CURRENT AFFAIRS – 03/08/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 03/08/2024
- 72% of personal income-tax payers opted for new tax regime in 2023-24/ 2023-24 में 72% व्यक्तिगत आयकरदाताओं ने नई कर व्यवस्था को चुना
- Centre reissues draft notification on ecosensitive areas in Western Ghats / केंद्र ने पश्चिमी घाट में पारिस्थितिकी संवेदनशील क्षेत्रों पर मसौदा अधिसूचना फिर से जारी की
- India selects 2 crew members for Axiom-4 mission to ISS / भारत ने आईएसएस के लिए एक्सिओम-4 मिशन के लिए 2 चालक दल के सदस्यों का चयन किया
- Axis of resistance/ प्रतिरोध की धुरी
- Mozambique / मोजाम्बिक
- An unstated shift in Modi’s economic direction / मोदी की आर्थिक दिशा में एक अघोषित बदलाव
- World Bank Group / विश्व बैंक समूह
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 03/08/2024
72% of personal income-tax payers opted for new tax regime in 2023-24/ 2023-24 में 72% व्यक्तिगत आयकरदाताओं ने नई कर व्यवस्था को चुना
Syllabus : GS 3 : Indian Economy
Source : The Hindu
In the financial year 2023-24, 72% of India’s income-tax payers chose the new tax regime, a rise attributed to recent enhancements in the 2023-24 Budget.
- Changes included reduced tax slabs, increased tax-free income limit, higher tax rebate, and a raised standard deduction, making the regime more attractive.
- By the July 31 deadline, income tax return filings rose 7.5% to a record 7.29 crore.
- Of the 7.28 crore returns filed for Assessment Year 2024-25, 5.27 crore were under the new regime, and 2.01 crore under the old regime.
- The new tax regime, introduced in 2020, became more attractive after changes in the 2023-24 Budget.
Old Tax Regime Vs. New Tax Regime
- Old Tax Regime Exemptions & Deductions:
- Allows over 70 exemptions and deductions, including HRA, LTA, and deductions under Section 80C (up to ₹1.5 lakh).
- Tax Slabs:₹0 – ₹2.5 lakh: Nil₹2.5 lakh – ₹5 lakh: 5%₹5 lakh – ₹10 lakh: 20%Above ₹10 lakh: 30%
- Standard Deduction: ₹50,000 available for salaried and pensioned individuals.
- Family Pension: Deduction of ₹15,000 or 1/3rd of the pension, whichever is lower.
- High Net Worth Individuals: Higher surcharge of 37% on income over ₹5 crore, leading to an effective tax rate of 42.74%.
- Leave Encashment Exemption: ₹3 lakh for non-government employees.
- Flexibility: Requires detailed documentation and claims of deductions and exemptions.
- New Tax Regime Exemptions & Deductions:
- No claims for most exemptions and deductions such as HRA, LTA, or Section 80C.
- Tax Slabs:₹0 – ₹3 lakh: Nil₹3 lakh – ₹6 lakh: 5%₹6 lakh – ₹9 lakh: 10%₹9 lakh – ₹12 lakh: 15%₹12 lakh – ₹15 lakh: 20%Above ₹15 lakh: 30%
- Standard Deduction: While the standard deduction is indeed ₹50,000 in both regimes, the Budget 2024 has increased it to ₹75,000 exclusively for the new tax regime.
- Family Pension: The increased deduction of ₹25,000 for family pension is also a recent change introduced in Budget 2024 and applies to the new tax regime.
- High Net Worth Individuals: Reduced surcharge from 37% to 25%, lowering effective tax rate to 39%.
- Leave Encashment Exemption: Increased from ₹3 lakh to ₹25 lakh.
- Default Regime: New regime is the default option; switching requires submission of Form 10IEA.
- Choosing between both:
- The old tax regime is advantageous for those with significant deductions and exemptions, while the new tax regime is beneficial for those preferring simplicity and lower tax rates without needing extensive documentation.
2023-24 में 72% व्यक्तिगत आयकरदाताओं ने नई कर व्यवस्था को चुना
वित्तीय वर्ष 2023-24 में, भारत के 72% आयकरदाताओं ने नई कर व्यवस्था को चुना, जिसमें वृद्धि का श्रेय 2023-24 के बजट में हाल ही में की गई वृद्धि को दिया जाता है।
- बदलावों में कर स्लैब में कमी, कर-मुक्त आय सीमा में वृद्धि, उच्च कर छूट और मानक कटौती में वृद्धि शामिल है, जिससे यह व्यवस्था और अधिक आकर्षक हो गई है।
- 31 जुलाई की समयसीमा तक, आयकर रिटर्न दाखिल करने वालों की संख्या 5% बढ़कर रिकॉर्ड 7.29 करोड़ हो गई।
- मूल्यांकन वर्ष 2024-25 के लिए दाखिल किए गए 28 करोड़ रिटर्न में से 5.27 करोड़ नई व्यवस्था के तहत और 2.01 करोड़ पुरानी व्यवस्था के तहत थे।
- 2020 में शुरू की गई नई कर व्यवस्था 2023-24 के बजट में बदलावों के बाद और अधिक आकर्षक हो गई।
पुरानी कर व्यवस्था बनाम नई कर व्यवस्था
- पुरानी कर व्यवस्था में छूट और कटौती:
- HRA, LTA और धारा 80C के तहत कटौती (₹1.5 लाख तक) सहित 70 से अधिक छूट और कटौती की अनुमति देता है।
- कर स्लैब:₹0 – ₹5 लाख: शून्य₹2.5 लाख – ₹5 लाख: 5%₹5 लाख – ₹10 लाख: 20%₹10 लाख से ऊपर: 30%
- मानक कटौती: वेतनभोगी और पेंशनभोगी व्यक्तियों के लिए ₹50,000 उपलब्ध है।
- पारिवारिक पेंशन: ₹15,000 या पेंशन का 1/3 भाग, जो भी कम हो, की कटौती।
- उच्च निवल संपत्ति वाले व्यक्ति: ₹5 करोड़ से अधिक की आय पर 37% का उच्च अधिभार, जिससे प्रभावी कर दर 74% हो जाती है।
- अवकाश नकदीकरण छूट: गैर-सरकारी कर्मचारियों के लिए ₹3 लाख।
- लचीलापन: विस्तृत दस्तावेज़ीकरण और कटौतियों और छूटों के दावों की आवश्यकता है।
- नई कर व्यवस्था छूट और कटौती:
- HRA, LTA या धारा 80C जैसी अधिकांश छूटों और कटौतियों के लिए कोई दावा नहीं।
- कर स्लैब: ₹0 – ₹3 लाख: शून्य ₹3 लाख – ₹6 लाख: 5% ₹6 लाख – ₹9 लाख: 10% ₹9 लाख – ₹12 लाख: 15% ₹12 लाख – ₹15 लाख: 20% ₹15 लाख से ऊपर: 30%
- मानक कटौती: जबकि दोनों व्यवस्थाओं में मानक कटौती वास्तव में ₹50,000 है, बजट 2024 ने इसे विशेष रूप से नई कर व्यवस्था के लिए ₹75,000 तक बढ़ा दिया है।
- पारिवारिक पेंशन: पारिवारिक पेंशन के लिए ₹25,000 की बढ़ी हुई कटौती भी बजट 2024 में शुरू किया गया एक हालिया बदलाव है और यह नई कर व्यवस्था पर लागू होता है।
- उच्च निवल संपत्ति वाले व्यक्ति: अधिभार 37% से घटाकर 25% किया गया, जिससे प्रभावी कर दर 39% हो गई।
- अवकाश नकदीकरण छूट: ₹3 लाख से बढ़ाकर ₹25 लाख किया गया।
- डिफ़ॉल्ट व्यवस्था: नई व्यवस्था डिफ़ॉल्ट विकल्प है; स्विच करने के लिए फॉर्म 10IEA जमा करना आवश्यक है।
- दोनों में से चुनना:
- पुरानी कर व्यवस्था उन लोगों के लिए फायदेमंद है जिनके पास महत्वपूर्ण कटौती और छूट है, जबकि नई कर व्यवस्था उन लोगों के लिए फायदेमंद है जो व्यापक दस्तावेज़ीकरण की आवश्यकता के बिना सादगी और कम कर दरों को पसंद करते हैं।
Centre reissues draft notification on ecosensitive areas in Western Ghats / केंद्र ने पश्चिमी घाट में पारिस्थितिकी संवेदनशील क्षेत्रों पर मसौदा अधिसूचना फिर से जारी की
Syllabus : GS 3 : Environment
Source : The Hindu
The Union government has reissued a draft notification classifying parts of the Western Ghats as Ecologically Sensitive Areas (ESAs) for the sixth time.
