CURRENT AFFAIRS – 15/11/2024
- CURRENT AFFAIRS – 15/11/2024
- AFSPA back in six violence-hit areas of Manipur /मणिपुर के छह हिंसा प्रभावित क्षेत्रों में AFSPA की वापसी
- The discovery of insulin and the ‘Flame of Hope’ /इंसुलिन की खोज और ‘आशा की लौ’
- Borderless Europe fights brain drain as talent heads to the wealthier north /सीमाहीन यूरोप प्रतिभा पलायन से लड़ रहा है, क्योंकि प्रतिभाएं उत्तर की ओर जा रही हैं
- Bubbling with life /जीवन से भरपूर
- Birsa Munda /बिरसा मुंडा
- A 2024 election result that leaves many astounded /2024 का चुनाव परिणाम जिसने कई लोगों को चौंका दिया
CURRENT AFFAIRS – 15/11/2024
AFSPA back in six violence-hit areas of Manipur /मणिपुर के छह हिंसा प्रभावित क्षेत्रों में AFSPA की वापसी
Syllabus : GS 3 : Internal Security
Source : The Hindu
The The Union Home Ministry has reimposed the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) in six police station limits of Manipur due to ongoing ethnic violence.
- The re-imposition, effective until March 2025, aims to assist security forces in controlling insurgent activities.
Analysis of the news:
- The Union Home Ministry reimposed AFSPA in Manipur on Thursday due to ethnic violence.
- Six police station limits in five districts have been declared “disturbed areas” for security operations.
- These areas include parts of Imphal West, Imphal East, Jiribam, Bishnupur, and Kangpokpi.
- AFSPA was withdrawn in April 2022 due to improved security, but the situation remains volatile.
- The reimposed AFSPA will be effective until March 31, 2025.
- The Army and Assam Rifles can operate freely without waiting for Magistrates or police.
- Ethnic violence between Meitei and Kuki-Zo people has led to over 240 deaths since May 2023.
- Recent violence since November 7 has killed at least 14 people.
- Central and State governments can issue disturbed area notifications under AFSPA.
Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, 1958 (AFSPA)
- AFSPA Act Overview : The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) is an Indian law that grants special powers to the armed forces in regions declared “disturbed areas.”The Act is designed to enable the military to act with more authority and less restriction in areas facing internal disturbances or insurgency.
- Imposition of AFSPA : AFSPA is imposed by the state or central government, based on the assessment of the security situation.A region is declared a “disturbed area” by the government, typically after an evaluation of violence, insurgency, or unrest.The government can impose AFSPA in such areas to allow security forces to operate more freely, even without a Magistrate’s permission.
- Who Can Impose : AFSPA The state or central government can declare areas as disturbed and impose AFSPA.The power to impose AFSPA lies with the Governor of a state or the central government.
- Need for AFSPA : It is seen as essential for maintaining law and order in areas facing insurgencies, militancy, or severe civil unrest.AFSPA allows security forces to act swiftly against insurgents and militants.
- Issues Associated with AFSPA : The law has been criticised for empowering security forces with excessive powers, leading to human rights abuses.Allegations of arbitrary arrests, extrajudicial killings, and torture are often raised against the military and police.Calls for its repeal stem from concerns over the violation of civil liberties, particularly in regions like Kashmir and Northeast India.Prolonged imposition of AFSPA in regions has sparked debates on its effectiveness and its negative impact on local populations.
