CURRENT AFFAIRS – 17/01/2025
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 17/01/2025
- ISRO executes satellite docking, places India in elite space club /इसरो ने सैटेलाइट डॉकिंग को अंजाम दिया, जिससे भारत को अंतरिक्ष के शीर्ष क्लब में शामिल किया गया
- Sriharikota to get third launch pad /श्रीहरिकोटा को तीसरा लॉन्च पैड मिलेगा
- Centre announces constitution of Eighth Pay Commission /केंद्र ने आठवें वेतन आयोग के गठन की घोषणा की
- Justice K. Vinod Chandran sworn in as SC judge; top court close to full strength /न्यायमूर्ति के. विनोद चंद्रन ने सुप्रीम कोर्ट के न्यायाधीश के रूप में शपथ ली; शीर्ष न्यायालय में पूर्ण क्षमता के करीब
- Phased Ceasefire in Gaza /गाजा में चरणबद्ध युद्धविराम
- An alliance of democracies with India at its core/भारत के साथ लोकतांत्रिक गठबंधन इसके मूल में है
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 17/01/2025
ISRO executes satellite docking, places India in elite space club /इसरो ने सैटेलाइट डॉकिंग को अंजाम दिया, जिससे भारत को अंतरिक्ष के शीर्ष क्लब में शामिल किया गया
Syllabus : GS 3 : Science and Technology
Source : The Hindu
ISRO Successfully Demonstrates Space Docking with SpaDeX Mission, Advancing India’s Space Station and Lunar Ambitions.
Analysis of the news:
- What is Space Docking?
- Space docking is the process of bringing two fast-moving spacecraft into the same orbit, maneuvering them close to each other, and finally joining them together.
- This capability is essential for missions requiring the assembly of large structures like space stations, refueling in orbit, or carrying crew and supplies to orbiting platforms.
- India’s successful docking demonstration makes it the fourth country globally, after the US, Russia, and China, to achieve this feat, marking a significant step in ISRO’s technological evolution.
Significance of the Achievement
- This accomplishment is critical for future space missions:
- Space Station Development: India’s Bharatiya Antariksh Station, planned by 2035, will rely on docking to assemble its modular components in orbit.
- Lunar Missions: Chandrayaan-4, India’s planned lunar sample-return mission, will require docking capabilities to transfer collected samples back to Earth.
- Human Spaceflight: Future manned missions, including those to the Moon by 2040, will depend on docking technology for crew and equipment transfers.
- Details of the Docking Experiment
- ISRO used two 220-kg satellites, SDX01 (“Chaser”) and SDX02 (“Target”), for the experiment. The process involved:
- Sequentially bringing the satellites closer, holding positions at key distances (5 km, 500 m, 3 m, etc.).
- Successfully joining and locking the satellites in orbit.
- Demonstrating combined control and functionality of the satellites as a composite unit.
- Future steps include sharing electrical power between the satellites and demonstrating “undocking,” where the satellites separate and drift apart.
- ISRO used two 220-kg satellites, SDX01 (“Chaser”) and SDX02 (“Target”), for the experiment. The process involved:
Challenges Overcome During the Mission
- The docking faced delays due to unexpected drifts and inaccuracies during initial attempts.
- ISRO refined simulations and conducted additional maneuvers to achieve the precise alignment needed for successful docking.
- This iterative process highlights ISRO’s growing expertise in handling complex space operations.
Key Technologies and Innovations
- Sensors: Advanced sensors like Laser Range Finder and Proximity and Docking Sensor were used for precise measurements.
- Navigation: A new processor based on satellite navigation determined the relative positions and velocities of the spacecraft.
- Simplified Mechanism: The androgynous docking system used only two motors, compared to the 24 used in international standards, demonstrating innovation and efficiency.
Future Implications
- This mission is a precursor to India’s broader space ambitions:
- Space Station: The Bharatiya Antariksh Station will use this technology for modular assembly.
- Lunar Exploration: Docking will be central to sample-return missions and potential human expeditions to the Moon.
- Autonomy: Developing autonomous docking systems will reduce dependency on navigation data, enhancing efficiency for future missions.
Conclusion
- The SpaDeX docking mission underscores India’s growing technological prowess in space exploration.
- It is a critical step toward ISRO’s ambitious goals of establishing a space station, conducting lunar sample-return missions, and enabling human exploration of the Moon, marking India’s ascent as a significant player in global space endeavors.
इसरो ने सैटेलाइट डॉकिंग को अंजाम दिया, जिससे भारत को अंतरिक्ष के शीर्ष क्लब में शामिल किया गया
इसरो ने स्पैडेक्स मिशन के साथ अंतरिक्ष डॉकिंग का सफलतापूर्वक प्रदर्शन किया, जिससे भारत के अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन और चंद्र महत्वाकांक्षाओं को बढ़ावा मिला।
समाचार का विश्लेषण:
- अंतरिक्ष डॉकिंग क्या है?
- अंतरिक्ष डॉकिंग दो तेज़ गति से चलने वाले अंतरिक्ष यान को एक ही कक्षा में लाने, उन्हें एक-दूसरे के करीब लाने और अंत में उन्हें एक साथ जोड़ने की प्रक्रिया है।
- यह क्षमता उन मिशनों के लिए आवश्यक है, जिनमें अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन जैसी बड़ी संरचनाओं को इकट्ठा करना, कक्षा में ईंधन भरना या परिक्रमा करने वाले प्लेटफ़ॉर्म पर चालक दल और आपूर्ति ले जाना शामिल है।
- भारत का सफल डॉकिंग प्रदर्शन इसे दुनिया भर में अमेरिका, रूस और चीन के बाद चौथा देश बनाता है, जिसने यह उपलब्धि हासिल की है, जो इसरो के तकनीकी विकास में एक महत्वपूर्ण कदम है।
उपलब्धि का महत्व
