CURRENT AFFAIRS – 04/12/2023
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 04/12/2023
- A.P. braces for heavy rainfall as Michaung intensifies
- Highest cases of sexual violence make Delhi most unsafe for women
- Re-criminalising adultery as a gender-neutral offence
- Why is Meta suing the U.S. Federal Trade Commission?
- The transformative benefits of population-level genome sequencing
- India, disability inclusion and the power of ‘by’
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 04/12/2023
A.P. braces for heavy rainfall as Michaung intensifies
(General Studies- Paper III)
Source : TH
A deep depression over the Bay of Bengal is intensifying and expected to evolve into Cyclone Michaung by December 3 morning.
- The India Meteorological Department predicts winds with a maximum sustained speed of 80 to 90 kmph, gusting up to 100 kmph.
Key Highlights
- Coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu are bracing for heavy rainfall.
- As of December, the deep depression is located about 420 km southeast of Chennai.
- The cyclonic storm is expected to reach the waters off southern Andhra Pradesh and north Tamil Nadu by December 4 morning.
- It will then move parallel to the coast, making landfall between Nellore and Machilipatnam on December 5.
- Cyclone Michaung is the fourth tropical cyclone of the year over the Bay of Bengal.
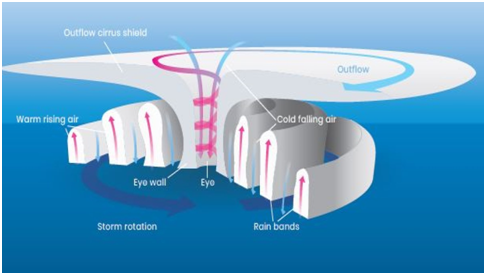
Understanding Tropical Cyclone
- Tropical cyclones, also known as hurricanes or typhoons in different regions, are powerful storm systems characterized by low-pressure centers, strong winds, and heavy rainfall.
- These storms typically form over warm ocean waters in tropical and subtropical regions.
- The process of tropical cyclone formation involves several key factors and stages:
- Warm Ocean Water:
- Tropical cyclones require warm ocean water as their primary energy source.
- Water temperatures need to be at least 26.5 degrees Celsius (80 degrees Fahrenheit) or higher to a significant depth (usually at least 50 meters or 164 feet).
- Warm water provides the necessary heat and moisture to fuel the storm.
- Atmospheric Instability:
- An unstable atmosphere is crucial for the development of a tropical cyclone.
- Warm air at the surface rises, creating a low-pressure area.
- As the air rises, it cools, and water vapour condenses to form clouds.
- The release of latent heat during condensation further warms the surrounding air, promoting additional upward motion.
- Coriolis Effect:
- The Coriolis effect, caused by the Earth’s rotation, is essential for cyclone formation.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, tropical cyclones spin counterclockwise, while in the Southern Hemisphere, they spin clockwise.
- Near the equator, the Coriolis effect is weak, so tropical cyclones rarely form within about 5 degrees of the equator.
- Disturbance or Initial Disturbance:
- A disturbance, often in the form of a cluster of thunderstorms, serves as the initial trigger for cyclone formation.
- This disturbance can be influenced by factors such as atmospheric waves, monsoons, or the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ).
- Low-Pressure Center:
- The disturbance evolves into a more organized system with a well-defined low-pressure center.
- The converging winds at the surface help to reinforce the low-pressure system, creating a feedback loop that enhances its development.
- Wind Circulation:
- As the system intensifies, the Coriolis effect causes the winds to circulate around the low-pressure center.
- A rotating system of winds develops, and the storm is classified as a tropical depression.
- If the tropical depression sustains its organization and the winds continue to strengthen, it can evolve into a tropical storm.
- The storm is then given a name.
- Hurricane Formation:
- If the tropical storm’s wind speeds reach a certain threshold (usually 74 mph or 119 km/h), it is upgraded to a hurricane (or typhoon, depending on the region).
- Hurricanes are categorized on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale based on their wind speed.