मणिपुर के छह हिंसा प्रभावित क्षेत्रों में AFSPA की वापसी
केंद्रीय गृह मंत्रालय ने मणिपुर में जारी जातीय हिंसा के कारण छह पुलिस थानों की सीमा में सशस्त्र बल (विशेष शक्तियां) अधिनियम (AFSPA) को फिर से लागू कर दिया है।
- मार्च 2025 तक प्रभावी इस पुनः लागू कानून का उद्देश्य विद्रोही गतिविधियों को नियंत्रित करने में सुरक्षा बलों की सहायता करना है।
समाचार का विश्लेषण:
- केंद्रीय गृह मंत्रालय ने जातीय हिंसा के कारण गुरुवार को मणिपुर में AFSPA को फिर से लागू कर दिया।
- सुरक्षा अभियानों के लिए पाँच जिलों के छह पुलिस थानों की सीमाओं को “अशांत क्षेत्र” घोषित किया गया है।
- इन क्षेत्रों में इम्फाल पश्चिम, इम्फाल पूर्व, जिरीबाम, बिष्णुपुर और कांगपोकपी के कुछ हिस्से शामिल हैं।
- सुरक्षा में सुधार के कारण अप्रैल 2022 में AFSPA को हटा लिया गया था, लेकिन स्थिति अभी भी अस्थिर बनी हुई है।
- पुनः लागू किया गया AFSPA 31 मार्च, 2025 तक प्रभावी रहेगा।
- सेना और असम राइफल्स मजिस्ट्रेट या पुलिस का इंतज़ार किए बिना स्वतंत्र रूप से काम कर सकते हैं।
- मई 2023 से मैतेई और कुकी-ज़ो लोगों के बीच जातीय हिंसा के कारण 240 से ज़्यादा मौतें हुई हैं।
- 7 नवंबर से हाल ही में हुई हिंसा में कम से कम 14 लोगों की मौत हो गई है।
- केंद्र और राज्य सरकारें AFSPA के तहत अशांत क्षेत्र अधिसूचनाएँ जारी कर सकती हैं।
सशस्त्र बल (विशेष शक्तियां) अधिनियम, 1958 (AFSPA)
- AFSPA अधिनियम अवलोकन: सशस्त्र बल (विशेष शक्तियां) अधिनियम (AFSPA) एक भारतीय कानून है जो “अशांत क्षेत्र” घोषित क्षेत्रों में सशस्त्र बलों को विशेष शक्तियां प्रदान करता है। यह अधिनियम सेना को आंतरिक अशांति या उग्रवाद का सामना करने वाले क्षेत्रों में अधिक अधिकार और कम प्रतिबंध के साथ कार्य करने में सक्षम बनाने के लिए बनाया गया है।
- AFSPA लागू करना: AFSPA राज्य या केंद्र सरकार द्वारा सुरक्षा स्थिति के आकलन के आधार पर लगाया जाता है। सरकार द्वारा किसी क्षेत्र को “अशांत क्षेत्र” घोषित किया जाता है, आमतौर पर हिंसा, उग्रवाद या अशांति के मूल्यांकन के बाद। सरकार ऐसे क्षेत्रों में AFSPA लगा सकती है ताकि सुरक्षा बलों को अधिक स्वतंत्र रूप से काम करने की अनुमति मिल सके, यहां तक कि मजिस्ट्रेट की अनुमति के बिना भी।
- कौन लगा सकता है: AFSPA राज्य या केंद्र सरकार क्षेत्रों को अशांत घोषित कर सकती है और AFSPA लगा सकती है। AFSPA लगाने का अधिकार किसी राज्य के राज्यपाल या केंद्र सरकार के पास होता है।
- अफस्पा की आवश्यकता: इसे उग्रवाद, उग्रवाद या गंभीर नागरिक अशांति का सामना करने वाले क्षेत्रों में कानून और व्यवस्था बनाए रखने के लिए आवश्यक माना जाता है। अफस्पा सुरक्षा बलों को उग्रवादियों और आतंकवादियों के खिलाफ तेजी से कार्रवाई करने की अनुमति देता है।
- अफस्पा से जुड़े मुद्दे: इस कानून की आलोचना सुरक्षा बलों को अत्यधिक शक्तियों से सशक्त बनाने के लिए की गई है, जिससे मानवाधिकारों का हनन होता है। सेना और पुलिस के खिलाफ अक्सर मनमानी गिरफ्तारी, न्यायेतर हत्या और यातना के आरोप लगाए जाते हैं। नागरिक स्वतंत्रता के उल्लंघन पर चिंताओं से इसके निरसन की मांग, विशेष रूप से कश्मीर और पूर्वोत्तर भारत जैसे क्षेत्रों में। क्षेत्रों में अफस्पा के लंबे समय तक लागू रहने से इसकी प्रभावशीलता और स्थानीय आबादी पर इसके नकारात्मक प्रभाव पर बहस छिड़ गई है।
The discovery of insulin and the ‘Flame of Hope’ /इंसुलिन की खोज और ‘आशा की लौ’
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
The article highlights the discovery of insulin, a pivotal medical breakthrough that transformed diabetes treatment.
- It traces the journey from early research to the development of recombinant DNA technology for mass insulin production, commemorating Sir Frederick Banting’s legacy on World Diabetes Day.
Endocrine Glands and Insulin Discovery
- Endocrine glands release hormones in small quantities to regulate bodily functions.
- The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine organ, controlling blood sugar through insulin.
- World Diabetes Day is observed on November 14 to honour Sir Frederick Banting.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)
- Type 1 diabetes (T1DM) is an autoimmune disease attacking insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- T1DM commonly affects children and young adults, with 9 million global cases.
- In India, the incidence of T1DM is 4.9 per 100,000 annually.
- The cause remains unclear, but genetic and environmental factors are suspected.
Historical Insights and Early Research
- Symptoms of diabetes were known in ancient civilizations but lacked scientific understanding.
- Paul Langerhans discovered the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas in 1869.
- In 1889, research linked the pancreas to blood sugar regulation.
Climax at the University of Toronto
- Frederick Banting, John Macleod, and Charles Best isolated insulin in 1921.
- James Collip purified insulin for human use, making it safe and effective.