- यह उपलब्धि भविष्य के अंतरिक्ष मिशनों के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है:
- अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन विकास: भारत का भारतीय अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन, जिसकी योजना 2035 तक बनाई जाएगी, कक्षा में अपने मॉड्यूलर घटकों को इकट्ठा करने के लिए डॉकिंग पर निर्भर करेगा।
- चंद्र मिशन: भारत के नियोजित चंद्र नमूना-वापसी मिशन, चंद्रयान-4 को एकत्रित नमूनों को वापस पृथ्वी पर स्थानांतरित करने के लिए डॉकिंग क्षमताओं की आवश्यकता होगी।
- मानव अंतरिक्ष उड़ान: भविष्य के मानवयुक्त मिशन, जिनमें 2040 तक चंद्रमा पर जाने वाले मिशन भी शामिल हैं, चालक दल और उपकरणों के स्थानांतरण के लिए डॉकिंग तकनीक पर निर्भर होंगे।
- डॉकिंग प्रयोग का विवरण
- इसरो ने प्रयोग के लिए दो 220 किलोग्राम के उपग्रहों, SDX01 (“चेज़र”) और SDX02 (“टारगेट”) का उपयोग किया। इस प्रक्रिया में शामिल थे:
- उपग्रहों को क्रमिक रूप से करीब लाना, महत्वपूर्ण दूरी (5 किमी, 500 मीटर, 3 मीटर, आदि) पर स्थिति बनाए रखना।
- उपग्रहों को सफलतापूर्वक कक्षा में जोड़ना और लॉक करना।
- एक समग्र इकाई के रूप में उपग्रहों के संयुक्त नियंत्रण और कार्यक्षमता का प्रदर्शन करना।
-
- भविष्य के कदमों में उपग्रहों के बीच विद्युत शक्ति साझा करना और “अनडॉकिंग” का प्रदर्शन करना शामिल है, जहाँ उपग्रह अलग हो जाते हैं और अलग हो जाते हैं।
मिशन के दौरान आने वाली चुनौतियाँ
- शुरुआती प्रयासों के दौरान अप्रत्याशित बहाव और अशुद्धियों के कारण डॉकिंग में देरी हुई।
- इसरो ने सफल डॉकिंग के लिए आवश्यक सटीक संरेखण प्राप्त करने के लिए सिमुलेशन को परिष्कृत किया और अतिरिक्त युद्धाभ्यास किए।
- यह पुनरावृत्तीय प्रक्रिया जटिल अंतरिक्ष संचालन को संभालने में इसरो की बढ़ती विशेषज्ञता को उजागर करती है।
मुख्य प्रौद्योगिकी और नवाचार
- सेंसर: सटीक माप के लिए लेजर रेंज फाइंडर और प्रॉक्सिमिटी और डॉकिंग सेंसर जैसे उन्नत सेंसर का उपयोग किया गया।
- नेविगेशन: सैटेलाइट नेविगेशन पर आधारित एक नए प्रोसेसर ने अंतरिक्ष यान की सापेक्ष स्थिति और वेग निर्धारित किया।
- सरलीकृत तंत्र: एंड्रोजेनस डॉकिंग सिस्टम ने अंतर्राष्ट्रीय मानकों में उपयोग किए जाने वाले 24 मोटर्स की तुलना में केवल दो मोटर्स का उपयोग किया, जो नवाचार और दक्षता को दर्शाता है।
भविष्य के निहितार्थ
- यह मिशन भारत की व्यापक अंतरिक्ष महत्वाकांक्षाओं का अग्रदूत है:
- अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन: भारतीय अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन मॉड्यूलर असेंबली के लिए इस तकनीक का उपयोग करेगा।
- चंद्र अन्वेषण: डॉकिंग नमूना-वापसी मिशन और चंद्रमा पर संभावित मानव अभियानों के लिए केंद्रीय होगी।
- स्वायत्तता: स्वायत्त डॉकिंग सिस्टम विकसित करने से नेविगेशन डेटा पर निर्भरता कम होगी, जिससे भविष्य के मिशनों के लिए दक्षता बढ़ेगी।
निष्कर्ष
- स्पेडेक्स डॉकिंग मिशन अंतरिक्ष अन्वेषण में भारत की बढ़ती तकनीकी शक्ति को रेखांकित करता है।
- यह अंतरिक्ष स्टेशन स्थापित करने, चंद्र नमूना वापसी मिशन संचालित करने और चंद्रमा पर मानव अन्वेषण को सक्षम करने के इसरो के महत्वाकांक्षी लक्ष्यों की दिशा में एक महत्वपूर्ण कदम है, जो वैश्विक अंतरिक्ष प्रयासों में एक महत्वपूर्ण खिलाड़ी के रूप में भारत के उदय को चिह्नित करता है।
Sriharikota to get third launch pad /श्रीहरिकोटा को तीसरा लॉन्च पैड मिलेगा
Syllabus : GS 3 : Science and Technology
Source : The Hindu
The Union Cabinet approved the construction of a third launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota, with an outlay of ₹3,984.86 crore.
Approval of Third Launch Pad
- The Union Cabinet has approved the construction of a third launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota.
- The project aims to strengthen India’s space infrastructure, with an allocated outlay of ₹3,984.86 crore.
Planned Timeline
- The construction of the launch pad is expected to be completed by early 2029, ensuring readiness for future space missions and advancements in space technology.
Facilitating Next-Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLVs)
- The third launch pad will support the launch of Next-Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLVs), which ISRO plans to operationalize by 2031.
- This development aligns with ISRO’s vision to cater to the growing demands of advanced and heavier-class launch vehicles.
Support for Human Spaceflight Missions
- The new launch pad will also play a key role in India’s manned spaceflight program, with the first mission targeted for 2026, as stated by ISRO Chairman V. Narayanan.
Universal and Adaptable Design
- The third launch pad is being designed with universal and adaptable configurations to support:
- NGLVs equipped with semi-cryogenic stages.
- Launch Vehicle Mark 3 (LVM3) and its enhanced configurations.
- Future advancements in launch vehicle technology.
Enhancing ISRO’s Launch Capabilities
- With the second launch pad in operation for nearly two decades, the addition of the third launch pad will act as a standby and expand India’s launch capacity, meeting the needs of evolving space transportation requirements.
Catering to Future Needs
- This facility is designed to address India’s space transportation demands for the next 25-30 years, supporting both heavier-class vehicles and advanced mission profiles.
Strategic Importance
- The establishment of the third launch pad underscores India’s commitment to enhancing its space exploration capabilities, enabling greater frequency and diversity in launch missions while strengthening its position in the global space sector.
Conclusion
- The approval for the third launch pad at SDSC Sriharikota marks a crucial step in enhancing ISRO’s space infrastructure. This new facility will support Next-Generation Launch Vehicles, manned space missions, and future technological advancements, strengthening India’s position in global space exploration. The project ensures ISRO’s readiness to meet evolving space transportation needs for the next 25-30 years.