- This draft, which imposes economic activity restrictions, has faced repeated objections from states. The new version coincides with recent Wayanad landslide events but is reportedly routine.
About Ecologically Sensitive Areas (ESAs)
- ESAs are regions recognized for their environmental significance, where human activities are regulated to protect biodiversity, ecosystems, and natural habitats.
- These areas are often home to endemic species of plants and animals and are crucial for maintaining ecological balance.
- The Environment (Protection) Act of 1986 allows the Central Government to restrict industrial activities in these sensitive areas to safeguard their ecological integrity.
- Although the term “Eco-Sensitive Zones” is not explicitly mentioned in the Act, provisions exist to prohibit or regulate activities based on biodiversity and environmental considerations.


Recommendations
- Gadgil Committee:
- The Gadgil Committee recommended declaring the entire Western Ghats region, covering 129,000 square kilometers, as ecologically sensitive.
- The committee proposed creating three zones: ESA 1, ESA 2, and ESA 3, with ESA 1 and ESA 2 facing the strictest restrictions on economic activity.
- States opposed these recommendations, leading to modifications..
- Kasturirangan Committee:
- The Kasturirangan Committee re-evaluated the protection measures and reduced the area of protected regions by half.
- The committee allowed states to propose their own ESA boundaries, with Kerala being the first to do so.
New Panel Formed by the Government
- In April 2022, the Centre formed another panel to “re-examine suggestions by these six state governments while keeping in view the conservation aspects of the disaster-prone pristine ecosystem, as well as rights, privileges, needs and developmental aspirations of the region”.
- The Centre and expert panel held 10 meetings with states having Western Ghats to discuss the fifth draft notification at various forums.
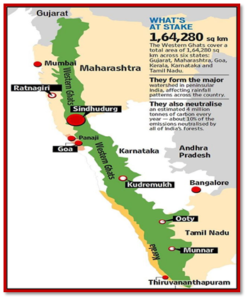
- The sixth draft notification, issued on Friday, declared 56,825.7 sq km of the Western Ghats as ESAs in the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
Way forward:
- Integrated Management Plans: The Government should develop and implement integrated management plans that balance ecological conservation with the developmental needs of the region.
- Enhanced Monitoring and Enforcement: There is a need to strengthen the regulatory framework by enhancing monitoring mechanisms and enforcing existing environmental laws more stringently.
केंद्र ने पश्चिमी घाट में पारिस्थितिकी संवेदनशील क्षेत्रों पर मसौदा अधिसूचना फिर से जारी की
केंद्र सरकार ने छठी बार पश्चिमी घाट के कुछ हिस्सों को पारिस्थितिकी रूप से संवेदनशील क्षेत्रों (ईएसए) के रूप में वर्गीकृत करने वाली एक मसौदा अधिसूचना फिर से जारी की है।
- र्थिक गतिविधि प्रतिबंध लगाने वाले इस मसौदे को राज्यों की ओर से बार-बार आपत्तियों का सामना करना पड़ा है। नया संस्करण हाल ही में वायनाड में हुए भूस्खलन की घटनाओं से मेल खाता है, लेकिन कथित तौर पर यह नियमित है।
पारिस्थितिक रूप से संवेदनशील क्षेत्रों (ESA) के बारे में
- ईएसए ऐसे क्षेत्र हैं जिन्हें उनके पर्यावरणीय महत्व के लिए पहचाना जाता है, जहाँ जैव विविधता, पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र और प्राकृतिक आवासों की रक्षा के लिए मानवीय गतिविधियों को विनियमित किया जाता है।
- ये क्षेत्र अक्सर पौधों और जानवरों की स्थानिक प्रजातियों का घर होते हैं और पारिस्थितिक संतुलन बनाए रखने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण होते हैं।
- पर्यावरण (संरक्षण) अधिनियम 1986 केंद्र सरकार को इन संवेदनशील क्षेत्रों में उनकी पारिस्थितिक अखंडता की रक्षा के लिए औद्योगिक गतिविधियों को प्रतिबंधित करने की अनुमति देता है।
- हालाँकि अधिनियम में “पारिस्थितिकी-संवेदनशील क्षेत्र” शब्द का स्पष्ट रूप से उल्लेख नहीं किया गया है, लेकिन जैव विविधता और पर्यावरणीय विचारों के आधार पर गतिविधियों को प्रतिबंधित या विनियमित करने के प्रावधान मौजूद हैं।
सिफ़ारिशें
- गाडगिल समिति:
- गाडगिल समिति ने 129,000 वर्ग किलोमीटर में फैले पूरे पश्चिमी घाट क्षेत्र को पारिस्थितिक रूप से संवेदनशील घोषित करने की सिफ़ारिश की।
- समिति ने तीन क्षेत्र बनाने का प्रस्ताव रखा: ESA 1, ESA 2 और ESA 3, जिसमें ESA 1 और ESA 2 को आर्थिक गतिविधि पर सबसे कड़े प्रतिबंधों का सामना करना पड़ेगा।
- राज्यों ने इन सिफ़ारिशों का विरोध किया, जिसके कारण संशोधन किए गए।
- कस्तूरीरंगन समिति:
- कस्तूरीरंगन समिति ने सुरक्षा उपायों का पुनर्मूल्यांकन किया और संरक्षित क्षेत्रों के क्षेत्र को आधे से कम कर दिया।
- समिति ने राज्यों को अपनी ईएसए सीमाएँ प्रस्तावित करने की अनुमति दी, जिसमें केरल ऐसा करने वाला पहला राज्य था।
सरकार द्वारा गठित नया पैनल
- अप्रैल 2022 में, केंद्र ने “आपदा-ग्रस्त प्राचीन पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र के संरक्षण पहलुओं के साथ-साथ क्षेत्र के अधिकारों, विशेषाधिकारों, आवश्यकताओं और विकासात्मक आकांक्षाओं को ध्यान में रखते हुए इन छह राज्य सरकारों द्वारा दिए गए सुझावों की फिर से जांच करने” के लिए एक और पैनल का गठन किया।
- केंद्र और विशेषज्ञ पैनल ने विभिन्न मंचों पर पांचवें मसौदा अधिसूचना पर चर्चा करने के लिए पश्चिमी घाट वाले राज्यों के साथ 10 बैठकें कीं।
- शुक्रवार को जारी छठे मसौदा अधिसूचना में गुजरात, महाराष्ट्र, गोवा, कर्नाटक, केरल और तमिलनाडु राज्यों में पश्चिमी घाट के 56,825.7 वर्ग किलोमीटर क्षेत्र को ईएसए घोषित किया गया।
आगे की राह:
- एकीकृत प्रबंधन योजनाएँ: सरकार को एकीकृत प्रबंधन योजनाएँ विकसित और लागू करनी चाहिए जो क्षेत्र की विकासात्मक आवश्यकताओं के साथ पारिस्थितिक संरक्षण को संतुलित करती हों।
- बढ़ी हुई निगरानी और प्रवर्तन: निगरानी तंत्र को बढ़ाकर और मौजूदा पर्यावरण कानूनों को और अधिक सख्ती से लागू करके नियामक ढांचे को मजबूत करने की आवश्यकता है।
India selects 2 crew members for Axiom-4 mission to ISS / भारत ने आईएसएस के लिए एक्सिओम-4 मिशन के लिए 2 चालक दल के सदस्यों का चयन किया
Syllabus : GS 3 : Science and Technology
Source : The Hindu
Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla and Group Captain Prasanth Balakrishnan Nair have been selected as prime and backup mission pilots, respectively, for the Axiom-4 mission to the International Space Station (ISS).