- Warm Ocean Water:

Highest cases of sexual violence make Delhi most unsafe for women
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : TH
Delhi has been identified as the most unsafe metropolitan city for women in India, as per the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) annual report for 2022.
- The city recorded an average of three rape cases daily, totaling 14,158 incidents of crime against women in the year.
- This marks the third consecutive year that Delhi has reported the highest number of crimes against women among 19 metropolitan cities.
Key Highlights
- Specific Crimes Against Women:
- Among the reported crimes, there were 1,204 cases of rape, 3,909 incidents of kidnapping or abduction of women, and 129 cases related to dowry deaths.
- Instances of cruelty by husbands or relatives accounted for 4,847 cases.
- A senior police officer acknowledges that in many cases of rape and assault, the victim and the accused are acquainted, making prevention challenging.
- Efforts are made to raise awareness through drives on safe and unsafe touch, especially in schools and colleges.
- The police conduct self-defense training camps for women and aim to convert complaints into FIRs.
- Police Efforts and Awareness:
- The police officer claims that the increase in reported cases indicates successful efforts to encourage more women to register complaints, reducing the number of unreported cases.
- The police have been working on converting complaints into First Information Reports (FIRs) and assert that the rise in reported cases reflects their efforts to combat crime.
- Overall Crime Trends:
- The report highlights an uptick in overall crime, including an increase in incidents against senior citizens (aged 60 or above) and a doubling of cybercrime cases.
- Delhi reported 501 cases of murder, 106 cases of human trafficking, and 7,400 incidents of crime against children, including 22 murders.
- Notably, the report reveals an alarming rise in child trafficking cases, with 492 minor boys trafficked compared to 113 girls in 2022. All trafficked individuals were reportedly recovered.

Re-criminalising adultery as a gender-neutral offence
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : TH
The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Home Affairs, examining three new criminal law Bills intended to replace the Indian Penal Code (IPC), Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), and the Indian Evidence Act, recommended the criminalization of adultery.
Key Highlights
- Recommendation for Gender-Neutral Approach:
- The Committee suggested criminalizing adultery but on gender-neutral lines, marking a departure from the previous discriminatory provision.
- This recommendation comes almost five years after the Supreme Court unanimously decriminalized adultery in 2018, citing reasons of discrimination.
- Errors and Dissent from Opposition MPs:
- The Bills, introduced in the Lok Sabha in August and referred to the Parliamentary Standing Committee, faced scrutiny and recommendations for over 50 changes.
- Opposition MPs, in their dissent notes, pointed out errors, questioned the lack of diversity in expert opinions, and expressed concerns about the rushed introduction of laws that are largely a replication of existing ones.
- Committee’s Rationale for Criminalization:
- The Committee reasoned that criminalizing adultery in a gender-neutral manner is crucial to safeguard the sanctity of the institution of marriage.
- It stated that the institution of marriage is considered sacred in Indian society, and there is a need to protect its sanctity.
- The Committee highlighted the need for gender neutrality in addressing the deficiencies of the previously revoked Section 497 of the IPC, which penalized only married men and reduced married women to the status of their husbands’ property.
- Opposition’s Perspective on Adultery:
- Opposition MPs, notably P. Chidambaram, stressed in dissent notes that adultery should not be considered a crime.
- They argued that interference by the state in the private lives of consenting adults should be avoided, emphasizing that marriage concerns only two individuals, and the state has no business entering their lives and punishing alleged wrongdoers.
- Adultery Laws in India:
- The Supreme Court in 2018 declared adultery not to be a crime but a civil wrong, striking down Section 497 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC).
- Recent recommendations suggest reintroducing adultery as a criminal offense but in a gender-neutral form.
- Legal experts argue that criminal law’s purpose is to prevent harm to the public, and personal choices, including adultery, should be protected.
- Global Comparisons:
- Adultery is considered a tort or civil wrong in some countries, allowing individuals to sue for damages, providing an alternative approach.
- Critics highlight that the law’s origin reflects Victorian morality and underscores the overemphasis on marriage as an institution.
