2024 को, केंद्र सरकार ने 1995 के वक्फ अधिनियम में संशोधन करने के लिए लोकसभा में एक विधेयक पेश किया।
- इस मसौदा कानून का नाम बदलकर एकीकृत वक्फ प्रबंधन, सशक्तीकरण, दक्षता और विकास अधिनियम, 2024 करने का प्रस्ताव है, जिसका उद्देश्य “वक्फ संपत्तियों के प्रशासन और प्रबंधन की दक्षता” में सुधार करना है।
- कई विपक्षी दलों ने सरकार पर हितधारकों के साथ पर्याप्त परामर्श के बिना विधेयक पेश करने का आरोप लगाया है, उनका दावा है कि यह मुस्लिम समुदाय के धार्मिक अधिकारों का अतिक्रमण करता है।
इस्लामिक कानून में वक्फ को समझना:
- इस्लामिक कानून में, वक्फ धार्मिक और धर्मार्थ उद्देश्यों के लिए ईश्वर के नाम पर समर्पित संपत्ति को संदर्भित करता है।
- वक्फ संपत्तियों में सार्वजनिक भलाई, मस्जिदों, स्कूलों या गरीबों का समर्थन करने के लिए अलग रखी गई चल या अचल संपत्तियां शामिल हैं।
- एक बार वक्फ के रूप में नामित होने के बाद ऐसी संपत्तियों को हस्तांतरित, बेचा या विरासत में नहीं दिया जा सकता है। गैर-मुस्लिम भी वक्फ बना सकते हैं यदि वे इस्लामी सिद्धांतों के अनुरूप हों।
भारत में वक्फ का विनियमन
- भारत में, वक्फ 1995 के वक्फ अधिनियम द्वारा शासित होते हैं।
- इस अधिनियम में वक्फ संपत्तियों की पहचान करने के लिए राज्य सरकार द्वारा सर्वेक्षण शामिल है, जिसकी सूची राज्य वक्फ बोर्ड द्वारा रखी जाती है।
- प्रत्येक वक्फ का प्रबंधन एक मुतवल्ली (संरक्षक) द्वारा किया जाता है, और वक्फ संपत्तियों को ट्रस्टों के समान माना जाता है, लेकिन बोर्ड द्वारा उन्हें भंग नहीं किया जा सकता है।
वक्फ बोर्ड की भूमिका
- 1995 का अधिनियम वक्फ संपत्ति प्रबंधन की देखरेख के लिए राज्य वक्फ बोर्ड की स्थापना करता है।
- बोर्ड में एक अध्यक्ष, राज्य सरकार के नामित व्यक्ति, मुस्लिम विधायक, इस्लामी विद्वान और मुतवल्ली शामिल होते हैं।
- प्रत्येक बोर्ड का प्रमुख एक पूर्णकालिक मुख्य कार्यकारी अधिकारी होता है, जो मुस्लिम होना चाहिए।
- बोर्ड वक्फ संपत्तियों का प्रबंधन करते हैं, खोई हुई संपत्तियों को वापस प्राप्त कर सकते हैं, और दो-तिहाई बहुमत से संपत्ति हस्तांतरण को मंजूरी दे सकते हैं।
- 2013 में संशोधनों ने वक्फ संपत्तियों को बेचना लगभग असंभव बना दिया।
केंद्रीय वक्फ परिषद
- अल्पसंख्यक मामलों के मंत्रालय के तहत केंद्रीय वक्फ परिषद पूरे देश में एक समान प्रशासन सुनिश्चित करती है।
- यह वक्फ मुद्दों और नीति विकास पर केंद्र सरकार को सलाह देती है।
प्रस्तावित कानून में मुख्य परिवर्तन
- वक्फ की परिभाषा: विधेयक परिभाषा को संशोधित करता है, ताकि कम से कम पांच साल तक इस्लाम का पालन करने वाले वैध संपत्ति मालिकों को औपचारिक कार्यों के माध्यम से वक्फ संपत्ति बनाने की आवश्यकता हो। विधेयक ‘उपयोग द्वारा वक्फ’ अवधारणा को समाप्त करता है।
- सरकारी संपत्ति: अधिनियम के लागू होने से पहले या बाद में वक्फ के रूप में पहचानी गई या घोषित की गई सरकारी संपत्तियों को वक्फ के रूप में मान्यता नहीं दी जाएगी।
