
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 31/12/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 31/12/2024
- Unconventional methods like AI-based warfare a big challenge, says Rajnath /राजनाथ ने कहा कि एआई आधारित युद्ध जैसे अपरंपरागत तरीके एक बड़ी चुनौती हैं
- Grave new world: human-induced loss of elders threatens various species /गंभीर नई दुनिया: बुजुर्गों की मानव-प्रेरित हानि विभिन्न प्रजातियों के लिए खतरा है
- NASA probe flies closer to the sun than any spacecraft /नासा जांच किसी भी अंतरिक्ष यान की तुलना में सूर्य के करीब उड़ती है
- National Green Tribunal (NGT) /राष्ट्रीय हरित अधिकरण (एनजीटी)
- Fishing Cat Collaring Project /फिशिंग कैट कॉलरिंग परियोजना
- States and the danger of poorly manufactured drugs /राज्य और खराब तरीके से निर्मित दवाओं का खतरा
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 31/12/2024
Unconventional methods like AI-based warfare a big challenge, says Rajnath /राजनाथ ने कहा कि एआई आधारित युद्ध जैसे अपरंपरागत तरीके एक बड़ी चुनौती हैं
Syllabus : GS 3 : Internal Security
Source : The Hindu
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh addressed the growing challenge posed by unconventional warfare methods, including Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based warfare, cyber attacks, and other advanced forms of conflict.
Types of Emerging Threats
- AI-Based Warfare: Leveraging AI for decision-making and automation in military operations could outpace traditional warfare tactics. AI can also be used in autonomous weapons, making the battlefield more complex and unpredictable.
- Cyber Attacks: Increasing reliance on digital infrastructure makes military systems vulnerable to cyber-attacks, which could disrupt command and control, intelligence systems, and critical infrastructure.
- Information Warfare: Manipulating public opinion and spreading misinformation can destabilize societies, making information control a critical element of modern conflicts.
- Electromagnetic Warfare: The use of electromagnetic fields to disable enemy communication and radar systems is emerging as a new mode of attack.
- Space Warfare: The militarization of space presents new vulnerabilities, with satellite systems becoming targets for cyber or physical attacks.
- Proxy Warfare: Involves the use of indirect methods such as using non-state actors to advance national interests, complicating the attribution of attacks.
Challenges in Combating New Threats
- The rapid evolution of these threats requires swift adaptation, with militaries needing to integrate new technologies, like AI, to counter them effectively.
- Traditional defence systems and training may not be sufficient to address such advanced threats, demanding a rethinking of defence strategies and tactics.
- Cybersecurity, in particular, requires ongoing innovation and vigilance to protect against increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
India’s Response to Emerging Threats
- Defence Minister Rajnath Singh emphasized the importance of mastering frontier technologies to keep up with evolving challenges.
- The government has focused on enhancing military training programs, particularly in areas like AI, communication technology, and leadership.
- Training centres like those in Mhow Cantonment are evolving their curricula to address these new challenges, preparing soldiers for future warfare.
- India’s defence exports have significantly increased, with a target of ₹50,000 crore by 2029, reflecting the country’s growing capabilities in advanced defence technology.
Way Forward: Strengthening Defence and Preparedness
- Invest in AI Research: Continued investment in AI research is crucial to develop new technologies and techniques to combat AI-driven threats.
- Develop AI-Powered Defenses: The development of AI-powered defenses, such as machine learning-based intrusion detection systems, is essential to detect and respond to advanced threats.
- Promote International Cooperation: International cooperation is needed to share information and best practices in combating AI-driven threats.
- Develop Ethical Guidelines: The development of ethical guidelines for the use of AI in cybersecurity is necessary to ensure that these technologies are used responsibly.
Conclusion
- The emergence of unconventional warfare methods presents new challenges for national security.
- India must prioritize advancements in frontier technologies like AI and cyber defense.
- Comprehensive strategies are essential for future readiness.