- Gender Neutrality Concerns:
- Making adultery laws gender-neutral addresses the issue of treating women as property but does not eliminate the fundamental problem of criminalizing actions based on the institution of marriage.
- Impact on LGBTQ+ Community:
- The application of gender-neutral provisions would depend on recognizing relationships as marriages, potentially affecting members of the LGBTQ+ community.
- Legislative Overruling of Judicial Pronouncements:
- While Parliament can overrule judicial rulings, such legislative actions are considered valid only if they address the legal basis of the earlier judgment.
- The legal test for validating legislation involves removing the defect pointed out in the judgment, ensuring that the altered legal position existed when the court rendered its decision.
- Recent court decisions emphasize that legislative validation should cure defects in earlier legislation and not merely seek to validate acts without addressing the underlying issues.
About Parliamentary Standing Committee on Home Affairs (SCOHA)
- The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Home Affairs (SCOHA) is a crucial department related standing committee (DRSC) within the Parliament of India.
- It plays a vital role in overseeing and evaluating legislative matters, domestic policy, internal security, and decision-making processes associated with the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The committee consists of 31 members in total, with 21 members representing the Lok Sabha and 10 members from the Rajya Sabha.
- Members are nominated by the Speaker of the Lok Sabha and the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, ensuring representation from both houses.
- The committee is reconstituted as needed to ensure continued effectiveness in its oversight role.
Why is Meta suing the U.S. Federal Trade Commission?
(General Studies- Paper III)
Source : TH
In a surprising turn of events, Meta, the parent company of Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Threads, filed a lawsuit against the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) on November 29.
- The legal action is an attempt by Meta to prevent the reopening of a prior privacy settlement that mandated a $5 billion payment by the social media giant.
Key Highlights
- Background of the Case:
- In 2019, Meta (formerly Facebook) agreed to a privacy settlement with the FTC, resulting in a $5 billion penalty—the largest ever imposed for privacy violations.
- The FTC, in May, proposed modifications to the 2019 agreement, citing Meta’s alleged non-compliance with the previous terms.
- The regulator accused Meta of misleading parents about the Messenger Kids app and misrepresenting app developers’ access to private user data.
- FTC’s Proposed Changes:
- Meta would be prohibited from profiting from data collected from users below 18.
- Restrictions on Meta’s use of data from virtual reality products.
- Limits on facial recognition technology use and enhanced user protections.
- Restrictions on Meta’s launch of new products and features.
- Meta’s Response and Lawsuit:
- Meta spokesperson Andy Stone labeled the FTC’s actions as a “political stunt” and accused the regulator of hindering discussions on the agreement.
- Stone claimed the FTC was singling out Meta while allowing Chinese companies like TikTok to operate without constraints on U.S. soil.
- In its November complaint against the FTC, Meta argued that ceasing the collection of children’s data, as proposed by the FTC, would severely impede its ability to market new products and services to a crucial user demographic.
- “Meta alleges that the FTC’s actions represent an “obvious power grab” and could cause “immediate and irreparable” harm to the company.
- Meta contends that restrictions on the collection and use of data from “Youth Users” would significantly hamper its marketing efforts to this key demographic.
- Impact of FTC’s Proposed Changes on Meta’s Business:
- Meta reported robust Q3 revenue of $34.15 billion, a 23% YoY increase.
- However, the company expressed concerns in its report about potential impacts on future financial results due to increasing legal and regulatory challenges.
- Meta highlighted the FTC’s efforts to modify the existing consent order and impose additional restrictions as a noteworthy challenge.
- The company contested the matter, emphasizing potential adverse effects on its business.
- Meta’s Claim Against FTC’s Authority:
- Meta claimed that the FTC’s proposed changes to the 2020 agreement violated due process and accused the regulator of playing an “unconstitutional dual role.”
- Meta clarified its intention to challenge the FTC’s structurally unconstitutional authority, particularly emphasizing the regulator’s dual role as a prosecutor and judge.
- Legal Position and Constitutional Challenge:
- Meta’s decision to sue the FTC is unprecedented and marks an aggressive stance.
