CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08/08/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08/08/2024
- Extra 100 gm crushes Vinesh’s Olympic dreams / 100 ग्राम अतिरिक्त खाने से विनेश का ओलंपिक सपना टूट गया
- Lok Sabha passes Finance Bill, amends provision on LTCG tax / लोकसभा ने वित्त विधेयक पारित किया, LTCG कर पर प्रावधान में संशोधन किया
- Tiny bones shed light on mystery ‘hobbits’ / छोटी हड्डियों ने रहस्यमयी ‘हॉबिट्स’ पर प्रकाश डाला
- After artificial intelligence, quantum computing eyes its big breakthrough moment / कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता के बाद, क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग अपनी बड़ी सफलता की ओर देख रही है
- Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve / गुरु घासीदास-तमोर पिंगला टाइगर रिजर्व
- Court shifts the tide on stray dog policy / कोर्ट ने आवारा कुत्तों की नीति पर रुख बदला
- United Nations (UN) / संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन)
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 08/08/2024
Extra 100 gm crushes Vinesh’s Olympic dreams / 100 ग्राम अतिरिक्त खाने से विनेश का ओलंपिक सपना टूट गया
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
Wrestler Vinesh Phogat’s Olympics campaign ended in disappointment when she was disqualified for being 100 grams over the 50kg limit before her final match.
- Despite efforts to cut weight, including a sauna session and haircut, she failed to meet the weight requirement.
- Phogat, who had previously defeated top competitors and made history as the first Indian woman wrestler to reach Olympic an Olympic final, was eliminated, and Cuban Yusneylis Guzman Lopez advanced to the final.
Weigh-in specifics
- About
- Weigh-ins take place in the morning for any wrestlers competing that day.
- The tournament for each weight class is contested over a two-day span. Hence, any wrestlers that make the finals or the repechage will have to make weight on both days.
- First weigh-in
- During the first weigh-in, wrestlers will have 30 minutes to make weight. Contestants are weighed with their singlets, but nothing else.
- Athletes will also be examined to make sure they have no signs of any contagious disease and that their fingernails are cut very short.
- During second day
- For any wrestlers competing on the second day, the weigh-in will last 15 minutes.
- This is a non-negotiable window during which the wrestler must make the required weight or risk disqualification.
- Weight tolerance in Olympics
- No more weight tolerance will be allowed for the second weigh-in.
- The Olympics follow a strict weight restriction without the 2kg weigh in tolerance.
- Two kilograms weight tolerance is allowed for World Cup and for the International Tournaments (Except UWW Ranking Events).
- Was a two-day weigh-in always the rule?
- In 2017, the UWW changed the format of Olympic wrestling.
- The Rio Olympics was the last time when wrestling was conducted as a single day event in a major international tournament.
- So instead of the competition in a weight category being conducted all in a day, they moved to a two-day system.
- This was done so that athletes wouldn’t lose a huge amount of weight on one day and compete.
The process of Olympic wrestling weigh-ins

Weight cut
- About
- In combat sports such as wrestling, boxing, and mixed martial arts, athletes compete in specific weight categories to ensure fair competition.
- These categories have strict rules that prevent athletes from participating if they exceed the designated weight limit.
- To meet these requirements, some athletes engage in a practice known as “weight cutting,” where they rapidly lose a set amount of weight just before the competition.
- This is done through various methods such as dehydration, restrictive dieting, and intense physical activity.
- While weight cutting is common, it can pose significant health risks and controversies surrounding its safety and fairness continue to be debated in the sports community.
- How do wrestlers cut weight?
- In many sports with weight categories, athletes often cut weight to fit into a lower category, typically reducing up to 10% of their body mass before major events.
- The most challenging period is the 24-48 hours before the competition, where athletes must shed the final, smallest margins of weight.
- After meeting the weight requirements and completing the weigh-in, athletes rehydrate and eat to regain energy and recover the fluids and body mass lost.
- Once the competition is over, they often start the weight-cutting cycle again for the next event.
The case of Vinesh Phogat
- About
- Vinesh has always struggled to cut weight for the 50kg category.
- She had been participating in the 53 kg category until recently before she made the switch to 50 kg. The switch was made at the trials in NIS, Patiala.
- Phogat’s usual weight is around 55-56 kg, which she has to cut to 50 kg on the days of competition.
- Keeping her body weight below 55-56 kg has proved to be quite tough as there isn’t much more weight to cut and cutting water weight by sweating out has proven to be extremely challenging for the Indian wrestler.
- Could Vinesh have salvaged a medal if she was injured?
- According to UWW, if an athlete is injured during the first day, he/she doesn’t have to attend the second weigh-in and will keep his/her results.
- In Vinesh’s case, she would have got the silver medal.
- But if an athlete is injured after Day 1 of the competition, they have to attend the second weigh-in.
- Why was she disqualified – Concerned Rules
- If an athlete does not attend or fails the weigh-in (the 1st or the 2nd weigh-in), he will be eliminated from the competition and ranked last, without rank.
100 ग्राम अतिरिक्त खाने से विनेश का ओलंपिक सपना टूट गया
पहलवान विनेश फोगट का ओलंपिक अभियान निराशा में समाप्त हो गया, जब उन्हें अपने अंतिम मैच से पहले 50 किलोग्राम की सीमा से 100 ग्राम अधिक वजन होने के कारण अयोग्य घोषित कर दिया गया।
- सौना सत्र और बाल कटवाने सहित वजन कम करने के प्रयासों के बावजूद, वह वजन की आवश्यकता को पूरा करने में विफल रही।
- फोगट, जिन्होंने पहले शीर्ष प्रतियोगियों को हराया था और ओलंपिक फाइनल में पहुंचने वाली पहली भारतीय महिला पहलवान के रूप में इतिहास बनाया था, को बाहर कर दिया गया, और क्यूबा की युस्नेलिस गुज़मैन लोपेज़ फाइनल में पहुँच गईं।
वजन मापने की विशिष्टता
- उस दिन प्रतिस्पर्धा करने वाले किसी भी पहलवान के लिए सुबह वजन मापने की प्रक्रिया होती है।
- प्रत्येक भार वर्ग के लिए प्रतियोगिता दो दिन की अवधि में होती है। इसलिए, जो भी पहलवान फाइनल या रेपेचेज में पहुंचते हैं, उन्हें दोनों दिन वजन मापना होगा।
- पहला वजन माप
- पहले वजन माप के दौरान, पहलवानों के पास वजन मापने के लिए 30 मिनट का समय होगा। प्रतियोगियों का वजन उनके सिंगलट से किया जाता है, लेकिन किसी और चीज से नहीं।
- एथलीटों की यह सुनिश्चित करने के लिए भी जांच की जाएगी कि उनमें किसी संक्रामक बीमारी के लक्षण तो नहीं हैं और उनके नाखून बहुत छोटे कटे हुए हैं।
- दूसरे दिन
- दूसरे दिन प्रतिस्पर्धा करने वाले किसी भी पहलवान के लिए, वजन मापने की प्रक्रिया 15 मिनट तक चलेगी।
- यह एक गैर-परक्राम्य अवधि है जिसके दौरान पहलवान को आवश्यक वजन मापना होगा या अयोग्य घोषित होने का जोखिम उठाना होगा।
- ओलंपिक में वजन सहनशीलता
- दूसरे वजन माप के लिए अधिक वजन सहनशीलता की अनुमति नहीं दी जाएगी।
- ओलंपिक में 2 किलोग्राम वजन सहनशीलता के बिना सख्त वजन प्रतिबंध का पालन किया जाता है।
- विश्व कप और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय टूर्नामेंट (UWW रैंकिंग इवेंट को छोड़कर) के लिए दो किलोग्राम वजन सहन करने की अनुमति है।
- क्या हमेशा दो दिन का वजन मापना नियम था?