राजनाथ ने कहा कि एआई आधारित युद्ध जैसे अपरंपरागत तरीके एक बड़ी चुनौती हैं
रक्षा मंत्री राजनाथ सिंह ने आर्टिफिशियल इंटेलिजेंस (एआई) आधारित युद्ध, साइबर हमले और संघर्ष के अन्य उन्नत रूपों सहित अपरंपरागत युद्ध विधियों से उत्पन्न बढ़ती चुनौतियों पर बात की।
उभरते खतरों के प्रकार
- AI-आधारित युद्ध: सैन्य अभियानों में निर्णय लेने और स्वचालन के लिए AI का लाभ उठाना पारंपरिक युद्ध रणनीति से आगे निकल सकता है। AI का उपयोग स्वायत्त हथियारों में भी किया जा सकता है, जिससे युद्ध का मैदान अधिक जटिल और अप्रत्याशित हो जाता है।
- साइबर हमले: डिजिटल बुनियादी ढांचे पर बढ़ती निर्भरता सैन्य प्रणालियों को साइबर हमलों के प्रति संवेदनशील बनाती है, जो कमांड और नियंत्रण, खुफिया प्रणालियों और महत्वपूर्ण बुनियादी ढांचे को बाधित कर सकती है।
- सूचना युद्ध: जनमत में हेरफेर करना और गलत सूचना फैलाना समाज को अस्थिर कर सकता है, जिससे सूचना नियंत्रण आधुनिक संघर्षों का एक महत्वपूर्ण तत्व बन जाता है।
- विद्युत चुम्बकीय युद्ध: दुश्मन के संचार और रडार सिस्टम को निष्क्रिय करने के लिए विद्युत चुम्बकीय क्षेत्रों का उपयोग हमले के एक नए तरीके के रूप में उभर रहा है।
- अंतरिक्ष युद्ध: अंतरिक्ष का सैन्यीकरण नई कमजोरियाँ प्रस्तुत करता है, जिसमें उपग्रह प्रणालियाँ साइबर या भौतिक हमलों का लक्ष्य बन जाती हैं।
- प्रॉक्सी युद्ध: इसमें राष्ट्रीय हितों को आगे बढ़ाने के लिए गैर-राज्य अभिनेताओं का उपयोग करने जैसे अप्रत्यक्ष तरीकों का उपयोग शामिल है, जिससे हमलों के लिए जिम्मेदार ठहराना जटिल हो जाता है।
नए खतरों से निपटने में चुनौतियाँ
- इन खतरों के तेजी से विकास के लिए तेजी से अनुकूलन की आवश्यकता है, सेनाओं को इनका प्रभावी ढंग से मुकाबला करने के लिए एआई जैसी नई तकनीकों को एकीकृत करने की आवश्यकता है।
- ऐसे उन्नत खतरों से निपटने के लिए पारंपरिक रक्षा प्रणालियाँ और प्रशिक्षण पर्याप्त नहीं हो सकते हैं, जिसके लिए रक्षा रणनीतियों और कार्यनीति पर पुनर्विचार की आवश्यकता है।
- विशेष रूप से, साइबर सुरक्षा के लिए निरंतर नवाचार और सतर्कता की आवश्यकता होती है, ताकि तेजी से परिष्कृत हो रहे साइबर हमलों से बचा जा सके।
उभरते खतरों के प्रति भारत की प्रतिक्रिया
- रक्षा मंत्री राजनाथ सिंह ने उभरती चुनौतियों से निपटने के लिए सीमांत प्रौद्योगिकियों में महारत हासिल करने के महत्व पर जोर दिया।
- सरकार ने सैन्य प्रशिक्षण कार्यक्रमों को बढ़ाने पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया है, विशेष रूप से एआई, संचार प्रौद्योगिकी और नेतृत्व जैसे क्षेत्रों में।
- महू छावनी जैसे प्रशिक्षण केंद्र इन नई चुनौतियों से निपटने के लिए अपने पाठ्यक्रम विकसित कर रहे हैं, जिससे सैनिकों को भविष्य के युद्ध के लिए तैयार किया जा सके।
- भारत के रक्षा निर्यात में उल्लेखनीय वृद्धि हुई है, जिसका लक्ष्य 2029 तक 50,000 करोड़ रुपये है, जो उन्नत रक्षा प्रौद्योगिकी में देश की बढ़ती क्षमताओं को दर्शाता है।
आगे की राह: रक्षा और तैयारियों को मजबूत करना
- एआई अनुसंधान में निवेश: एआई-संचालित खतरों से निपटने के लिए नई तकनीकों और तकनीकों को विकसित करने के लिए एआई अनुसंधान में निरंतर निवेश महत्वपूर्ण है।
- एआई-संचालित सुरक्षा विकसित करें: मशीन लर्निंग-आधारित घुसपैठ का पता लगाने वाली प्रणालियों जैसे एआई-संचालित सुरक्षा का विकास, उन्नत खतरों का पता लगाने और उनका जवाब देने के लिए आवश्यक है।
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग को बढ़ावा दें: एआई-संचालित खतरों से निपटने में सूचना और सर्वोत्तम प्रथाओं को साझा करने के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग की आवश्यकता है।
- नैतिक दिशा-निर्देश विकसित करें: साइबर सुरक्षा में एआई के उपयोग के लिए नैतिक दिशा-निर्देशों का विकास यह सुनिश्चित करने के लिए आवश्यक है कि इन तकनीकों का उपयोग जिम्मेदारी से किया जाए।
निष्कर्ष
- अपरंपरागत युद्ध विधियों का उदय राष्ट्रीय सुरक्षा के लिए नई चुनौतियाँ प्रस्तुत करता है।
- भारत को एआई और साइबर रक्षा जैसी अग्रणी तकनीकों में प्रगति को प्राथमिकता देनी चाहिए।
- भविष्य की तैयारी के लिए व्यापक रणनीतियाँ आवश्यक हैं।
Grave new world: human-induced loss of elders threatens various species /गंभीर नई दुनिया: बुजुर्गों की मानव-प्रेरित हानि विभिन्न प्रजातियों के लिए खतरा है
Syllabus : GS 3 : Environment
Source : The Hindu
The article discusses the vital role of elder animals in ecosystems, highlighting their contributions to species survival and conservation.