- The legal action followed a federal judge’s approval of the FTC’s proceedings against Meta.
- Meta’s lawsuit focuses on questioning the constitutionality of the FTC’s structural characteristics, particularly its dual role.
- The company seeks to address concerns about due process and its right to a jury trial.
- If Meta succeeds, it could set a precedent for other companies facing regulatory scrutiny to challenge the FTC’s impartiality and demand jury trials.
- This shift might pose challenges for swift enforcement actions by regulators like the SEC against major tech firms in the future.
- Regulatory Landscape and Potential Implications:
- Meta’s legal challenge could have broader implications for the regulatory landscape, impacting not only the FTC but also other regulatory bodies dealing with Big Tech companies.
- A successful challenge may obstruct regulators, including the SEC, from conducting rapid enforcement actions against major tech corporations in the future.
The transformative benefits of population-level genome sequencing
(General Studies- Paper III)
Source : TH
Over the last decade, genomics has experienced a revolutionary shift driven by advancements in sequencing technologies.
- These technologies have substantially increased throughput and reduced the cost of whole-genome sequencing.
Key Highlights
- The transformative impact of these technologies is evident in the emergence of population-scale genome-sequencing programs.
- These initiatives involve deciphering the complete genetic makeup of large populations, providing unprecedented insights into human diversity.
- UK’s Milestone: Half a Million Whole-Genome Sequences:
- The UK announced the completion of half a million whole-genome sequences, constituting nearly 0.7% of its population.
- This milestone represents a significant achievement in the field of genomics.
- Population-scale genomic datasets hold far-reaching implications for both immediate and long-term advancements in the biological sciences.
- The wealth of genetic information contributes to a deeper understanding of human genetics and its impact on health.
- Early Initiatives: The deCODE Genomics Project:
- The deCODE genomics initiative, launched in 1996 in Iceland, marked an early effort in large-scale population genetic studies.
- Over a decade, a substantial portion of the Icelandic population participated in genetic studies, laying the groundwork for subsequent programs.
- deCODE significantly improved the understanding of disease genetics and demonstrated the utility of large-scale genomic data in risk assessment.
- The project also played a crucial role in developing methods, infrastructure, and standards for handling genomic data.
- Global Proliferation of Population-Scale Genome Initiatives:
- deCODE’s success, coupled with the increasing availability of sequencing technologies, led to the proliferation of population-scale genome initiatives worldwide.
- Numerous pilot programs were initiated over the last decade.
- While early projects worked with hundreds to thousands of genomes, recent endeavors have leaped to sequencing hundreds of thousands (lakhs) of genomes.
- This signifies a significant expansion in the scale and scope of genomic initiatives.
- Bioethics and Integration with Medical Records:
- Large-scale genomic initiatives, including deCODE, spurred discussions on bioethics, highlighting the ethical considerations associated with handling vast amounts of genetic data.
- The projects laid the groundwork for integrating medical records with individuals’ genealogies.
- This integration has facilitated the development of new drugs and therapeutics based on genetic insights.
- Future Implications and Advancements:
- Population-scale genomic data holds promise for advancing precision medicine and public health.
- The wealth of genetic information can lead to more personalized and effective healthcare interventions.
- The completion of half a million whole-genome sequences in the UK reflects ongoing advancements in genomics.
- Continuous progress in sequencing technologies is expected to further enhance our understanding of human genetics and its applications in various fields.
- Global Proliferation of Population-Scale Genome Initiatives:
- The UK’s ‘100K Genome’ project, one of the first population-scale efforts, aimed to integrate genomics into routine healthcare.
- Presently, over a dozen countries, including the U.S., have genome programs sequencing a lakh genomes or more.
- Initiatives by pharmaceutical giants like Regeneron Genetics Center, AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Roche, and Meharry Medical College plan to sequence over five lakh individuals of African ancestry through the Diversity Human Genome Initiative.
- Global Initiatives in Progress:
- The AllofUS program in the U.S., funded by the National Institutes of Health, targets genetic information collection from a million individuals.