- 2017 में, UWW ने ओलंपिक कुश्ती के प्रारूप को बदल दिया।
- रियो ओलंपिक आखिरी बार था जब कुश्ती किसी प्रमुख अंतरराष्ट्रीय टूर्नामेंट में एक दिवसीय आयोजन के रूप में आयोजित की गई थी।
- इसलिए एक दिन में सभी भार वर्ग में प्रतियोगिता आयोजित करने के बजाय, वे दो दिवसीय प्रणाली में चले गए।
- ऐसा इसलिए किया गया ताकि एथलीट एक दिन में बहुत अधिक वजन कम न करें और प्रतिस्पर्धा न करें।
ओलंपिक कुश्ती वजन-मापन की प्रक्रिया
वजन कम करना
- कुश्ती, मुक्केबाजी और मिश्रित मार्शल आर्ट जैसे लड़ाकू खेलों में, एथलीट निष्पक्ष प्रतिस्पर्धा सुनिश्चित करने के लिए विशिष्ट वजन श्रेणियों में प्रतिस्पर्धा करते हैं।
- इन श्रेणियों में सख्त नियम हैं जो एथलीटों को निर्दिष्ट वजन सीमा से अधिक होने पर भाग लेने से रोकते हैं।
- इन आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने के लिए, कुछ एथलीट “वजन कम करना” नामक अभ्यास में शामिल होते हैं, जहाँ वे प्रतियोगिता से ठीक पहले तेजी से एक निश्चित मात्रा में वजन कम करते हैं।
- यह निर्जलीकरण, प्रतिबंधात्मक आहार और तीव्र शारीरिक गतिविधि जैसे विभिन्न तरीकों के माध्यम से किया जाता है।
- जबकि वजन कम करना आम बात है, यह महत्वपूर्ण स्वास्थ्य जोखिम पैदा कर सकता है और इसकी सुरक्षा और निष्पक्षता को लेकर खेल समुदाय में विवाद जारी है।
पहलवान अपना वजन कैसे कम करते हैं?
- वजन श्रेणियों वाले कई खेलों में, एथलीट अक्सर कम श्रेणी में फिट होने के लिए अपना वजन कम करते हैं, आमतौर पर प्रमुख आयोजनों से पहले अपने शरीर के वजन का 10% तक कम करते हैं।
- सबसे चुनौतीपूर्ण अवधि प्रतियोगिता से 24-48 घंटे पहले की होती है, जहाँ एथलीटों को वजन का अंतिम, सबसे छोटा मार्जिन कम करना होता है।
- वजन की आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने और वजन मापने के बाद, एथलीट पुनः हाइड्रेट होते हैं और ऊर्जा प्राप्त करने तथा खोए हुए तरल पदार्थ और शरीर के द्रव्यमान को पुनः प्राप्त करने के लिए खाते हैं।
- प्रतियोगिता समाप्त होने के बाद, वे अक्सर अगले आयोजन के लिए वजन घटाने का चक्र फिर से शुरू करते हैं।
विनेश फोगट का मामला
- के बारे में
- विनेश को हमेशा 50 किग्रा वर्ग के लिए वजन घटाने में संघर्ष करना पड़ा है।
- वह हाल ही में 50 किग्रा में स्विच करने से पहले 53 किग्रा वर्ग में भाग ले रही थी। यह स्विच NIS, पटियाला में ट्रायल में किया गया था।
- फोगट का सामान्य वजन लगभग 55-56 किग्रा है, जिसे प्रतियोगिता के दिनों में उसे 50 किग्रा तक कम करना पड़ता है।
- अपने शरीर के वजन को 55-56 किग्रा से कम रखना काफी कठिन साबित हुआ है क्योंकि घटाने के लिए अधिक वजन नहीं है और पसीना बहाकर पानी का वजन कम करना भारतीय पहलवान के लिए बेहद चुनौतीपूर्ण साबित हुआ है।
क्या विनेश चोटिल होने पर पदक बचा सकती थी?
- यूडब्ल्यूडब्ल्यू के अनुसार, यदि कोई एथलीट पहले दिन चोटिल हो जाता है, तो उसे दूसरे वजन-माप में भाग लेने की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है और उसके परिणाम सुरक्षित रहेंगे।
- विनेश के मामले में, उसे रजत पदक मिलता।
- लेकिन यदि कोई एथलीट प्रतियोगिता के पहले दिन के बाद चोटिल हो जाता है, तो उसे दूसरे वजन-माप में भाग लेना पड़ता है।
उसे अयोग्य क्यों ठहराया गया – संबंधित नियम
- यदि कोई एथलीट वजन-माप (पहला या दूसरा वजन-माप) में भाग नहीं लेता है या असफल हो जाता है, तो उसे प्रतियोगिता से बाहर कर दिया जाएगा और बिना रैंक के अंतिम स्थान पर रखा जाएगा।
Lok Sabha passes Finance Bill, amends provision on LTCG tax / लोकसभा ने वित्त विधेयक पारित किया, LTCG कर पर प्रावधान में संशोधन किया
Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity
Source : The Hindu
The Finance Bill, 2024 was passed by the Lok Sabha, incorporating an amendment on long-term capital gains (LTCG) tax, allowing taxpayers to choose between a new lower rate of 12.5% without indexation or the old 20% rate with indexation benefits.
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman defended the Budget proposals, focusing on tax simplification and investment promotion.
- Opposition protests over GST on insurance premiums led to a walkout.
What is a Finance Bill?
Definition and Purpose
- Introduction: The Finance Bill is introduced in the Lok Sabha following the Union Budget presented by the Finance Minister. It encompasses the financial proposals for the upcoming financial year.
- Once passed by Parliament and assented to by the President, it becomes the Finance Act for that year, effectively giving legal force to the budgetary measures.
Types of Financial Bills
- Type (I) – Article 117 (1)
- Scope: Contains matters both related to the Money Bill and general legislation.
- Introduction: Can be introduced only in the Lok Sabha, with a Presidential recommendation.
- Legislative Process:
- Rajya Sabha can suggest amendments, which Lok Sabha may accept or reject.
- In case of a deadlock, a joint sitting of both Houses may be convened by the President.
- The President can assent, withhold assent, or return the bill for reconsideration.
- Type (II) – Article 117 (3)
- Scope: Deals with provisions involving expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India but does not include Money Bill matters.
- Introduction: Can be introduced in either House of Parliament.
- Legislative Process: Governed by procedures applicable to ordinary bills, requiring Presidential recommendation for consideration.
Difference Between Money Bill and Finance Bill
| Aspect | Money Bill | Finance Bill |
| Definition | Contains provisions related exclusively to taxation, borrowing of money by the government, and expenditure from or receipt to the Consolidated Fund of India. | Covers a broader range of financial matters, including provisions related to taxation but may also include general legislation or expenditure not strictly related to the Consolidated Fund. |
| Introduction | Can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha. | Type (I) can be introduced only in the Lok Sabha. Type (II) can be introduced in either House. |
| Certification | Certified as a Money Bill by the Speaker of Lok Sabha. | Not certified as a Money Bill. |
| Rajya Sabha’s Role | Cannot amend or reject the Money Bill. | Can recommend amendments to Type (I); Type (II) is treated like an ordinary bill. |
| Approval Process | Must be passed by Lok Sabha and can be sent to Rajya Sabha for recommendations. Lok Sabha can reject Rajya Sabha’s recommendations. If not acted upon by Rajya Sabha within 14 days, deemed passed. | Must be passed by both Houses. In case of disagreement, a joint sitting of both Houses can be summoned by the President for Type (I). Type (II) follows ordinary bill procedures. |
| Presidential Recommendation | Required for introduction in Lok Sabha. | Required for Type (I); not necessarily for Type (II). |
| Amendments | No amendments allowed by Rajya Sabha. | Rajya Sabha can suggest amendments for Type (I); Type (II) follows ordinary bill procedures. |
| Deadlock Resolution | No provision for joint sitting; Lok Sabha’s decision is final. | President can summon a joint sitting of both Houses for Type (I). Type (II) is resolved through ordinary legislative procedures. |
लोकसभा ने वित्त विधेयक पारित किया, LTCG कर पर प्रावधान में संशोधन किया
वित्त विधेयक, 2024 को लोकसभा ने पारित कर दिया, जिसमें दीर्घकालिक पूंजीगत लाभ (LTCG) कर पर संशोधन शामिल है, जिससे करदाताओं को इंडेक्सेशन के बिना 12.5% की नई कम दर या इंडेक्सेशन लाभों के साथ पुरानी 20% दर के बीच चयन करने की अनुमति मिलती है।
- वित्त मंत्री निर्मला सीतारमण ने कर सरलीकरण और निवेश प्रोत्साहन पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हुए बजट प्रस्तावों का बचाव किया।
- बीमा प्रीमियम पर जीएसटी को लेकर विपक्ष के विरोध के कारण सदन से बहिर्गमन हुआ।
वित्त विधेयक क्या है?