- लाभार्थी: विधेयक विधवाओं, तलाकशुदा महिलाओं और अनाथों को वक्फ संपत्तियों से लाभ उठाने की अनुमति देता है।
- सर्वेक्षण की जिम्मेदारी: सर्वेक्षण आयुक्तों के बजाय जिला कलेक्टर या समकक्ष अधिकारी वक्फ संपत्तियों का सर्वेक्षण करेंगे।
- वक्फ संपत्तियों के लिए एक केंद्रीकृत पंजीकरण प्रणाली स्थापित की जाएगी, और कानून के लागू होने के छह महीने के भीतर रिकॉर्ड अपलोड किए जाने चाहिए।
- विवादित संपत्तियां: विधेयक धारा 40 को हटा देता है, जो पहले वक्फ न्यायाधिकरणों को वक्फ की स्थिति निर्धारित करने की अनुमति देता था। इसके बजाय, जिला कलेक्टर अंतिम निर्धारण करेंगे और राजस्व रिकॉर्ड को अपडेट करेंगे। अंतिम रिपोर्ट प्रस्तुत किए जाने तक विवादित संपत्तियों को वक्फ बोर्ड द्वारा नियंत्रित नहीं किया जा सकता है।
- गैर-मुस्लिम समावेशन: विधेयक गैर-मुस्लिमों को केंद्रीय वक्फ परिषद, राज्य वक्फ बोर्ड और वक्फ न्यायाधिकरणों में शामिल करने की अनुमति देता है। यह केंद्र को धार्मिक प्रतिबंधों के बिना परिषद में तीन संसद सदस्यों को नियुक्त करने की अनुमति देता है और राज्य बोर्डों को दो गैर-मुस्लिम और दो महिलाओं को शामिल करने की आवश्यकता होती है।
- वक्फ न्यायाधिकरण: विधेयक वक्फ न्यायाधिकरणों को तीन-सदस्यीय से दो-सदस्यीय निकायों में बदल देता है, जिसमें एक जिला न्यायाधीश और एक संयुक्त सचिव रैंक का अधिकारी होता है। न्यायाधिकरणों को छह महीने के भीतर विवादों को हल करना होगा, जिसे बढ़ाया जा सकता है।
- लेखा परीक्षा और निरीक्षण: विधेयक केंद्र को भारत के नियंत्रक और महालेखा परीक्षक द्वारा नियुक्त लेखा परीक्षकों द्वारा वक्फ के लेखा परीक्षा को निर्देशित करने का अधिकार देता है। वक्फ बोर्ड को वार्षिक ऑडिट करना होगा और उचित खाते न रखने पर दंड का सामना करना होगा।
- न्यायिक हस्तक्षेप: न्यायालय अब वक्फ विवादों में हस्तक्षेप कर सकते हैं, जिससे उच्च न्यायालय में अपील की जा सकेगी और न्यायाधिकरण के निर्णयों की अंतिमता समाप्त हो जाएगी।
संभावित निहितार्थ
- कुछ विद्वानों ने संशोधनों को सकारात्मक बताया है, लेकिन संविधान के अनुच्छेद 25 के तहत धार्मिक स्वतंत्रता का उल्लंघन किए बिना वक्फ संपत्तियों की सुरक्षा के उपायों की आवश्यकता पर बल दिया है।
- सवाल यह है कि क्या हिंदू मंदिर बोर्डों में इसी तरह की गैर-मुस्लिम भागीदारी स्वीकार्य होगी और आर्थिक उदारीकरण के सिद्धांतों के विपरीत बढ़ते सरकारी नियंत्रण की आलोचना की।
- कांग्रेस के नेतृत्व वाले भारत ब्लॉक के विरोध के बाद विधेयक को आगे की जांच के लिए एक संयुक्त संसदीय पैनल को भेजा गया है।
The top court as custodian of liberties / स्वतंत्रता के संरक्षक के रूप में शीर्ष न्यायालय
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- The Supreme Court of India granted bail to former Delhi Deputy Chief Minister Manish Sisodia, emphasising the importance of individual liberties and the right to a speedy trial.