- Launched recently, this initiative aims to sequence over a million genomes in the European Union.
- A large-scale genome program focusing on sequencing three million genomes from African populations is underway.
- The Emirati genome program plans to sequence over a million samples, with 400,000 samples already completed.
- Diverse Objectives of Population-Scale Genome Efforts:
- Many programs leverage unique population compositions to understand disease prevalence and identify biomarkers for diseases.
- This informs the discovery of novel therapeutic targets.
- Some efforts aim to build scalable public health initiatives where genomic data plays a crucial role in decision-making and medical care.
- The UK’s ‘100K Genome’ initiative demonstrated that 18.5% of the program’s findings were actionable, providing direct healthcare benefits to participants.
- Cost Reduction and Increasing Accessibility
- The cost of whole-genome sequencing is decreasing, making it more accessible.
- The falling costs, coupled with growing evidence of data usefulness, suggest a significant number of people globally may have their whole genome sequenced in the coming decade.
- Whole-genome sequencing information derived from routine diagnostic workups and newborn screening for diseases is becoming more feasible.
- Ethical Challenges and Regulatory Frameworks:
- Population-scale genome programs pose new ethical challenges, including concerns related to the ethics of genome access and discoveries based on genomic data.
- Ensuring equitable representation and access to the benefits of genomic discoveries is a significant concern, addressing issues like over-representation of certain ethnic groups in datasets.
- Genomic Initiatives in Asia, With a Focus on India:
- Led by multiple partners across Asia, the GenomeAsia project aims to sequence a lakh whole genomes from diverse populations in the continent.
- An initial pilot dataset included genomes of 1,739 individuals from 219 population groups in 64 countries.
- IndiGen Pilot Programme:
- India’s pilot program, IndiGen, offered insights into over a thousand genomes from individuals in cosmopolitan areas, providing information on treatable genetic diseases, drug efficacy, toxicity, and rare disorders.
- A larger initiative, GenomeIndia, plans to sequence 10,000 whole genomes from diverse population groups.
- Long-Term Impact and Future Prospects:
- Population-scale genomics has implications beyond individual health, contributing to our understanding of human evolution, migration patterns, and adaptation to diverse environments.
- Population-scale genomics significantly contributes to advancing knowledge in human biology.
- Positioned at the forefront of a genomic revolution, population-scale genomics is set to revolutionize healthcare, personalized medicine, and our understanding of medical and biological landscapes.
- The day when a billion genomes are sequenced in a single project is approaching rapidly.
- The time is near for individuals to acquire the right to access and understand their own genome sequences, reflecting a shift toward personalized genomics.
What is ‘genome sequencing’?
- Genome sequencing is a scientific process that involves determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome.
- The genome is the entire set of genetic material, including genes and non-coding sequences, that makes up an organism’s hereditary information.
- Key Concepts:
- DNA and Genetic Code:
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is a molecule that contains the instructions an organism needs to develop, live, and reproduce.
- The genetic code within DNA is composed of nucleotide sequences represented by the letters A (adenine), T (thymine), C (cytosine), and G (guanine).
- Genome Composition:
- The genome of an organism is the complete set of its DNA, including all of its genes.
- Genes are specific sequences of DNA that code for proteins or functional RNA molecules, playing a crucial role in the organism’s structure and function.
- Genome Sequencing Process:
- The process begins with the collection of DNA from the organism.
- This could be a small sample of blood, saliva, or tissues.
- The DNA is then extracted from the sample using laboratory techniques.
- The extracted DNA is broken into smaller fragments, making it more manageable for sequencing.
- Various sequencing technologies, such as Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), are employed to determine the order of nucleotides in these DNA fragments.
- The sequencing machines generate vast amounts of data, and bioinformatics tools are used to analyze and assemble the fragments into a complete genome sequence.
- DNA and Genetic Code:

India, disability inclusion and the power of ‘by’
(General Studies- Paper II)
Source : TH
Disability, encompassing social, economic, and gender vulnerabilities, demands nuanced considerations for equitable action.