- Leonard Thompson received the first successful insulin injection in 1922.
- Banting and Macleod were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1923, amidst credit controversies.
Mass Production and Modern Advances
- Banting sold insulin’s patent to the University of Toronto for $1 to ensure widespread production.
- Recombinant DNA technology in the 1980s enabled mass production of human insulin from bacteria.
इंसुलिन की खोज और ‘आशा की लौ’
लेख में इंसुलिन की खोज पर प्रकाश डाला गया है, जो एक महत्वपूर्ण चिकित्सा सफलता है जिसने मधुमेह के उपचार को बदल दिया।
- यह प्रारंभिक शोध से लेकर बड़े पैमाने पर इंसुलिन उत्पादन के लिए पुनः संयोजक डीएनए तकनीक के विकास तक की यात्रा का पता लगाता है, जो विश्व मधुमेह दिवस पर सर फ्रेडरिक बैंटिंग की विरासत को याद करता है।
अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियाँ और इंसुलिन की खोज
- अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियाँ शारीरिक कार्यों को विनियमित करने के लिए कम मात्रा में हार्मोन जारी करती हैं।
- अग्नाशय एक अंतःस्रावी और बहिःस्रावी अंग है, जो इंसुलिन के माध्यम से रक्त शर्करा को नियंत्रित करता है।
- सर फ्रेडरिक बैंटिंग के सम्मान में 14 नवंबर को विश्व मधुमेह दिवस मनाया जाता है।
टाइप 1 मधुमेह मेलिटस (T1DM)
- टाइप 1 मधुमेह (T1DM) एक स्वप्रतिरक्षी रोग है जो अग्न्याशय में इंसुलिन-उत्पादक कोशिकाओं पर हमला करता है।
- T1DM आमतौर पर बच्चों और युवा वयस्कों को प्रभावित करता है, जिसके वैश्विक स्तर पर 9 मिलियन मामले हैं।
- भारत में, T1DM की घटना प्रति वर्ष 100,000 में 9 है।
- कारण स्पष्ट नहीं है, लेकिन आनुवंशिक और पर्यावरणीय कारकों पर संदेह है।
ऐतिहासिक अंतर्दृष्टि और प्रारंभिक शोध
- मधुमेह के लक्षण प्राचीन सभ्यताओं में ज्ञात थे, लेकिन वैज्ञानिक समझ का अभाव था।
- पॉल लैंगरहैंस ने 1869 में अग्न्याशय में लैंगरहैंस के आइलेट्स की खोज की।
- 1889 में, शोध ने अग्न्याशय को रक्त शर्करा विनियमन से जोड़ा।
टोरंटो विश्वविद्यालय में चरमोत्कर्ष
- फ्रेडरिक बैंटिंग, जॉन मैकलियोड और चार्ल्स बेस्ट ने 1921 में इंसुलिन को अलग किया।
- जेम्स कोलिप ने मानव उपयोग के लिए इंसुलिन को शुद्ध किया, जिससे यह सुरक्षित और प्रभावी हो गया।
- लियोनार्ड थॉम्पसन को 1922 में पहला सफल इंसुलिन इंजेक्शन मिला।
- बैंटिंग और मैकलियोड को क्रेडिट विवादों के बीच 1923 में नोबेल पुरस्कार से सम्मानित किया गया।
बड़े पैमाने पर उत्पादन और आधुनिक प्रगति
- बैंटिंग ने व्यापक उत्पादन सुनिश्चित करने के लिए इंसुलिन का पेटेंट टोरंटो विश्वविद्यालय को $1 में बेच दिया।
- 1980 के दशक में पुनः संयोजक डीएनए तकनीक ने बैक्टीरिया से मानव इंसुलिन के बड़े पैमाने पर उत्पादन को सक्षम किया।
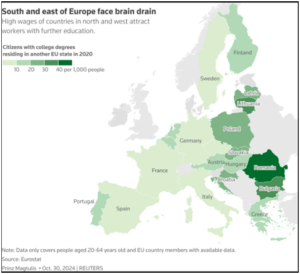
Borderless Europe fights brain drain as talent heads to the wealthier north /सीमाहीन यूरोप प्रतिभा पलायन से लड़ रहा है, क्योंकि प्रतिभाएं उत्तर की ओर जा रही हैं
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
Portugal is facing a significant migration crisis, particularly among young professionals, due to low wages, high taxes, and a housing crisis.
- In response, the government has proposed tax breaks and housing assistance to retain talent.
- However, many remain sceptical about the effectiveness of these measures in improving job opportunities.
Portugal’s Efforts to Retain Young Talent
- Government Measures
- The government is offering tax breaks for young workers, including a potential 100% income tax exemption.
- Additional housing assistance is being provided to make staying in Portugal more attractive for young people.
- Tax and Wage Disparities
- Portugal has the eighth-highest tax burden in the OECD.