- The decision highlighted issues with India’s criminal justice system, including prolonged pretrial detentions and the misuse of stringent penal laws like the PMLA.
Previous judgments on the ‘Right to Speedy Trial’:
- The Supreme Court referenced its earlier judgments, including Kashmira Singh (1977), P. Chidambaram (2020), and Satender Kumar Antil (2022), which establish that the right to a speedy trial is fundamental under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- The Court’s decision in Arnab Manoranjan Goswami vs The State of Maharashtra and Ors. (2020) was cited, reinforcing that liberty is a core component of constitutionalism.
- In recent scenario, the SC relied on its earlier order dated October 30, 2023, in Manish Sisodia vs Central Bureau of Investigation, which highlighted concerns about the large volume of evidence (56,000 pages of documents and 456 witnesses) potentially causing significant delays in trial proceedings.
Constitutional Mandate
- The Supreme Court ruled that the right to bail in cases of delay should be integrated into Section 439 CrPC and Section 45 of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
- The judgement is significant due to concerns over the misuse of stringent penal laws and oppressive application of the PMLA.
- The Court highlighted the low conviction rate under the PMLA, with only 40 convictions out of over 5,000 cases in the last decade.
Challenges in the Criminal Justice System
- The criminal justice system faces significant challenges due to delays, where procedural complexities become punitive.
- Issues like justice being hindered by legal technicalities are recognized in cases such as Sushil Kumar Sen (1975) and Rani Kusum (2005).
Concerns Raised
- Despite its merits, the judgement raises concerns about prolonged custodial confinement based on prosecutorial assurances.
- Relying on the prosecutor’s statements for trial timelines and charge sheet filing can contradict principles of natural justice and fair trial procedures.
The Guarantee of Civil Liberties
- Constitutional Foundation: The Supreme Court emphasized that individual liberties should not be contingent on the discretion of the prosecution.
- In judgments like Maneka Gandhi v. Union of India (1978), the Court expanded the understanding of due process, emphasising that any deprivation of liberty must follow fair, just, and reasonable procedures.
- Judicial Responsibility: The judgment aims to prevent the misuse of stringent laws like the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) and to uphold the dignity and rights of individuals.
- In Rana Ayyub v. Directorate of Enforcement (2023), the Supreme Court emphasized judicial oversight in PMLA enforcement while ensuring trials follow underlying offenses.
- Public’s trust on Judiciary: Presently, the Apex Court pointed out the flawed tendency of some judges to deny bail unnecessarily, ignoring the principle of timely trials. This may lead to loss of public trust in the judiciary.
- Call for Systemic Change: The ruling urges a reevaluation of the political and legal systems to prioritize justice and individual rights over personal vendettas.
- State of Maharashtra v. Rani Kusum (2005) underscores the necessity for reforms to address delays in the judicial process.
- Bail is the Rule, Not the Exception: The Supreme Court’s decision in granting bail to Manish Sisodia reinforces the principle that bail is the rule, not the exception.
Restoring Liberty
- By granting Mr. Sisodia bail, the Supreme Court has addressed previous ambiguities and upheld the principles of bail and individual freedom.
- The judgement aims to prevent undertrials from languishing in custody, losing their freedom, reputation, privacy, and dignity without accountability.
- The nation must shift its political focus away from personal animosities towards justice and dignity for all, revitalising democracy.
Conclusion
- The article concludes with a personal reflection that the Court’s decision is a step toward ensuring that undertrials are not unjustly detained.
- It calls for a national shift in politics toward justice and dignity, emphasising the role of the judiciary in safeguarding civil liberties.
What is Money Laundering?
- About:
- Money laundering is a complex process used by individuals and organisations to conceal the origins of illegally obtained money. It involves making illicit funds appear legitimate through a series of transactions.