- This follows a joint ISRO-NASA initiative announced during Prime Minister Modi’s U.S. visit in June 2023.
- The mission will involve scientific research and technology demonstrations, enhancing cooperation between ISRO and NASA. Training begins in August 2024.
Note: Shukla will be the second Indian to go to space. So far, Wing Commander (Retired) Rakesh Sharma is the only Indian to go to space in 1984.
About Axiom-4 Mission
- The Axiom-4 mission is a private spaceflight to the International Space Station.
- It is operated by Axiom Space and used a SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft.
- The mission marks NASA’s fourth private astronaut mission, organized in partnership with Axiom Space.
- The mission is part of NASA’s broader strategy to transition low Earth orbit activities from government-led initiatives to a marketplace where NASA is one of many customers.
- It involves transporting astronauts to the ISS aboard SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft for a fourteen-day mission duration.
Crew:
- Peggy Whitson: A veteran astronaut with extensive experience, having completed multiple missions to the ISS.
- Sławosz Uznanski: A Polish astronaut joining the mission, marking a significant milestone for Poland in space exploration.
- Tibor Kapu: A Hungarian astronaut, adding to the diversity of the mission crew.
- Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla: An Indian astronaut, making headlines as part of this international crew.
Mission Objectives:
- Commercial Space Endeavours:
- Axiom-4 aims to facilitate commercial activities in space, including scientific research, technological development, and space tourism.
- The mission will help demonstrate the viability of commercial space stations as a platform for business and innovation.
- International Collaboration:
- Axiom-4 is set to carry a diverse crew of astronauts from different countries, reflecting the growing international interest in space exploration.
- This mission will strengthen partnerships between nations and contribute to global space initiatives.
- Research and Development:
- The mission will support various scientific experiments and technological tests in the unique microgravity environment of space.
- Research areas include materials science, biology, Earth observation, and more, with the potential to yield groundbreaking discoveries and innovations.
Significance of the mission:
- It will help in increasing global access to space
- It will normalise living and working in microgravity.
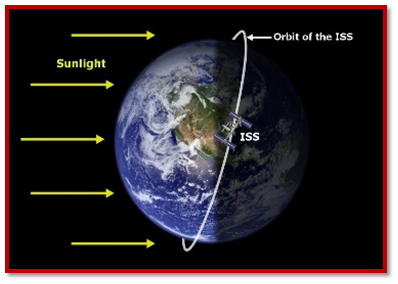
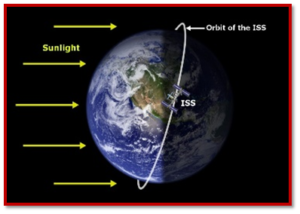
International Space Station (ISS)
- The International Space Station (ISS) is a large spacecraft that orbits Earth in low-earth orbit, approximately 400 km above the Earth’s surface.
- It serves as a space laboratory where astronauts conduct experiments in microgravity conditions.
Key Points:
- Operational Status: Currently, the ISS is the only operational space laboratory. It has been continuously inhabited since 2000.
- Participants: The ISS is a collaborative effort involving five space agencies:
- NASA (United States)
- Roscosmos (Russia)
- JAXA (Japan)
- ESA (Europe)
- CSA (Canada)
- Orbit and Speed: The ISS completes approximately 16 orbits around the Earth daily, with each orbit taking about one and a half hours.
- Purpose: It serves as a platform for various scientific experiments, space exploration studies, and technological advancements in a zero-gravity environment.
भारत ने आईएसएस के लिए एक्सिओम-4 मिशन के लिए 2 चालक दल के सदस्यों का चयन किया
ग्रुप कैप्टन शुभांशु शुक्ला और ग्रुप कैप्टन प्रशांत बालकृष्णन नायर को अंतर्राष्ट्रीय अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन (ISS) के लिए एक्सिओम-4 मिशन के लिए क्रमशः प्राइम और बैकअप मिशन पायलट के रूप में चुना गया है।
- यह जून 2023 में प्रधानमंत्री मोदी की अमेरिकी यात्रा के दौरान घोषित इसरो-नासा की संयुक्त पहल का अनुसरण करता है।
- इस मिशन में वैज्ञानिक अनुसंधान और प्रौद्योगिकी प्रदर्शन शामिल होंगे, जिससे इसरो और नासा के बीच सहयोग बढ़ेगा। प्रशिक्षण अगस्त 2024 में शुरू होगा।
नोट: शुक्ला अंतरिक्ष में जाने वाले दूसरे भारतीय होंगे। अब तक विंग कमांडर (सेवानिवृत्त) राकेश शर्मा 1984 में अंतरिक्ष में जाने वाले एकमात्र भारतीय हैं।
एक्सिओम-4 मिशन के बारे में
- एक्सिओम-4 मिशन अंतर्राष्ट्रीय अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन के लिए एक निजी अंतरिक्ष उड़ान है।
- इसे एक्सिओम स्पेस द्वारा संचालित किया जाता है और इसमें स्पेसएक्स क्रू ड्रैगन अंतरिक्ष यान का उपयोग किया जाता है।
- यह मिशन नासा के चौथे निजी अंतरिक्ष यात्री मिशन को चिह्नित करता है, जिसे एक्सिओम स्पेस के साथ साझेदारी में आयोजित किया गया है।
- यह मिशन नासा की व्यापक रणनीति का हिस्सा है, जो पृथ्वी की निचली कक्षा की गतिविधियों को सरकार के नेतृत्व वाली पहलों से ऐसे बाज़ार में स्थानांतरित करने की है, जहाँ नासा कई ग्राहकों में से एक है।
- इसमें चौदह दिनों की मिशन अवधि के लिए स्पेसएक्स के ड्रैगन अंतरिक्ष यान में अंतरिक्ष यात्रियों को आईएसएस तक पहुँचाना शामिल है।
चालक दल:
- पेगी व्हिटसन: व्यापक अनुभव वाली एक अनुभवी अंतरिक्ष यात्री, जिसने आईएसएस के लिए कई मिशन पूरे किए हैं।
- स्लावोज़ उज़्नान्स्की: मिशन में शामिल होने वाले एक पोलिश अंतरिक्ष यात्री, अंतरिक्ष अन्वेषण में पोलैंड के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण मील का पत्थर साबित हुए।
- टिबोर कापू: एक हंगेरियन अंतरिक्ष यात्री, जो मिशन चालक दल की विविधता को बढ़ाता है।