- The average after-tax income in Portugal is much lower than in countries like the Netherlands, incentivizing migration.
- Concerns Over Housing and Job Opportunities
- Many young people are sceptical about job prospects and housing affordability.
- The housing crisis is worsened by wealthy foreigners attracted by tax breaks and easy residency rights.
- The Brain Drain Problem
- About 850,000 Portuguese nationals aged 15-39 currently live abroad.
- Emigration results in significant loss of tax revenue and social security contributions, costing Portugal billions each year.
- EU-Wide Issue
- Portugal’s talent flight is part of a broader issue affecting Southern and Central Europe.
- Workers migrate to wealthier northern European countries for better wages and career opportunities.
- This migration contributes to regional labour shortages and hampers economic growth.
सीमाहीन यूरोप प्रतिभा पलायन से लड़ रहा है, क्योंकि प्रतिभाएं उत्तर की ओर जा रही हैं
पुर्तगाल में कम वेतन, उच्च कर और आवास संकट के कारण, विशेष रूप से युवा पेशेवरों के बीच, एक महत्वपूर्ण प्रवासन संकट का सामना करना पड़ रहा है।
- इसके जवाब में, सरकार ने प्रतिभा को बनाए रखने के लिए कर छूट और आवास सहायता का प्रस्ताव दिया है।
- हालांकि, नौकरी के अवसरों में सुधार करने में इन उपायों की प्रभावशीलता के बारे में कई लोग संशय में हैं।
युवा प्रतिभाओं को बनाए रखने के लिए पुर्तगाल के प्रयास
- सरकारी उपाय
- सरकार युवा कर्मचारियों को कर में छूट दे रही है, जिसमें संभावित 100% आयकर छूट भी शामिल है।
- युवा लोगों के लिए पुर्तगाल में रहना अधिक आकर्षक बनाने के लिए अतिरिक्त आवास सहायता प्रदान की जा रही है।
- कर और वेतन असमानताएँ
- पुर्तगाल OECD में आठवाँ सबसे अधिक कर भार वाला देश है।
- पुर्तगाल में कर के बाद औसत आय नीदरलैंड जैसे देशों की तुलना में बहुत कम है, जो प्रवास को प्रोत्साहित करती है।
- आवास और नौकरी के अवसरों पर चिंताएँ
- बहुत से युवा नौकरी की संभावनाओं और आवास की सामर्थ्य के बारे में संशय में हैं।
- कर छूट और आसान निवास अधिकारों से आकर्षित होने वाले धनी विदेशियों के कारण आवास संकट और भी बदतर हो गया है।
- प्रतिभा पलायन की समस्या
- वर्तमान में 15-39 वर्ष की आयु के लगभग 850,000 पुर्तगाली नागरिक विदेश में रहते हैं।
- प्रवास के परिणामस्वरूप कर राजस्व और सामाजिक सुरक्षा योगदान में महत्वपूर्ण हानि होती है, जिससे पुर्तगाल को हर साल अरबों का नुकसान होता है।
- यूरोपीय संघ-व्यापी मुद्दा
- पुर्तगाल की प्रतिभा पलायन दक्षिणी और मध्य यूरोप को प्रभावित करने वाले एक व्यापक मुद्दे का हिस्सा है।
- बेहतर वेतन और करियर के अवसरों के लिए श्रमिक उत्तरी यूरोपीय देशों में पलायन करते हैं। यह पलायन क्षेत्रीय श्रम की कमी में योगदान देता है और आर्थिक विकास को बाधित करता है।
Bubbling with life /जीवन से भरपूर
Syllabus : Prelims Fact
Source : The Hindu
Scientists recently discovered the world’s largest coral near the Solomon Islands in the Pacific Ocean, spanning over two basketball courts.
- This unique 300-year-old coral highlights the resilience of marine life amidst the global coral crisis, offering hope for conservation efforts.

Analysis of the news:
- A massive coral, the largest ever discovered, has been found near the Solomon Islands in the Pacific Ocean.
- The coral stretches over an area larger than two basketball courts.
- Initially mistaken for a shipwreck, it is believed to be about 300 years old.
- Unlike coral reefs made of multiple colonies, this coral is a single, solitary structure.
- It serves as an essential habitat for various marine species, from small crustaceans to larger fish.
- The discovery is significant amid the global coral crisis, which has been worsened by climate change.
- The coral’s resilience offers hope for the survival of similar ecosystems.
- Scientists hope the discovery will inspire more research and conservation efforts to protect coral habitats.