- परिभाषा और उद्देश्य
- परिचय: वित्त विधेयक वित्त मंत्री द्वारा प्रस्तुत केंद्रीय बजट के बाद लोकसभा में पेश किया जाता है। इसमें आगामी वित्तीय वर्ष के लिए वित्तीय प्रस्ताव शामिल होते हैं।
- संसद द्वारा पारित होने और राष्ट्रपति द्वारा स्वीकृत होने के बाद, यह उस वर्ष के लिए वित्त अधिनियम बन जाता है, जो प्रभावी रूप से बजटीय उपायों को कानूनी बल देता है।
वित्तीय विधेयकों के टाइप
- टाइप (I) – अनुच्छेद 117 (1)
- दायरा: इसमें धन विधेयक और सामान्य कानून दोनों से संबंधित मामले शामिल हैं।
- परिचय: राष्ट्रपति की सिफारिश के साथ केवल लोकसभा में ही पेश किया जा सकता है।
- विधायी प्रक्रिया:
- राज्यसभा संशोधन सुझा सकती है, जिसे लोकसभा स्वीकार या अस्वीकार कर सकती है।
- गतिरोध की स्थिति में, राष्ट्रपति द्वारा दोनों सदनों की संयुक्त बैठक बुलाई जा सकती है।
- राष्ट्रपति विधेयक को स्वीकृति दे सकते हैं, स्वीकृति रोक सकते हैं या पुनर्विचार के लिए वापस कर सकते हैं।
- टाइप (II) – अनुच्छेद 117 (3)
- कार्यक्षेत्र: भारत की संचित निधि से व्यय से संबंधित प्रावधानों से संबंधित है, लेकिन इसमें धन विधेयक मामले शामिल नहीं हैं।
- परिचय: संसद के किसी भी सदन में पेश किया जा सकता है।
- विधायी प्रक्रिया: सामान्य विधेयकों पर लागू प्रक्रियाओं द्वारा शासित, विचार के लिए राष्ट्रपति की सिफारिश की आवश्यकता होती है।
धन विधेयक और वित्त विधेयक के बीच अंतर
| पहलू | धन विधेयक | वित्त विधेयक |
| परिभाषा | इसमें विशेष रूप से कराधान, सरकार द्वारा धन उधार लेने और भारत की संचित निधि से व्यय या प्राप्ति से संबंधित प्रावधान शामिल हैं। | कराधान से संबंधित प्रावधानों सहित वित्तीय मामलों की एक व्यापक श्रेणी को शामिल करता है, लेकिन इसमें सामान्य कानून या व्यय भी शामिल हो सकते हैं जो समेकित निधि से सख्ती से संबंधित नहीं हैं। |
| परिचय | केवल लोकसभा में ही प्रस्तुत किया जा सकता है। | टाइप (I) को केवल लोकसभा में पेश किया जा सकता है। टाइप (II) को किसी भी सदन में पेश किया जा सकता है। |
| प्रमाणन | लोकसभा अध्यक्ष द्वारा धन विधेयक के रूप में प्रमाणित। | धन विधेयक के रूप में प्रमाणित नहीं है। |
| राज्यसभा की भूमिका | धन विधेयक में संशोधन या अस्वीकृति नहीं की जा सकती। | टाइप (I) में संशोधन की सिफारिश कर सकता है; टाइप (II) को एक साधारण विधेयक की तरह माना जाता है। |
| अनुमोदन प्रक्रिया | लोकसभा द्वारा पारित किया जाना चाहिए और सिफारिशों के लिए राज्यसभा को भेजा जा सकता है। लोकसभा राज्यसभा की सिफारिशों को अस्वीकार कर सकती है। यदि 14 दिनों के भीतर राज्यसभा द्वारा इस पर कार्रवाई नहीं की जाती है, तो इसे पारित माना जाता है। | दोनों सदनों द्वारा पारित किया जाना चाहिए। असहमति के मामले में, टाइप (I) के लिए राष्ट्रपति द्वारा दोनों सदनों की संयुक्त बैठक बुलाई जा सकती है। टाइप (II) सामान्य विधेयक प्रक्रियाओं का पालन करता है। |
| राष्ट्रपति की सिफारिश | लोकसभा में प्रस्तुत करने के लिए आवश्यक। | टाइप (I) के लिए आवश्यक; टाइप (II) के लिए आवश्यक नहीं है। |
| संशोधन | राज्यसभा द्वारा किसी संशोधन की अनुमति नहीं। | राज्यसभा टाइप (I) के लिए संशोधन सुझा सकती है; टाइप (II) सामान्य विधेयक प्रक्रियाओं का पालन करता है। |
| गतिरोध समाधान | संयुक्त बैठक का कोई प्रावधान नहीं; लोकसभा का निर्णय अंतिम होता है। | राष्ट्रपति टाइप (I) के लिए दोनों सदनों की संयुक्त बैठक बुला सकते हैं। टाइप (II) को सामान्य विधायी प्रक्रियाओं के माध्यम से हल किया जाता है। |
Tiny bones shed light on mystery ‘hobbits’ / छोटी हड्डियों ने रहस्यमयी ‘हॉबिट्स’ पर प्रकाश डाला
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
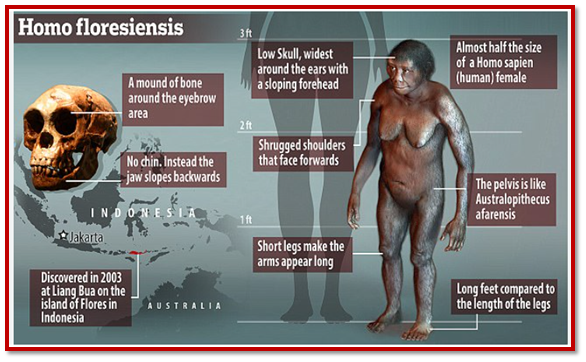
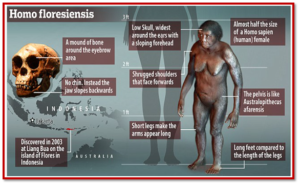
Recent findings from Flores Island reveal that Homo floresiensis, previously thought to be about 1.06 metres tall, were only around one metre tall 700,000 years ago.
- This suggests that they evolved from larger Homo erectus, adapting through island dwarfism after reaching the island via deep-sea migration.
Analysis of the news:
- Discovery: A tiny upper arm bone and some teeth from Homo floresiensis were found on Flores Island, Indonesia, providing new insights into their size evolution.
- Significance: The arm bone is identified as the smallest humerus fossil of an adult hominin ever discovered.
- New Findings: The fossils suggest that Homo floresiensis stood about one metre tall around 700,000 years ago, which is smaller than previous estimates of around 1.06 metres.
- Previous Estimates: Earlier findings, including teeth and jawbones from around 60,000 years ago, had indicated a height of approximately 1.06 metres.
- Evolutionary Debate: Two main theories exist:
- Theory 1: Homo floresiensis evolved from a small hominin that arrived on Flores about a million years ago.
- Theory 2: Homo erectus, a larger hominin, arrived on the island, and through island dwarfism, evolved into the smaller Homo floresiensis over the next 300,000 years.
- Island Dwarfism: The phenomenon where larger animals reduce in size due to limited resources and space on isolated islands.
- About other animals: Other small mammals, including a cow-sized relative of the elephant, were also present on the island.
- Migration Hypothesis: It is suggested that Homo erectus may have reached Flores by crossing deep-sea barriers, potentially using natural debris for rafting.
- Survival: Once isolated, these hominins adapted and evolved into distinct forms, surviving on the island for hundreds of thousands of years.