- ग्रुप कैप्टन शुभांशु शुक्ला: एक भारतीय अंतरिक्ष यात्री, जो इस अंतर्राष्ट्रीय चालक दल के हिस्से के रूप में सुर्खियाँ बटोर रहा है।
मिशन के उद्देश्य:
- वाणिज्यिक अंतरिक्ष प्रयास:
- एक्सिओम-4 का उद्देश्य अंतरिक्ष में वाणिज्यिक गतिविधियों को सुविधाजनक बनाना है, जिसमें वैज्ञानिक अनुसंधान, तकनीकी विकास और अंतरिक्ष पर्यटन शामिल हैं।
- यह मिशन व्यवसाय और नवाचार के लिए एक मंच के रूप में वाणिज्यिक अंतरिक्ष स्टेशनों की व्यवहार्यता को प्रदर्शित करने में मदद करेगा।
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग:
- एक्सिओम-4 विभिन्न देशों के अंतरिक्ष यात्रियों के एक विविध दल को ले जाने के लिए तैयार है, जो अंतरिक्ष अन्वेषण में बढ़ती अंतर्राष्ट्रीय रुचि को दर्शाता है।
- यह मिशन देशों के बीच साझेदारी को मजबूत करेगा और वैश्विक अंतरिक्ष पहलों में योगदान देगा।
- अनुसंधान और विकास:
- यह मिशन अंतरिक्ष के अनूठे सूक्ष्म गुरुत्वाकर्षण वातावरण में विभिन्न वैज्ञानिक प्रयोगों और तकनीकी परीक्षणों का समर्थन करेगा।
- अनुसंधान क्षेत्रों में पदार्थ विज्ञान, जीव विज्ञान, पृथ्वी अवलोकन और बहुत कुछ शामिल है, जिसमें अभूतपूर्व खोजों और नवाचारों को जन्म देने की क्षमता है।
मिशन का महत्व:
- इससे अंतरिक्ष तक वैश्विक पहुँच बढ़ाने में मदद मिलेगी
- इससे माइक्रोग्रैविटी में रहना और काम करना सामान्य हो जाएगा।
अंतर्राष्ट्रीय अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन (ISS)
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन (ISS) एक बड़ा अंतरिक्ष यान है जो पृथ्वी की सतह से लगभग 400 किमी ऊपर, पृथ्वी की निचली कक्षा में परिक्रमा करता है।
- यह एक अंतरिक्ष प्रयोगशाला के रूप में कार्य करता है जहाँ अंतरिक्ष यात्री माइक्रोग्रैविटी स्थितियों में प्रयोग करते हैं।
मुख्य बिंदु:
- परिचालन स्थिति: वर्तमान में, ISS एकमात्र चालू अंतरिक्ष प्रयोगशाला है। यह 2000 से लगातार काम कर रही है।
- प्रतिभागी: ISS पाँच अंतरिक्ष एजेंसियों से जुड़ा एक सहयोगात्मक प्रयास है:
- NASA (संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका)
- रोस्कोस्मोस (रूस)
- JAXA (जापान)
- ESA (यूरोप)
- CSA (कनाडा)
- कक्षा और गति: ISS प्रतिदिन पृथ्वी के चारों ओर लगभग 16 परिक्रमाएँ पूरी करता है, जिसमें प्रत्येक परिक्रमा में लगभग डेढ़ घंटे का समय लगता है।
- उद्देश्य: यह शून्य-गुरुत्वाकर्षण वातावरण में विभिन्न वैज्ञानिक प्रयोगों, अंतरिक्ष अन्वेषण अध्ययनों और तकनीकी प्रगति के लिए एक मंच के रूप में कार्य करता है।
Axis of resistance/ प्रतिरोध की धुरी
Term In News
Recently, the Hamas leader was assassinated in an airstrike in Tehran and experts believe that Iran could hike up attacks against Israel through its allies – Axis of resistance.
About Axis of resistance:
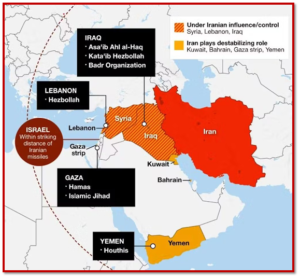
- It is a coalition of Iranian-backed groups.
- The coalition’s name is said to be inspired by former US President George W Bush’s use of the term ‘axis of evil’ — referring to Iran, Iraq and North Korea.
- Formation
- The roots of the ‘axis of resistance’ go back to the Iranian Revolution of 1979, which paved the way for radical Shia Muslim clerics to come to power.
- To expand its political and military influence in a region where most powers such as US-ally Saudi Arabia are Sunni-majority nations, Iran’s new regime began to support non-state actors.
- Another reason for this was to deter threats from Israel and the US — Iran has seen Israel’s creation in 1948 as a means for the US (and the West) to influence the region for its strategic interests.
- Group members
- Hezbollah: Shiite militant organization
- Hamas: Palestinian Sunni militant group in Gaza
- Palestinian Islamic Jihad(PIJ): Sunni Islamist militant group, Palestine
- Houthis: Zaydi Shia militant group, Yemen
प्रतिरोध की धुरी
हाल ही में तेहरान में हवाई हमले में हमास नेता की हत्या कर दी गई और विशेषज्ञों का मानना है कि ईरान अपने सहयोगियों – प्रतिरोध की धुरी के माध्यम से इजरायल के खिलाफ हमले बढ़ा सकता है।
प्रतिरोध की धुरी के बारे में:
- यह ईरान समर्थित समूहों का गठबंधन है।
- गठबंधन का नाम पूर्व अमेरिकी राष्ट्रपति जॉर्ज डब्ल्यू बुश द्वारा ‘बुराई की धुरी’ शब्द के इस्तेमाल से प्रेरित बताया जाता है – जिसका संदर्भ ईरान, इराक और उत्तर कोरिया से है।
गठन
- प्रतिरोध की धुरी’ की जड़ें 1979 की ईरानी क्रांति से जुड़ी हैं, जिसने कट्टरपंथी शिया मुस्लिम मौलवियों के सत्ता में आने का मार्ग प्रशस्त किया।
- ऐसे क्षेत्र में अपने राजनीतिक और सैन्य प्रभाव का विस्तार करने के लिए, जहां अमेरिका के सहयोगी सऊदी अरब जैसी अधिकांश शक्तियां सुन्नी बहुल राष्ट्र हैं, ईरान के नए शासन ने गैर-राज्य अभिनेताओं का समर्थन करना शुरू कर दिया।
- इसका एक अन्य कारण इजरायल और अमेरिका से खतरों को रोकना था – ईरान ने 1948 में इजरायल के निर्माण को अमेरिका (और पश्चिम) द्वारा अपने रणनीतिक हितों के लिए क्षेत्र को प्रभावित करने के साधन के रूप में देखा है।
समूह के सदस्य
- हिजबुल्लाह: शिया उग्रवादी संगठन
- हमास: गाजा में फिलिस्तीनी सुन्नी उग्रवादी समूह
- फिलिस्तीनी इस्लामिक जिहाद (PIJ): सुन्नी इस्लामवादी उग्रवादी समूह, फिलिस्तीन
- हौथी: ज़ायदी शिया उग्रवादी समूह, यमन
Mozambique / मोजाम्बिक
Location In News
The shipments of Tur/Pigeon peas from Nacala Port in Mozambique, disrupted by an “anti-India” group, have resumed after the Ministry of Consumer Affairs raised the issue with the Ministry of External Affairs.

About Mozambique:
- Location: It is a country in Southern Africa and is located in the Southern and Eastern Hemispheres of the Earth.
- The country also has a coastline on the Indian Ocean to the east.
- The island countries and territories of Madagascar, Comoros, and Mayotte are separated from Mozambique by the Mozambique Channel.