जीवन से भरपूर
वैज्ञानिकों ने हाल ही में प्रशांत महासागर में सोलोमन द्वीप के पास दुनिया का सबसे बड़ा मूंगा खोजा है, जो दो बास्केटबॉल कोर्ट में फैला हुआ है।
- यह अनोखा 300 साल पुराना मूंगा वैश्विक मूंगा संकट के बीच समुद्री जीवन की लचीलापन को उजागर करता है, जो संरक्षण प्रयासों के लिए आशा प्रदान करता है।
समाचार का विश्लेषण:
- प्रशांत महासागर में सोलोमन द्वीप के पास अब तक खोजा गया सबसे बड़ा मूंगा पाया गया है।
- यह मूंगा दो बास्केटबॉल कोर्ट से भी बड़े क्षेत्र में फैला हुआ है।
- शुरुआत में इसे जहाज़ का मलबा समझ लिया गया था, लेकिन माना जाता है कि यह लगभग 300 साल पुराना है।
- कई कॉलोनियों से बनी कोरल रीफ़ के विपरीत, यह कोरल एक एकल, एकाकी संरचना है।
- यह छोटे क्रस्टेशियंस से लेकर बड़ी मछलियों तक, विभिन्न समुद्री प्रजातियों के लिए एक आवश्यक आवास के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- यह खोज वैश्विक कोरल संकट के बीच महत्वपूर्ण है, जो जलवायु परिवर्तन से और भी बदतर हो गया है।
- कोरल का लचीलापन समान पारिस्थितिकी तंत्रों के अस्तित्व के लिए आशा प्रदान करता है।
- वैज्ञानिकों को उम्मीद है कि यह खोज कोरल आवासों की रक्षा के लिए और अधिक शोध और संरक्षण प्रयासों को प्रेरित करेगी।
Birsa Munda /बिरसा मुंडा
In News
Prime Minister Narendra Modi will launch a commemorative stamp and coin to honour tribal icon Birsa Munda’s 150th birth anniversary.
- He will also inaugurate and lay the foundation for tribal welfare projects worth over ₹6,640 crore in Jamui, Bihar.
More About Birsa Munda (1875–1900):
- Birthplace: Ulihatu, Ranchi, Bihar (now Jharkhand)
- Ethnicity: Munda tribe
- Movement: Led the Ulgulan (Munda Rebellion) against British colonial rule.
- Key Objective: Fought for the rights of tribal communities, land rights, and against exploitation by landlords and the British.
- Role: Considered a freedom fighter, social reformer, and religious leader.
- Religious Influence: Promoted the Birsait religion, encouraging Munda tribes to reject foreign influence.
- Major Achievements: Revived tribal culture and resistance, became a symbol of tribal pride.
- Legacy: Revered as “Dharti Aba” (Father of the Earth), and his contribution is honoured across India..
बिरसा मुंडा
प्रधानमंत्री नरेंद्र मोदी आदिवासी नेता बिरसा मुंडा की 150वीं जयंती के उपलक्ष्य में एक स्मारक डाक टिकट और सिक्का जारी करेंगे।
- वह बिहार के जमुई में ₹6,640 करोड़ से अधिक की आदिवासी कल्याण परियोजनाओं का उद्घाटन और शिलान्यास भी करेंगे।
बिरसा मुंडा (1875-1900) के बारे में अधिक जानकारी:
- जन्मस्थान: उलीहातु, रांची, बिहार (अब झारखंड)
- जातीयता: मुंडा जनजाति
- आंदोलन: ब्रिटिश औपनिवेशिक शासन के खिलाफ उलगुलान (मुंडा विद्रोह) का नेतृत्व किया।
- मुख्य उद्देश्य: आदिवासी समुदायों के अधिकारों, भूमि अधिकारों और जमींदारों और अंग्रेजों द्वारा शोषण के खिलाफ लड़ाई लड़ी।
- भूमिका: एक स्वतंत्रता सेनानी, समाज सुधारक और धार्मिक नेता माने जाते हैं।
- धार्मिक प्रभाव: बिरसाइत धर्म को बढ़ावा दिया, मुंडा जनजातियों को विदेशी प्रभाव को अस्वीकार करने के लिए प्रोत्साहित किया।
- प्रमुख उपलब्धियाँ: आदिवासी संस्कृति और प्रतिरोध को पुनर्जीवित किया, आदिवासी गौरव का प्रतीक बन गए।
- विरासत: “धरती आबा” (पृथ्वी के पिता) के रूप में सम्मानित, और उनके योगदान को पूरे भारत में सम्मानित किया जाता है।
A 2024 election result that leaves many astounded /2024 का चुनाव परिणाम जिसने कई लोगों को चौंका दिया
Editorial Analysis: Syllabus : GS 2 : Governance & International Relations
Source : The Hindu
Context :
- In recent years, democracies worldwide, including India, face rising authoritarian pressures that challenge institutional independence, media freedom, and civic rights.
- Factors such as socioeconomic disparities, identity politics, and populism fuel this trend, undermining democratic ideals.
- Safeguarding India’s democratic framework requires vigilance, institutional resilience, and public commitment to core democratic values.