श्रीहरिकोटा को तीसरा लॉन्च पैड मिलेगा
केंद्रीय मंत्रिमंडल ने श्रीहरिकोटा के सतीश धवन अंतरिक्ष केंद्र (एसडीएससी) में 3,984.86 करोड़ रुपये की लागत से तीसरे लॉन्च पैड के निर्माण को मंजूरी दी।
तीसरे लॉन्च पैड की स्वीकृति
- केंद्रीय मंत्रिमंडल ने श्रीहरिकोटा के सतीश धवन अंतरिक्ष केंद्र (एसडीएससी) में तीसरे लॉन्च पैड के निर्माण को मंजूरी दे दी है।
- इस परियोजना का उद्देश्य भारत के अंतरिक्ष बुनियादी ढांचे को मजबूत करना है, जिसके लिए 3,984.86 करोड़ रुपये का आवंटन किया गया है।
योजनाबद्ध समयरेखा
- लॉन्च पैड का निर्माण 2029 की शुरुआत तक पूरा होने की उम्मीद है, जिससे भविष्य के अंतरिक्ष मिशनों और अंतरिक्ष प्रौद्योगिकी में प्रगति के लिए तत्परता सुनिश्चित होगी।
अगली पीढ़ी के लॉन्च वाहनों (एनजीएलवी) की सुविधा
- तीसरा लॉन्च पैड अगली पीढ़ी के लॉन्च वाहनों (एनजीएलवी) के प्रक्षेपण का समर्थन करेगा, जिसे इसरो 2031 तक चालू करने की योजना बना रहा है।
- यह विकास उन्नत और भारी श्रेणी के लॉन्च वाहनों की बढ़ती मांगों को पूरा करने के लिए इसरो के दृष्टिकोण के अनुरूप है।
मानव अंतरिक्ष उड़ान मिशनों के लिए समर्थन
- नया लॉन्च पैड भारत के मानवयुक्त अंतरिक्ष उड़ान कार्यक्रम में भी महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाएगा, जिसका पहला मिशन 2026 के लिए लक्षित है, जैसा कि इसरो के अध्यक्ष वी. नारायणन ने कहा है।
सार्वभौमिक और अनुकूलनीय डिजाइन
- तीसरे लॉन्च पैड को सार्वभौमिक और अनुकूलनीय विन्यास के साथ डिजाइन किया जा रहा है, ताकि निम्नलिखित का समर्थन किया जा सके:
- अर्ध-क्रायोजेनिक चरणों से सुसज्जित NGLV।
- लॉन्च व्हीकल मार्क 3 (LVM3) और इसके उन्नत विन्यास।
- लॉन्च व्हीकल तकनीक में भविष्य की उन्नति।
इसरो की लॉन्च क्षमताओं को बढ़ाना
- दूसरे लॉन्च पैड के लगभग दो दशकों से संचालन में होने के साथ, तीसरे लॉन्च पैड के जुड़ने से स्टैंडबाय के रूप में कार्य करेगा और भारत की लॉन्च क्षमता का विस्तार होगा, जिससे अंतरिक्ष परिवहन की उभरती आवश्यकताओं की पूर्ति होगी।
भविष्य की आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करना
- यह सुविधा अगले 25-30 वर्षों के लिए भारत की अंतरिक्ष परिवहन मांगों को पूरा करने के लिए डिज़ाइन की गई है, जो भारी श्रेणी के वाहनों और उन्नत मिशन प्रोफाइल दोनों का समर्थन करती है।
रणनीतिक महत्व
- तीसरे लॉन्च पैड की स्थापना भारत की अंतरिक्ष अन्वेषण क्षमताओं को बढ़ाने, लॉन्च मिशनों में अधिक आवृत्ति और विविधता को सक्षम करने और वैश्विक अंतरिक्ष क्षेत्र में अपनी स्थिति को मजबूत करने की प्रतिबद्धता को रेखांकित करती है।
निष्कर्ष
- एसडीएससी श्रीहरिकोटा में तीसरे लॉन्च पैड के लिए स्वीकृति इसरो के अंतरिक्ष बुनियादी ढांचे को बढ़ाने में एक महत्वपूर्ण कदम है। यह नई सुविधा अगली पीढ़ी के प्रक्षेपण यान, मानवयुक्त अंतरिक्ष मिशन और भविष्य की तकनीकी प्रगति का समर्थन करेगी, जिससे वैश्विक अंतरिक्ष अन्वेषण में भारत की स्थिति मजबूत होगी। यह परियोजना अगले 25-30 वर्षों के लिए अंतरिक्ष परिवहन की उभरती जरूरतों को पूरा करने के लिए इसरो की तत्परता सुनिश्चित करती है।
Centre announces constitution of Eighth Pay Commission /केंद्र ने आठवें वेतन आयोग के गठन की घोषणा की
Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity
Source : The Hindu
The Eighth Pay Commission has been approved by the Union government to address the long-standing demands of employees and trade unions for wage and pension revisions.
Approval of Eighth Pay Commission
- The Union government has approved the establishment of the Eighth Pay Commission, fulfilling the long-standing demand of Central trade unions and employees’ organizations.
Beneficiaries
- The recommendations of the Pay Commission will benefit approximately 50 lakh employees and 65 lakh pensioners, including serving and retired defense personnel.
- Delhi alone houses around 4 lakh Union government employees.
Composition and Appointment
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has approved the formation of the commission ahead of the Seventh Pay Commission’s term ending in 2026.
- The Chairperson and two members will be appointed soon, with the chair traditionally being a retired Supreme Court judge (e.g., Justice A.K. Mathur headed the Seventh Pay Commission).
Impact of Recommendations
- The recommendations will serve as the basis for wage settlements in public sector undertakings and similar pay revisions in States.
- The Seventh Pay Commission’s implementation in 2016 cost the exchequer ₹1 lakh crore in the fiscal year 2016-17.
Economic and Social Benefits
- The decision is expected to boost consumption and economic growth while improving the quality of life for government employees.
- It reflects the government’s commitment to enhancing employee welfare.
Trade Union Reactions
- Trade unions welcomed the move and emphasized the need for clear terms of reference, particularly on “living wage” and “living pension” concepts.
- The Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh-backed Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh (BMS) appreciated the decision and urged for the early constitution of the panel.
Timeline for Recommendations
- As per precedence, a Pay Commission usually takes about two years to submit its report, making this early approval significant for timely implementation.
Significance
- The establishment of the Eighth Pay Commission underscores the government’s proactive approach to addressing employee demands and ensuring their financial well-being, further contributing to economic growth.
Conclusion
- The approval of the Eighth Pay Commission highlights the government’s commitment to employee welfare and economic growth. Its timely formation will address wage and pension demands, benefiting millions of employees and pensioners while boosting consumption and overall economic activity.