छोटी हड्डियों ने रहस्यमयी ‘हॉबिट्स’ पर प्रकाश डाला
फ्लोरेस द्वीप से प्राप्त हालिया खोजों से पता चलता है कि होमो फ्लोरेसेंसिस, जिसे पहले लगभग 1.06 मीटर लंबा माना जाता था, 700,000 साल पहले केवल एक मीटर लंबा था।
- इससे पता चलता है कि वे बड़े होमो इरेक्टस से विकसित हुए, गहरे समुद्र में प्रवास के माध्यम से द्वीप पर पहुंचने के बाद द्वीप बौनेपन के माध्यम से अनुकूलन किया।
समाचार का विश्लेषण:
- खोज: इंडोनेशिया के फ्लोरेस द्वीप पर होमो फ्लोरेसेंसिस की एक छोटी सी ऊपरी बांह की हड्डी और कुछ दांत पाए गए, जिससे उनके आकार के विकास के बारे में नई जानकारी मिली।
- महत्व: बांह की हड्डी की पहचान वयस्क होमिनिन के अब तक खोजे गए सबसे छोटे ह्यूमरस जीवाश्म के रूप में की गई है।
- नए निष्कर्ष: जीवाश्मों से पता चलता है कि होमो फ्लोरेसेंसिस लगभग 700,000 साल पहले लगभग एक मीटर लंबा था, जो पिछले अनुमानों के लगभग 06 मीटर से छोटा है।
- पिछले अनुमान: लगभग 60,000 साल पहले के दांतों और जबड़े की हड्डियों सहित पहले के निष्कर्षों ने लगभग 06 मीटर की ऊंचाई का संकेत दिया था।
विकासवादी बहस: दो मुख्य सिद्धांत मौजूद हैं:
-
- सिद्धांत 1: होमो फ्लोरेसेंसिस एक छोटे होमिनिन से विकसित हुआ जो लगभग दस लाख साल पहले फ्लोरेस पर आया था।
- सिद्धांत 2: होमो इरेक्टस, एक बड़ा होमिनिन, द्वीप पर आया, और द्वीप बौनेपन के माध्यम से, अगले 300,000 वर्षों में छोटे होमो फ्लोरेसेंसिस में विकसित हुआ।
- द्वीप बौनापन: वह घटना जिसमें अलग-थलग द्वीपों पर सीमित संसाधनों और स्थान के कारण बड़े जानवर आकार में कम हो जाते हैं।
- अन्य जानवरों के बारे में: हाथी के एक गाय के आकार के रिश्तेदार सहित अन्य छोटे स्तनधारी भी द्वीप पर मौजूद थे।
- प्रवास परिकल्पना: यह सुझाव दिया जाता है कि होमो इरेक्टस संभवतः राफ्टिंग के लिए प्राकृतिक मलबे का उपयोग करके गहरे समुद्र की बाधाओं को पार करके फ्लोरेस तक पहुँच सकता है।
- अस्तित्व: एक बार अलग-थलग पड़ने के बाद, ये होमिनिन अनुकूलित हुए और अलग-अलग रूपों में विकसित हुए, सैकड़ों हज़ारों वर्षों तक द्वीप पर जीवित रहे।
After artificial intelligence, quantum computing eyes its big breakthrough moment / कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता के बाद, क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग अपनी बड़ी सफलता की ओर देख रही है
Syllabus : GS 3: Science and Technology
Source : The Hindu
The news highlights the transformative potential of quantum computing, focusing on Riverlane’s advancements with its quantum decoder chip.
- It underscores the challenges of scaling up and error correction, while major tech companies invest heavily, signaling future regulatory considerations and profound technological impacts.
Overview of Quantum Computing:
- Technological Promise:
- Quantum computing is poised to revolutionise fields such as drug development and climate change by performing tasks beyond the capabilities of conventional computers.
- Riverlane, a Cambridge-based company, is at the forefront with its quantum decoder chip, which addresses error correction issues inherent in quantum computing.
Key Components and Concepts
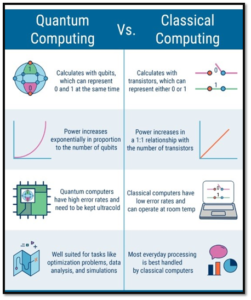
- Quantum Bits (Qubits):
- Unlike classical bits (0 or 1), qubits can represent all values between 0 and 1 simultaneously, similar to dimmer switches versus simple on/off states.
- This capability allows quantum computers to handle a vast amount of information, making them suitable for simulating complex quantum systems.
- Error Correction and Control:
- Quantum systems require precise control over qubits due to their susceptibility to errors and noise.
- Effective error correction is crucial for reliable quantum computing, with ongoing research focusing on shielding hardware and developing algorithms to manage errors.
Current Limitations and Challenges
- Operation Scale:
- Present-day quantum computers can manage approximately 1,000 operations before errors overwhelm them.
- The challenge lies in scaling up the technology while maintaining accuracy and integrating error correction.
- Exponential Growth:
- The benefits of quantum computing increase exponentially with the scale of the machine, allowing it to tackle increasingly complex problems.
- However, the number of components and time required for operations also grows, presenting scalability challenges.
Industry and Regulatory Impact
- Major Investments:
- Leading tech companies, including Google, IBM, Microsoft, and Amazon, are heavily investing in quantum technology, focusing on qubit generation and error reduction.
- This competitive investment underscores the significant potential and importance of quantum computing.
- Regulatory Considerations:
- With quantum computing’s potential to disrupt current cryptographic systems and create new materials, there is a growing need for regulatory frameworks.
- The technology’s implications are prompting regulators to anticipate and address future challenges, learning from past experiences with technologies like AI.
Future Outlook
- Progress and Potential:
- The quality of qubits has improved, making this an exciting time for quantum technology. The primary challenge remains scaling up and integrating effective error correction.
- Quantum computing is expected to solve problems that are currently unsolvable, driving further research and development in the field.
कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता के बाद, क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग अपनी बड़ी सफलता की ओर देख रही है
यह खबर क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग की परिवर्तनकारी क्षमता पर प्रकाश डालती है, जिसमें रिवरलेन की क्वांटम डिकोडर चिप के साथ प्रगति पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया गया है।
- यह स्केलिंग और त्रुटि सुधार की चुनौतियों को रेखांकित करता है, जबकि प्रमुख तकनीकी कंपनियाँ भारी निवेश करती हैं, जो भविष्य के विनियामक विचारों और गहन तकनीकी प्रभावों का संकेत देता है।
क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग का अवलोकन:
- तकनीकी वादा:
- क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग पारंपरिक कंप्यूटरों की क्षमताओं से परे कार्य करके दवा विकास और जलवायु परिवर्तन जैसे क्षेत्रों में क्रांति लाने के लिए तैयार है।
- कैम्ब्रिज स्थित कंपनी रिवरलेन अपने क्वांटम डिकोडर चिप के साथ सबसे आगे है, जो क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग में निहित त्रुटि सुधार मुद्दों को संबोधित करती है।
मुख्य घटक और अवधारणाएँ
- क्वांटम बिट्स (क्यूबिट्स):
- शास्त्रीय बिट्स (0 या 1) के विपरीत, क्यूबिट्स 0 और 1 के बीच सभी मानों को एक साथ दर्शा सकते हैं, डिमर स्विच बनाम सरल ऑन/ऑफ अवस्थाओं के समान।
- यह क्षमता क्वांटम कंप्यूटरों को बहुत अधिक जानकारी संभालने की अनुमति देती है, जिससे वे जटिल क्वांटम सिस्टम को सिम्युलेट करने के लिए उपयुक्त हो जाते हैं।
- त्रुटि सुधार और नियंत्रण:
- क्वांटम सिस्टम को त्रुटियों और शोर के प्रति उनकी संवेदनशीलता के कारण क्यूबिट्स पर सटीक नियंत्रण की आवश्यकता होती है।
- विश्वसनीय क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग के लिए प्रभावी त्रुटि सुधार महत्वपूर्ण है, जिसमें चल रहे शोध में हार्डवेयर को ढालने और त्रुटियों को प्रबंधित करने के लिए एल्गोरिदम विकसित करने पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया गया है।
वर्तमान सीमाएँ और चुनौतियाँ
- ऑपरेशन स्केल:
- वर्तमान क्वांटम कंप्यूटर त्रुटियों से अभिभूत होने से पहले लगभग 1,000 ऑपरेशन प्रबंधित कर सकते हैं।
- चुनौती सटीकता बनाए रखते हुए और त्रुटि सुधार को एकीकृत करते हुए तकनीक को बढ़ाने में निहित है।
- घातीय वृद्धि:
- क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग के लाभ मशीन के पैमाने के साथ तेजी से बढ़ते हैं, जिससे यह तेजी से जटिल समस्याओं से निपटने में सक्षम होता है।
- हालांकि, संचालन के लिए आवश्यक घटकों और समय की संख्या भी बढ़ती है, जिससे स्केलेबिलिटी चुनौतियाँ सामने आती हैं।
उद्योग और नियामक प्रभाव
- प्रमुख निवेश:
- Google, IBM, Microsoft और Amazon सहित अग्रणी तकनीकी कंपनियाँ क्वांटम तकनीक में भारी निवेश कर रही हैं, जो कि क्यूबिट पीढ़ी और त्रुटि में कमी पर ध्यान केंद्रित कर रही हैं।
- यह प्रतिस्पर्धी निवेश क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग की महत्वपूर्ण क्षमता और महत्व को रेखांकित करता है।
- नियामक विचार:
- क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग की वर्तमान क्रिप्टोग्राफ़िक प्रणालियों को बाधित करने और नई सामग्री बनाने की क्षमता के साथ, नियामक ढाँचों की बढ़ती आवश्यकता है।
- प्रौद्योगिकी के निहितार्थ नियामकों को भविष्य की चुनौतियों का अनुमान लगाने और उनका समाधान करने के लिए प्रेरित कर रहे हैं, AI जैसी तकनीकों के साथ पिछले अनुभवों से सीख रहे हैं।
भविष्य का दृष्टिकोण
- प्रगति और संभावनाएँ:
- क्यूबिट की गुणवत्ता में सुधार हुआ है, जिससे क्वांटम प्रौद्योगिकी के लिए यह एक रोमांचक समय बन गया है। प्राथमिक चुनौती प्रभावी त्रुटि सुधार को बढ़ाना और एकीकृत करना है।
- क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग से ऐसी समस्याओं को हल करने की उम्मीद है जो वर्तमान में हल नहीं हो पा रही हैं, जिससे इस क्षेत्र में आगे अनुसंधान और विकास को बढ़ावा मिलेगा।
Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve / गुरु घासीदास-तमोर पिंगला टाइगर रिजर्व
Location In News
Chhattisgarh has approved the creation of the Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve, the third largest in India.