Challenges Facing Indian Democracy
- Systemic Obstacles to Fair Functioning:
- Despite being the world’s largest democracy, India faces complex systemic issues that challenge its democratic institutions.
- Social inequalities, economic disparities, and regional divides often complicate governance and weaken the public’s trust in democratic systems.
- Polarisation and Identity Politics:
- Growing polarisation along caste, religion, and regional lines impacts the spirit of democracy.
- This focus on divisions can create an environment conducive to authoritarian tendencies.
Democratic Backsliding in Global Context
- Global Rise of Authoritarianism:
- In recent years, several democracies worldwide have experienced a drift toward authoritarianism.
- Nations like Hungary and Turkey, once praised for their democratic structures, have witnessed a tightening of control by leaders, who exploit existing institutions to centralise power and undermine checks and balances.
- Lessons for India:
- The experience of these nations serves as a cautionary tale for India.
- Independent courts and a free press uphold democracy, but leaders often undermine them for personal power.
- Democratic safeguards like judiciary and press freedom weaken when leaders use populism to consolidate unchecked authority.
Socioeconomic Inequality and Democratic Vulnerabilities
- Socioeconomic Disparities:
- Economic inequality in India poses a significant risk to democratic health.
- The growing divide between urban and rural populations weakens democratic representation and fuels political resentment.
- Socioeconomic inequalities often lead to resentment, which political leaders exploit to gain support and power.
- Impact on Voter Demographics:
- A large segment of the population, particularly the rural and economically marginalised, is susceptible to populist promises.
- Leaders who prioritise identity-based appeals over developmental policies can exploit these divisions to consolidate power, as seen globally.
Erosion of Democratic Institutions
- Weakening of Institutional Independence:
- Over time, democratic institutions in India, such as the judiciary, the Election Commission, and investigative agencies, have faced accusations of politicisation.
- This politicisation can dilute the neutrality of these bodies, making it difficult to ensure fair governance and eroding public trust in democracy.
- Media Control and Information Manipulation:
- An independent press is essential to a functioning democracy, yet concerns over media ownership, government influence, and censorship are increasing.
- The concentration of media ownership and pressure on journalists restricts critical coverage, allowing leaders to control narratives and shape public opinion.
Authoritarian Tendencies in Indian Governance
- Centralization of Power:
- The increasing centralization of authority within the executive branch has led to concerns over the weakening of federalism.
- While centralised decision-making can provide quick responses in crisis situations, unchecked central authority risks undermining state autonomy and creating a lopsided power structure.
- Restrictive Policies on Civil Liberties:
- The use of restrictive laws and regulations, such as those related to national security or sedition, raises concerns about stifling dissent.
- Democracies thrive on open debate and criticism, yet limitations on civil liberties in the name of order and security may limit the scope for healthy public discourse.
- Populism and Identity Politics:
- Populist narratives that exploit religious and caste-based identities have gained traction, often sidelining critical issues.
- While such promises can secure electoral wins, they undermine the democratic ideal of governance that serves all citizens equally.
The Need for Strengthening Democratic Principles
- Reinforcing Institutional Independence:
- Safeguarding the autonomy of democratic institutions is crucial to ensuring accountability and transparency.
- Strengthening the judiciary, Election Commission, and other key institutions can reinforce public trust and help prevent power consolidation.
- Media Freedom and Transparency:
- Ensuring freedom of the press and supporting independent journalism are essential for maintaining transparency and accountability.
- A robust and unbiased media enables informed citizenry, critical discourse, and checks on power.
Lessons from Global Democratic Decline
- Importance of Vigilance Against Authoritarian Drift:
- The experiences of other democracies demonstrate the gradual nature of authoritarian shifts.
- By remaining vigilant and fostering a culture of accountability, India can mitigate the risks of democratic backsliding.
- Encouraging Social Cohesion:
- In a country as diverse as India, promoting social cohesion and unity across different communities is critical to a healthy democracy.
- Policies that prioritise inclusivity over identity politics help reduce divisions that can be exploited by authoritarian forces.
Conclusion
- Democracy is India’s strength, rooted in its Constitution and values of freedom, equality, and secularism.
- Upholding these principles amidst challenges requires a commitment from both leaders and citizens to protect democratic ideals.