Importance of Elders in the Animal Kingdom
- Elder animals, from elephant matriarchs to shark grandmothers, guide their families through life’s challenges, imparting crucial knowledge.
- The roles of older animals are crucial across species, particularly in how they stabilize social hierarchies and pass on knowledge for survival.
Aging in the Wild
- Aging varies across species, with older individuals often holding significant roles in social stability and knowledge transmission.
- Researchers highlight that the loss of older individuals due to factors like habitat destruction, hunting, and climate change can significantly impact species, particularly long-lived animals.
- These elders are vital for passing on cultural practices and knowledge of adaptation.
- Elder individuals in long-lived species are essential for knowledge transmission, assisted parental care, and survival strategies in harsh environments.
Examples of Elder Roles in Animal Social Structures
- Elephants: African elephants rely heavily on matriarchs, the oldest females, for survival. Studies show that elephant herds with older matriarchs respond more effectively to threats, such as lion roars. In their absence, younger elephants struggle to adapt and may even face increased risks of conflict with humans.
- Orcas: Older female orcas undergo menopause, enabling them to assist in raising their daughters’ calves. This behavior, known as the grandmother hypothesis, is crucial for the survival of orca populations, as older females help guide the young to feeding grounds and protect them from predators.
Impact of Human Activities on Elders
- Human activities like climate change and habitat destruction threaten the survival of elder animals, leading to cascading effects on the social structure and behavior of species.
- In species like elephants and orcas, the loss of elders disrupts social stability and makes it more challenging for younger members to thrive, increasing stress and vulnerability.
Longevity Conservation Paradigm
- The concept of longevity conservation is introduced, advocating for the protection of older individuals in species conservation efforts.
- This includes preserving age structure, which is critical in long-lived species that rely on older individuals for reproduction, migration, and cultural transmission of knowledge.
- This paradigm is particularly important for species in fluctuating environments, such as fish and reptiles, where older individuals contribute more to reproduction and survival.
Challenges in Implementing Conservation Strategies
- Implementing longevity conservation strategies is challenging, particularly in multi-species fisheries like those in India, where different species grow at different rates and require different management approaches. Fishing gear cannot easily target specific species or ages.
- Despite the benefits, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has not yet recognized the loss of older individuals as a primary criterion for listing species as threatened.
Conclusion
- Protecting elder animals is crucial for biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
- Their knowledge, experience, and roles in social structures help ensure species’ survival, especially in the face of environmental changes and human disturbances.
- Efforts to protect these individuals through strategies like age-based fisheries management can aid in conservation, though significant challenges remain in implementing these strategies.
गंभीर नई दुनिया: बुजुर्गों की मानव-प्रेरित हानि विभिन्न प्रजातियों के लिए खतरा है
लेख में पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र में वृद्ध पशुओं की महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका पर चर्चा की गई है तथा प्रजातियों के अस्तित्व और संरक्षण में उनके योगदान पर प्रकाश डाला गया है।
जानवरों के साम्राज्य में बुजुर्गों का महत्व
- हाथी की कुलमाता से लेकर शार्क की दादी तक, बुजुर्ग जानवर अपने परिवारों को जीवन की चुनौतियों से गुज़रने में मार्गदर्शन करते हैं, और महत्वपूर्ण ज्ञान प्रदान करते हैं।
- बड़े जानवरों की भूमिकाएँ सभी प्रजातियों में महत्वपूर्ण हैं, खासकर इस बात में कि वे सामाजिक पदानुक्रम को कैसे स्थिर करते हैं और जीवित रहने के लिए ज्ञान कैसे देते हैं।
जंगल में बुढ़ापा
- विभिन्न प्रजातियों में बुढ़ापा अलग-अलग होता है, जिसमें वृद्ध व्यक्ति अक्सर सामाजिक स्थिरता और ज्ञान संचरण में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं।
- शोधकर्ताओं ने इस बात पर प्रकाश डाला है कि आवास विनाश, शिकार और जलवायु परिवर्तन जैसे कारकों के कारण वृद्ध व्यक्तियों की हानि प्रजातियों, विशेष रूप से लंबे समय तक रहने वाले जानवरों को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से प्रभावित कर सकती है।