केंद्र ने आठवें वेतन आयोग के गठन की घोषणा की
- कर्मचारियों और ट्रेड यूनियनों की वेतन और पेंशन संशोधन की लंबे समय से चली आ रही मांगों को पूरा करने के लिए केंद्र सरकार ने आठवें वेतन आयोग को मंजूरी दे दी है।
आठवें वेतन आयोग की मंजूरी
- केंद्र सरकार ने केंद्रीय ट्रेड यूनियनों और कर्मचारी संगठनों की लंबे समय से चली आ रही मांग को पूरा करते हुए आठवें वेतन आयोग के गठन को मंजूरी दे दी है।
लाभार्थी
- वेतन आयोग की सिफारिशों से लगभग 50 लाख कर्मचारियों और 65 लाख पेंशनभोगियों को लाभ होगा, जिनमें सेवारत और सेवानिवृत्त रक्षा कर्मी शामिल हैं।
- अकेले दिल्ली में ही केंद्र सरकार के लगभग 4 लाख कर्मचारी हैं।
संरचना और नियुक्ति
- प्रधानमंत्री नरेंद्र मोदी ने 2026 में समाप्त होने वाले सातवें वेतन आयोग के कार्यकाल से पहले आयोग के गठन को मंजूरी दे दी है।
- अध्यक्ष और दो सदस्यों की नियुक्ति जल्द ही की जाएगी, जिसका अध्यक्ष पारंपरिक रूप से सेवानिवृत्त सुप्रीम कोर्ट के न्यायाधीश होंगे (जैसे, न्यायमूर्ति ए.के. माथुर सातवें वेतन आयोग के अध्यक्ष थे)।
सिफारिशों का प्रभाव
- सिफारिशें सार्वजनिक क्षेत्र के उपक्रमों में वेतन समझौते और राज्यों में इसी तरह के वेतन संशोधन के लिए आधार का काम करेंगी।
- 2016 में सातवें वेतन आयोग के कार्यान्वयन से वित्त वर्ष 2016-17 में राजकोष पर ₹1 लाख करोड़ का बोझ पड़ा।
आर्थिक और सामाजिक लाभ
- इस निर्णय से उपभोग और आर्थिक वृद्धि को बढ़ावा मिलने की उम्मीद है, साथ ही सरकारी कर्मचारियों के जीवन की गुणवत्ता में सुधार होगा।
- यह कर्मचारी कल्याण को बढ़ाने के लिए सरकार की प्रतिबद्धता को दर्शाता है।
ट्रेड यूनियन की प्रतिक्रियाएँ
- ट्रेड यूनियनों ने इस कदम का स्वागत किया और संदर्भ की स्पष्ट शर्तों की आवश्यकता पर बल दिया, विशेष रूप से “जीवित मजदूरी” और “जीवित पेंशन” अवधारणाओं पर।
- राष्ट्रीय स्वयंसेवक संघ समर्थित भारतीय मजदूर संघ (बीएमएस) ने निर्णय की सराहना की और पैनल के शीघ्र गठन का आग्रह किया।
सिफारिशों के लिए समयसीमा
- पूर्वानुमान के अनुसार, वेतन आयोग को अपनी रिपोर्ट प्रस्तुत करने में आमतौर पर लगभग दो साल लगते हैं, जिससे समय पर कार्यान्वयन के लिए यह प्रारंभिक स्वीकृति महत्वपूर्ण हो जाती है।
महत्व
- आठवें वेतन आयोग की स्थापना कर्मचारियों की मांगों को संबोधित करने और उनकी वित्तीय भलाई सुनिश्चित करने के लिए सरकार के सक्रिय दृष्टिकोण को रेखांकित करती है, जो आर्थिक विकास में और योगदान देती है।
निष्कर्ष
- आठवें वेतन आयोग की स्वीकृति कर्मचारी कल्याण और आर्थिक विकास के प्रति सरकार की प्रतिबद्धता को दर्शाती है। इसका समय पर गठन वेतन और पेंशन संबंधी मांगों को संबोधित करेगा, जिससे लाखों कर्मचारियों और पेंशनभोगियों को लाभ होगा और साथ ही उपभोग और समग्र आर्थिक गतिविधि को बढ़ावा मिलेगा।
Justice K. Vinod Chandran sworn in as SC judge; top court close to full strength /न्यायमूर्ति के. विनोद चंद्रन ने सुप्रीम कोर्ट के न्यायाधीश के रूप में शपथ ली; शीर्ष न्यायालय में पूर्ण क्षमता के करीब
Syllabus : GS 2 : Indian Polity
Source : The Hindu
Chief Justice of India Sanjiv Khanna administered the oath of office to the new Supreme Court judge Justice Krishnan Vinod Chandran on Thursday.
- Justice Chandran was formerly the Chief Justice of the Patna High Court. His appointment has raised the judicial strength of the Supreme Court to 33, one short of the full sanctioned strength.
- The Supreme Court Collegium had recommended Justice Chandran to the Union government for appointment as a top court judge on January 7.
How are Supreme Court Judges Appointed?
- Composition and Strength of the Supreme Court:
- Originally, the Supreme Court had eight judges (one chief justice and seven others).
- The Parliament has increased the number of judges over time.
- The current strength of the Supreme Court is 34 judges (one chief justice and 33 others).
Qualifications for Appointment as a Judge:
- According to Article 124(3) of the Constitution, a person can be appointed as a judge of the Supreme Court if he or she:
- A person must be a citizen of India.
- Must have served as a judge of a High Court for at least five years or two such courts in succession.
- Alternatively, must have been an advocate of a High Court for at least ten years or two or more such courts in succession.
- Must be a distinguished jurist in the opinion of the president.
Appointment:
- The Judges of the Supreme Court are appointed by the President under clause (2) of Article 124 of the Constitution.
- The President consults with judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts to make informed appointments.
Oath of Office:
- Every appointed judge must make and subscribe to an oath before the President or an appointed person.
- The oath includes commitments to uphold the Constitution, sovereignty and integrity of India, and perform duties without fear or favor.
Tenure and Resignation:
- There is no prescribed minimum age limit for a judge’s appointment.
- A judge of the Supreme Court serves until they reach the age of 65 years.
- However, a judge may resign before reaching the age of 65 years by tendering their resignation to the President.
Salaries and Allowances:
- Salaries, allowances, privileges, leave, and pension of Supreme Court judges are determined by Parliament.
- The Salaries, Pension, and Allowances of the Supreme Court Judges are charged upon the Consolidated Fund of India.
Post-retirement Restrictions:
- After retirement, a judge of the Supreme Court is prohibited from practicing law in any court in India or pleading before any government authority.
- As per Article 128 of Indian Constitution, any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit and act as a Supreme Court judge by the Chief Justice of India with the prior permission of the President of India.
Removal:
- A judge of the Supreme Court can only be removed from office by an order of the President.
- The removal process requires an address by each House of Parliament, supported by a special majority i.e., a majority of the total membership of that House and a majority of not less than two-thirds of the members present and voting.
- The grounds for removal are proven misbehaviour or incapacity.
- Parliament has the authority to regulate the procedure for presenting the address and investigating and proving the misbehaviour or incapacity of a judge.
- Once appointed, judges can serve until the age of 65 and cannot be removed during their tenure except for proved misbehaviour or incapacity.
Collegium System for Judicial Appointments:
- Judges of the higher judiciary are appointed through the collegium system.
- The collegium, consisting of the Chief Justice of India and the four senior-most judges of the Supreme Court, decides on appointments, elevations, and transfers of Judges.
- The term “collegium” is not mentioned in the Indian Constitution but has been established through judicial pronouncements.
न्यायमूर्ति के. विनोद चंद्रन ने सुप्रीम कोर्ट के न्यायाधीश के रूप में शपथ ली; शीर्ष न्यायालय में पूर्ण क्षमता के करीब
भारत के मुख्य न्यायाधीश संजीव खन्ना ने गुरुवार को सुप्रीम कोर्ट के नए न्यायाधीश न्यायमूर्ति कृष्णन विनोद चंद्रन को पद की शपथ दिलाई।
- न्यायमूर्ति चंद्रन पहले पटना उच्च न्यायालय के मुख्य न्यायाधीश थे। उनकी नियुक्ति से सुप्रीम कोर्ट में न्यायाधीशों की संख्या बढ़कर 33 हो गई है, जो स्वीकृत पूर्ण संख्या से एक कम है।
- सुप्रीम कोर्ट कॉलेजियम ने 7 जनवरी को केंद्र सरकार को न्यायमूर्ति चंद्रन को शीर्ष अदालत के न्यायाधीश के रूप में नियुक्त करने की सिफारिश की थी।
सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के न्यायाधीशों की नियुक्ति कैसे की जाती है?