2024 का चुनाव परिणाम जिसने कई लोगों को चौंका दिया
संदर्भ :
- हाल के वर्षों में, भारत सहित दुनिया भर के लोकतंत्रों को बढ़ते अधिनायकवादी दबावों का सामना करना पड़ रहा है, जो संस्थागत स्वतंत्रता, मीडिया की स्वतंत्रता और नागरिक अधिकारों को चुनौती देते हैं।
- सामाजिक-आर्थिक असमानताएँ, पहचान की राजनीति और लोकलुभावनवाद जैसे कारक इस प्रवृत्ति को बढ़ावा देते हैं, जो लोकतांत्रिक आदर्शों को कमज़ोर करते हैं।
- भारत के लोकतांत्रिक ढांचे की सुरक्षा के लिए सतर्कता, संस्थागत लचीलापन और मूल लोकतांत्रिक मूल्यों के प्रति जनता की प्रतिबद्धता की आवश्यकता है।
भारतीय लोकतंत्र के सामने चुनौतियाँ
- निष्पक्ष कामकाज में प्रणालीगत बाधाएँ:
- दुनिया का सबसे बड़ा लोकतंत्र होने के बावजूद, भारत जटिल प्रणालीगत मुद्दों का सामना कर रहा है जो इसके लोकतांत्रिक संस्थानों को चुनौती देते हैं।
- सामाजिक असमानताएँ, आर्थिक असमानताएँ और क्षेत्रीय विभाजन अक्सर शासन को जटिल बनाते हैं और लोकतांत्रिक प्रणालियों में जनता के विश्वास को कमज़ोर करते हैं।
- ध्रुवीकरण और पहचान की राजनीति:
- जाति, धर्म और क्षेत्रीय आधार पर बढ़ता ध्रुवीकरण लोकतंत्र की भावना को प्रभावित करता है।
- विभाजन पर यह ध्यान अधिनायकवादी प्रवृत्तियों के लिए अनुकूल वातावरण बना सकता है।
वैश्विक संदर्भ में लोकतांत्रिक पतन
- अधिनायकवाद का वैश्विक उदय:
- हाल के वर्षों में, दुनिया भर के कई लोकतंत्रों ने अधिनायकवाद की ओर झुकाव का अनुभव किया है।
- हंगरी और तुर्की जैसे राष्ट्र, जो कभी अपने लोकतांत्रिक ढांचे के लिए प्रशंसित थे, ने नेताओं द्वारा नियंत्रण को कड़ा होते देखा है, जो सत्ता को केंद्रीकृत करने और जाँच और संतुलन को कम करने के लिए मौजूदा संस्थानों का शोषण करते हैं।
- भारत के लिए सबक:
- इन देशों का अनुभव भारत के लिए एक चेतावनी की कहानी के रूप में कार्य करता है।
- स्वतंत्र न्यायालय और एक स्वतंत्र प्रेस लोकतंत्र को बनाए रखते हैं, लेकिन नेता अक्सर व्यक्तिगत शक्ति के लिए उन्हें कमजोर करते हैं।
- न्यायपालिका और प्रेस की स्वतंत्रता जैसे लोकतांत्रिक सुरक्षा उपाय कमजोर हो जाते हैं जब नेता अनियंत्रित अधिकार को मजबूत करने के लिए लोकलुभावनवाद का उपयोग करते हैं।
सामाजिक-आर्थिक असमानता और लोकतांत्रिक कमजोरियाँ
- सामाजिक-आर्थिक असमानताएँ:
- भारत में आर्थिक असमानता लोकतांत्रिक स्वास्थ्य के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण जोखिम पैदा करती है।
- शहरी और ग्रामीण आबादी के बीच बढ़ता विभाजन लोकतांत्रिक प्रतिनिधित्व को कमजोर करता है और राजनीतिक आक्रोश को बढ़ाता है।
- सामाजिक-आर्थिक असमानताएँ अक्सर आक्रोश को जन्म देती हैं, जिसका राजनीतिक नेता समर्थन और शक्ति प्राप्त करने के लिए शोषण करते हैं।
- मतदाता जनसांख्यिकी पर प्रभाव:
- जनसंख्या का एक बड़ा हिस्सा, विशेष रूप से ग्रामीण और आर्थिक रूप से हाशिए पर पड़े लोग, लोकलुभावन वादों के प्रति संवेदनशील होते हैं।
- विकास नीतियों पर पहचान आधारित अपील को प्राथमिकता देने वाले नेता, सत्ता को मजबूत करने के लिए इन विभाजनों का फायदा उठा सकते हैं, जैसा कि वैश्विक स्तर पर देखा गया है।
लोकतांत्रिक संस्थाओं का क्षरण
- संस्थागत स्वतंत्रता का कमजोर होना:
- समय के साथ, भारत में न्यायपालिका, चुनाव आयोग और जांच एजेंसियों जैसी लोकतांत्रिक संस्थाओं पर राजनीतिकरण के आरोप लगे हैं।
- यह राजनीतिकरण इन निकायों की तटस्थता को कमजोर कर सकता है, जिससे निष्पक्ष शासन सुनिश्चित करना मुश्किल हो जाता है और लोकतंत्र में जनता का विश्वास खत्म हो जाता है।