- ये बुजुर्ग सांस्कृतिक प्रथाओं और अनुकूलन के ज्ञान को आगे बढ़ाने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण हैं।
- लंबे समय तक जीवित रहने वाली प्रजातियों में बुजुर्ग व्यक्ति ज्ञान संचरण, सहायक माता-पिता की देखभाल और कठोर वातावरण में जीवित रहने की रणनीतियों के लिए आवश्यक हैं।
पशु सामाजिक संरचनाओं में बुजुर्गों की भूमिका के उदाहरण
- हाथी: अफ्रीकी हाथी जीवित रहने के लिए सबसे बूढ़ी मादाओं, यानी कुलमाता पर बहुत अधिक निर्भर करते हैं। अध्ययनों से पता चलता है कि बड़ी उम्र की कुलमाता वाले हाथियों के झुंड शेर की दहाड़ जैसे खतरों का अधिक प्रभावी ढंग से जवाब देते हैं। उनकी अनुपस्थिति में, युवा हाथियों को अनुकूलन करने में कठिनाई होती है और उन्हें मनुष्यों के साथ संघर्ष के बढ़ते जोखिम का भी सामना करना पड़ सकता है।
- ओर्कास: वृद्ध मादा ओर्का रजोनिवृत्ति से गुजरती हैं, जिससे वे अपनी बेटियों के बछड़ों को पालने में सहायता कर पाती हैं। यह व्यवहार, जिसे दादी परिकल्पना के रूप में जाना जाता है, ओर्का आबादी के अस्तित्व के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है, क्योंकि वृद्ध मादाएं बच्चों को चारागाह तक ले जाने और शिकारियों से उनकी रक्षा करने में मदद करती हैं।
बुजुर्गों पर मानवीय गतिविधियों का प्रभाव
- जलवायु परिवर्तन और आवास विनाश जैसी मानवीय गतिविधियाँ वृद्ध जानवरों के अस्तित्व को खतरे में डालती हैं, जिससे प्रजातियों की सामाजिक संरचना और व्यवहार पर व्यापक प्रभाव पड़ता है।
- हाथियों और ओर्का जैसी प्रजातियों में, बुजुर्गों की हानि सामाजिक स्थिरता को बाधित करती है और युवा सदस्यों के लिए पनपना अधिक चुनौतीपूर्ण बना देती है, जिससे तनाव और भेद्यता बढ़ जाती है।
दीर्घायु संरक्षण प्रतिमान
- दीर्घायु संरक्षण की अवधारणा पेश की गई है, जो प्रजातियों के संरक्षण प्रयासों में वृद्ध व्यक्तियों की सुरक्षा की वकालत करती है।
- इसमें आयु संरचना को संरक्षित करना शामिल है, जो लंबे समय तक जीवित रहने वाली प्रजातियों में महत्वपूर्ण है जो प्रजनन, प्रवास और ज्ञान के सांस्कृतिक संचरण के लिए वृद्ध व्यक्तियों पर निर्भर हैं।
- यह प्रतिमान विशेष रूप से परिवर्तनशील वातावरण में रहने वाली प्रजातियों, जैसे कि मछली और सरीसृपों के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है, जहाँ वृद्ध व्यक्ति प्रजनन और अस्तित्व में अधिक योगदान देते हैं।
संरक्षण रणनीतियों को लागू करने में चुनौतियाँ
- दीर्घायु संरक्षण रणनीतियों को लागू करना चुनौतीपूर्ण है, विशेष रूप से भारत जैसे बहु-प्रजाति मत्स्य पालन में, जहाँ विभिन्न प्रजातियाँ अलग-अलग दरों पर बढ़ती हैं और उन्हें अलग-अलग प्रबंधन दृष्टिकोणों की आवश्यकता होती है। मछली पकड़ने का गियर आसानी से विशिष्ट प्रजातियों या उम्र को लक्षित नहीं कर सकता है।
- लाभों के बावजूद, प्रकृति के संरक्षण के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय संघ (IUCN) ने अभी तक वृद्ध व्यक्तियों के नुकसान को प्रजातियों को खतरे में डालने के लिए प्राथमिक मानदंड के रूप में मान्यता नहीं दी है।
निष्कर्ष
- वृद्ध जानवरों की सुरक्षा जैव विविधता और पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र स्थिरता के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
- सामाजिक संरचनाओं में उनका ज्ञान, अनुभव और भूमिकाएँ प्रजातियों के अस्तित्व को सुनिश्चित करने में मदद करती हैं, खासकर पर्यावरणीय परिवर्तनों और मानवीय गड़बड़ी के सामने।
- आयु-आधारित मत्स्य प्रबंधन जैसी रणनीतियों के माध्यम से इन व्यक्तियों की रक्षा करने के प्रयास संरक्षण में सहायता कर सकते हैं, हालाँकि इन रणनीतियों को लागू करने में महत्वपूर्ण चुनौतियाँ बनी हुई हैं।
NASA probe flies closer to the sun than any spacecraft /नासा जांच किसी भी अंतरिक्ष यान की तुलना में सूर्य के करीब उड़ती है
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
On December 24, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe made history by flying closer to the sun than any spacecraft before.
- It reached a distance of 6.1 million kilometers from the sun’s surface, with its heat shield exposed to temperatures above 930°C.
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe:
- Overview
- The Parker Solar Probe is a NASA spacecraft designed to study the Sun.
- Launched on August 12, 2018, it is on a seven-year mission to get closer to the Sun than any spacecraft before.
- Mission Objectives
- The primary goal is to understand the Sun’s outer atmosphere, called the corona, and its behavior.
- It aims to uncover the origins of solar wind and understand how solar storms (coronal mass ejections) affect Earth.
- The probe seeks to answer why the Sun’s corona is hotter than its surface.
- Heat Shield Technology
- The spacecraft is equipped with a heat shield to protect it from extreme temperatures, with the Sun’s heat reaching over 930°C.
- Despite the intense heat, the probe’s instruments are kept near room temperature (around 29°C).
- Future Milestones
- The Parker Solar Probe will make multiple close passes to gather more data, with significant flybys scheduled in 2025.