- Stages of Money Laundering:
- Placement: The initial stage where illicit funds are introduced into the financial system. This can involve deposits into bank accounts, currency exchanges, or purchases of valuable assets.
- Layering: The process of separating the illicit funds from their source through a series of complex financial transactions. This often involves transferring funds between accounts or across borders to obscure their origin.
- Integration: The final stage where the laundered funds are reintroduced into the economy as legitimate funds. This can involve investing in businesses, purchasing real estate, or other means of legitimising the funds.
- Methods of Money Laundering:
- Structuring (Smurfing): Breaking up large amounts of cash into smaller, less conspicuous amounts that are then deposited into bank accounts.
- Trade-Based Laundering: Using trade transactions to move value across borders and disguise the origins of illicit funds.
- Shell Companies: Creating companies with no legitimate business activity to funnel illicit funds through legitimate-looking transactions.
- Real Estate: Purchasing real estate with illicit funds and then selling it to convert the value into legitimate assets.
What is PMLA, 2002?
- About:
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA) is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted to prevent money laundering and provide for the confiscation of property derived from money laundering.
- It aims to combat money laundering related to illegal activities such as drug trafficking, smuggling, and terrorism financing.
- Key Provisions of PMLA:
- Offences and Penalties: PMLA defines money laundering offences and imposes penalties for such activities. It includes rigorous imprisonment and fines for offenders.
- Attachment and Confiscation of Property: The Act allows for the attachment and confiscation of property involved in money laundering. It provides for the establishment of an Adjudicating Authority to oversee these proceedings.
- Reporting Requirements: PMLA mandates certain entities, such as banks and financial institutions, to maintain records of transactions and report suspicious transactions to the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU).
- Designated Authority and Appellate Tribunal: The Act establishes a Designated Authority to assist in the investigation and prosecution of money laundering offences. It also provides for the establishment of an Appellate Tribunal to hear appeals against orders of the Adjudicating Authority.
- Objectives of PMLA:
- Prevention: To prevent money laundering by implementing stringent measures and monitoring financial transactions.
- Detection: To detect and investigate instances of money laundering through proper enforcement and regulatory mechanisms.
- Confiscation: To confiscate properties derived from money laundering activities to deter offenders and disrupt illicit financial flows.
- International Cooperation: To facilitate international cooperation in combating money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
- Recent Amendments to PMLA, 2002:
- Clarification about the Position of Proceeds of Crime: Proceeds of the Crime not only includes the property derived from scheduled offence but would also include any other property derived or obtained indulging into any criminal activity relate-able or similar to the scheduled offence.