- Bordering countries: Zimbabwe, Eswatini, South Africa, Zambia, Malawi, and Tanzania.
- Rivers: It is drained by several significant rivers, with the Zambezi being the largest and other rivers are Limpopo, Licungo, Lurio, Rovuma etc.
- Major Lakes: Lake Malawi(Nyasa)
- Highest Peak: Mount Binga
- Capital: Maputo is the country’s capital while the largest city is Matola.
- Natural Resources: The country’s principal natural resources are natural gas, coal, mineral, sand, hydropower, and most likely oil.
मोजाम्बिक
मोजाम्बिक के नाकाला बंदरगाह से तुअर/अरहर दाल की खेप को एक “भारत विरोधी” समूह द्वारा बाधित कर दिया गया था, लेकिन उपभोक्ता मामलों के मंत्रालय द्वारा विदेश मंत्रालय के समक्ष यह मुद्दा उठाए जाने के बाद यह खेप फिर से शुरू हो गई है।
मोजाम्बिक के बारे में:
- स्थान: यह दक्षिणी अफ्रीका में स्थित एक देश है और पृथ्वी के दक्षिणी और पूर्वी गोलार्ध में स्थित है।
- देश के पूर्व में हिंद महासागर पर एक तटरेखा भी है।
- मेडागास्कर, कोमोरोस और मैयट के द्वीप देश और क्षेत्र मोजाम्बिक चैनल द्वारा मोजाम्बिक से अलग होते हैं।
- सीमावर्ती देश: जिम्बाब्वे, इस्वातिनी, दक्षिण अफ्रीका, जाम्बिया, मलावी और तंजानिया।
- नदियाँ: यह कई महत्वपूर्ण नदियों द्वारा बहती है, जिनमें ज़ाम्बेज़ी सबसे बड़ी है और अन्य नदियाँ लिम्पोपो, लिकुंगो, लुरियो, रोवुमा आदि हैं।
- प्रमुख झीलें: मलावी झील (न्यासा)
- सबसे ऊँची चोटी: माउंट बिंगा
- राजधानी: मापुटो देश की राजधानी है जबकि सबसे बड़ा शहर मटोला है।
- प्राकृतिक संसाधन: देश के प्रमुख प्राकृतिक संसाधन प्राकृतिक गैस, कोयला, खनिज, रेत, जल विद्युत और सबसे अधिक संभावना तेल हैं।
An unstated shift in Modi’s economic direction / मोदी की आर्थिक दिशा में एक अघोषित बदलाव
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 & 3 : Governance & Indian Economy
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- The article discusses India’s new Employment Linked Incentive (ELI) scheme, marking a shift from previous economic policies focused on GDP growth to direct job creation.
- It critiques past strategies like ‘Make in India’ and production-linked incentives, highlighting the need for employment-focused policies to address the country’s job deficit.
Introduction: A Shift in Economic Policy
- The Indian government has announced a new Employment Linked Incentive (ELI) scheme aimed at encouraging companies to hire more employees by providing financial incentives for each new hire.
- This initiative marks a significant departure from previous economic policies, reflecting a shift from a reliance on GDP growth to a focus on job creation and addressing the capital-labour imbalance.
About Employment Linked Incentives (ELI)
- The ELI scheme is an acknowledgment of the shortcomings of previous strategies, offering direct incentives to corporations to increase employment rather than relying on indirect methods.
- By lowering marginal labour costs, ELI is expected to encourage companies to hire more people, paralleling the logic of production incentives in the PLI scheme.
- Unlike the Production Linked Incentive (PLI), which focuses on increasing production, Employment Linked Incentive (ELI) aims to ensure that the economic benefits reach the workforce, thereby addressing the broader goal of economic development and improved living standards.
Government’s Failure of Initiatives
- Previous Economic Strategies: Over the past decade, the Indian government relied on traditional economic models, such as the trickle-down approach and production-linked incentives (PLI), which did not yield the expected job growth.
- Initiatives like “Make in India” and corporate tax cuts aimed to stimulate investment but failed to translate into significant employment opportunities.
- Jobless Growth: Despite policies designed to boost production, employment growth has been stagnant, with a study indicating a negligible employment growth rate of just 0.01%.
Issue of Job and Ideas Deficit
- Jobs Deficit: The scarcity of jobs in the economy has led to politically driven proposals, such as job reservations for locals, reflecting the urgent need for effective job creation strategies.
- Simply criticising such proposals without offering viable alternatives is counterproductive, highlighting the need for innovative ideas to address the employment deficit.
- Ideas Deficit: While traditional economic reforms are often cited as solutions, the ELI scheme offers a novel approach, aiming to rectify the capital-labour imbalance and stimulate job growth in a tangible way.
- Unemployment Trends: The unemployment rate has shown fluctuations, with a reported decline from 6.0% in 2017-18 to 3.2% in 2022-23.
What can be done?
- Policy Shift: The ELI scheme represents a significant policy shift towards prioritizing job creation over mere economic output. By encouraging firms to hire rather than invest solely in automation, it aims to address the capital-labour imbalance in the economy.
- Support for MSMEs: Special focus on micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) is crucial, as they employ a substantial portion of the workforce.
- Alignment of Goals: Need to Collaborate among various ministries, particularly finance, skill development, and labour, is essential to ensure that skill development aligns with industry needs, enhancing employability and job creation.
Conclusion: A Step Towards Inclusive Economic Growth
- Whether or not ELI proves to be a panacea for joblessness, it represents a significant policy innovation that moves away from trickle-down economics towards more direct, bottom-up interventions.
- The scheme reflects a willingness to adopt ideas from across the political spectrum for the greater national interest, as evidenced by its inclusion in the national budget.
- Ultimately, the ELI scheme signifies a readiness to explore new avenues for economic development, prioritising job creation and equitable growth as key objectives for India’s future.
More About Employment-Linked Incentive Schemes
- The Centre will implement three schemes for “employment-linked incentive” as part of the Prime Minister’s package, focusing on enrolment in the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO).
- First Scheme- This scheme will provide one-month wage to all persons newly entering the workforce in all formal sectors. The direct benefit transfer of one-month salary in 3 instalments to first-time employees, as registered in the EPFO, will be up to Rs. 15,000. The eligibility limit will be a salary of Rs. 1 lakh per month. The scheme is expected to benefit 210 lakh youth.
- Second scheme- An incentive will be provided at specified scale directly both to the employee and the employer with respect to their EPFO contribution in the first 4 years of employment. The scheme is expected to benefit 30 lakh youth entering employment, and their employers.
- Third scheme- This employer-focussed scheme will cover additional employment in all sectors. All additional employment within a salary of Rs.1 lakh per month will be counted. The government will reimburse to employers up to Rs. 3,000 per month for 2 years towards their EPFO contribution for each additional employee. The scheme is expected to incentivize additional employment of 50 lakh persons.
- Skilling programme- A new centrally sponsored scheme will be launched to skill 20 lakh youth over a 5-year period. 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes will be upgraded in hub and spoke arrangements with outcome orientation.
- Internship in Top Companies- A comprehensive scheme for providing internship opportunities in 500 top companies to 1 crore youth in 5 years. They will gain exposure for 12 months to real-life business environment, varied professions and employment opportunities. An internship allowance of Rs. 5,000 per month along with a one-time assistance of Rs. 6,000 will be provided. Companies will be expected to bear the training cost and 10 per cent of the internship cost from their CSR funds.
The relationship between economic growth and employment in India
- Job Creation Challenge: The report emphasizes that job creation remains one of India’s most significant macroeconomic challenges. Despite the pursuit of high GDP growth, the report suggests that the correlation between economic growth and employment generation has weakened over time.