नासा जांच किसी भी अंतरिक्ष यान की तुलना में सूर्य के करीब उड़ती है
24 दिसंबर को, नासा के पार्कर सोलर प्रोब ने किसी भी अंतरिक्ष यान की तुलना में सूर्य के सबसे करीब उड़ान भरकर इतिहास रच दिया।
- यह सूर्य की सतह से 1 मिलियन किलोमीटर की दूरी पर पहुंचा, इसकी हीट शील्ड 930 डिग्री सेल्सियस से अधिक तापमान के संपर्क में थी।
नासा का पार्कर सोलर प्रोब:
- अवलोकन
- पार्कर सोलर प्रोब नासा का एक अंतरिक्ष यान है जिसे सूर्य का अध्ययन करने के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया है।
- 12 अगस्त, 2018 को लॉन्च किया गया, यह किसी भी अंतरिक्ष यान की तुलना में सूर्य के सबसे करीब पहुंचने के लिए सात साल के मिशन पर है।
- मिशन के उद्देश्य
- प्राथमिक लक्ष्य सूर्य के बाहरी वायुमंडल, जिसे कोरोना कहा जाता है, और उसके व्यवहार को समझना है।
- इसका उद्देश्य सौर हवा की उत्पत्ति को उजागर करना और यह समझना है कि सौर तूफान (कोरोनल मास इजेक्शन) पृथ्वी को कैसे प्रभावित करते हैं।
- जांच यह उत्तर देने का प्रयास करती है कि सूर्य का कोरोना उसकी सतह से अधिक गर्म क्यों है।
- हीट शील्ड तकनीक
- अंतरिक्ष यान को अत्यधिक तापमान से बचाने के लिए हीट शील्ड से सुसज्जित किया गया है, जिसमें सूर्य की गर्मी 930 डिग्री सेल्सियस से अधिक तक पहुँच जाती है।
- तीव्र गर्मी के बावजूद, जांच के उपकरणों को कमरे के तापमान (लगभग 29 डिग्री सेल्सियस) के करीब रखा जाता है।
- भविष्य की उपलब्धियाँ
- पार्कर सोलर प्रोब अधिक डेटा एकत्र करने के लिए कई नज़दीकी चक्कर लगाएगा, जिसमें 2025 में महत्वपूर्ण फ्लाईबाई निर्धारित है।
National Green Tribunal (NGT) /राष्ट्रीय हरित अधिकरण (एनजीटी)
In News
The National Green Tribunal has sought a response from the Central Pollution Control Board and Jaipur’s District Magistrate in a matter related to several students getting hospitalised after a suspected gas leak in the Rajasthan capital.

About National Green Tribunal:
- It was established in 2010 under the National Green Tribunal Act, 2010 for effective and expeditious disposal of cases relating to environmental protection and conservation of forests and other natural resources.
- It is a specialized body equipped with the necessary expertise to handle environmental disputes involving multi-disciplinary issues.
- The Tribunal shall not be bound by the procedure laid down under the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, but shall be guided by principles of natural justice.
- The Tribunal is mandated to make and endeavour for disposal of applications or appeals finally within 6 months of filing of the case.
- Locations: New Delhi is the Principal Place of Sitting of the Tribunal and Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata and Chennai shall be the other four place of sitting of the Tribunal.
- Composition of NGT: The Tribunal comprises:
- Chairperson: A retired Supreme Court judge.
- Judicial members: Retired High Court judges.
- Expert members: Professionals with at least 15 years of experience in fields related to environment or forest conservation.
राष्ट्रीय हरित अधिकरण (एनजीटी)
राष्ट्रीय हरित अधिकरण (एनजीटी) ने राजस्थान की राजधानी में संदिग्ध गैस रिसाव के बाद कई छात्रों के अस्पताल में भर्ती होने से संबंधित मामले में केंद्रीय प्रदूषण नियंत्रण बोर्ड और जयपुर के जिला मजिस्ट्रेट से जवाब मांगा है।
राष्ट्रीय हरित अधिकरण के बारे में:
- इसकी स्थापना 2010 में राष्ट्रीय हरित अधिकरण अधिनियम, 2010 के तहत पर्यावरण संरक्षण और वनों तथा अन्य प्राकृतिक संसाधनों के संरक्षण से संबंधित मामलों के प्रभावी और शीघ्र निपटान के लिए की गई थी।
- यह बहु-विषयक मुद्दों से जुड़े पर्यावरणीय विवादों को संभालने के लिए आवश्यक विशेषज्ञता से लैस एक विशेष निकाय है।
- न्यायाधिकरण सिविल प्रक्रिया संहिता, 1908 के तहत निर्धारित प्रक्रिया से बाध्य नहीं होगा, बल्कि प्राकृतिक न्याय के सिद्धांतों द्वारा निर्देशित होगा।
- न्यायाधिकरण को मामला दायर करने के 6 महीने के भीतर आवेदनों या अपीलों का अंतिम रूप से निपटान करने का अधिकार है।
- स्थान: नई दिल्ली न्यायाधिकरण का मुख्य बैठने का स्थान है और भोपाल, पुणे, कोलकाता और चेन्नई न्यायाधिकरण के बैठने के अन्य चार स्थान होंगे।
- एनजीटी की संरचना: न्यायाधिकरण में शामिल हैं:
- अध्यक्ष: सर्वोच्च न्यायालय के सेवानिवृत्त न्यायाधीश।
- न्यायिक सदस्य: उच्च न्यायालय के सेवानिवृत्त न्यायाधीश।
- विशेषज्ञ सदस्य: पर्यावरण या वन संरक्षण से संबंधित क्षेत्रों में कम से कम 15 वर्ष का अनुभव रखने वाले पेशेवर।
Fishing Cat Collaring Project /फिशिंग कैट कॉलरिंग परियोजना
In News
The Wildlife Institute of India-Dehradun is set to launch India’s first Fishing Cat Collaring Project at Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary.