- Money Laundering Redefined: Money Laundering was not an independent crime rather depended on another crime, known as the predicate offence or scheduled offence. The amendment seeks to treat money laundering as a stand-alone crime.
स्वतंत्रता के संरक्षक के रूप में शीर्ष न्यायालय
Context :
- भारत के सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने दिल्ली के पूर्व उपमुख्यमंत्री मनीष सिसोदिया को जमानत दे दी, जिसमें व्यक्तिगत स्वतंत्रता और त्वरित सुनवाई के अधिकार के महत्व पर जोर दिया गया।
- इस निर्णय ने भारत की आपराधिक न्याय प्रणाली के मुद्दों को उजागर किया, जिसमें लंबे समय तक पूर्व-परीक्षण हिरासत और पीएमएलए जैसे कठोर दंड कानूनों का दुरुपयोग शामिल है।
‘शीघ्र सुनवाई के अधिकार’ पर पिछले निर्णय:
- सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने कश्मीरा सिंह (1977), पी. चिदंबरम (2020) और सतेंद्र कुमार अंतिल (2022) सहित अपने पहले के निर्णयों का संदर्भ दिया, जो यह स्थापित करते हैं कि संविधान के अनुच्छेद 21 के तहत त्वरित सुनवाई का अधिकार मौलिक है।
- अर्नब मनोरंजन गोस्वामी बनाम महाराष्ट्र राज्य और अन्य (2020) में न्यायालय के निर्णय का हवाला दिया गया, जिसमें इस बात पर बल दिया गया कि स्वतंत्रता संवैधानिकता का एक मुख्य घटक है।
- हाल के परिदृश्य में, सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने मनीष सिसोदिया बनाम केंद्रीय जांच ब्यूरो में 30 अक्टूबर, 2023 को दिए गए अपने पहले के आदेश पर भरोसा किया, जिसमें साक्ष्य की बड़ी मात्रा (56,000 पृष्ठों के दस्तावेज और 456 गवाह) के बारे में चिंताओं को उजागर किया गया था, जो संभावित रूप से मुकदमे की कार्यवाही में महत्वपूर्ण देरी का कारण बन सकते हैं।
संवैधानिक जनादेश
- सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने फैसला सुनाया कि देरी के मामलों में जमानत के अधिकार को धारा 439 सीआरपीसी और धन शोधन निवारण अधिनियम (पीएमएलए) की धारा 45 में एकीकृत किया जाना चाहिए।
- कड़े दंड कानूनों के दुरुपयोग और पीएमएलए के दमनकारी आवेदन पर चिंताओं के कारण यह निर्णय महत्वपूर्ण है।
- न्यायालय ने पीएमएलए के तहत कम सजा दर पर प्रकाश डाला, पिछले दशक में 5,000 से अधिक मामलों में से केवल 40 में सजा हुई।
आपराधिक न्याय प्रणाली में चुनौतियाँ
- आपराधिक न्याय प्रणाली देरी के कारण महत्वपूर्ण चुनौतियों का सामना करती है, जहाँ प्रक्रियात्मक जटिलताएँ दंडात्मक हो जाती हैं।
- कानूनी तकनीकीताओं द्वारा न्याय में बाधा उत्पन्न करने जैसे मुद्दों को सुशील कुमार सेन (1975) और रानी कुसुम (2005) जैसे मामलों में पहचाना गया है।
उठाई गई चिंताएँ
- अपनी खूबियों के बावजूद, यह निर्णय अभियोजन पक्ष के आश्वासनों के आधार पर लंबे समय तक हिरासत में रखने के बारे में चिंताएँ उठाता है।
- मुकदमे की समयसीमा और आरोप-पत्र दाखिल करने के लिए अभियोजक के बयानों पर निर्भर रहना प्राकृतिक न्याय और निष्पक्ष सुनवाई प्रक्रियाओं के सिद्धांतों का खंडन कर सकता है।
नागरिक स्वतंत्रता की गारंटी
- संवैधानिक आधार: सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने इस बात पर जोर दिया कि व्यक्तिगत स्वतंत्रता अभियोजन पक्ष के विवेक पर निर्भर नहीं होनी चाहिए।
- मेनका गांधी बनाम भारत संघ (1978) जैसे निर्णयों में, न्यायालय ने उचित प्रक्रिया की समझ का विस्तार किया, इस बात पर जोर देते हुए कि स्वतंत्रता के किसी भी वंचन में निष्पक्ष, न्यायसंगत और उचित प्रक्रियाओं का पालन किया जाना चाहिए।
- न्यायिक जिम्मेदारी: इस निर्णय का उद्देश्य धन शोधन निवारण अधिनियम (पीएमएलए) जैसे कड़े कानूनों के दुरुपयोग को रोकना और व्यक्तियों की गरिमा और अधिकारों को बनाए रखना है।