- मीडिया नियंत्रण और सूचना हेरफेर:
- एक स्वतंत्र प्रेस एक कार्यशील लोकतंत्र के लिए आवश्यक है, फिर भी मीडिया स्वामित्व, सरकारी प्रभाव और सेंसरशिप पर चिंताएँ बढ़ रही हैं।
- मीडिया स्वामित्व का संकेन्द्रण और पत्रकारों पर दबाव आलोचनात्मक कवरेज को प्रतिबंधित करता है, जिससे नेताओं को आख्यानों को नियंत्रित करने और जनमत को आकार देने की अनुमति मिलती है।
भारतीय शासन में सत्तावादी प्रवृत्तियाँ
- सत्ता का केंद्रीकरण:
- कार्यकारी शाखा के भीतर अधिकार के बढ़ते केंद्रीकरण ने संघवाद के कमज़ोर होने की चिंताएँ पैदा की हैं।
- जबकि केंद्रीकृत निर्णय-निर्माण संकट की स्थितियों में त्वरित प्रतिक्रियाएँ प्रदान कर सकता है, अनियंत्रित केंद्रीय प्राधिकरण राज्य की स्वायत्तता को कमज़ोर करने और एक असंतुलित सत्ता संरचना बनाने का जोखिम उठाता है।
- नागरिक स्वतंत्रता पर प्रतिबंधात्मक नीतियाँ:
- राष्ट्रीय सुरक्षा या राजद्रोह से संबंधित प्रतिबंधात्मक कानूनों और विनियमों का उपयोग असहमति को दबाने के बारे में चिंताएँ पैदा करता है।
- लोकतंत्र खुली बहस और आलोचना पर पनपते हैं, फिर भी व्यवस्था और सुरक्षा के नाम पर नागरिक स्वतंत्रता पर सीमाएँ स्वस्थ सार्वजनिक विमर्श की गुंजाइश को सीमित कर सकती हैं।
- लोकलुभावनवाद और पहचान की राजनीति:
- धार्मिक और जाति-आधारित पहचानों का शोषण करने वाले लोकलुभावन आख्यानों ने जोर पकड़ा है, जो अक्सर महत्वपूर्ण मुद्दों को दरकिनार कर देते हैं।
- जबकि ऐसे वादे चुनावी जीत सुनिश्चित कर सकते हैं, वे शासन के लोकतांत्रिक आदर्श को कमजोर करते हैं जो सभी नागरिकों की समान रूप से सेवा करता है।
लोकतांत्रिक सिद्धांतों को मजबूत करने की आवश्यकता
- संस्थागत स्वतंत्रता को मजबूत करना:
- लोकतांत्रिक संस्थाओं की स्वायत्तता की रक्षा करना जवाबदेही और पारदर्शिता सुनिश्चित करने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
- न्यायपालिका, चुनाव आयोग और अन्य प्रमुख संस्थाओं को मजबूत करने से जनता का भरोसा मजबूत हो सकता है और सत्ता के एकीकरण को रोकने में मदद मिल सकती है।
- मीडिया की स्वतंत्रता और पारदर्शिता:
- पारदर्शिता और जवाबदेही बनाए रखने के लिए प्रेस की स्वतंत्रता सुनिश्चित करना और स्वतंत्र पत्रकारिता का समर्थन करना आवश्यक है।
- एक मजबूत और निष्पक्ष मीडिया सूचित नागरिकों, आलोचनात्मक प्रवचन और सत्ता पर नियंत्रण को सक्षम बनाता है।
वैश्विक लोकतांत्रिक गिरावट से सबक
- सत्तावादी बहाव के खिलाफ सतर्कता का महत्व:
- अन्य लोकतंत्रों के अनुभव सत्तावादी बदलावों की क्रमिक प्रकृति को प्रदर्शित करते हैं।
- सतर्क रहकर और जवाबदेही की संस्कृति को बढ़ावा देकर, भारत लोकतांत्रिक पतन के जोखिमों को कम कर सकता है।
- सामाजिक सामंजस्य को प्रोत्साहित करना:
- भारत जैसे विविधतापूर्ण देश में, विभिन्न समुदायों में सामाजिक सामंजस्य और एकता को बढ़ावा देना एक स्वस्थ लोकतंत्र के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
- पहचान की राजनीति पर समावेशिता को प्राथमिकता देने वाली नीतियाँ उन विभाजनों को कम करने में मदद करती हैं जिनका सत्तावादी ताकतों द्वारा फायदा उठाया जा सकता है।
निष्कर्ष
- लोकतंत्र भारत की ताकत है, जो इसके संविधान और स्वतंत्रता, समानता और धर्मनिरपेक्षता के मूल्यों में निहित है।
- चुनौतियों के बीच इन सिद्धांतों को कायम रखने के लिए नेताओं और नागरिकों दोनों की ओर से लोकतांत्रिक आदर्शों की रक्षा करने की प्रतिबद्धता की आवश्यकता होती है।