Analysis of the news:
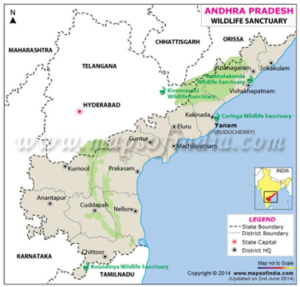
India’s First Fishing Cat Collaring Project:
- The Wildlife Institute of India-Dehradun is executing India’s first Fishing Cat Collaring Project as part of the second fishing cat census.
- This three-year project aims to study the species’ home range, behaviour, habitat ecology, feeding habits, and space use.
- The project plans to collar 10 fishing cats with lightweight GIS-equipped devices.
- The collaring is expected to be completed by March or April 2025.
Fishing Cats

- Scientific Name: Prionailurus viverrinus.
- Description:
- It is twice the size of a house cat.
- The fishing cat is nocturnal (active at night) and apart from fish also preys on frogs, crustaceans, snakes, birds, and scavenges on carcasses of larger animals.
- The species breed all year round.
- They spend most of their lives in areas of dense vegetation close to water bodies and are excellent swimmers.
Habitat:
- Fishing cats have a patchy distribution along the Eastern Ghats. They abound in estuarine floodplains, tidal mangrove forests and also inland freshwater habitats.
- Apart from Sundarbans in West Bengal and Bangladesh, fishing cats inhabit the Chilika lagoon and surrounding wetlands in Odisha, Coringa and Krishna mangroves in Andhra Pradesh.
Threats:
- A major threat for fishing cats is the destruction of wetlands, their preferred habitat.
- Shrimp farming is another growing threat to the mangrove habitats of the Fishing Cat.
- This unique cat also faces threats from hunting for meat and skin.
- Tribal hunters indulge in ritual hunting practices throughout the year.
- It is also occasionally poached for its skin.
Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix II
- Indian Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Spanning 235 square kilometers, Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary (CWS) is India’s second-largest mangrove habitat.
- It is home to the endangered fishing cat.
- Located in the Godavari estuary, the sanctuary lies at the confluence of the Coringa River and the Bay of Bengal in Kakinada, Andhra Pradesh.
- Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary in the Krishna estuarine forest area is another habitat for the fishing cat..
फिशिंग कैट कॉलरिंग परियोजना
भारतीय वन्यजीव संस्थान-देहरादून कोरिंगा वन्यजीव अभयारण्य में भारत की पहली फिशिंग कैट कॉलरिंग परियोजना शुरू करने जा रहा है।
खबर का विश्लेषण:
भारत की पहली फिशिंग कैट कॉलरिंग परियोजना:
- भारतीय वन्यजीव संस्थान-देहरादून दूसरी फिशिंग कैट जनगणना के हिस्से के रूप में भारत की पहली फिशिंग कैट कॉलरिंग परियोजना को क्रियान्वित कर रहा है।
- इस तीन वर्षीय परियोजना का उद्देश्य प्रजातियों की घरेलू सीमा, व्यवहार, आवास पारिस्थितिकी, भोजन की आदतों और स्थान के उपयोग का अध्ययन करना है।
- इस परियोजना में हल्के जीआईएस-सुसज्जित उपकरणों के साथ 10 फिशिंग कैट को कॉलर लगाने की योजना है।
- कॉलरिंग मार्च या अप्रैल 2025 तक पूरी होने की उम्मीद है।
मछली पकड़ने वाली बिल्लियाँ:
वैज्ञानिक नाम: प्रियोनेलुरस विवरिनस।
- विवरण:
- यह घरेलू बिल्ली से दुगुना बड़ा होता है।
- फिशिंग कैट रात्रिचर (रात में सक्रिय) होती है और मछलियों के अलावा मेंढक, क्रस्टेशियन, सांप, पक्षियों का भी शिकार करती है और बड़े जानवरों के शवों को खाती है।
- यह प्रजाति पूरे साल प्रजनन करती है।
- वे अपना अधिकांश जीवन जल निकायों के करीब घने वनस्पति वाले क्षेत्रों में बिताते हैं और बेहतरीन तैराक होते हैं।
निवास स्थान:
- फिशिंग कैट का पूर्वी घाट के साथ-साथ वितरण छिटपुट है। वे मुहाना के बाढ़ के मैदानों, ज्वारीय मैंग्रोव जंगलों और अंतर्देशीय मीठे पानी के आवासों में भी प्रचुर मात्रा में पाए जाते हैं।
- पश्चिम बंगाल और बांग्लादेश में सुंदरबन के अलावा, फिशिंग कैट ओडिशा में चिलिका लैगून और आसपास की आर्द्रभूमि, आंध्र प्रदेश में कोरिंगा और कृष्णा मैंग्रोव में निवास करती हैं।
खतरे:
- फिशिंग कैट के लिए एक बड़ा खतरा आर्द्रभूमि का विनाश है, जो उनका पसंदीदा आवास है।
- झींगा पालन फिशिंग कैट के मैंग्रोव आवासों के लिए एक और बढ़ता हुआ खतरा है।
- इस अनोखी बिल्ली को मांस और त्वचा के लिए शिकार से भी खतरा है।
- आदिवासी शिकारी पूरे साल अनुष्ठानिक शिकार प्रथाओं में लिप्त रहते हैं।