Chhattisgarh cleared a proposal to notify a new tiger reserve
- Chhattisgarh has approved the creation of the Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve – the third largest in the country (spanning 2,829 square kilometres).
- Andhra Pradesh’s Nagarjunasagar Srisailam Tiger Reserve is the country’s largest tiger reserve, covering 3,296.31 sq km.
- Manas Tiger Reserve in Assam is the second largest with an area of 2,837.1 sq km. Both have 58 tigers.
- The decision comes after the Chhattisgarh High Court granted four weeks to the state government to clear its stand on declaring that area a tiger reserve.
Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve
- The combined areas of the Guru Ghasidas National Park and Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary has been declared as a Tiger Reserve.
- The newly created reserve integrates an existing national park with a wildlife sanctuary.
- It is located in the northern part of the state, bordering Madhya Pradesh and Jharkhand.
- Guru Ghasidas National Park – in Koriya district
- Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary – in Surajpur district of the state
- This region is located in the districts of Manendragarh-Chirmiri-Bharatpur, Koriya, Surajpur and Balrampur.
- This will be the fourth Tiger Reserve in Chhattisgarh, after the Udanti-Sitanadi, Achanakmar, and Indravati Reserves.
Process of notification of Tiger Reserves
- Tiger Reserves are notified by State Governments as per provisions of Section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 on advice of the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- The following steps are involved in the notification:
- Proposal is obtained from the State.
- In-principle approval is communicated from the National Tiger Conservation Authority, soliciting detailed proposals under section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- National Tiger Conservation Authority recommends the proposal to the State after due diligence.
- The State Government notifies the area as a Tiger Reserve.
Can tiger reserves be altered and de-notified?
- These processes are governed by Section 38W of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Regarding de-notification, it says:
- No alteration in the boundaries of a tiger reserve shall be made except on a recommendation of the Tiger Conservation Authority and the approval of the National Board for Wild Life.
- No State Government shall de-notify a tiger reserve, except in public interest with the approval of the Tiger Conservation Authority and the National Board for Wild Life.
गुरु घासीदास-तमोर पिंगला टाइगर रिजर्व
छत्तीसगढ़ ने भारत में तीसरा सबसे बड़ा गुरु घासीदास-तमोर पिंगला टाइगर रिजर्व बनाने को मंजूरी दे दी है।
छत्तीसगढ़ ने एक नए बाघ अभयारण्य को अधिसूचित करने के प्रस्ताव को मंजूरी दी
- छत्तीसगढ़ ने गुरु घासीदास-तमोर पिंगला टाइगर रिजर्व के निर्माण को मंजूरी दे दी है – जो देश का तीसरा सबसे बड़ा (2,829 वर्ग किलोमीटर में फैला हुआ) है।
- आंध्र प्रदेश का नागार्जुनसागर श्रीशैलम टाइगर रिजर्व देश का सबसे बड़ा बाघ अभयारण्य है, जो 3,296.31 वर्ग किलोमीटर में फैला हुआ है।
- असम का मानस टाइगर रिजर्व 2,837.1 वर्ग किलोमीटर के क्षेत्रफल के साथ दूसरा सबसे बड़ा है। दोनों में 58 बाघ हैं।
- छत्तीसगढ़ उच्च न्यायालय द्वारा राज्य सरकार को उस क्षेत्र को बाघ अभयारण्य घोषित करने पर अपना रुख स्पष्ट करने के लिए चार सप्ताह का समय दिए जाने के बाद यह निर्णय लिया गया है।
गुरु घासीदास-तमोर पिंगला टाइगर रिजर्व
- गुरु घासीदास राष्ट्रीय उद्यान और तमोर पिंगला वन्यजीव अभयारण्य के संयुक्त क्षेत्र को बाघ अभयारण्य घोषित किया गया है।
- नए बनाए गए इस रिजर्व में मौजूदा राष्ट्रीय उद्यान को वन्यजीव अभयारण्य के साथ एकीकृत किया गया है।
- यह राज्य के उत्तरी भाग में स्थित है, जो मध्य प्रदेश और झारखंड की सीमा पर है।
- गुरु घासीदास राष्ट्रीय उद्यान – कोरिया जिले में
- तमोर पिंगला वन्यजीव अभ्यारण्य – राज्य के सूरजपुर जिले में
- यह क्षेत्र मनेंद्रगढ़-चिरमिरी-भरतपुर, कोरिया, सूरजपुर और बलरामपुर जिलों में स्थित है।
- उदंती-सीतानदी, अचानकमार और इंद्रावती रिजर्व के बाद यह छत्तीसगढ़ का चौथा टाइगर रिजर्व होगा।
टाइगर रिजर्व की अधिसूचना की प्रक्रिया
- राष्ट्रीय बाघ संरक्षण प्राधिकरण की सलाह पर वन्यजीव (संरक्षण) अधिनियम, 1972 की धारा 38V के प्रावधानों के अनुसार राज्य सरकारों द्वारा टाइगर रिजर्व को अधिसूचित किया जाता है।
- अधिसूचना में निम्नलिखित चरण शामिल हैं:
- राज्य से प्रस्ताव प्राप्त किया जाता है।
- वन्यजीव (संरक्षण) अधिनियम, 1972 की धारा 38V के तहत विस्तृत प्रस्ताव मांगते हुए राष्ट्रीय बाघ संरक्षण प्राधिकरण से सैद्धांतिक मंजूरी प्राप्त की जाती है।
- राष्ट्रीय बाघ संरक्षण प्राधिकरण उचित जांच के बाद राज्य को प्रस्ताव की सिफारिश करता है।
- राज्य सरकार क्षेत्र को बाघ अभयारण्य के रूप में अधिसूचित करती है।
क्या बाघ अभयारण्यों को बदला और विमुक्त किया जा सकता है?
- ये प्रक्रियाएँ वन्यजीव (संरक्षण) अधिनियम, 1972 की धारा 38W द्वारा शासित होती हैं।
- विमुक्ति के संबंध में, इसमें कहा गया है:
- बाघ संरक्षण प्राधिकरण की सिफारिश और राष्ट्रीय वन्य जीव बोर्ड की स्वीकृति के अलावा बाघ अभयारण्य की सीमाओं में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं किया जाएगा।
- कोई भी राज्य सरकार बाघ संरक्षण प्राधिकरण और राष्ट्रीय वन्य जीव बोर्ड की स्वीकृति के साथ सार्वजनिक हित में छोड़कर बाघ अभयारण्य को विमुक्त नहीं करेगी।
Court shifts the tide on stray dog policy / कोर्ट ने आवारा कुत्तों की नीति पर रुख बदला
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 : Governance & Social Justice : Health & Education
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- The Supreme Court ruled against indiscriminate killing of stray dogs, favouring sterilisation per the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960, and the new ABC Rules, 2023.