- Weakening Employment Elasticity: Employment elasticity, which measures the extent to which employment grows when GDP grows by one unit, has consistently declined since the 1980s. This decline indicates that a 1% increase in GDP now results in less than a 1% increase in employment.
- Recent Trends: The period from 2017 to 2021 showed a notable improvement in employment. However, this improvement came with nuances. While employment numbers increased, it’s essential to distinguish between jobs created due to economic growth and those created out of necessity (self-employment).
- Quality of Jobs: The SWI 2023 report underscores the importance of considering the quality of jobs created. Not all employment opportunities are equal, and the report highlights the prevalence of self-employment, which often lacks regular wages and job security.
- Impact on Women: The changing employment landscape disproportionately affects women. Although women accounted for half of the lost employment during the specified period, they received only a third of the increase in formal employment. This shift also saw more individuals turning to self-employment due to economic distress.
- Uncorrelated Growth: The report’s broader takeaway is that over the long run, GDP growth and employment growth have been uncorrelated in India. This suggests that policies solely oriented towards achieving higher GDP growth rates may not necessarily lead to accelerated job creation.
The US perspective
- In contrast to India’s GDP-centric approach, the United States, the world’s largest economy, places a strong emphasis on employment levels.
- The Chairman of the US Federal Reserve, Jay Powell, consistently highlights the importance of achieving full employment while maintaining price stability.
Why does India not prioritize employment to the same degree?
- Historical Perspective: India’s approach to economic development has been influenced by its post-independence history. When India gained independence in 1947, it faced widespread poverty, and economic growth was seen as a means to uplift the masses.
- Development Paradigm: India adopted a development paradigm that prioritized industrialization and capital-intensive sectors. The belief was that as industries expanded, they would naturally absorb labor.
- Policy Framework: India’s economic policies, especially since the 1991 economic reforms, have largely centered on liberalization, privatization, and globalization. These policies aimed to attract foreign investment and promote private sector growth, often with an emphasis on manufacturing and services. While these policies aimed at increasing overall economic output, they did not always address the issue of employment directly.
- Data Focus: Economic policymakers often rely on GDP growth as a quantifiable and easily measurable metric to gauge economic performance. Employment data can be more complex to collect and interpret, and the focus on GDP growth has made it the primary indicator of success.
- Political Considerations: Political leaders and parties have, at times, used the promise of high GDP growth as a way to gain popular support and demonstrate economic progress to the electorate. This political narrative has reinforced the emphasis on GDP growth.
- Globalization Trends: The global trend toward globalization and competitiveness has also influenced India’s priorities. The country has sought to position itself as a global economic player, and this often involves pursuing policies that align with international economic norms, including a focus on GDP growth.
- Lack of Comprehensive Social Safety Nets: India’s social safety nets and social security systems have historically been limited in coverage and effectiveness. As a result, there may be a perception that focusing on GDP growth is essential to lifting people out of poverty, as job opportunities are seen as the primary means of economic betterment.
मोदी की आर्थिक दिशा में एक अघोषित बदलाव
संदर्भ :
- लेख में भारत की नई रोजगार से जुड़ी प्रोत्साहन (ईएलआई) योजना पर चर्चा की गई है, जो जीडीपी वृद्धि पर केंद्रित पिछली आर्थिक नीतियों से सीधे रोजगार सृजन की ओर बदलाव को दर्शाती है।
- यह ‘मेक इन इंडिया’ और उत्पादन से जुड़ी प्रोत्साहन जैसी पिछली रणनीतियों की आलोचना करता है, तथा देश में रोजगार की कमी को दूर करने के लिए रोजगार-केंद्रित नीतियों की आवश्यकता पर प्रकाश डालता है।
परिचय: आर्थिक नीति में बदलाव
- भारत सरकार ने एक नई रोजगार से जुड़ी प्रोत्साहन (ईएलआई) योजना की घोषणा की है, जिसका उद्देश्य प्रत्येक नए कर्मचारी को वित्तीय प्रोत्साहन प्रदान करके कंपनियों को अधिक कर्मचारी नियुक्त करने के लिए प्रोत्साहित करना है।
- यह पहल पिछली आर्थिक नीतियों से एक महत्वपूर्ण बदलाव को दर्शाती है, जो जीडीपी वृद्धि पर निर्भरता से रोजगार सृजन पर ध्यान केंद्रित करने और पूंजी-श्रम असंतुलन को संबोधित करने की ओर बदलाव को दर्शाती है।
रोजगार से जुड़ी प्रोत्साहन (ELI) के बारे में
- ईएलआई योजना पिछली रणनीतियों की कमियों की स्वीकृति है, जो अप्रत्यक्ष तरीकों पर निर्भर रहने के बजाय निगमों को रोजगार बढ़ाने के लिए प्रत्यक्ष प्रोत्साहन प्रदान करती है।
- सीमांत श्रम लागत को कम करके, ईएलआई से कंपनियों को अधिक लोगों को काम पर रखने के लिए प्रोत्साहित करने की उम्मीद है, जो पीएलआई योजना में उत्पादन प्रोत्साहन के तर्क के समानांतर है।
- उत्पादन से जुड़े प्रोत्साहन (पीएलआई) के विपरीत, जो उत्पादन बढ़ाने पर ध्यान केंद्रित करता है, रोजगार से जुड़े प्रोत्साहन (ईएलआई) का उद्देश्य यह सुनिश्चित करना है कि आर्थिक लाभ कार्यबल तक पहुँचें, जिससे आर्थिक विकास और बेहतर जीवन स्तर के व्यापक लक्ष्य को संबोधित किया जा सके।
पहलों में सरकार की विफलता
- पिछली आर्थिक रणनीतियाँ: पिछले दशक में, भारत सरकार ने पारंपरिक आर्थिक मॉडल, जैसे कि ट्रिकल-डाउन दृष्टिकोण और उत्पादन से जुड़े प्रोत्साहन (पीएलआई) पर भरोसा किया, जिससे अपेक्षित नौकरी वृद्धि नहीं हुई।
- “मेक इन इंडिया” और कॉर्पोरेट कर कटौती जैसी पहलों का उद्देश्य निवेश को प्रोत्साहित करना था, लेकिन वे महत्वपूर्ण रोजगार अवसरों में तब्दील नहीं हो पाईं।
- बेरोज़गारी वृद्धि: उत्पादन को बढ़ावा देने के लिए बनाई गई नीतियों के बावजूद, रोज़गार वृद्धि स्थिर रही है, एक अध्ययन में केवल 01% की नगण्य रोज़गार वृद्धि दर का संकेत दिया गया है।
नौकरी और विचारों की कमी का मुद्दा
- नौकरियों की कमी: अर्थव्यवस्था में नौकरियों की कमी के कारण स्थानीय लोगों के लिए नौकरी आरक्षण जैसे राजनीतिक रूप से प्रेरित प्रस्ताव सामने आए हैं, जो प्रभावी नौकरी सृजन रणनीतियों की तत्काल आवश्यकता को दर्शाते हैं।
- व्यवहार्य विकल्प पेश किए बिना ऐसे प्रस्तावों की आलोचना करना उल्टा है, जो रोजगार की कमी को दूर करने के लिए नवीन विचारों की आवश्यकता को उजागर करता है।
- विचारों की कमी: जबकि पारंपरिक आर्थिक सुधारों को अक्सर समाधान के रूप में उद्धृत किया जाता है, ईएलआई योजना एक नया दृष्टिकोण प्रदान करती है, जिसका उद्देश्य पूंजी-श्रम असंतुलन को सुधारना और मूर्त रूप से नौकरी वृद्धि को प्रोत्साहित करना है।
- बेरोजगारी के रुझान: बेरोजगारी दर में उतार-चढ़ाव देखा गया है, जो 2017-18 में 0% से घटकर 2022-23 में 3.2% हो गई है।
क्या किया जा सकता है?