- कभी-कभी इसकी खाल के लिए भी इसका अवैध शिकार किया जाता है।
संरक्षण स्थिति:
- IUCN रेड लिस्ट: असुरक्षित
- CITES: परिशिष्ट II
- भारतीय वन्यजीव संरक्षण अधिनियम, 1972: अनुसूची I
- कोरिंगा वन्यजीव अभयारण्य:
- 235 वर्ग किलोमीटर में फैला, कोरिंगा वन्यजीव अभयारण्य (CWS) भारत का दूसरा सबसे बड़ा मैंग्रोव आवास है।
- यह लुप्तप्राय मछली पकड़ने वाली बिल्ली का घर है।
- गोदावरी मुहाने पर स्थित यह अभयारण्य आंध्र प्रदेश के काकीनाडा में कोरिंगा नदी और बंगाल की खाड़ी के संगम पर स्थित है।
- कृष्णा मुहाना वन क्षेत्र में कृष्णा वन्यजीव अभयारण्य मछली पकड़ने वाली बिल्ली का एक और आवास है।
States and the danger of poorly manufactured drugs /राज्य और खराब तरीके से निर्मित दवाओं का खतरा
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 : Social Justice – Health
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- Recent incidents involving NSQ drugs have raised concerns, with five young mothers in Ballari, Karnataka, allegedly dying due to contaminated drugs manufactured by a pharmaceutical company in West Bengal.
Incidents of Not of Standard Quality (NSQ) Drugs in India
- The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940, allows pharmaceutical companies to sell their drugs across the country, even if they are licensed and inspected only in the state where the manufacturing facility is located.
- This regulatory gap makes it difficult for states like Karnataka to prevent poorly manufactured drugs from flooding local pharmacies, leading to significant public health risks.
Problems Faced by States in Addressing NSQ Drugs
- Some states face challenges in dealing with drugs manufactured outside their jurisdiction.
- Drug inspectors can only prosecute pharmaceutical companies, which is a time-consuming process.
- During the trial, manufacturers from other states can continue selling their products, as only the home-state drug inspectors have the authority to cancel or suspend manufacturing licenses.
Proposed Solutions to Address the Issue
- One cost-effective solution is to promote information sharing between the drug control departments of different states and public procurement agencies.
- A centralized database of test results from central and state drug testing laboratories would allow drug inspectors and procurement officials to track drug failures across states. This would help in adopting a risk-based approach for enforcement and procurement decisions.
- Centralized inspection reports and licensing information from state drug inspectors should also be made available in one database.
- This would allow procurement agencies to verify pharmaceutical companies’ credentials and avoid the purchase of low-quality drugs.
Benefits of a Centralized Database
- A centralized database would assist procurement agencies the state agencies in verifying the quality of pharmaceutical manufacturers before purchasing drugs.
- This would help prevent incidents like the recent scandal in Maharashtra, where spurious antibiotics were sold to public hospitals.
- By tracking manufacturers with poor inspection records, procurement officers can prioritize suppliers from states known for rigorous inspections, ultimately improving public health outcomes.
Additional Recommendations
- A central register should be created by the Union Ministry of Health to record pharmaceutical manufacturers blacklisted by procurement agencies for supplying NSQ drugs. This would help eliminate bad players from the market.
- States should be empowered with legal authority to block manufacturers from other states from selling drugs within their jurisdiction if the drugs have caused adverse health effects, such as deaths, until the manufacturers rectify the issue.
Conclusion:
- The issue of NSQ drugs in India highlights significant regulatory gaps and public health risks.
- Strengthening information sharing through centralized databases can improve drug quality control.
- Empowering states with legal authority and advocating for legislative reforms will ensure better monitoring and enforcement, improving drug safety across the nation.