- राणा अय्यूब बनाम प्रवर्तन निदेशालय (2023) में, सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने पीएमएलए प्रवर्तन में न्यायिक निगरानी पर जोर दिया, जबकि यह सुनिश्चित किया कि परीक्षण अंतर्निहित अपराधों का पालन करें।
- न्यायपालिका पर जनता का भरोसा: वर्तमान में, सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने समय पर परीक्षण के सिद्धांत की अनदेखी करते हुए कुछ न्यायाधीशों की अनावश्यक रूप से जमानत देने से इनकार करने की दोषपूर्ण प्रवृत्ति की ओर इशारा किया। इससे न्यायपालिका में जनता का भरोसा खत्म हो सकता है।
- व्यवस्थागत बदलाव का आह्वान: यह निर्णय व्यक्तिगत प्रतिशोध पर न्याय और व्यक्तिगत अधिकारों को प्राथमिकता देने के लिए राजनीतिक और कानूनी प्रणालियों के पुनर्मूल्यांकन का आग्रह करता है।
- महाराष्ट्र राज्य बनाम रानी कुसुम (2005) न्यायिक प्रक्रिया में देरी को दूर करने के लिए सुधारों की आवश्यकता को रेखांकित करता है।
- जमानत नियम है, अपवाद नहीं: मनीष सिसोदिया को जमानत देने के सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के फैसले ने इस सिद्धांत को पुष्ट किया है कि जमानत नियम है, अपवाद नहीं।
स्वतंत्रता बहाल करना
- श्री सिसोदिया को जमानत देकर, सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने पिछली अस्पष्टताओं को संबोधित किया है और जमानत और व्यक्तिगत स्वतंत्रता के सिद्धांतों को बरकरार रखा है।
- इस निर्णय का उद्देश्य विचाराधीन कैदियों को हिरासत में सड़ने से रोकना है, जिससे उनकी स्वतंत्रता, प्रतिष्ठा, गोपनीयता और जवाबदेही के बिना सम्मान की हानि हो।
- राष्ट्र को अपना राजनीतिक ध्यान व्यक्तिगत दुश्मनी से हटाकर सभी के लिए न्याय और सम्मान की ओर लगाना चाहिए, ताकि लोकतंत्र को पुनर्जीवित किया जा सके।
निष्कर्ष
- लेख का समापन एक व्यक्तिगत विचार के साथ होता है कि न्यायालय का निर्णय यह सुनिश्चित करने की दिशा में एक कदम है कि विचाराधीन कैदियों को अनुचित रूप से हिरासत में न रखा जाए।
- यह न्याय और सम्मान की ओर राजनीति में राष्ट्रीय बदलाव का आह्वान करता है, नागरिक स्वतंत्रता की रक्षा में न्यायपालिका की भूमिका पर जोर देता है।
मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग क्या है?
के बारे में:
-
- मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग एक जटिल प्रक्रिया है जिसका उपयोग व्यक्तियों और संगठनों द्वारा अवैध रूप से प्राप्त धन की उत्पत्ति को छिपाने के लिए किया जाता है। इसमें कई लेन-देन के माध्यम से अवैध धन को वैध दिखाना शामिल है।
- मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग के चरण:
- प्लेसमेंट: प्रारंभिक चरण जहां अवैध धन को वित्तीय प्रणाली में पेश किया जाता है। इसमें बैंक खातों में जमा, मुद्रा विनिमय या मूल्यवान संपत्तियों की खरीद शामिल हो सकती है।
- लेयरिंग: जटिल वित्तीय लेनदेन की एक श्रृंखला के माध्यम से अवैध धन को उनके स्रोत से अलग करने की प्रक्रिया। इसमें अक्सर खातों के बीच या सीमाओं के पार धन को स्थानांतरित करना शामिल होता है ताकि उनके मूल को छिपाया जा सके।
- एकीकरण: अंतिम चरण जहां लॉन्डर किए गए धन को वैध धन के रूप में अर्थव्यवस्था में फिर से पेश किया जाता है। इसमें व्यवसायों में निवेश करना, अचल संपत्ति खरीदना या धन को वैध बनाने के अन्य तरीके शामिल हो सकते हैं।
- मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग के तरीके:
- स्ट्रक्चरिंग (स्मर्फिंग): बड़ी मात्रा में नकदी को छोटी, कम स्पष्ट मात्रा में तोड़ना जिन्हें फिर बैंक खातों में जमा किया जाता है।
- व्यापार आधारित लॉन्ड्रिंग: सीमा पार मूल्य स्थानांतरित करने और अवैध धन की उत्पत्ति को छिपाने के लिए व्यापार लेनदेन का उपयोग करना।
- शेल कंपनियाँ: वैध दिखने वाले लेनदेन के माध्यम से अवैध धन को प्रवाहित करने के लिए बिना किसी वैध व्यावसायिक गतिविधि वाली कंपनियाँ बनाना।
- रियल एस्टेट: अवैध धन से रियल एस्टेट खरीदना और फिर उसे बेचकर मूल्य को वैध संपत्ति में बदलना।
PMLA, 2002 क्या है?