- This judgement emphasises constitutional compassion, scientific temper, and humanism, supporting humane population control methods endorsed by WHO, over unscientific culling practices.
Supreme Court Ruling on Stray Dogs Case
- The Supreme Court of India delivered a final judgement on a 15-year-old case titled Animal Welfare Board of India & Anr Versus People for Elimination of Stray Troubles & Ors, also known as the All India Stray Dogs case or AWBI vs. PEST.
- The case concerned the rights of municipal and local authorities to cull stray dogs to manage populations and prevent rabies and human-animal conflicts.
- The judgement, delivered on July 12, has drawn both praise and criticism.
Central vs. State and Municipal Laws
- The legal conflict was between State and Municipal laws, which allowed the killing of stray dogs, and Central laws, specifically the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (PCA) Act, 1960, and the Animal Birth Control (ABC) Rules, 2001, which prohibited such actions.
- Various High Courts had differing opinions, with some supporting local authority discretion to kill stray dogs, while others emphasised adherence to Central laws.
Supreme Court’s Final Mandate
- The Supreme Court acknowledged changes in the legislative landscape, particularly with the introduction of the new Animal Birth Control (ABC) Rules, 2023, which align with the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (PCA) Act, 1960, to prohibit wanton killing and promote sterilisation.
- It directed that the governing law should remain the Central law (PCA Act 1960 and ABC Rules, 2023), prohibiting the killing of stray dogs.
- Parties with grievances regarding the new laws can challenge them in the relevant High Courts.
Constitutional Compassion and Duties
- The judgement highlighted the constitutional value of compassion towards all living beings, referring to Article 51A(g) of the Indian Constitution, which mandates citizens to protect and improve the environment and show compassion for living creatures.
Scientific Approach to Stray Dog Management
- The Supreme Court endorsed the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recommendation for sterilisation as the only effective and humane method to control stray dog populations.
- A 2014 report by the Bombay Municipal Corporation supported sterilisation over killing, citing it as the only scientific solution.
- Historical data showed that killing stray dogs did not effectively reduce populations; for example, the Bombay Municipality killed 4.5 lakh stray dogs between 1984 and 1994 without reducing their numbers.
Promoting Scientific Temper and Humanism
- The article argues for adopting scientific methods and humanism, as promoted by Article 51A(h) of the Constitution, over unscientific and inhumane practices like culling stray dogs.
- The importance of maintaining the bond between humans and dogs, domesticated around 10,000 years ago, is emphasised.
- The Supreme Court’s decision is portrayed as a positive step towards a humane and scientifically backed approach to managing stray dog populations.
Article 51A(g) of the Indian Constitution
- Article 51A(g) of the Indian Constitution mandates that it is the duty of every Indian citizen to protect and improve the natural environment, including forests, lakes, rivers, and wildlife, and to show compassion for all living creatures.
- It emphasises environmental stewardship and ethical treatment of animals.
Article 51A(h) of the Indian Constitution
- Article 51A(h) of the Indian Constitution stipulates that it is the duty of every citizen to develop a scientific temper, humanism, and the spirit of inquiry and reform.
- It emphasises fostering a rational and humane approach to societal issues, including respect for science and human values.
The Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (PCA) Act, 1960, and the Animal Birth Control (ABC) Rules are:
- The PCA Act, 1960 was enacted by the Parliament of India to prevent the infliction of unnecessary pain or suffering on animals and to amend the laws relating to the prevention of cruelty to animals.
- The PCA Act, 1960 and ABC Rules, 2001 prohibit the killing of stray dogs and mandate sterilization as the only scientific and humane method of controlling stray dog populations.
- The new ABC Rules, 2023 notified under the PCA Act, 1960 also prohibit wanton killing of stray dogs by municipalities and require them to follow sterilization.
- The Act defines “animal” as any living creature other than a human being. It establishes the Animal Welfare Board of India to promote animal welfare.
- Chapter III of the Act lists different forms of cruelty to animals that are banned, including those related to work animals, captivity, ownership, abuse, mutilation or killing.
- Chapter IV deals with experiments on animals. While it does not make experiments unlawful for the advancement of knowledge, it allows the Board to advise the government to create a committee to control and supervise such experiments.
- Chapter V outlines restrictions, procedures and offences related to performing animals. The Central Government can prohibit any animal from exhibition or training through notification.
Note: In 2022, the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying submitted a draft Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (Amendment) Bill 2022 for public comment. The draft includes 61 amendments to further clarify the law and make punishments more stringent.
Issues due to stray dogs in India:
- Population: India has an estimated 60 million stray dogs, making it the country with the highest number of stray dogs globally.
- Rabies Incidence: India accounts for 36% of global rabies deaths and 65% of rabies deaths in the South-East Asia region.
- Between 2012 and 2022, the National Rabies Control Program reported 6,644 clinically suspected cases of rabies in humans.
- Dog Bite Cases: Reports indicate that major cities have seen alarming numbers of dog bite incidents. For example, Delhi’s Safdarjung Hospital and Ram Manohar Lohia Hospital recorded nearly 48,000 dog bite cases in just six months. In Kerala alone, there were over 1.9 lakh dog bite cases last year, with 21 deaths attributed to rabies.
Way forward:
- Enhanced Public Awareness and Education: Need to implement nationwide campaigns to educate the public on responsible pet ownership, the importance of sterilization, and the humane treatment of stray dogs.
- Strengthening Enforcement of Existing Laws: Need to ensure that municipalities and local authorities are adequately trained and funded to implement the ABC Rules effectively.