- सर्वोच्च न्यायालय की संरचना और शक्ति:
- मूल रूप से, सर्वोच्च न्यायालय में आठ न्यायाधीश (एक मुख्य न्यायाधीश और सात अन्य) थे।\
- संसद ने समय के साथ न्यायाधीशों की संख्या में वृद्धि की है।
- सर्वोच्च न्यायालय की वर्तमान शक्ति 34 न्यायाधीश (एक मुख्य न्यायाधीश और 33 अन्य) है।
न्यायाधीश के रूप में नियुक्ति के लिए योग्यताएँ:
- संविधान के अनुच्छेद 124(3) के अनुसार, किसी व्यक्ति को सर्वोच्च न्यायालय का न्यायाधीश नियुक्त किया जा सकता है यदि वह:
- व्यक्ति भारत का नागरिक होना चाहिए।
- कम से कम पाँच वर्षों तक किसी उच्च न्यायालय या लगातार दो ऐसे न्यायालयों के न्यायाधीश के रूप में कार्य किया हो।
- वैकल्पिक रूप से, कम से कम दस वर्षों तक किसी उच्च न्यायालय या लगातार दो या अधिक ऐसे न्यायालयों का अधिवक्ता रहा हो।
- राष्ट्रपति की राय में एक प्रतिष्ठित न्यायविद होना चाहिए।
नियुक्ति:
- संविधान के अनुच्छेद 124 के खंड (2) के तहत राष्ट्रपति द्वारा सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के न्यायाधीशों की नियुक्ति की जाती है।
- राष्ट्रपति सूचित नियुक्तियाँ करने के लिए सर्वोच्च न्यायालय और उच्च न्यायालयों के न्यायाधीशों से परामर्श करते हैं।
पद की शपथ:
- प्रत्येक नियुक्त न्यायाधीश को राष्ट्रपति या किसी नियुक्त व्यक्ति के समक्ष शपथ लेनी चाहिए और उस पर हस्ताक्षर करना चाहिए।
- शपथ में भारत के संविधान, संप्रभुता और अखंडता को बनाए रखने और बिना किसी भय या पक्षपात के कर्तव्यों का पालन करने की प्रतिबद्धता शामिल है।
कार्यकाल और त्यागपत्र:
- न्यायाधीश की नियुक्ति के लिए कोई न्यूनतम आयु सीमा निर्धारित नहीं है।
- सर्वोच्च न्यायालय का न्यायाधीश 65 वर्ष की आयु तक कार्य करता है।
- हालाँकि, कोई न्यायाधीश राष्ट्रपति को अपना त्यागपत्र देकर 65 वर्ष की आयु तक पहुँचने से पहले त्यागपत्र दे सकता है।
वेतन और भत्ते:
- सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के न्यायाधीशों के वेतन, भत्ते, विशेषाधिकार, छुट्टी और पेंशन संसद द्वारा निर्धारित किए जाते हैं।
- सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के न्यायाधीशों के वेतन, पेंशन और भत्ते भारत की संचित निधि पर निर्भर करते हैं।
सेवानिवृत्ति के बाद प्रतिबंध:
- सेवानिवृत्ति के बाद, सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के न्यायाधीश को भारत में किसी भी न्यायालय में कानून का अभ्यास करने या किसी सरकारी प्राधिकरण के समक्ष दलील देने से प्रतिबंधित किया जाता है।
- भारतीय संविधान के अनुच्छेद 128 के अनुसार, भारत के राष्ट्रपति की पूर्व अनुमति से भारत के मुख्य न्यायाधीश द्वारा भारत के सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के किसी भी सेवानिवृत्त न्यायाधीश को सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के न्यायाधीश के रूप में वापस बुलाया जा सकता है।
हटाना:
- सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के किसी न्यायाधीश को केवल राष्ट्रपति के आदेश से ही पद से हटाया जा सकता है।
- हटाने की प्रक्रिया के लिए संसद के प्रत्येक सदन द्वारा विशेष बहुमत अर्थात उस सदन की कुल सदस्यता के बहुमत और उपस्थित तथा मतदान करने वाले सदस्यों के कम से कम दो-तिहाई बहुमत द्वारा समर्थित अभिभाषण की आवश्यकता होती है।
- हटाने का आधार सिद्ध दुर्व्यवहार या अक्षमता है।
- संसद के पास अभिभाषण प्रस्तुत करने और न्यायाधीश के दुर्व्यवहार या अक्षमता की जांच करने और उसे साबित करने की प्रक्रिया को विनियमित करने का अधिकार है।
- एक बार नियुक्त होने के बाद, न्यायाधीश 65 वर्ष की आयु तक सेवा कर सकते हैं और सिद्ध दुर्व्यवहार या अक्षमता को छोड़कर अपने कार्यकाल के दौरान उन्हें हटाया नहीं जा सकता।
न्यायिक नियुक्तियों के लिए कॉलेजियम प्रणाली:
- उच्च न्यायपालिका के न्यायाधीशों की नियुक्ति कॉलेजियम प्रणाली के माध्यम से की जाती है।
- भारत के मुख्य न्यायाधीश और सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के चार वरिष्ठतम न्यायाधीशों से मिलकर बना कॉलेजियम न्यायाधीशों की नियुक्तियों, पदोन्नति और स्थानांतरण पर निर्णय लेता है।
- “कॉलेजियम” शब्द का उल्लेख भारतीय संविधान में नहीं है, लेकिन न्यायिक घोषणाओं के माध्यम से इसकी स्थापना की गई है।
Phased Ceasefire in Gaza /गाजा में चरणबद्ध युद्धविराम
In News
A phased ceasefire deal was brokered in Doha, Qatar, aiming to address the Gaza conflict.
Analysis of the news:
- Phased Ceasefire and Exchange of Detainees
- In the first 42-day phase, Hamas will release 33 hostages, while Israel will free 900-1,650 Palestinian detainees, including those detained post-October 7, 2023.
- This phase sets the groundwork for eventual Israeli withdrawal from Gaza, including critical areas like the Netzarim and Philadelphi Corridors, contingent on subsequent negotiations.
- The phased structure aims to build trust while addressing humanitarian concerns.
- Geopolitical and Domestic Shifts Enabling the Deal
- Key changes in Israel’s political landscape, such as Gideon Sa’ar joining Netanyahu’s coalition, diluted the influence of far-right figures.
- International pressure, particularly from the U.S. under Biden and President-elect Trump, further propelled the ceasefire.
- Netanyahu’s strategic considerations for leveraging U.S. relations during Trump’s second term also influenced his decision to accept the agreement.