- नीति में बदलाव: ईएलआई योजना केवल आर्थिक उत्पादन पर नौकरी सृजन को प्राथमिकता देने की दिशा में एक महत्वपूर्ण नीतिगत बदलाव का प्रतिनिधित्व करती है। फर्मों को केवल स्वचालन में निवेश करने के बजाय काम पर रखने के लिए प्रोत्साहित करके, इसका उद्देश्य अर्थव्यवस्था में पूंजी-श्रम असंतुलन को दूर करना है।
- एमएसएमई के लिए सहायता: सूक्ष्म, लघु और मध्यम उद्यमों (एमएसएमई) पर विशेष ध्यान देना महत्वपूर्ण है, क्योंकि वे कार्यबल के एक बड़े हिस्से को रोजगार देते हैं।
- लक्ष्यों का संरेखण: विभिन्न मंत्रालयों, विशेष रूप से वित्त, कौशल विकास और श्रम के बीच सहयोग की आवश्यकता है, ताकि यह सुनिश्चित किया जा सके कि कौशल विकास उद्योग की जरूरतों के साथ संरेखित हो, रोजगार क्षमता और नौकरी सृजन को बढ़ाए।
निष्कर्ष: समावेशी आर्थिक विकास की दिशा में एक कदम
- ईएलआई बेरोजगारी के लिए रामबाण साबित हो या न हो, यह एक महत्वपूर्ण नीतिगत नवाचार का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है जो ट्रिकल-डाउन अर्थशास्त्र से अधिक प्रत्यक्ष, नीचे से ऊपर के हस्तक्षेप की ओर जाता है।
- यह योजना व्यापक राष्ट्रीय हित के लिए राजनीतिक स्पेक्ट्रम के सभी पक्षों से विचारों को अपनाने की इच्छा को दर्शाती है, जैसा कि राष्ट्रीय बजट में इसके समावेश से स्पष्ट है।
- अंततः, ईएलआई योजना भारत के भविष्य के लिए प्रमुख उद्देश्यों के रूप में रोजगार सृजन और समान विकास को प्राथमिकता देते हुए आर्थिक विकास के लिए नए रास्ते तलाशने की तत्परता को दर्शाती है।
रोजगार-संबंधी प्रोत्साहन योजनाओं के बारे में अधिक जानकारी
- केंद्र सरकार प्रधानमंत्री पैकेज के तहत “रोजगार से जुड़े प्रोत्साहन” के लिए तीन योजनाएं लागू करेगी, जिसका फोकस कर्मचारी भविष्य निधि संगठन (ईपीएफओ) में नामांकन पर होगा।
- पहली योजना- यह योजना सभी औपचारिक क्षेत्रों में कार्यबल में प्रवेश करने वाले सभी नए व्यक्तियों को एक महीने का वेतन प्रदान करेगी। ईपीएफओ में पंजीकृत पहली बार के कर्मचारियों को 3 किस्तों में एक महीने के वेतन का प्रत्यक्ष लाभ हस्तांतरण 15,000 रुपये तक होगा। पात्रता सीमा 1 लाख रुपये प्रति माह का वेतन होगी। इस योजना से 210 लाख युवाओं को लाभ मिलने की उम्मीद है।
- दूसरी योजना- रोजगार के पहले 4 वर्षों में उनके ईपीएफओ योगदान के संबंध में कर्मचारी और नियोक्ता दोनों को सीधे निर्दिष्ट पैमाने पर प्रोत्साहन प्रदान किया जाएगा। इस योजना से रोजगार में प्रवेश करने वाले 30 लाख युवाओं और उनके नियोक्ताओं को लाभ मिलने की उम्मीद है।
- तीसरी योजना- यह नियोक्ता-केंद्रित योजना सभी क्षेत्रों में अतिरिक्त रोजगार को कवर करेगी। प्रत्येक अतिरिक्त कर्मचारी के लिए ईपीएफओ अंशदान के लिए 2 वर्षों के लिए 3,000 प्रति माह। इस योजना से 50 लाख लोगों को अतिरिक्त रोजगार मिलने की उम्मीद है।
- कौशल कार्यक्रम- 5 वर्ष की अवधि में 20 लाख युवाओं को कौशल प्रदान करने के लिए एक नई केंद्र प्रायोजित योजना शुरू की जाएगी। 1,000 औद्योगिक प्रशिक्षण संस्थानों को हब और स्पोक व्यवस्था में परिणाम उन्मुखीकरण के साथ उन्नत किया जाएगा।
- शीर्ष कंपनियों में इंटर्नशिप- 5 वर्षों में 1 करोड़ युवाओं को 500 शीर्ष कंपनियों में इंटर्नशिप के अवसर प्रदान करने के लिए एक व्यापक योजना। उन्हें 12 महीनों के लिए वास्तविक जीवन के कारोबारी माहौल, विविध व्यवसायों और रोजगार के अवसरों का अनुभव मिलेगा। 6,000 रुपये की एकमुश्त सहायता के साथ 5,000 रुपये प्रति माह का इंटर्नशिप भत्ता प्रदान किया जाएगा। कंपनियों से अपेक्षा की जाएगी कि वे अपने सीएसआर फंड से प्रशिक्षण लागत और इंटर्नशिप लागत का 10 प्रतिशत वहन करें।
भारत में आर्थिक विकास और रोजगार के बीच संबंध
- नौकरी सृजन चुनौती: रिपोर्ट इस बात पर जोर देती है कि नौकरी सृजन भारत की सबसे महत्वपूर्ण व्यापक आर्थिक चुनौतियों में से एक है। उच्च जीडीपी वृद्धि की खोज के बावजूद, रिपोर्ट बताती है कि आर्थिक विकास और रोजगार सृजन के बीच संबंध समय के साथ कमजोर हुआ है।
- कमजोर होती रोजगार लोच: रोजगार लोच, जो जीडीपी में एक इकाई की वृद्धि होने पर रोजगार की वृद्धि की सीमा को मापती है, 1980 के दशक से लगातार घट रही है। यह गिरावट दर्शाती है कि जीडीपी में 1% की वृद्धि से अब रोजगार में 1% से भी कम वृद्धि होती है।
- हाल के रुझान: 2017 से 2021 की अवधि में रोजगार में उल्लेखनीय सुधार हुआ। हालाँकि, यह सुधार बारीकियों के साथ आया। जबकि रोजगार संख्या में वृद्धि हुई है, आर्थिक विकास के कारण सृजित नौकरियों और आवश्यकता (स्व-रोजगार) से सृजित नौकरियों के बीच अंतर करना आवश्यक है।
- नौकरियों की गुणवत्ता: SWI 2023 रिपोर्ट सृजित नौकरियों की गुणवत्ता पर विचार करने के महत्व को रेखांकित करती है। सभी रोजगार अवसर समान नहीं होते हैं, और रिपोर्ट स्व-रोजगार के प्रचलन पर प्रकाश डालती है, जिसमें अक्सर नियमित वेतन और नौकरी की सुरक्षा का अभाव होता है।
- महिलाओं पर प्रभाव: बदलते रोजगार परिदृश्य का महिलाओं पर असमान रूप से प्रभाव पड़ता है। यद्यपि निर्दिष्ट अवधि के दौरान खोए गए रोजगार में से आधे महिलाओं के थे, लेकिन उन्हें औपचारिक रोजगार में वृद्धि का केवल एक तिहाई ही प्राप्त हुआ। इस बदलाव ने आर्थिक संकट के कारण अधिक व्यक्तियों को स्वरोजगार की ओर मुड़ते हुए भी देखा।
- असंबंधित विकास: रिपोर्ट का व्यापक निष्कर्ष यह है कि लंबे समय में, भारत में जीडीपी विकास और रोजगार वृद्धि असंबंधित रही है। इससे पता चलता है कि केवल उच्च जीडीपी विकास दर प्राप्त करने के लिए उन्मुख नीतियों से आवश्यक रूप से त्वरित रोजगार सृजन नहीं हो सकता है।
अमेरिकी परिप्रेक्ष्य
- भारत के जीडीपी-केंद्रित दृष्टिकोण के विपरीत, दुनिया की सबसे बड़ी अर्थव्यवस्था, संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका, रोजगार के स्तर पर बहुत जोर देता है।
- अमेरिकी फेडरल रिजर्व के अध्यक्ष, जे पॉवेल, मूल्य स्थिरता बनाए रखते हुए पूर्ण रोजगार प्राप्त करने के महत्व पर लगातार प्रकाश डालते हैं।
भारत रोजगार को उसी हद तक प्राथमिकता क्यों नहीं देता?