राज्य और खराब तरीके से निर्मित दवाओं का खतरा
संदर्भ :
- NSQ दवाओं से जुड़ी हाल की घटनाओं ने चिंता बढ़ा दी है, कर्नाटक के बल्लारी में पांच युवा माताओं की मौत कथित तौर पर पश्चिम बंगाल में एक दवा कंपनी द्वारा निर्मित दूषित दवाओं के कारण हुई।
भारत में मानक गुणवत्ता (NSQ) के अनुरूप नहीं दवाओं की घटनाएँ
- ड्रग्स एंड कॉस्मेटिक्स एक्ट, 1940, दवा कंपनियों को देश भर में अपनी दवाएँ बेचने की अनुमति देता है, भले ही उन्हें लाइसेंस प्राप्त हो और उनका निरीक्षण केवल उसी राज्य में हो जहाँ विनिर्माण सुविधा स्थित है।
- यह विनियामक अंतर कर्नाटक जैसे राज्यों के लिए खराब तरीके से निर्मित दवाओं को स्थानीय फार्मेसियों में आने से रोकना मुश्किल बनाता है, जिससे सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य को महत्वपूर्ण जोखिम होता है।
NSQ दवाओं से निपटने में राज्यों के सामने आने वाली समस्याएँ
- कुछ राज्यों को अपने अधिकार क्षेत्र के बाहर निर्मित दवाओं से निपटने में चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ता है।
- ड्रग इंस्पेक्टर केवल दवा कंपनियों पर मुकदमा चला सकते हैं, जो एक समय लेने वाली प्रक्रिया है।
- मुकदमे के दौरान, अन्य राज्यों के निर्माता अपने उत्पादों को बेचना जारी रख सकते हैं, क्योंकि केवल गृह-राज्य के ड्रग इंस्पेक्टरों के पास विनिर्माण लाइसेंस रद्द करने या निलंबित करने का अधिकार होता है।
समस्या के समाधान के लिए प्रस्तावित समाधान
- एक लागत प्रभावी समाधान विभिन्न राज्यों के औषधि नियंत्रण विभागों और सार्वजनिक खरीद एजेंसियों के बीच सूचना साझाकरण को बढ़ावा देना है।
- केंद्रीय और राज्य औषधि परीक्षण प्रयोगशालाओं से परीक्षण परिणामों का एक केंद्रीकृत डेटाबेस औषधि निरीक्षकों और खरीद अधिकारियों को राज्यों में औषधि विफलताओं को ट्रैक करने की अनुमति देगा। इससे प्रवर्तन और खरीद निर्णयों के लिए जोखिम-आधारित दृष्टिकोण अपनाने में मदद मिलेगी।
- राज्य औषधि निरीक्षकों से केंद्रीकृत निरीक्षण रिपोर्ट और लाइसेंसिंग जानकारी भी एक डेटाबेस में उपलब्ध कराई जानी चाहिए।
- इससे खरीद एजेंसियों को दवा कंपनियों की साख सत्यापित करने और कम गुणवत्ता वाली दवाओं की खरीद से बचने में मदद मिलेगी।
केंद्रीकृत डेटाबेस के लाभ
- एक केंद्रीकृत डेटाबेस दवा खरीदने से पहले दवा निर्माताओं की गुणवत्ता को सत्यापित करने में खरीद एजेंसियों और राज्य एजेंसियों की सहायता करेगा।
- इससे महाराष्ट्र में हाल ही में हुए घोटाले जैसी घटनाओं को रोकने में मदद मिलेगी, जहां सार्वजनिक अस्पतालों को नकली एंटीबायोटिक्स बेचे गए थे।
- खराब निरीक्षण रिकॉर्ड वाले निर्माताओं को ट्रैक करके, खरीद अधिकारी कठोर निरीक्षण के लिए जाने जाने वाले राज्यों के आपूर्तिकर्ताओं को प्राथमिकता दे सकते हैं, जिससे अंततः सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य परिणामों में सुधार होगा।
अतिरिक्त सिफारिशें
- एनएसक्यू दवाओं की आपूर्ति के लिए खरीद एजेंसियों द्वारा ब्लैकलिस्ट किए गए दवा निर्माताओं को रिकॉर्ड करने के लिए केंद्रीय स्वास्थ्य मंत्रालय द्वारा एक केंद्रीय रजिस्टर बनाया जाना चाहिए। इससे बाजार से बुरे खिलाड़ियों को बाहर निकालने में मदद मिलेगी।
- राज्यों को कानूनी अधिकार दिया जाना चाहिए कि वे अन्य राज्यों के निर्माताओं को अपने अधिकार क्षेत्र में दवाएँ बेचने से तब तक रोकें जब तक कि निर्माता समस्या का समाधान न कर लें, अगर दवाओं से स्वास्थ्य पर प्रतिकूल प्रभाव पड़ता है, जैसे कि मृत्यु।
निष्कर्ष:
- भारत में NSQ दवाओं का मुद्दा महत्वपूर्ण विनियामक अंतराल और सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य जोखिमों को उजागर करता है।
- केंद्रीकृत डेटाबेस के माध्यम से सूचना साझा करने को मजबूत करने से दवा की गुणवत्ता नियंत्रण में सुधार हो सकता है।
- राज्यों को कानूनी अधिकार देने और विधायी सुधारों की वकालत करने से बेहतर निगरानी और प्रवर्तन सुनिश्चित होगा, जिससे पूरे देश में दवा सुरक्षा में सुधार होगा।