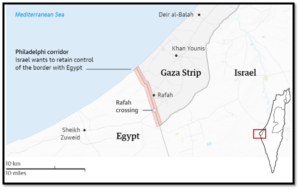
- Key Terms and Implications
- Withdrawal from the Philadelphi Corridor:
- Israel’s commitment to vacate this critical buffer zone by the end of phase one addresses long-standing Egyptian and Hamas demands.
- However, Israeli officials remain cautious, leaving room for renegotiation based on security concerns.
- Prisoner Exchange Dynamics:
- Israel’s history of high-stakes prisoner swaps resurfaces, with at least 250 life-sentenced detainees set for release. This concession risks political backlash, challenging Israel’s 2014 law limiting such exchanges.
- Withdrawal from the Philadelphi Corridor:
Implications for Hamas and Israel
- Hamas:
- The ceasefire offers Hamas breathing space to regroup, rebuild its resources, and maintain its influence in Gaza. Its evolving tactics and local command strength highlight resilience, despite leadership losses.
- Hamas appears to be positioning itself for a permanent role in Gaza’s governance, emulating Hezbollah’s integration into Lebanon’s post-war framework.
- Israel:
- Despite military successes against Hamas and Hezbollah, Israel’s core objective of eradicating Hamas from Gaza remains unmet. While the deal secures the release of hostages, Netanyahu risks domestic criticism for perceived concessions, potentially weakening his far-right support.
Conclusion: A Complex Road Ahead
- The ceasefire reflects a temporary pause in violence and opens pathways for broader negotiations, including reconstruction and governance in Gaza.
- However, unresolved security and political challenges highlight the fragility of this agreement, leaving the region’s long-term stability uncertain.
About Gaza Strip

- Location: It is a Palestinian enclave on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea.
- It shares a border with Israel and Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula.
- The Gaza Strip along with the West Bank makes up the State of Palestine. Both these territories are separated by Israel.
- Administration: Since winning a majority in 2006, the Gaza Strip has been ruled by Hamas, which is considered a politico-military organisation.
- Occupied: Israel controls the air space over Gaza and its shoreline. It has imposed restrictions on the movement of goods into the Gaza Strip. Egypt also controls one of Gaza’s borders and has at times restricted movement.
- Conflict: Gaza Strip is described as the ‘world’s largest open-air prison’ due to the strict movement restrictions placed by Israel on its nearly 2 million residents.
गाजा में चरणबद्ध युद्धविराम
- गाजा संघर्ष को संबोधित करने के उद्देश्य से कतर के दोहा में चरणबद्ध युद्धविराम समझौता किया गया।
समाचार का विश्लेषण:
- चरणबद्ध युद्धविराम और बंदियों की अदला-बदली
- पहले 42-दिवसीय चरण में, हमास 33 बंधकों को रिहा करेगा, जबकि इज़राइल 900-1,650 फ़िलिस्तीनी बंदियों को रिहा करेगा, जिनमें 7 अक्टूबर, 2023 के बाद हिरासत में लिए गए लोग भी शामिल हैं।
- यह चरण गाजा से अंततः इज़राइली वापसी के लिए आधार तैयार करता है, जिसमें नेटज़ारिम और फ़िलाडेल्फ़ी कॉरिडोर जैसे महत्वपूर्ण क्षेत्र शामिल हैं, जो बाद की वार्ताओं पर निर्भर हैं।
- चरणबद्ध संरचना का उद्देश्य मानवीय चिंताओं को संबोधित करते हुए विश्वास का निर्माण करना है।
- भू-राजनीतिक और घरेलू बदलाव जो समझौते को सक्षम बनाते हैं
- इज़राइल के राजनीतिक परिदृश्य में महत्वपूर्ण परिवर्तन, जैसे कि गिदोन सा’आर नेतन्याहू के गठबंधन में शामिल हो गए, ने दूर-दराज़ के लोगों के प्रभाव को कम कर दिया।
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय दबाव, विशेष रूप से बिडेन और राष्ट्रपति-चुनाव ट्रम्प के तहत यू.एस. से, युद्धविराम को और आगे बढ़ाया।
- ट्रम्प के दूसरे कार्यकाल के दौरान अमेरिकी संबंधों को बेहतर बनाने के लिए नेतन्याहू के रणनीतिक विचारों ने भी समझौते को स्वीकार करने के उनके निर्णय को प्रभावित किया।
मुख्य शब्द और निहितार्थ
- फिलाडेल्फी कॉरिडोर से वापसी:
- चरण एक के अंत तक इस महत्वपूर्ण बफर जोन को खाली करने की इजरायल की प्रतिबद्धता लंबे समय से चली आ रही मिस्र और हमास की मांगों को संबोधित करती है।
- हालांकि, इजरायल के अधिकारी सतर्क बने हुए हैं, जिससे सुरक्षा चिंताओं के आधार पर फिर से बातचीत की गुंजाइश बनी हुई है।
कैदी विनिमय गतिशीलता:
- इजरायल में उच्च-दांव वाले कैदी अदला-बदली का इतिहास फिर से सामने आया है, जिसमें कम से कम 250 आजीवन कारावास की सजा पाए कैदियों को रिहा किया जाना तय है। इस रियायत से राजनीतिक प्रतिक्रिया का जोखिम है, जो इस तरह के आदान-प्रदान को सीमित करने वाले इजरायल के 2014 के कानून को चुनौती देता है।
हमास और इजरायल के लिए निहितार्थ
- हमास:
- युद्ध विराम हमास को फिर से संगठित होने, अपने संसाधनों का पुनर्निर्माण करने और गाजा में अपना प्रभाव बनाए रखने के लिए सांस लेने की जगह देता है। नेतृत्व के नुकसान के बावजूद इसकी विकसित रणनीति और स्थानीय कमांड की ताकत लचीलापन को उजागर करती है।
- हमास गाजा के शासन में एक स्थायी भूमिका के लिए खुद को तैयार करता हुआ प्रतीत होता है, जो लेबनान के युद्ध-पश्चात ढांचे में हिजबुल्लाह के एकीकरण का अनुकरण करता है।
इजराइल:
- हमास और हिजबुल्लाह के खिलाफ सैन्य सफलताओं के बावजूद, गाजा से हमास को खत्म करने का इजराइल का मुख्य उद्देश्य पूरा नहीं हुआ है। जबकि यह समझौता बंधकों की रिहाई को सुरक्षित करता है, नेतन्याहू कथित रियायतों के लिए घरेलू आलोचना का जोखिम उठाते हैं, जिससे संभावित रूप से उनका दूर-दराज़ समर्थन कमज़ोर हो सकता है।
निष्कर्ष: आगे एक जटिल रास्ता
- युद्धविराम हिंसा में एक अस्थायी विराम को दर्शाता है और गाजा में पुनर्निर्माण और शासन सहित व्यापक वार्ता के लिए रास्ते खोलता है।
- हालांकि, अनसुलझे सुरक्षा और राजनीतिक चुनौतियां इस समझौते की नाजुकता को उजागर करती हैं, जिससे क्षेत्र की दीर्घकालिक स्थिरता अनिश्चित हो जाती है।
गाजा पट्टी के बारे में
- स्थान: यह भूमध्य सागर के तट पर एक फिलिस्तीनी क्षेत्र है।
- यह इजरायल और मिस्र के सिनाई प्रायद्वीप के साथ सीमा साझा करता है।
- पश्चिमी तट के साथ गाजा पट्टी फिलिस्तीन राज्य बनाती है। इन दोनों क्षेत्रों को इजरायल अलग करता है।
- प्रशासन: 2006 में बहुमत जीतने के बाद से, गाजा पट्टी पर हमास का शासन है, जिसे एक राजनीतिक-सैन्य संगठन माना जाता है।
- कब्ज़ा: इजरायल गाजा और उसके तटरेखा पर हवाई क्षेत्र को नियंत्रित करता है। इसने गाजा पट्टी में माल की आवाजाही पर प्रतिबंध लगा दिए हैं। मिस्र भी गाजा की एक सीमा को नियंत्रित करता है और कई बार आवाजाही को प्रतिबंधित करता है।
- संघर्ष: गाजा पट्टी को ‘दुनिया की सबसे बड़ी खुली हवा वाली जेल’ के रूप में वर्णित किया जाता है, क्योंकि इजरायल ने अपने लगभग 2 मिलियन निवासियों पर सख्त आवाजाही प्रतिबंध लगा रखे हैं।
An alliance of democracies with India at its core/भारत के साथ लोकतांत्रिक गठबंधन इसके मूल में है
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 : International Relations
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- The article emphasizes the need for stronger collaboration between Europe and India to address global challenges, focusing on trade, defense, technology, and geopolitical dynamics. It advocates forming a democratic alliance to counter the rising influence of autocratic powers like Russia and China.