कोर्ट ने आवारा कुत्तों की नीति पर रुख बदला
संदर्भ:
- सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने आवारा कुत्तों की अंधाधुंध हत्या के खिलाफ फैसला सुनाया, तथा पशु क्रूरता निवारण अधिनियम, 1960 और नए ABC नियम, 2023 के अनुसार नसबंदी का पक्ष लिया।
- यह फैसला संवैधानिक करुणा, वैज्ञानिक सोच और मानवतावाद पर जोर देता है, तथा अवैज्ञानिक तरीके से कुत्तों को मारने की प्रथाओं के बजाय WHO द्वारा समर्थित मानवीय जनसंख्या नियंत्रण विधियों का समर्थन करता है।
आवारा कुत्तों के मामले पर सुप्रीम कोर्ट का फैसला
- भारत के सुप्रीम कोर्ट ने 15 साल पुराने एक मामले पर अंतिम फैसला सुनाया, जिसका शीर्षक था एनिमल वेलफेयर बोर्ड ऑफ इंडिया एंड एन.आर. बनाम पीपुल फॉर एलिमिनेशन ऑफ स्ट्रे ट्रबल एंड ऑर्स, जिसे ऑल इंडिया स्ट्रे डॉग्स केस या AWBI बनाम PEST के नाम से भी जाना जाता है।
- यह मामला नगरपालिका और स्थानीय अधिकारियों के अधिकारों से संबंधित था, ताकि आवारा कुत्तों की आबादी को नियंत्रित किया जा सके और रेबीज तथा मानव-पशु संघर्ष को रोका जा सके।
- 12 जुलाई को सुनाए गए इस फैसले की प्रशंसा और आलोचना दोनों हुई।
केंद्रीय बनाम राज्य और नगरपालिका कानून
- कानूनी संघर्ष राज्य और नगरपालिका कानूनों के बीच था, जो आवारा कुत्तों को मारने की अनुमति देते थे, और केंद्रीय कानून, विशेष रूप से पशु क्रूरता निवारण (पीसीए) अधिनियम, 1960, और पशु जन्म नियंत्रण (एबीसी) नियम, 2001, जो इस तरह की कार्रवाइयों को प्रतिबंधित करते थे।
- विभिन्न उच्च न्यायालयों की अलग-अलग राय थी, जिनमें से कुछ ने आवारा कुत्तों को मारने के लिए स्थानीय प्राधिकरण के विवेक का समर्थन किया, जबकि अन्य ने केंद्रीय कानूनों के पालन पर जोर दिया।
सर्वोच्च न्यायालय का अंतिम आदेश
- सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने विधायी परिदृश्य में बदलावों को स्वीकार किया, विशेष रूप से नए पशु जन्म नियंत्रण (एबीसी) नियम, 2023 की शुरूआत के साथ, जो पशु क्रूरता निवारण (पीसीए) अधिनियम, 1960 के साथ संरेखित है, जो बेवजह हत्या को प्रतिबंधित करता है और नसबंदी को बढ़ावा देता है।
- इसने निर्देश दिया कि शासकीय कानून केंद्रीय कानून (पीसीए अधिनियम 1960 और एबीसी नियम, 2023) बना रहना चाहिए, जो आवारा कुत्तों को मारने पर रोक लगाता है।
- नए कानूनों के बारे में शिकायत करने वाले पक्ष उन्हें संबंधित उच्च न्यायालयों में चुनौती दे सकते हैं।
संवैधानिक करुणा और कर्तव्य
- निर्णय में भारतीय संविधान के अनुच्छेद 51ए(जी) का हवाला देते हुए सभी जीवित प्राणियों के प्रति करुणा के संवैधानिक मूल्य पर प्रकाश डाला गया, जो नागरिकों को पर्यावरण की रक्षा और सुधार करने तथा जीवित प्राणियों के प्रति करुणा दिखाने का आदेश देता है।
आवारा कुत्तों के प्रबंधन के लिए वैज्ञानिक दृष्टिकोण
- सर्वोच्च न्यायालय ने आवारा कुत्तों की आबादी को नियंत्रित करने के लिए एकमात्र प्रभावी और मानवीय विधि के रूप में नसबंदी के लिए विश्व स्वास्थ्य संगठन (डब्ल्यूएचओ) की सिफारिश का समर्थन किया।
- बॉम्बे नगर निगम की 2014 की एक रिपोर्ट ने इसे एकमात्र वैज्ञानिक समाधान बताते हुए हत्या के बजाय नसबंदी का समर्थन किया।
- ऐतिहासिक डेटा से पता चला है कि आवारा कुत्तों को मारने से आबादी में प्रभावी रूप से कमी नहीं आई; उदाहरण के लिए, बॉम्बे नगर पालिका ने 1984 और 1994 के बीच 5 लाख आवारा कुत्तों को उनकी संख्या कम किए बिना मार दिया।
वैज्ञानिक दृष्टिकोण और मानवतावाद को बढ़ावा देना
- लेख में संविधान के अनुच्छेद 51ए(एच) द्वारा प्रचारित वैज्ञानिक तरीकों और मानवतावाद को अपनाने का तर्क दिया गया है, जो आवारा कुत्तों को मारने जैसी अवैज्ञानिक और अमानवीय प्रथाओं पर आधारित है।
- लगभग 10,000 साल पहले पालतू बनाए गए कुत्तों और मनुष्यों के बीच के बंधन को बनाए रखने के महत्व पर जोर दिया गया है।
- सुप्रीम कोर्ट के फैसले को आवारा कुत्तों की आबादी के प्रबंधन के लिए मानवीय और वैज्ञानिक रूप से समर्थित दृष्टिकोण की दिशा में एक सकारात्मक कदम के रूप में चित्रित किया गया है।
भारतीय संविधान का अनुच्छेद 51ए(जी)
- भारतीय संविधान का अनुच्छेद 51ए(जी) यह अनिवार्य करता है कि प्रत्येक भारतीय नागरिक का कर्तव्य है कि वह वन, झील, नदी और वन्यजीवों सहित प्राकृतिक पर्यावरण की रक्षा और सुधार करे तथा सभी जीवित प्राणियों के प्रति दया दिखाए।
- यह पर्यावरण संरक्षण और पशुओं के प्रति नैतिक व्यवहार पर जोर देता है।
भारतीय संविधान का अनुच्छेद 51ए(एच)
- भारतीय संविधान का अनुच्छेद 51ए(एच) यह निर्धारित करता है कि प्रत्येक नागरिक का कर्तव्य है कि वह वैज्ञानिक दृष्टिकोण, मानवतावाद और जांच और सुधार की भावना विकसित करे।
- यह विज्ञान और मानवीय मूल्यों के सम्मान सहित सामाजिक मुद्दों के प्रति तर्कसंगत और मानवीय दृष्टिकोण को बढ़ावा देने पर जोर देता है।
पशु क्रूरता निवारण (पीसीए) अधिनियम, 1960 और पशु जन्म नियंत्रण (एबीसी) नियम हैं:
- पीसीए अधिनियम, 1960 को भारत की संसद द्वारा पशुओं को अनावश्यक दर्द या पीड़ा पहुँचाने से रोकने और पशुओं के प्रति क्रूरता निवारण से संबंधित कानूनों में संशोधन करने के लिए अधिनियमित किया गया था।
- पीसीए अधिनियम, 1960 और एबीसी नियम, 2001 आवारा कुत्तों की हत्या पर रोक लगाते हैं और आवारा कुत्तों की आबादी को नियंत्रित करने के एकमात्र वैज्ञानिक और मानवीय तरीके के रूप में नसबंदी को अनिवार्य बनाते हैं।
- पीसीए अधिनियम, 1960 के तहत अधिसूचित नए एबीसी नियम, 2023 भी नगर पालिकाओं द्वारा आवारा कुत्तों की बेवजह हत्या पर रोक लगाते हैं और उन्हें नसबंदी का पालन करने की आवश्यकता होती है।
- अधिनियम में “पशु” को मनुष्य के अलावा किसी भी जीवित प्राणी के रूप में परिभाषित किया गया है। यह पशु कल्याण को बढ़ावा देने के लिए भारतीय पशु कल्याण बोर्ड की स्थापना करता है।
- अधिनियम के अध्याय III में जानवरों के प्रति क्रूरता के विभिन्न रूपों को सूचीबद्ध किया गया है, जो प्रतिबंधित हैं, जिनमें काम करने वाले जानवरों, कैद, स्वामित्व, दुर्व्यवहार, विकृति या हत्या से संबंधित हैं।
- अध्याय IV जानवरों पर प्रयोगों से संबंधित है। हालांकि यह ज्ञान के विकास के लिए प्रयोगों को गैरकानूनी नहीं बनाता है, लेकिन यह बोर्ड को ऐसे प्रयोगों को नियंत्रित करने और उनकी निगरानी करने के लिए सरकार को एक समिति बनाने की सलाह देने की अनुमति देता है।
- अध्याय V जानवरों के प्रदर्शन से संबंधित प्रतिबंधों, प्रक्रियाओं और अपराधों की रूपरेखा तैयार करता है। केंद्र सरकार अधिसूचना के माध्यम से किसी भी जानवर को प्रदर्शन या प्रशिक्षण से प्रतिबंधित कर सकती है।
नोट: 2022 में, मत्स्य पालन, पशुपालन और डेयरी मंत्रालय ने सार्वजनिक टिप्पणी के लिए पशुओं के प्रति क्रूरता निवारण (संशोधन) विधेयक 2022 का मसौदा प्रस्तुत किया। इस मसौदे में कानून को और स्पष्ट करने तथा दंड को और अधिक कठोर बनाने के लिए 61 संशोधन शामिल हैं।
भारत में आवारा कुत्तों के कारण होने वाली समस्याएँ:
- जनसंख्या: भारत में अनुमानित 60 मिलियन आवारा कुत्ते हैं, जो इसे दुनिया भर में सबसे ज़्यादा आवारा कुत्तों वाला देश बनाता है।
- रेबीज की घटनाएँ: भारत में वैश्विक रेबीज से होने वाली मौतों का 36% और दक्षिण-पूर्व एशिया क्षेत्र में रेबीज से होने वाली मौतों का 65% हिस्सा है।
- 2012 और 2022 के बीच, राष्ट्रीय रेबीज नियंत्रण कार्यक्रम ने मनुष्यों में रेबीज के 6,644 चिकित्सकीय रूप से संदिग्ध मामलों की सूचना दी।
- कुत्ते के काटने के मामले: रिपोर्ट बताती हैं कि प्रमुख शहरों में कुत्तों के काटने की घटनाओं की संख्या चिंताजनक है। उदाहरण के लिए, दिल्ली के सफ़दरजंग अस्पताल और राम मनोहर लोहिया अस्पताल ने सिर्फ़ छह महीनों में लगभग 48,000 कुत्तों के काटने के मामले दर्ज किए। अकेले केरल में, पिछले साल कुत्तों के काटने के 1.9 लाख से ज़्यादा मामले सामने आए, जिनमें से 21 मौतें रेबीज के कारण हुईं।
आगे की राह:
- बढ़ी हुई सार्वजनिक जागरूकता और शिक्षा: ज़िम्मेदार पालतू जानवरों के स्वामित्व, नसबंदी के महत्व और आवारा कुत्तों के साथ मानवीय व्यवहार के बारे में लोगों को शिक्षित करने के लिए राष्ट्रव्यापी अभियान लागू करने की ज़रूरत है।
- मौजूदा कानूनों के प्रवर्तन को मजबूत करना: यह सुनिश्चित करने की आवश्यकता है कि नगर पालिकाओं और स्थानीय प्राधिकारियों को एबीसी नियमों को प्रभावी ढंग से लागू करने के लिए पर्याप्त प्रशिक्षण और वित्त पोषण मिले।
United Nations (UN) / संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन)
International Organizations
- The United Nations (UN) is an international organization founded in 1945. It is currently made up of 193 Member States.