- के बारे में:
- मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग रोकथाम अधिनियम, 2002 (PMLA) भारत की संसद का एक अधिनियम है जिसे मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग को रोकने और मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग से प्राप्त संपत्ति को जब्त करने के लिए अधिनियमित किया गया है।
- इसका उद्देश्य नशीली दवाओं की तस्करी, तस्करी और आतंकवाद के वित्तपोषण जैसी अवैध गतिविधियों से संबंधित मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग से निपटना है।
PMLA के मुख्य प्रावधान:
-
- अपराध और दंड: PMLA मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग अपराधों को परिभाषित करता है और ऐसी गतिविधियों के लिए दंड लगाता है। इसमें अपराधियों के लिए कठोर कारावास और जुर्माना शामिल है।
- संपत्ति की कुर्की और जब्ती: अधिनियम मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग में शामिल संपत्ति की कुर्की और जब्ती की अनुमति देता है। यह इन कार्यवाहियों की देखरेख के लिए एक न्यायाधिकरण की स्थापना का प्रावधान करता है।
- रिपोर्टिंग आवश्यकताएँ: PMLA कुछ संस्थाओं, जैसे बैंकों और वित्तीय संस्थानों को लेनदेन के रिकॉर्ड बनाए रखने और वित्तीय खुफिया इकाई (FIU) को संदिग्ध लेनदेन की रिपोर्ट करने का आदेश देता है।
- नामित प्राधिकरण और अपीलीय न्यायाधिकरण: अधिनियम मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग अपराधों की जांच और अभियोजन में सहायता के लिए एक नामित प्राधिकरण की स्थापना करता है।
- यह न्यायाधिकरण के आदेशों के खिलाफ अपील सुनने के लिए एक अपीलीय न्यायाधिकरण की स्थापना का भी प्रावधान करता है।
- PMLA के उद्देश्य:
- रोकथाम: कड़े उपायों को लागू करके और वित्तीय लेनदेन की निगरानी करके मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग को रोकना।
- पता लगाना: उचित प्रवर्तन और नियामक तंत्रों के माध्यम से मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग के मामलों का पता लगाना और उनकी जाँच करना।
- जब्ती: अपराधियों को रोकने और अवैध वित्तीय प्रवाह को बाधित करने के लिए मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग गतिविधियों से प्राप्त संपत्तियों को जब्त करना।
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग: मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग और आतंकवादी वित्तपोषण गतिविधियों से निपटने में अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग को सुविधाजनक बनाना।
पीएमएलए, 2002 में हाल ही में किए गए संशोधन:
-
- अपराध की आय की स्थिति के बारे में स्पष्टीकरण: अपराध की आय में न केवल अनुसूचित अपराध से प्राप्त संपत्ति शामिल है, बल्कि अनुसूचित अपराध से संबंधित या समान किसी भी आपराधिक गतिविधि में लिप्त होने से प्राप्त या प्राप्त की गई कोई अन्य संपत्ति भी शामिल होगी।
- मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग को फिर से परिभाषित किया गया: मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग एक स्वतंत्र अपराध नहीं था, बल्कि यह किसी अन्य अपराध पर निर्भर था, जिसे प्रिडिकेट अपराध या अनुसूचित अपराध के रूप में जाना जाता था। संशोधन मनी लॉन्ड्रिंग को एक स्वतंत्र अपराध के रूप में मानने का प्रयास करता है।
United Nations (UN) / संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन)
International Organizations
The United Nations (UN) is an international organization founded in 1945. It is currently made up of 193 Member States.

United Nations (UN) Specialized Agencies:
- Articles 57 and 63 of the United Nations (UN) Charter provides provision of creating specialized agencies.
UNCTAD
- UNCTAD supports developing countries to access the benefits of a globalized economy more fairly and effectively.