- ऐतिहासिक परिप्रेक्ष्य: आर्थिक विकास के लिए भारत का दृष्टिकोण उसके स्वतंत्रता के बाद के इतिहास से प्रभावित है। जब भारत ने 1947 में स्वतंत्रता प्राप्त की, तो उसे व्यापक गरीबी का सामना करना पड़ा, और आर्थिक विकास को जनता के उत्थान के साधन के रूप में देखा गया।
- विकास प्रतिमान: भारत ने एक विकास प्रतिमान अपनाया जिसमें औद्योगिकीकरण और पूंजी-गहन क्षेत्रों को प्राथमिकता दी गई। विश्वास यह था कि जैसे-जैसे उद्योग फैलेंगे, वे स्वाभाविक रूप से श्रम को अवशोषित करेंगे।
- नीतिगत ढाँचा: भारत की आर्थिक नीतियाँ, विशेष रूप से 1991 के आर्थिक सुधारों के बाद से, मुख्य रूप से उदारीकरण, निजीकरण और वैश्वीकरण पर केंद्रित रही हैं। इन नीतियों का उद्देश्य विदेशी निवेश को आकर्षित करना और निजी क्षेत्र के विकास को बढ़ावा देना था, जिसमें अक्सर विनिर्माण और सेवाओं पर जोर दिया जाता था। जबकि इन नीतियों का उद्देश्य समग्र आर्थिक उत्पादन को बढ़ाना था, लेकिन वे हमेशा सीधे तौर पर रोज़गार के मुद्दे को संबोधित नहीं करती थीं।
- डेटा फ़ोकस: आर्थिक नीति निर्माता अक्सर आर्थिक प्रदर्शन को मापने के लिए एक मात्रात्मक और आसानी से मापने योग्य मीट्रिक के रूप में जीडीपी वृद्धि पर भरोसा करते हैं। रोज़गार डेटा एकत्र करना और व्याख्या करना अधिक जटिल हो सकता है, और जीडीपी वृद्धि पर ध्यान केंद्रित करने से यह सफलता का प्राथमिक संकेतक बन गया है।
- राजनीतिक विचार: राजनीतिक नेताओं और दलों ने, कई बार, लोकप्रिय समर्थन हासिल करने और मतदाताओं को आर्थिक प्रगति दिखाने के तरीके के रूप में उच्च जीडीपी वृद्धि के वादे का इस्तेमाल किया है। इस राजनीतिक कथा ने जीडीपी वृद्धि पर जोर दिया है।
- वैश्वीकरण के रुझान: वैश्वीकरण और प्रतिस्पर्धात्मकता की ओर वैश्विक रुझान ने भी भारत की प्राथमिकताओं को प्रभावित किया है। देश ने खुद को एक वैश्विक आर्थिक खिलाड़ी के रूप में स्थापित करने की कोशिश की है, और इसमें अक्सर ऐसी नीतियों का पालन करना शामिल है जो अंतरराष्ट्रीय आर्थिक मानदंडों के साथ संरेखित हों, जिसमें जीडीपी वृद्धि पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना शामिल है।
- व्यापक सामाजिक सुरक्षा जाल का अभाव: भारत के सामाजिक सुरक्षा जाल और सामाजिक सुरक्षा प्रणालियाँ ऐतिहासिक रूप से कवरेज और प्रभावशीलता में सीमित रही हैं। परिणामस्वरूप, ऐसी धारणा हो सकती है कि लोगों को गरीबी से बाहर निकालने के लिए जीडीपी वृद्धि पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना आवश्यक है, क्योंकि नौकरी के अवसरों को आर्थिक बेहतरी के प्राथमिक साधन के रूप में देखा जाता है।
World Bank Group / विश्व बैंक समूह
International Organizations

| Establishment | July 1944, during the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference at Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, USA. |
| Initial Purpose | To help rebuild European nations devastated by World War II; Later expanded to include global development and poverty reduction. |
| Components | International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) International Development Association (IDA) International Finance Corporation (IFC)
Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID) |
| Membership | 189 member countries. |
| Headquarters | Washington, D.C., United States. |
| Main Functions | Provides loans, credits, and grants; offers technical expertise and policy advice; researches development issues. |
| Funding | Through issuance of bonds in the international financial markets and earnings from its investments. |
| Governance | Led by a President, with a Board of Governors and a Board of Executive Directors. |
| India’s Involvement | Founding member since 1944. First loan approved in 1949 for Indian Railways. |
विश्व बैंक समूह
अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठन
| स्थापना | जुलाई 1944, ब्रेटन वुड्स, न्यू हैम्पशायर, संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका में संयुक्त राष्ट्र मौद्रिक और वित्तीय सम्मेलन के दौरान। |
| प्रारंभिक उद्देश्य | द्वितीय विश्व युद्ध में तबाह हुए यूरोपीय देशों के पुनर्निर्माण में मदद करना; बाद में वैश्विक विकास और गरीबी उन्मूलन को शामिल करने के लिए इसका विस्तार किया गया। |
| घटक | अंतर्राष्ट्रीय पुनर्निर्माण एवं विकास बैंक (आईबीआरडी) अंतर्राष्ट्रीय विकास संघ (आईडीए) अंतर्राष्ट्रीय वित्त निगम (आईएफसी)
बहुपक्षीय निवेश गारंटी एजेंसी (एमआईजीए) अंतर्राष्ट्रीय निवेश विवाद निपटान केंद्र (आईसीएसआईडी) |
| सदस्यता | 189 सदस्य देश। |
| मुख्यालय | वाशिंगटन, डी.सी., संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका। |
| मुख्य कार्य | ऋण, क्रेडिट और अनुदान प्रदान करता है; तकनीकी विशेषज्ञता और नीति सलाह प्रदान करता है; विकास के मुद्दों पर शोध करता है। |
| वित्तपोषण | अंतर्राष्ट्रीय वित्तीय बाजारों में बांड जारी करने और अपने निवेशों से आय अर्जित करने के माध्यम से। |
| शासन | एक राष्ट्रपति के नेतृत्व में, एक बोर्ड ऑफ गवर्नर्स और एक कार्यकारी निदेशकों के बोर्ड के साथ। |
| भारत की भागीदारी | 1944 से संस्थापक सदस्य। भारतीय रेलवे के लिए 1949 में पहला ऋण स्वीकृत किया गया। |