United Nations (UN) International Court of Justice
- The International Court of Justice is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations. It was established in June 1945 by the Charter of the United Nationsand began work in April 1946.
- The ICJ is the successor of the Permanent Court of International Justice (PCIJ), which was established by the League of Nations in 1920.
United Nations (UN) Secretariat
- The Secretariat comprises the Secretary-General and tens of thousands of international UN staff members who carry out the day-to-day work of the UN as mandated by the General Assembly and the Organization’s other principal organs.
- The Secretary-Generalis chief administrative officer of the Organization, appointed by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council for a five-year, renewable term.
- UN staff members are recruited internationally and locally, and work in duty stations and on peacekeeping missions all around the world.
United Nations (UN) Funds and Programmes
UNICEF:
- The United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF),originally known as the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund, was created by the United Nations General Assembly in 1946, to provide emergency food and healthcare to children and mothers in countries that had been devastated by World War II.
- In 1950,UNICEF’s mandate was extended to address the long-term needs of children and women in developing countries
- In 1953, it became a permanent part of the United Nations System, and the words “international” and “emergency” were dropped from the organization’s name, though it retained the original acronym, “UNICEF”.
- Executive Board:A 36-member board establishes policies, approves programs and oversees administrative and financial plans. The members are government representatives who are elected by the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), usually for three-year terms.
- UNICEF relies on contributions from governments and private donors.
- UNICEF’s Supply Division Is based in Copenhagen (Denmark) and serves as the primary point of distribution for such essential items as vaccines, antiretroviral medicines for children and mothers with HIV, nutritional supplements, emergency shelters, family reunification, and educational supplies.
UNFPA:
- The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA),formerly the United Nations Fund for Population Activities, is the United Nations sexual and reproductive health agency.
- Its mission is to deliver a world where every pregnancy is wanted, ‘every childbirth is safe’ and every young person’s potential is fulfilled.
- In 2018, UNFPA launched efforts to achieve three transformative results, ambitions that promise to change the world for every man, woman and young person:
- Ending unmet need for family planning
- Ending preventable maternal death
- Ending gender-based violence and harmful practices
Will be continue…
संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन)
अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संगठन
- संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन) एक अंतरराष्ट्रीय संगठन है जिसकी स्थापना 1945 में हुई थी। वर्तमान में इसके 193 सदस्य देश हैं।
संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन) अंतर्राष्ट्रीय न्यायालय
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय न्यायालय संयुक्त राष्ट्र का प्रमुख न्यायिक अंग है। इसकी स्थापना जून 1945 में संयुक्त राष्ट्र के चार्टर द्वारा की गई थी और इसने अप्रैल 1946 में काम करना शुरू किया था।
- आईसीजे, स्थायी अंतर्राष्ट्रीय न्याय न्यायालय (पीसीआईजे) का उत्तराधिकारी है, जिसे 1920 में राष्ट्र संघ द्वारा स्थापित किया गया था।
संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन) सचिवालय
- सचिवालय में महासचिव और यूएन के हज़ारों अंतरराष्ट्रीय कर्मचारी शामिल होते हैं जो महासभा और संगठन के अन्य प्रमुख अंगों द्वारा अधिदेशित यूएन के दिन-प्रतिदिन के काम को अंजाम देते हैं।
- महासचिव संगठन का मुख्य प्रशासनिक अधिकारी होता है, जिसे सुरक्षा परिषद की सिफारिश पर महासभा द्वारा पाँच साल के नवीकरणीय कार्यकाल के लिए नियुक्त किया जाता है।
- यूएन के कर्मचारी अंतरराष्ट्रीय और स्थानीय स्तर पर भर्ती किए जाते हैं और दुनिया भर में ड्यूटी स्टेशनों और शांति अभियानों पर काम करते हैं।
संयुक्त राष्ट्र (यूएन) कोष और कार्यक्रम
यूनिसेफ:
- संयुक्त राष्ट्र बाल कोष (यूनिसेफ), जिसे मूल रूप से संयुक्त राष्ट्र अंतर्राष्ट्रीय बाल आपातकालीन कोष के रूप में जाना जाता है, 1946 में संयुक्त राष्ट्र महासभा द्वारा द्वितीय विश्व युद्ध से तबाह हुए देशों में बच्चों और माताओं को आपातकालीन भोजन और स्वास्थ्य सेवा प्रदान करने के लिए बनाया गया था।
- 1950 में, विकासशील देशों में बच्चों और महिलाओं की दीर्घकालिक जरूरतों को पूरा करने के लिए यूनिसेफ के जनादेश को बढ़ाया गया था
- 1953 में, यह संयुक्त राष्ट्र प्रणाली का एक स्थायी हिस्सा बन गया, और संगठन के नाम से “अंतर्राष्ट्रीय” और “आपातकाल” शब्द हटा दिए गए, हालांकि इसने मूल संक्षिप्त नाम “यूनिसेफ” को बरकरार रखा।
- कार्यकारी बोर्ड: 36 सदस्यीय बोर्ड नीतियां बनाता है, कार्यक्रमों को मंजूरी देता है और प्रशासनिक और वित्तीय योजनाओं की देखरेख करता है। सदस्य सरकार के प्रतिनिधि होते हैं जिन्हें संयुक्त राष्ट्र आर्थिक और सामाजिक परिषद (ECOSOC) द्वारा चुना जाता है, आमतौर पर तीन साल के कार्यकाल के लिए।
- यूनिसेफ सरकारों और निजी दाताओं से योगदान पर निर्भर करता है।
- यूनिसेफ का आपूर्ति प्रभाग कोपेनहेगन (डेनमार्क) में स्थित है और यह टीके, एचआईवी से पीड़ित बच्चों और माताओं के लिए एंटीरेट्रोवायरल दवाइयाँ, पोषण संबंधी पूरक, आपातकालीन आश्रय, परिवार पुनर्मिलन और शैक्षिक आपूर्ति जैसी आवश्यक वस्तुओं के वितरण के प्राथमिक बिंदु के रूप में कार्य करता है।
UNFPA:
- संयुक्त राष्ट्र जनसंख्या कोष (यूएनएफपीए), जिसे पहले जनसंख्या गतिविधियों के लिए संयुक्त राष्ट्र कोष कहा जाता था, संयुक्त राष्ट्र की यौन और प्रजनन स्वास्थ्य एजेंसी है।
- इसका मिशन एक ऐसी दुनिया बनाना है जहाँ हर गर्भावस्था वांछित हो, ‘हर प्रसव सुरक्षित हो’ और हर युवा व्यक्ति की क्षमता पूरी हो।
- 2018 में, यूएनएफपीए ने तीन परिवर्तनकारी परिणाम प्राप्त करने के प्रयास शुरू किए, महत्वाकांक्षाएँ जो हर पुरुष, महिला और युवा व्यक्ति के लिए दुनिया को बदलने का वादा करती हैं:
- परिवार नियोजन की अधूरी ज़रूरत को समाप्त करना
- रोकथाम योग्य मातृ मृत्यु को समाप्त करना
- लिंग आधारित हिंसा और हानिकारक प्रथाओं को समाप्त करना
Will be continue…