- It helps to use trade, investment, finance, and technology as vehicles for inclusive and sustainable development.
UNODC
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is a global leader in the fight against illicit drugs and international crime.
- It was established in 1997through a merger between the United Nations Drug Control Programme and the Centre for International Crime Prevention.
- UNODC is mandated to assist Member States in their struggle against illicit drugs, crime and terrorism.
UNHCR
- The office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) was created in 1950, during the aftermath of the Second World War, to help millions of Europeans who had fled or lost their homes.
- In 1954, UNHCR won the Nobel Peace Prize for its ground-breaking work in Europe.
- The start of the 21st century has seen UNHCR help with major refugee crises in Africa, the Middle East and Asia.
- It also uses its expertise to help many internally displaced by conflict and expanded its role in helping stateless people.
ESCAP
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) is the main economic and social development centre of the UN in the region, headquartered in Bangkok (Thailand) in 1947.
- It responds to the development needs and priorities of the region through its convening authority, economic and social analysis, normative standard-setting and technical assistance.
संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन)
अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठन
संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन) एक अंतरराष्ट्रीय संगठन है जिसकी स्थापना 1945 में हुई थी। वर्तमान में इसके 193 सदस्य देश हैं।
संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन) विशेष एजेंसियां:
- संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन) चार्टर के अनुच्छेद 57 और 63 में विशेष एजेंसियों के निर्माण का प्रावधान है।
UNCTAD
- यूएनसीटीएडी विकासशील देशों को वैश्वीकृत अर्थव्यवस्था के लाभों को अधिक निष्पक्ष और प्रभावी ढंग से प्राप्त करने में सहायता करता है।
- यह समावेशी और सतत विकास के लिए व्यापार, निवेश, वित्त और प्रौद्योगिकी का उपयोग करने में मदद करता है।
UNODC
- संयुक्त राष्ट्र कार्यालय ड्रग्स और अपराध (यूएनओडीसी) अवैध ड्रग्स और अंतरराष्ट्रीय अपराध के खिलाफ लड़ाई में एक वैश्विक नेता है।
- इसकी स्थापना 1997 में संयुक्त राष्ट्र ड्रग नियंत्रण कार्यक्रम और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय अपराध रोकथाम केंद्र के बीच विलय के माध्यम से की गई थी।
- यूएनओडीसी को अवैध ड्रग्स, अपराध और आतंकवाद के खिलाफ उनके संघर्ष में सदस्य राज्यों की सहायता करने का अधिकार है।
UNHCR
- संयुक्त राष्ट्र शरणार्थी उच्चायुक्त (यूएनएचसीआर) का कार्यालय 1950 में द्वितीय विश्व युद्ध के बाद, लाखों यूरोपीय लोगों की मदद करने के लिए बनाया गया था, जो भाग गए थे या अपना घर खो चुके थे।
- 1954 में, UNHCR ने यूरोप में अपने अभूतपूर्व कार्य के लिए नोबेल शांति पुरस्कार जीता।
- 21वीं सदी की शुरुआत में UNHCR ने अफ्रीका, मध्य पूर्व और एशिया में प्रमुख शरणार्थी संकटों में मदद की है।
- यह संघर्ष के कारण आंतरिक रूप से विस्थापित कई लोगों की मदद करने के लिए अपनी विशेषज्ञता का उपयोग करता है और राज्यविहीन लोगों की मदद करने में अपनी भूमिका का विस्तार करता है।
ESCAP
- एशिया और प्रशांत के लिए संयुक्त राष्ट्र आर्थिक और सामाजिक आयोग (ESCAP) इस क्षेत्र में संयुक्त राष्ट्र का मुख्य आर्थिक और सामाजिक विकास केंद्र है, जिसका मुख्यालय 1947 में बैंकॉक (थाईलैंड) में है।
- यह अपने संयोजक प्राधिकरण, आर्थिक और सामाजिक विश्लेषण, मानक मानक-निर्धारण और तकनीकी सहायता के माध्यम से क्षेत्र की विकास आवश्यकताओं और प्राथमिकताओं पर प्रतिक्रिया करता है।