- With 1.3 billion people globally living with disabilities, predominantly in developing and rural areas, existing systems often exclude them, leading to increased instances of poverty, limited educational access, and social and economic discrimination.
Key Highlights
- Approximately 1.3 billion people globally live with disabilities, with 80% in developing countries and 70% residing in rural areas.
- Current societal structures are designed without considering the needs of people with disabilities, resulting in exclusion and discrimination across various domains.
- Importance of Inclusion:
- Including people with disabilities in the workforce can potentially boost global GDP by 3% to 7%, according to the International Labour Organization (ILO).
- Advocacy for the right to equal treatment and opportunities at work, emphasizing abilities rather than focusing on disabilities.
- The importance of disability inclusion aligns with the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, emphasizing changing societal attitudes and perceptions to foster inclusion.
- Key Considerations:
- “For” vs. “By” Approach: Highlighting the difference between actions done “for” persons with disabilities and actions done “by” them, emphasizing the importance of including them in the decision-making process.
- Rural Challenges for Persons with Disabilities in India
- In India, addressing the challenges faced by persons with disabilities in rural areas is crucial, considering the heightened difficulties they encounter compared to their urban counterparts.
- Government schemes and the UDID card aim to support them, but awareness and last-mile connectivity are essential.
- Rural regions face issues of limited education and employment opportunities, exclusion from developmental schemes, and higher vulnerability to climate-related calamities.
- Capacity-building of community leaders is pivotal for advocating government benefits at the grassroots level.
- Persons with disabilities in rural areas face greater challenges, including limited access to education and employment opportunities.
- Persons with disabilities in rural areas encounter restricted access to education, employment, and developmental schemes.
- They are often viewed as objects of charity rather than individuals with agency capable of participating in decision-making processes.
- Rural areas, dependent on agriculture, are at heightened risk of climate calamities, affecting water, food, and overall livelihoods.
- Role of Private Sector and SPARK Project:
- The private sector plays a crucial role in promoting the employment of persons with disabilities, requiring a robust legal framework and building companies’ confidence in hiring and retaining such workers.
- SPARK Project:
- The SPARK project, initiated by the ILO and IFAD, empowers persons with disabilities in rural areas.
- Disability Inclusion Facilitators (DIFs) are trained to engage with communities, raise awareness, and facilitate the inclusion of women with disabilities in self-help groups for economic development.
- Poverty and the Challenges:
- Evidence suggests a bi-directional link between poverty, nutrition, hunger, and disability.
- Inclusive opportunities and employment in rural areas are essential to address these challenges.
- Given the historical marginalization of persons with disabilities and challenges in achieving Sustainable Development Goals, a fundamental shift in commitment, solidarity, financing, and action is critical.
- It is imperative to prioritize the voices and needs of persons with disabilities at the center of the global development agenda for true social justice.
What is Unique Disability ID (UDID) card?
- The Unique Disability ID (UDID) card is an initiative by the Government of India aimed at providing a unique identification to persons with disabilities.
- Launched as part of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act (2016), the UDID card serves as a tool to streamline and simplify the process of availing various benefits and schemes meant for persons with disabilities.
- Key Features of the UDID Card:
- Each person with a disability is assigned a unique ID that helps in easy identification and verification.
- The card contains comprehensive information about the individual, including personal details, type of disability, and other relevant data.
- The UDID card facilitates access to various government services, benefits, and schemes meant for persons with disabilities.
- The card follows a standardized format, making it recognizable and uniform across different regions and authorities.
- Individuals can access and download their UDID cards online, making it convenient for them to have a digital or physical copy as needed.
- Purpose of the UDID Card:
- Benefit Disbursement: The card simplifies the process of disbursing benefits and assistance to persons with disabilities by ensuring accurate identification.
- Inclusive Policies: It supports the implementation of inclusive policies and initiatives by the government.
- Prevention of Fraud: The unique ID helps prevent fraud and ensures that benefits reach the intended beneficiaries.