Strengthening EU-India Relations for a Democratic Alliance
- The year 2024 marked a pivotal period globally, with super-election events shaping the world’s democracies. As 2025 unfolds, it presents an opportunity for democracies to regroup and forge new ways to support one another.
- Among these partnerships, the relationship between Europe and India stands out. While historically strong in strategic intent, it has struggled with effective delivery, and now is the time for transformation.
Challenges in EU-India Relations
- For over 17 years, the focus of EU-India relations has been the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) negotiations. These prolonged discussions have overshadowed other critical areas of collaboration.
- A successful FTA between the world’s largest democracy and its biggest trading bloc could serve as a cornerstone to counter rising protectionist trends and foster economic and geopolitical strength. However, the complexity of negotiations has delayed progress, necessitating a broader and more pragmatic approach to collaboration.
Moving Beyond Trade
- While an FTA remains crucial, it is equally important to pivot towards geostrategic issues that transcend trade. This involves high-level political dialogue focusing on:
- Economic security through resilient supply chains.
- Defense cooperation to address shared security challenges
- Joint innovation in areas like space exploration, emerging technologies, and critical industries such as pharmaceuticals.
Geopolitical Dynamics and Shared Challenges
- Europe and India face intricate geopolitical dynamics. Europe has expressed frustration over India’s response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and its longstanding ties with Moscow.
- These ties are rooted in history, just as India navigates its complex rivalry with China. Despite cooperation within BRICS, India remains cautious about Beijing’s growing influence, which aligns with its broader democratic values.
- India’s engagement with both Russia and China reflects its strategic need to avoid being entangled in power blocs as the world polarizes into democratic and autocratic alliances. However, Europe’s economic dependence on China also highlights double standards.
- A mutual understanding must be established, recognizing that the “No Limits” partnership between Russia and China poses a shared threat to the democratic world.
Building a Practical Framework
- To strengthen this partnership, a series of pragmatic steps must be implemented:
- Trade and Investment: Break down barriers incrementally and foster investment in critical industries.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Reduce dependence on China by creating alternative supply chains, with India positioned as a “Trusted Partner.”
- Defense Collaboration: Accelerate EU-India defense discussions to complement India’s strong ties with the U.S., enhancing security guarantees.
- Technology Leadership: Deepen cooperation in emerging technologies like quantum computing and biotech to counter China’s global dominance.Strengthening Defense and Technology Collaboration
- India’s defense cooperation with the U.S., as its “Major Defense Partner” and member of the Quad, serves as a model for Europe.
- EU-India defense collaboration should scale up, with Europe offering investments and advanced weapons to replace India’s reliance on Russian arms.
- Space exploration is another promising area where both sides can pool resources and expertise for mutual benefit.
- In technology, the EU-India Trade and Technology Council (TTC) mirrors similar frameworks with the U.S., yet it remains underutilized.
- Drawing inspiration from the U.S.-India iCET initiative, Europe and India can prioritize collaboration in critical and emerging technologies to address the existential challenge posed by China’s dominance.
A Broader Vision for EU-India Ties
- Beyond economic and strategic ties, fostering stronger people-to-people connections can deepen mutual understanding.
- Educational and cultural exchanges will play a pivotal role in building a relationship based on trust and shared democratic values.
Conclusion
- In the next decade, India is poised to become the world’s third-largest economy, presenting vast opportunities for Europe. More importantly, the strategic goal should be to form a robust alliance of democracies, with India as a central pillar. By addressing shared challenges, embracing mutual strengths, and promoting tangible collaboration, Europe, India, and the U.S. can build an unstoppable democratic coalition capable of countering autocratic powers and ensuring a secure, prosperous future.
भारत के साथ लोकतांत्रिक गठबंधन इसके मूल में है
संदर्भ:
- लेख में वैश्विक चुनौतियों का समाधान करने के लिए यूरोप और भारत के बीच मजबूत सहयोग की आवश्यकता पर जोर दिया गया है, जिसमें व्यापार, रक्षा, प्रौद्योगिकी और भू-राजनीतिक गतिशीलता पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया गया है। यह रूस और चीन जैसी निरंकुश शक्तियों के बढ़ते प्रभाव का मुकाबला करने के लिए एक लोकतांत्रिक गठबंधन बनाने की वकालत करता है।
एक लोकतांत्रिक गठबंधन के लिए यूरोपीय संघ-भारत संबंधों को मजबूत करना
- वर्ष 2024 वैश्विक स्तर पर एक महत्वपूर्ण अवधि है, जिसमें सुपर-चुनाव की घटनाओं ने दुनिया के लोकतंत्रों को आकार दिया है। जैसे-जैसे 2025 सामने आता है, यह लोकतंत्रों के लिए फिर से संगठित होने और एक-दूसरे का समर्थन करने के नए तरीके बनाने का अवसर प्रस्तुत करता है।
- इन साझेदारियों में, यूरोप और भारत के बीच संबंध सबसे अलग हैं। रणनीतिक इरादे में ऐतिहासिक रूप से मजबूत होने के बावजूद, इसने प्रभावी वितरण के साथ संघर्ष किया है, और अब परिवर्तन का समय है।
यूरोपीय संघ-भारत संबंधों में चुनौतियाँ
- 17 से अधिक वर्षों से, यूरोपीय संघ-भारत संबंधों का ध्यान मुक्त व्यापार समझौते (FTA) वार्ता पर रहा है। इन लंबी चर्चाओं ने सहयोग के अन्य महत्वपूर्ण क्षेत्रों को पीछे छोड़ दिया है। दुनिया के सबसे बड़े लोकतंत्र और उसके सबसे बड़े व्यापारिक ब्लॉक के बीच एक सफल FTA, बढ़ते संरक्षणवादी रुझानों का मुकाबला करने और आर्थिक और भू-राजनीतिक ताकत को बढ़ावा देने के लिए आधारशिला के रूप में काम कर सकता है। हालाँकि, वार्ता की जटिलता ने प्रगति में देरी की है, जिससे सहयोग के लिए एक व्यापक और अधिक व्यावहारिक दृष्टिकोण की आवश्यकता है।
व्यापार से आगे बढ़ना
- जबकि FTA महत्वपूर्ण बना हुआ है, व्यापार से परे भू-रणनीतिक मुद्दों की ओर बढ़ना भी उतना ही महत्वपूर्ण है। इसमें उच्च-स्तरीय राजनीतिक संवाद शामिल है, जो निम्न पर केंद्रित है:
- लचीली आपूर्ति श्रृंखलाओं के माध्यम से आर्थिक सुरक्षा।
- साझा सुरक्षा चुनौतियों का समाधान करने के लिए रक्षा सहयोग
- अंतरिक्ष अन्वेषण, उभरती प्रौद्योगिकियों और फार्मास्यूटिकल्स जैसे महत्वपूर्ण उद्योगों जैसे क्षेत्रों में संयुक्त नवाचार।
- भू-राजनीतिक गतिशीलता और साझा चुनौतियाँ
- यूरोप और भारत जटिल भू-राजनीतिक गतिशीलता का सामना कर रहे हैं। यूरोप ने यूक्रेन पर रूस के आक्रमण और मॉस्को के साथ उसके दीर्घकालिक संबंधों पर भारत की प्रतिक्रिया पर निराशा व्यक्त की है।
- ये संबंध इतिहास में निहित हैं, ठीक उसी तरह जैसे भारत चीन के साथ अपनी जटिल प्रतिद्वंद्विता को आगे बढ़ाता है। ब्रिक्स के भीतर सहयोग के बावजूद, भारत बीजिंग के बढ़ते प्रभाव के बारे में सतर्क है, जो इसके व्यापक लोकतांत्रिक मूल्यों के साथ संरेखित है।
- रूस और चीन दोनों के साथ भारत की भागीदारी, दुनिया के लोकतांत्रिक और निरंकुश गठबंधनों में ध्रुवीकृत होने के दौरान शक्ति ब्लॉकों में उलझने से बचने की इसकी रणनीतिक आवश्यकता को दर्शाती है। हालाँकि, चीन पर यूरोप की आर्थिक निर्भरता भी दोहरे मानदंडों को उजागर करती है।
- एक पारस्परिक समझ स्थापित की जानी चाहिए, यह पहचानते हुए कि रूस और चीन के बीच “कोई सीमा नहीं” साझेदारी लोकतांत्रिक दुनिया के लिए एक साझा खतरा है।
एक व्यावहारिक रूपरेखा का निर्माण
- इस साझेदारी को मजबूत करने के लिए, व्यावहारिक कदमों की एक श्रृंखला को लागू किया जाना चाहिए:
- व्यापार और निवेश: बाधाओं को क्रमिक रूप से तोड़ना और महत्वपूर्ण उद्योगों में निवेश को बढ़ावा देना।
- आपूर्ति श्रृंखला लचीलापन: वैकल्पिक आपूर्ति श्रृंखलाएँ बनाकर चीन पर निर्भरता कम करें, जिसमें भारत को “विश्वसनीय भागीदार” के रूप में स्थापित किया जाए।
- रक्षा सहयोग: भारत के अमेरिका के साथ मजबूत संबंधों को पूरक बनाने के लिए यूरोपीय संघ-भारत रक्षा चर्चाओं में तेजी लाना, सुरक्षा गारंटी को बढ़ाना।
- प्रौद्योगिकी नेतृत्व: चीन के वैश्विक प्रभुत्व का मुकाबला करने के लिए क्वांटम कंप्यूटिंग और बायोटेक जैसी उभरती प्रौद्योगिकियों में सहयोग को गहरा करें। रक्षा और प्रौद्योगिकी सहयोग को मजबूत करना
- भारत का अमेरिका के साथ रक्षा सहयोग, इसके “प्रमुख रक्षा साझेदार” और क्वाड के सदस्य के रूप में, यूरोप के लिए एक मॉडल के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- यूरोप द्वारा रूसी हथियारों पर भारत की निर्भरता को बदलने के लिए निवेश और उन्नत हथियारों की पेशकश के साथ यूरोपीय संघ-भारत रक्षा सहयोग को बढ़ाया जाना चाहिए।
- अंतरिक्ष अन्वेषण एक और आशाजनक क्षेत्र है जहाँ दोनों पक्ष आपसी लाभ के लिए संसाधनों और विशेषज्ञता को एक साथ ला सकते हैं।
- प्रौद्योगिकी में, यूरोपीय संघ-भारत व्यापार और प्रौद्योगिकी परिषद (TTC) अमेरिका के समान ढाँचे को दर्शाता है, फिर भी इसका कम उपयोग किया जाता है।
- यू.एस.-भारत iCET पहल से प्रेरणा लेते हुए, यूरोप और भारत चीन के प्रभुत्व द्वारा उत्पन्न अस्तित्वगत चुनौती का समाधान करने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण और उभरती प्रौद्योगिकियों में सहयोग को प्राथमिकता दे सकते हैं।
यूरोपीय संघ-भारत संबंधों के लिए एक व्यापक दृष्टिकोण
- आर्थिक और रणनीतिक संबंधों से परे, लोगों के बीच मजबूत संबंधों को बढ़ावा देने से आपसी समझ गहरी हो सकती है।
- शैक्षिक और सांस्कृतिक आदान-प्रदान विश्वास और साझा लोकतांत्रिक मूल्यों पर आधारित संबंध बनाने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाएंगे।
निष्कर्ष
- अगले दशक में, भारत दुनिया की तीसरी सबसे बड़ी अर्थव्यवस्था बनने के लिए तैयार है, जो यूरोप के लिए विशाल अवसर प्रस्तुत करता है। इससे भी महत्वपूर्ण बात यह है कि रणनीतिक लक्ष्य लोकतंत्रों का एक मजबूत गठबंधन बनाना होना चाहिए, जिसमें भारत एक केंद्रीय स्तंभ हो। साझा चुनौतियों का समाधान करके, आपसी ताकतों को अपनाकर और ठोस सहयोग को बढ़ावा देकर, यूरोप, भारत और अमेरिका एक अजेय लोकतांत्रिक गठबंधन बना सकते हैं जो निरंकुश शक्तियों का मुकाबला करने और एक सुरक्षित, समृद्ध भविष्य सुनिश्चित करने में सक्षम हो।